Has 3D Already Failed? The sequel, part one: RealDlighted
Thursday | January 20, 2011 open printable version
open printable version
Kristin here–
On August 28, 2009, I posted an entry called “Has 3-D Already Failed?” As I wrote then, my title was deliberately provocative. It depended on which of two yardsticks you measured success by:
1. If you’re Jeffrey Katzenberg and want every theater in the world now showing 35mm films to convert to digital 3-D, then the answer is probably yes. That goal is unlikely to be met within the next few decades, by which time the equipment now being installed will almost certainly have been replaced by something else.
2. It also seems possible that the powers that be will decide that 3-D has reached a saturation point, or nearly so. 3-D films are now a regular but very minority product in Hollywood. They justify their existence by bringing in more at the box-office than do 2-D versions of the same films. Maybe the films that wouldn’t really benefit from 3-D, like Julie & Julia, will continue to be made in 2-D. 3-D is an add-on to a digital projector, so theaters can remove it to show 2-D films. Or a multiplex might reserve two or three of its theaters for 3-D and use the rest for traditional screenings.
If the second, more modest goal is the one many Hollywood studios are aiming at, then no, 3-D hasn’t failed. But as for 3-D being the one technology that will “save” the movies from competition from games, iTunes, and TV, I remain skeptical.
So, nearly 17 months later, where do we stand? There has been a considerable increase in the number of screens with 3D projection systems, from 4,400 in May 2010 to 8,770 in early December. That’s out of roughly 38,000. This growth presumably came in response to the huge success of Avatar and Alice in Wonderland. Anne Thompson’s “Year-End Box Office Wrap 2010” quotes Don Harris, Paramount’s executive vice-president of distribution: “There are more screens, so a theater can now handle anywhere from two to three 3-D films at one time.” By year’s end, there were roughly 13,000 3D-equipped screens outside the North American market. The number of 3D films per year has grown from 2 in 2008 to 11 in 2009 to 22 in 2010 to an announced 30+ for this year.
Thompson also points out two other important strengths of 3D films: they sell a lot of tickets abroad, often earning three times as much as in the North American market, and they have led to theatrical income is “again the leading film revenue stream.” Of course, that’s partly due to the drop in DVD sales.
Yet for some the bloom seems to be off the rose. Low-budget exploitation films in 3D, films shot in 2D and converted for 3D release, filmgoer impatience with ticket surcharges and clunky glasses, and a general decline in the novelty value of 3D have all combined to leave its future still in doubt.
Before going more deeply into those problems, though, let’s look at the box-office successes, or apparent successes, of 3D films in 2010.
3D props up the box office
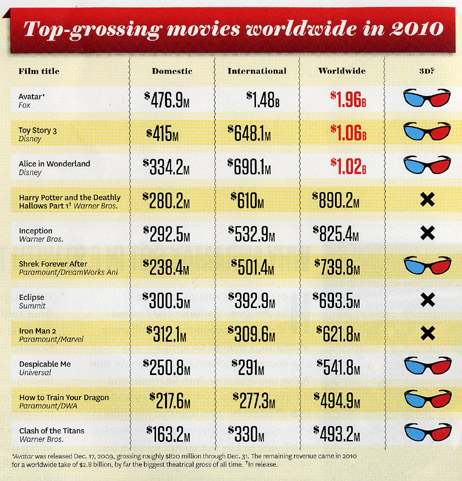
This week’s print version of The Hollywood Reporter heralds 2010 as “The year that was saved by 3D.” (For subscribers, the article is online, though it lacks the charts.) As Pamela McClintock, author of this excellent article, points out, “Of the top 20 films at the domestic box office, 11 were 3D titles (out of a total of 22 major 3D releases). Why the fat grosses? On average, a 3D title can expect to make 30 percent more because of the 30 percent upcharge for a 3D ticket.” (The accompanying chart, below, covers only the top 11 titles.)
(I will step in here and point out something that never seems to get mentioned in coverage of 3D, which is that part of that fee goes to pay for the glasses.)
Moreover, overseas markets, which have been making up an increasing portion of most big films’ worldwide grosses, are adding 3D screens like crazy. “The U.K., China, Russia, Japan, France, Germany, China and Russia in particular have seen a surge in digital-theater installations.” Given that the U.S. is still making more 3D films than most of these countries, Hollywood is getting a generous slice of that box-office income. Some films thought to be disappointments in the States did well worldwide, such as Clash of the Titans, with $493.2 million, and The Last Airbender, with $318.9 million.
Of course, there have been underperformers: Cats and Dogs: the Revenge of Kitty Galore, The Voyage of the Dawn Treader, and Gulliver’s Travels, most notably. McClintock points out, “It’s almost certain that Deathly Hallows would have jumped the $1 billion mark worldwide had it been released in 3D, but Warners didn’t want to tarnish the franchise.” As it is, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows Part 1 has grossed $937,257,461 worldwide and is still in distribution.
Another thing that McClintock points out that most commentators ignore is that making a film in 3D adds to its budget, on average about $20 million for a two-hour feature. The alternative practice of shooting a film in 2D and then converting it to 3D is common. That costs about $100,000 or more a minute, or about $12 million for a two-hour film. (James Cameron, who ought to know, says a quality job would be $15 million or more.) For a movie that grosses in the hundreds of millions, that’s pretty small, but it’s not insignificant for a more modest film.
Let’s think about that for a moment. Jeffrey Katzenberg and James Cameron may still expect that all films will someday be made in 3D. But, to take one example I’ve seen people use in recent months, do we really think The Kids Are All Right would be enhanced by 3D? Even if some people do, the film cost only around $4 million to make and grossed a little under $30 million worldwide. Would $20 million spent on 3D cause it to gross over $50 million to make up the difference?*
Or does it?
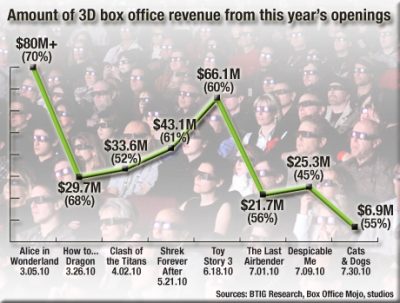
Despite the fact that 3D brought in higher grosses for the more successful films in that format last year, some experts are pointing to a decline in revenues over the year. In July of last year, Daniel Frankel published a widely cited chart called “The Rise & Fall of 3D” on The Wrap showing that since the release of Avatar the previous December, the proportion of the opening weekend box-office for major films coming from 3D screenings had declined:
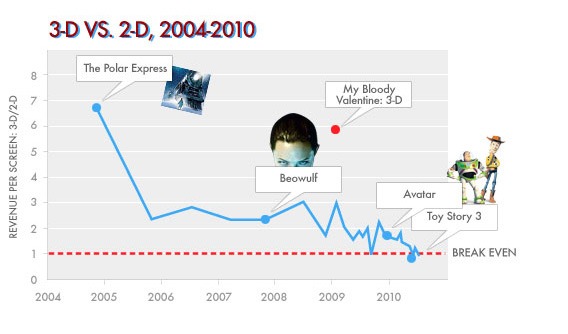
Then in August Slate posted a more detailed study by Daniel Engber bluntly entitled “Is 3-D Dead in the Water?” Engber took issue with Frankel’s chart saying that it did not reflect problems with a shortage of 3D screens available during the release of these films. But Engber didn’t disagree that 3D’s share of a film’s income has been falling. Quite the contrary, he thought it the decline was even greater. Taking a different approach that basically compares per-screen averages for 3D and 2D screening of the same film, he came up with a new chart:
The chart below—created with enormous help from Slate designer Holly Allen—shows the ratio of 3-D revenue to 2-D revenue, on a per-screen basis, for almost every major three-dimensional release going back to the beginning of the current revival.
Here’s the simplest way to interpret this graph: 3-D has been getting less and less profitable, relative to 2-D, over the past five years. It’s an ominous, downward trend that started long before Avatar and Alice in Wonderland and continued after. (The red dotted line represents a break-even point, where screenings in 3-D and 2-D theaters make exactly the same amount of money.)
(I can’t go into the details here, but Engber presents additional charts and information; it’s a must-read for anyone interested in 3D, pro or con.)
Last year the big complaint from Katzenberg and other 3D purveyors was that there weren’t enough theaters to screen all the films that were coming out in that format. Katzenberg is still not satisfied with the rate at which theaters are converting screens to 3D, but maybe exhibitors have realized that there is not as much future in it as they had been led to believe. Given that most multiplexes have two, three, or even four screens capable of showing 3D films, the rate of conversion is likely to slow, if it hasn’t already.
Toy Story 3‘s release seems to have marked the point where some industry analysts began to notice the downward trend in 3D revenues in comparison to 2D. Its opening offers an insight into whether the drop is real or just an apparent effect of too many 3D films vying for too few screens, as is so often claimed. Media financial analyst Richard Greenfield pointed out that the film’s percentage of revenue from 3D screens was 1% less than with Shrek Forever After (released May 21). Toy Story 3 had made 60% of its opening weekend box office on 3D screens, while Shrek Forever After (released May 21) had made 61% and Alice in Wonderland (March 5) had made 70%.
1% may not sound like a lot, but Toy Story 3 was released on the largest number of 3D screens of any film to that date. In that case, it could not be claimed that the drop resulted from too many 3D films jostling for screens. On the contrary, one would expect a rise.
Not only that, but Engber points out that the 2D versions of Toy Story 3 actually outperformed the 3D ones:
Then we come to the weekend of June 18, 2010, when Toy Story 3 opened in more than 4,000 theaters around the country. It was a huge weekend for the Pixar film—one of the biggest of all time, in fact, with more than $110 million in total revenue, and $66 million from 3-D. Yet a close look at the numbers shows something else: On average, Toy Story 3 pulled in $27,000 for every theater showing the movie in 3-D, and $28,000 for every one that showed it flat. In other words, the net effect of showing Woody, Buzz, and friends in full stereo depth was negative 5 percent. The format was losing money.
One could posit, of course, that the 2D screenings simply benefited from the overflow from sold-out 3D screenings. People who wanted to see the film in 3D had to settle. But that still doesn’t explain the drop in comparison to earlier films given the fact that Toy Story 3 opened on the largest number of 3D screens. At least two tickets to the film in 2D were sold to people who had the option of going to a 3D screening: David and me.
Engber goes on to consider some explanations for the decline, some of the same basic ones I’ll discuss here. He concludes that the situation is dire for 3D: “For mainstream movies that can be viewed in either format, the added benefit of screening in three dimensions is trending toward zero.”
Is 3D TV competing with theatrical or hurting it?
There seems to be an assumption that pop culture is headed toward a time when new media in general are delivered in 3D. The assumption is that 3D television will help boost sales of movies on DVD and Blu-ray. Maybe, but the sales of 3D TVs have been reported as lower than expected. According to a revealing article in Variety, Samsung projected that it would sell 3 million units in 2010 and sold less than 2 million: “According to several electronics makers, the biz will be concerned if the negativity continues six months from now.” Screen Digest’s year-end summary of 3D TV’s prospects (“After one year of 3D in the home,” December 2010 issue) points out that not only do 3D sets cost half again as much as 2D ones, but they are also mostly 44” or over, larger than most people can afford even in 2D sets.
That’s not the only cost holding back sales of sets. According to Variety: “The main reasons for holding out have been the pricey pairs of active-shutter glasses (sold for around $150 or more) that can be cumbersome to wear, easy to break and require batteries that run out. At the same time, there hasn’t been much 3D content to watch on the new sets.”
Sets with these active-shutter glasses come with one pair included. The things are bulky and require batteries. New 3D TV models are in the pipeline, some that work with lighter polarized glasses costing more like $20, with  four pairs included. As Bob Mayson president of consumer electronics for RealD (a major 3D theatrical supplier) told Variety, “You won’t have a Super Bowl party with active eyewear. With passive eyewear [i.e, those polarized glasses] you can buy a bag of glasses from Costco and be in business.”
four pairs included. As Bob Mayson president of consumer electronics for RealD (a major 3D theatrical supplier) told Variety, “You won’t have a Super Bowl party with active eyewear. With passive eyewear [i.e, those polarized glasses] you can buy a bag of glasses from Costco and be in business.”
Maybe guys who sit around drinking beer and watching the Super Bowl will get used to seeing each other wearing plastic glasses. Still, I have long been of the opinion that until 3D technology reaches a point where the glasses are unnecessary, the format can’t be universally viable. Toshiba and Sony have prototypes of such sets at technology fairs, but they reportedly won’t reach consumers for three to five years. I’m curious to know what the 3D effect will look like if you’re not sitting at exactly the right spot in front of the screen. From what I’ve read, you have to be positioned not only in front but also close. An excellent article in Wired summing up the obstacles to watching 3D on TV says the depth effect is limited to about four feet. In fact, there already are monitors for 3D without glasses (mainly available in Japan); they’re used mainly to display ads in stores. But in October Toshiba showed off two models intended for the home (left). The monitors are 12″ and 20″ and the optimum viewing distance is 90 cm for the larger monitor; that’s about three feet. They can project 3D to nine points in the room, but it sounds downright impossible for that many people to perch at precise points, all about a yard from the screen. Bigger versions will no doubt follow.
More content is coming for 3D TV, but again according to Variety, many content-providers are
focused on high-profile fare like sports and concerts, because as long as 3D TV requires glasses, it will only be used for event programming, not casual viewing. It may be tough to broadcast the Super Bowl in full 3D, outside of relying on a conversion, however, given that too many seats in the stadium would have to be removed for the 3D cameras. Networks could use robotic and remote-controlled 3D cameras but those are still too new of technologies to rely on yet.
Screen Digest ‘s year-end summary of 3D TV focuses on other obstacles, primarily the lack of content:
As recently as early September 2010 two thirds of the 21 3D BD [Blu-ray Disc] titles confirmed for US release in 2010 were tired to exclusive bundling deals with 3D hardware, leaving only seven available for purchase in store. By November, the total 3D BD slate had increased to 37 titles, 25 of which had been confirmed for retail sale by the year end. Furthermore, many of the biggest titles (including Avatar, the Shrek franchise, Monsters v Aliens, Ice Age 3) were still tied into exclusive bundles. By comparison, at the end of Blu-ray’s first year of availability (2006) 135 titles had been released on the format in the U.S.
I’m sure the brand partnerships between the TV makers and the studios have saved a lot in advertising, but it’s hard to imagine investing in a new technology when every time you want a popular film title, you have to buy a TV set to go with it. No doubt the availability of films to buy will increase, but the introductory approach seems a strange way to go about fostering interest in 3D movies on TV.
The Screen Digest article makes another interesting point. Initially, “3D in the home was conceived first and foremost as an attempt to mirror the revenues proven in the cinema—a 20 per cent premium over 2D features.” But much 3D TV content is also surprisingly like 2D TV content: “Ten percent of the cinema features have been dance or music, with a further four per cent including live sports and opera. This suggests an appetite for content that has traditionally been better suited to live television transmission than physical or cinematic tradition.” That further suggests that in the long run, people may be keener on 3D TV than on theatrical films in 3D—just the opposite of the studios’ hopes as they went in for 3D.
Beyond film and TV content, there is also the likelihood that 3D video-game playing through the large monitor will take up some of the time spent in front of the appliance. There’s also the fact that streaming or downloading 3D films requires far more bandwidth than 2D movies, though methods of compression are being developed.
The Screen Digest author predicts that by the end of 2014, 25% of American homes will have 3D TV. The question remains: What will people be watching?
Next week: Part two: RealDsgusted
*No doubt some cost-cutting is possible. Still, Tsui Hark’s Flying Swords of Dragon Inn (announced for a 2011 release), shot with the relatively inexpensive Red 3D digital camera, is budgeted at approximately $35 million. The difference between that and his usual cost per film could easily include $15-20 million for 3D. See Filmsmash for information and numerous photos derived from Chinese sites; the latter include images of the camera and of shooting in front of a green screen.
By Sam Spratt at Gizmodo