Archive for 2008
Preserving two masters
Kristin here—
This past weekend the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Cinematheque played host to Stefan Drössler, the head of the Filmmuseum in Munich. The Filmmuseum is a major force in film restoration, and on Saturday we were treated to a much longer print of Ernst Lubitsch’s 1922 epic, Das Weib des Pharao, than had previously been available.
Lubitsch on the verge of going Hollywood
This restoration came too late for me to see it before my book on the director’s silent features, Herr Lubitsch Goes to Hollywood (2005), was published. Not that that was a problem. I was dealing largely with style in that book, and the old version furnished plenty of examples to support my point. I argued that Das Weib was a turning point in Lubitsch’s career. It was the first film he made after the German ban on film imports was lifted and he was able to see recent Hollywood films for the first time since the war. It was also made with American financing, offering him the chance to work with American cameras and lighting equipment—an opportunity that gave him much more stylistic flexibility.
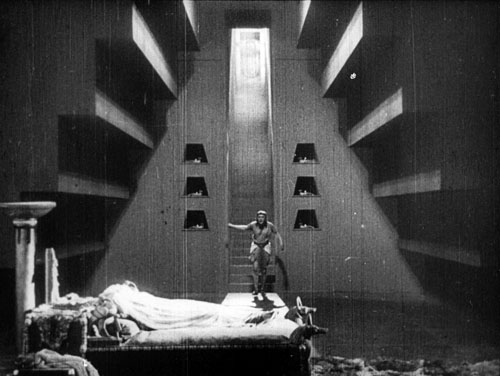
As a result, Lubitsch goes from using mostly flat, frontal light to employing the recently developed three-point lighting system. The frame above shows a very Hollywood-style lighting layout, and that’s fairly typical of this film.
Of course, it was a treat to see the film with so much new material. As I recall, the old version ran about 40 minutes, while this one is 110 minutes. There’s still footage missing, replaced in this print by still photographs and summary intertitles. Still, the plot makes a lot more sense. For the most part, the visual quality is better. The restoration depended on footage supplied by a number of archives, however, and the occasional inferior shot indicates that a less well-preserved print had to be used as source material.
The story, set in ancient Egypt, is rather clichéd and the characters little more than ciphers. The interest lies mainly in the style and the majestic scale of the production. Given a much larger budget than usual and a longer shooting schedule, Lubitsch distinctly outdid his own earlier historical dramas, Madame Dubarry (1919) and Anna Boleyn (1921). Reportedly 8000 extras participated in the battle and crowd scenes, and the sets were erected on a colossal scale. Designer Ernst Stern was a serious Egyptology buff, and despite occasional lapses, the sets, props, and hieroglyphs are a lot more authentic than those in most movies set in this era. The film’s cast also includes a remarkable line-up of some of the most prominent actors of its day: Paul Wegener, Albert Bassermann, Harry Liedtke, and Emil Jannings (above).
Perhaps, as happened recently with Metropolis, a new, complete version of Das Weib des Pharao will someday be found. As Stefan said, however, more footage from Lubitsch’s last German film, Die Flamme (1922) would be even more welcome. An intimate drama starring Pola Negri, it survives in only one tantalizing reel. That footage reveals the director’s rapidly growing grasp of continuity editing as well as three-point lighting. Clearly he was ready to make the move to Hollywood and to even further development as a filmmaker. (My own dream film to be rediscovered would be Kiss Me Again, a completely lost 1925 Warner Bros. feature. Odds are pretty good that the one film Lubitsch made between The Marriage Circle and Lady Windermere’s Fan would be a masterpiece.)
A new Walter Ruttmann DVD
Seeing a 35mm print of such a restoration well projected is the ideal, of course, especially with an expert pianist like the Cinematheque’s David Drazin providing the accompaniment. For those who can’t get to such screenings or who want to study its restorations, the Filmmuseum also makes many of its restorations, as well as art and avant-garde films, available on DVD.
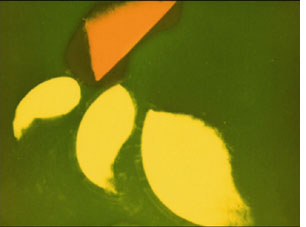 Stefan gave us a copy of one of the latest of these, a Walther (or Walter, as he sometimes spelled it) Ruttmann disc entitled “Berlin, die Sinfonie der Grossstadt & Melodie der Welt.” Actually, that’s a bit misleading, since the DVD actually contains a great deal more than those two features. All of Ruttmann’s surviving films up to 1931 are included. He was on the forefront of abstract animation, and the full series, Lichtspiel Opus I (1921), Opus II (1922), Opus III (1924), and Opus IV (1925), is included here. All have musical accompaniment, including Hanns Eisler’s 1927 score for Opus III. (That’s a frame from Opus I on the left.)
Stefan gave us a copy of one of the latest of these, a Walther (or Walter, as he sometimes spelled it) Ruttmann disc entitled “Berlin, die Sinfonie der Grossstadt & Melodie der Welt.” Actually, that’s a bit misleading, since the DVD actually contains a great deal more than those two features. All of Ruttmann’s surviving films up to 1931 are included. He was on the forefront of abstract animation, and the full series, Lichtspiel Opus I (1921), Opus II (1922), Opus III (1924), and Opus IV (1925), is included here. All have musical accompaniment, including Hanns Eisler’s 1927 score for Opus III. (That’s a frame from Opus I on the left.)
In addition, there’s a group of charming advertising films, all animated. These tend to be abstract and only bring in the product near the end. In doing the short for Excelsior tires, however, Ruttmann obviously found a round, nearly abstract shape that he could play with. A  tire rolls around in a flat landscape, having adventures that include going up and down the Excelsior factory smokestack and being threatened by spiky shapes that fail to puncture it.
tire rolls around in a flat landscape, having adventures that include going up and down the Excelsior factory smokestack and being threatened by spiky shapes that fail to puncture it.
Apart from these shorts, the two-disc set includes as bonuses a series of 22 paintings and drawings by Ruttmann, a number of texts by and about him, photographs, and so on. There’s also a CD-ROM section with additional documentation, plus a small booklet.
The two features are restorations. If you’ve only seen Berlin on a mediocre 16mm copy, this version should be a revelation. Its visual quality is gorgeous, and it has the original Edmund Meisel score, well played and well synched. The “symphony” aspect of the film makes a lot more sense with this accompaniment.
Melodie der Welt is credited with being the first German sound feature. It’s a lot simpler than Berlin. Financed  by a steamship company, it purports to follow a sailor on a huge liner around the world to exotic countries. Ruttmann takes footage from English, Greek, Japanese, and other cultures and cuts them together by topic to emphasize the similarities. Religious ceremonies are compared, military exercises intercut, children’s games assembled into a montage, people playing music (right), and so on. The laudable goal is to make customs of “exotic” peoples seem less remote and strange by showing them doing things that are not all that different from what Europeans do. A pity this was happening just before the Nazis sought to eradicate such notions of universal humanity.
by a steamship company, it purports to follow a sailor on a huge liner around the world to exotic countries. Ruttmann takes footage from English, Greek, Japanese, and other cultures and cuts them together by topic to emphasize the similarities. Religious ceremonies are compared, military exercises intercut, children’s games assembled into a montage, people playing music (right), and so on. The laudable goal is to make customs of “exotic” peoples seem less remote and strange by showing them doing things that are not all that different from what Europeans do. A pity this was happening just before the Nazis sought to eradicate such notions of universal humanity.
This set is just about ideal as a presentation of Ruttmann’s work in this period. I hope that someday a print of his 1933 fiction feature, Acciaio, will become available. It was made in Italy, and although it has been many years since I’ve seen it, I remember it as a very good film with spectacular documentary-style scenes shot in a steel mill—and as a forerunner of Neorealism.
David and I look forward to seeing Stefan at next summer’s Il Cinema Ritrovato festival in Bologna and to whatever new treasures he and his fellow archivists have restored.
Fast forward, now pause
DB here:
Since Kristin got back from Petra (glimpses of her trip are here), we’ve been busy checking the page proofs of the third edition of Film History: An Introduction. It’s due out in February and we have to go over the whole enormous thing, since we’ve made adjustments to almost every chapter. There will be updates of several chapters, as well as two new chapters taking into account developments since our last edition (written in the fall of 2001). We’re also expanding our Notes and Queries supplements, which will appear online. Already our new introduction, discussing some approaches to historical research, is available elsewhere on this site.
This task hasn’t given us much time for blogging. Now, though, we are in a small hiatus before the final push, so each of us hopes to finish a blog entry this week. Kristin will write about a recent visit to Madison of Stefan Droessler, head of the Munich Film Archive. He gave lectures and screened a reconstructed Lubitsch film, The Wife of the Pharaoh (1922). My entry will focus on Wong Kar-wai’s Ashes of Time Redux. I hope to point out some interesting differences among the versions of this remarkable movie.
But to keep your eyes warm, three quick items of note.
I probably don’t have to urge you to see the new Criterion edition of Chungking Express, out in both standard and Blu-ray editions. It’s the Miramax/ Rolling Thunder version, in a crisp transfer with a nice range of color and detail. (I don’t have Blu-ray and so can’t report on that disc.) There’s also a precious 1996 British TV episode in which WKW and a beer-guzzling Chris Doyle tour some Hong Kong locales we see in the movie, tossing out technical information along the way. The show also supplies a more or less documentary record of the Midnight Express fast-food counter a couple of years after the film. Still later, the success of Wong’s film led the owner to upgrade it, with results you can see at the end of this entry.
In the supplementary short, Chris Doyle catches himself talking like a critic and says it’s because “I’ve been reading Tony Rayns.” Not by chance, the Criterion set includes a superb commentary track by Tony, who has worked closely with Wong and Doyle for years. Tony’s fluent discussion anticipates practically every question you might ask about the movie, including why Faye Wong wears a United Airlines uniform.
Chungking Express is my favorite of Wong’s work, but that’s not the main reason I devoted a chapter to it in Planet Hong Kong. I think it’s an important film historically. In the context of Hong Kong cinema, it was as much a breakthrough as was Days of Being Wild, but its offhandedness made it seem more innocuous. Wong makes daring use of plot structure: two stories, barely linked, that connect thematically rather than causally. (We also examine this aspect in one section of Film Art.) Further, Chungking Express is an exhilarating instance of a type of storytelling that fascinates me, what I call “network narrative” and that I analyze in one essay in Poetics of Cinema. Finally, because this film was more widely seen than Wong’s earlier work, it identified him with a particular style: dazzlingly composed shots alternating with smeared and rushed ones, pulsations of saturated color, precise matching of image to music, and a tone of wistful romanticism. Who else could make such an engaging movie about two guys whose girlfriends have left them?
Across his career, Wong’s technique has been more varied than the flash-and-grab breeziness of Chungking Express, Fallen Angels, and Happy Together suggests. The blurred imagery and stuttering slow motion proved easy to mimic and even parody (in Wong Jing’s Whatever You Want, 1994). In the Mood for Love and 2046 returned to the more precise and controlled staging, the nearly abstract use of setting, and the tight close-ups of Wong’s earliest films. For all their virtues, though, these late movies lack the sheer ingratiating zest of Chungking Express. If My Blueberry Nights disappointed you (as it did me), revisit the original and watch it jump off the screen. Keep an eye peeled for those reflections.
Speaking of new DVDs, today the UPS man lugged a Fox Murnau/ Borzage box to our door. This cost more than my first car (and weighs about the same), but it’s a better bargain. My oil-leaking ‘62 Impala did not come fully loaded with Sunrise and City Girl and Seventh Heaven. Dedicated Fox archivist Schawn Belston has labored hard to create this remarkable collection, as robust a contribution to our understanding of film history as his Ford at Fox box a year ago. Tucked inside the chocolate-colored case are twelve films and two handsome books with texts by Janet Bergstrom. An entire book is devoted to the lost Four Devils, and one disc houses a lengthy documentary on the two directors.
Many of the early thirties Borzages are new to me, and I can’t wait to see them. But Kristin and I are very happy to have two lesser-known titles that we love, Lucky Star (1929) and Lazybones (1925). The latter is a striking example of the trend toward the “soft style” of cinematography that swept Hollywood in the 1920s (and that Kristin analyzes in The Classical Hollywood Cinema). Even men were shot with filters, gauzes, and selective focus, creating lyrical images like the one of our hero above. The soft style was about as popular then as the dark, earth-and-steel tonalities we find in so many films today. When our travails with Film History are ended, we look forward to digging into this new Fox treasure chest.
Finally, why not try to identify a mystery movie like the one above? In an email Joe Lindner, archivist at the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences, writes:
The Nitrate Film Interest Group of the Association of Moving Image Archivists has put together a page on flickr where archivists can post images of unidentified films. The submissions have tended towards silent films and nitrate prints, but sound films and safety elements are welcome as well. The page is also set up for short video clips, and the first video post has just been uploaded from a new scan of a 28mm print in the Academy Film Archive’s collection. This is also a good resource for anyone out there seeking help in identifying film elements, and you do not have to be a member of AMIA to submit images.
This is a remarkable site, and the images are tantalizing. As of this writing, several films have already been identified.
So, three snacks to tide us all over. Check in later this week for some new stuff, when our eyes will focus again.
Stepping into a movie
KT here-
This past weekend I returned from a tour of ancient sites in Jordan. I didn’t plan to see any movies during the trip, but in a way it was a movie that sent me there.
 I suspect that, like me, many people first become aware of the ancient city of Petra when they watch the climactic scene of Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade. Indie and his companions ride through a tall, narrow canyon and emerge to confront a huge red rock-cut building (above).
I suspect that, like me, many people first become aware of the ancient city of Petra when they watch the climactic scene of Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade. Indie and his companions ride through a tall, narrow canyon and emerge to confront a huge red rock-cut building (above).
That’s not a set. It was shot at Petra in southern Jordan. The canyon is real. It’s called the Siq (“shaft” in Arabic), and it’s a dramatic crack that runs for about a mile between tall, undulating cliffs of red sandstone (on the lower layers, where most of the city’s buildings were carved) and white sandstone (on the upper layers). The other structures include a theater, temples, and many tombs.
As I learned a bit more about Petra as a real place, I conceived an ambition to visit it—not for its Indiana Jones connection but because it is such an extraordinary archaeological site. In fact, last year it was voted one of the new seven wonders of the world.
I was one of seven members of a London-based tour, plus our lecturer and local guide. There are many ancient sites in Jordan, but Petra was left until the end. What, after all, could hope to follow it and not seem a let-down?
No, I didn’t go to see movies, but I discovered it’s pretty hard to escape them. References and connections tend to pop up.
We approached the entrance to Petra through the usual rows of souvenir and refreshment stalls. Some entrepreneurs were exploiting the Indiana Jones connection. Images from posters adorned coffee shops, and more than one shop had hats on sale. They weren’t really much like the famous felt fedora, being mostly of leather and not quite the right shape.
Right beside the Indiana Jones stalls, there was the Titanic Coffee Shop. My companions were mystified as to why anyone would choose that name. To me it seemed pretty obvious. American movies are popular, and why not name your shop after the most popular of them all? There was a restaurant near our hotel called Mystic Pizza. I didn’t see any images from the film on the outside, and I didn’t go inside to find out if there were any there.
Back in early October I reported on Captain Abu Raed, reportedly the first fiction feature made in Jordan in fifty years. There doesn’t seem to be any big stigma against films, though. I saw theaters and video-rental shops, some of the latter adorned with unlicensed paintings of Mickey Mouse.
Our last stop after Petra before returning to Amman was the Wadi Rum (below), an austerely beautiful landscape of desert and small, craggy mountains. The film motif followed us. Part of Lawrence of Arabia was shot there. On the spot where the real Lawrence had trod, the real Peter O’Toole sang, “The Man Who Broke the Bank at Monte Carlo.”
His majesty the American, leaping for the moon
DB here:
 Douglas Fairbanks is remembered today as the nimble, insouciant hero of a string of swashbuckling films: The Mark of Zorro (1920), The Three Musketeers (1921), Robin Hood (1922), The Thief of Baghdad (1924), Don Q Son of Zorro (1925), and The Black Pirate (1926). He is the primary subject of a gorgeously illustrated, solidly researched new biography by Jeffrey Vance with Tony Maietta. Proceeding film by film, the authors interweave his life story with production data and summaries of critical reception. While tracing his career, they make an intriguing case that Fairbanks’ 1920s features more or less founded the modern film of action and adventure.
Douglas Fairbanks is remembered today as the nimble, insouciant hero of a string of swashbuckling films: The Mark of Zorro (1920), The Three Musketeers (1921), Robin Hood (1922), The Thief of Baghdad (1924), Don Q Son of Zorro (1925), and The Black Pirate (1926). He is the primary subject of a gorgeously illustrated, solidly researched new biography by Jeffrey Vance with Tony Maietta. Proceeding film by film, the authors interweave his life story with production data and summaries of critical reception. While tracing his career, they make an intriguing case that Fairbanks’ 1920s features more or less founded the modern film of action and adventure.
In the five years before The Mark of Zorro, Fairbanks made twenty-nine features and shorts. Vance and Maietta are enlightening on this period, but they treat it as prologue to the more spectacular work. Now, as if to counterbalance their book, comes a new Flicker Alley DVD collection, Douglas Fairbanks: A Modern Musketeer, gathering ten of the early films along with a very pretty copy of The Mark of Zorro and Fairbanks’ last modern-day movie, The Nut (1921), made because he wasn’t sure that Zorro would be a hit. (It was.) To the DVD package Vance and Maietta have contributed an informative booklet and they offer enlightening conversation in a commentary track for A Modern Musketeer (1917).
 Kristin and I have long been fans of the pre-Zorro titles. Kristin wrote an appreciation of the early films for a Pordenone catalogue, and I studied Wild and Woolly (1917) as an early prototype of Hollywood narration. (1) There’s no denying that the 1920s costume pictures offer dashing spectacle and derring-do. But the 1915-1920 films are something special—lively, lilting, and unexpectedly peculiar. (2)
Kristin and I have long been fans of the pre-Zorro titles. Kristin wrote an appreciation of the early films for a Pordenone catalogue, and I studied Wild and Woolly (1917) as an early prototype of Hollywood narration. (1) There’s no denying that the 1920s costume pictures offer dashing spectacle and derring-do. But the 1915-1920 films are something special—lively, lilting, and unexpectedly peculiar. (2)
Before he became Fairbanks, he was Doug, the relentlessly cheerful American optimist. This star image was created very quickly, in films and in public events that made him seem the nicest guy in the country. His manic energy came to incarnate the new pace of American cinema, and his films helped shape the emerging precepts of Hollywood storytelling.
Doug
Consider his contemporaries. William S. Hart keeps his distance; perhaps his severe remoteness comes from secret pain. The result is a man you respect and admire but can hardly love. Mary Pickford, though, is lovable, and so is Chapin, although his cruel streak complicates things. But Doug is quintessentially likable. His early films present us with a brash youth who is all pep and pluck, bouncing with barely contained energy, unselfconscious in his engulfing enthusiasm for life. Today he could be elected President, the ultimate guy to have a beer with. (In real life Fairbanks was a teetotaler.)
 There is no guile in him, no hidden agenda. When he’s brimming with delight, as he often is, he flings his arms out wide. In another actor this would be hamminess, but for Doug it’s simply an effort to embrace the world. Any social embarrassments he commits—and they are plenty—he acknowledges with a puzzled frown before flicking on an incandescent grin. Who else makes movies with titles like The Habit of Happiness (1916) and He Comes Up Smiling (1918)?
There is no guile in him, no hidden agenda. When he’s brimming with delight, as he often is, he flings his arms out wide. In another actor this would be hamminess, but for Doug it’s simply an effort to embrace the world. Any social embarrassments he commits—and they are plenty—he acknowledges with a puzzled frown before flicking on an incandescent grin. Who else makes movies with titles like The Habit of Happiness (1916) and He Comes Up Smiling (1918)?
But how can such a genial fellow yield any drama? Give him an idée fixe, a cockeyed hobby or life philosophy into which he can pour his adrenaline. Now add a goal, something that his obsession blocks or unexpectedly helps him attain. Toss in the staples of romantic comedy: a good-humored maiden uncertain how to tame this creature of nature, a few old fogeys, some unscrupulous rivals. Hardened crooks may make an appearance as well. Be sure to include some tables, chairs, sofas, or horses for him to vault over, as well as some perches near the ceiling or on the roof; Doug feels most comfortable lounging high up. Add windows, for his inevitable defenestration. (In a poem about him, Jean Epstein wrote, “Windows are the only doors.”) There should also be chases. Other comedy stars run because they must. Doug’s joy in flat-out sprinting suggests that he welcomes the chance to flush a little hyperactivity out of his system. At the story’s climax he must save the day, taming his obsession and achieving his purpose while acceding to the claims of the practical world.
An early example is His Picture in the Papers (1916). In this satire on vegetarianism and the American lust for publicity, Doug works for his father’s health-food firm, even though he prefers thick steaks. But he’s full of ideas for promoting the product. Doug needs money to marry his equally carnivorous girlfriend, but his father will give him the dough only if Doug can pitch their line of dietary supplements. Doug vows to get his picture in every newspaper in town. While he launches a series of high-profile stunts—wrecking his car, entering a prizefight, brawling on an Atlantic City beach—his sweetheart’s father is pursued by a gang called the Weazels, who try to extort money from him.
The two plotlines converge, with Doug stopping a train wreck and winning a place on the front pages. (In a sly dig at the press, each news story contradicts the others.) The movie is a little disjointed, but several scenes are remarkable, not least a boxing match in an actual athletic club before an audience of cheering Fairbanks pals. And there is more than one funny framing, notably a nice planimetric one showing all our principals lined up and reading different newspapers celebrating Doug’s triumph.
As the title indicates, in The Matrimaniac (1916) Doug’s goal is elopement, which he pursues obsessively. He evades a rival suitor, his girlfriend’s father, a sheriff, and a posse of city officials in order to tie the knot in a gag that must have looked radically up-to-date. Reaching for the Moon gives us a more philosophical Doug, a naive disciple of self-help books that urge him to strive, to concentrate, and above all to keep his eye on the most supreme goal he can imagine. He ends up in New Jersey.
Wild and Woolly (1917) casts Doug as the son of a railroad tycoon. Although he lives in Manhattan, he dreams of being a cowboy. His bedroom boasts a teepee, and he practices his roping skills on the butler. Sent out to Bitter Creek to investigate a deal, he encounters the rugged frontier of his dreams, complete with shootouts, town dances, and hard-drinking cowpokes. But all of this is a show, staged by the locals to make him look favorably on a railroad spur. In another twist, a crooked Indian agent uses the charade to rob the bank and stir up an Indian settlement. Now Doug’s obsessions prove really useful, as his cowboy skills rescue the town.
Wild and Woolly is among the very best of the surviving early Fairbanks titles, and its adroit storytelling is still admirable today. The best-known version was a very poor print, salvaged from the Czech archives and still circulating on barely visible VHS and public-domain DVD copies. Forget those. On the Flicker Alley collection the image quality, while not perfect, allows this trim little masterpiece to be appreciated. (3)
“Always chivalrous, always misunderstood,” reads one intertitle in another gem, A Modern Musketeer. Here Doug is possessed by the spirit of D’Artagnan, simply because while he was in the womb his mother was reading The Three Musketeers. He manages to live up to his heritage as he overcomes a philandering rival and a bloodthirsty Indian. The climactic chase takes place at the Grand Canyon, affording Doug a chance to shinny up and down cliffs and do handstands along a precipice.
Doug never does things by halves. In Flirting with Fate, he is a starving artist, out of money and apparently unloved by his girl. The logical solution is to hire a killer to end his misery. Of course Doug’s fortunes instantly change, and life becomes worth living, but then he must somehow find his assassin and call off the hit.
Many of the early films show the protagonist fully formed as a cross between a cheerleader and a track star. But Fairbanks made a big success on stage playing a sissy. The task in such a plot is to turn him into a red-blooded man. His first film, The Lamb replayed this lamb-into-lion plot, which also served as the basis for Buster Keaton’s first feature, The Saphead (1920).
In the Flicker Alley collection, this strain of Doug’s work is represented by The Mollycoddle (1920). Doug is the descendant of hard-bitten westerners, but growing up in England has made him a fop. Coming to America with a batch of wealthy Yanks, he is a continual figure of fun, waving his monocle and cigarette holder. Once in Arizona, however, he’s confronted with a diamond-smuggling racket. He starts to channel his ancestors and turns into a hell-for-leather hero. He allies with a tribe of exploited Indians to capture the gang, in the process indulging in leaps, falls, canyon-scaling, and fistfights in raging rapids.
The titles often invoke craziness, vide the Matrimaniac, The Nut, and Manhattan Madness (1916). But this motif is carried to an extreme in one of the strangest pictures of the still-emerging Hollywood cinema. When the Clouds Roll By (1919) crams in enough gimmicks for three Doug stories. First, our hero is neurotically superstitious. He will climb over a building to avoid letting a black cat cross his path. He meets a girl who is as superstitious as he is, so after a session at the Ouija board, they seem a good match.
 At the same time, however, a psychiatrist is making Doug the subject of a demonic experiment: Can one drive a person to madness and suicide? Through bribes and surveillance, Dr. Metz turns Doug’s life into hell—botching his romance, getting him disowned by his father, and even inducing nightmares. As if all this weren’t enough, the last reel jams in a train crash, a bursting dam, and a flood. Before this overwhelming climax, When the Clouds Roll By isn’t so much funny as eerily paranoiac. The way Dr. Metz’s Mabuse-like scheme enfolds everyone is as anxiety-provoking as anything in a film noir. This dreamlike movie ends on a surrealist note: Doug and his sweetheart get married when flood waters carry a church past them.
At the same time, however, a psychiatrist is making Doug the subject of a demonic experiment: Can one drive a person to madness and suicide? Through bribes and surveillance, Dr. Metz turns Doug’s life into hell—botching his romance, getting him disowned by his father, and even inducing nightmares. As if all this weren’t enough, the last reel jams in a train crash, a bursting dam, and a flood. Before this overwhelming climax, When the Clouds Roll By isn’t so much funny as eerily paranoiac. The way Dr. Metz’s Mabuse-like scheme enfolds everyone is as anxiety-provoking as anything in a film noir. This dreamlike movie ends on a surrealist note: Doug and his sweetheart get married when flood waters carry a church past them.
Across these films, in fact, the Fairbanks persona starts to disintegrate. Somewhat like those naïve Capra heroes of the 1930s (Mr. Deeds, Mr. Smith) who turn into melancholy victims in Meet John Doe and It’s a Wonderful Life, Doug becomes more brooding and helpless. In Reaching for the Moon, his absurd dream of glory is revealed as just that, a dream. When the Clouds Roll By saves itself from despair through splashy last-minute rescues.
Fairbanks was evidently becoming uncomfortable in cosmopolitan comedy. His taste for large-scale stunts and tests of prowess led him to the costume sagas of the 1920s. In the process, as Vance and Maietta point out, he cleared the way for Keaton and Harold Lloyd. Both comics would sometimes play obtuse idlers in the Lamb mode, and both would take thrill comedy to new heights. But avoiding Fairbanks’ ebullient optimism, Keaton brought a perplexity to every situation, along with an angular athleticism and a geometrical conception of plotting and shot composition. Lloyd frankly presented a hero lacking social intelligence, afflicted with a stammer or shyness or even cowardice, always desperate to fit in. Both men deepened the possibilities of modern-day comedy, thriving in the niche vacated by Fairbanks.
Bug and Mr. E
For nine of the early films, Fairbanks had the help of John Emerson and Anita Loos. All three worked on the stories, with Emerson usually directing and Loos writing the scripts and intertitles. The collaboration lasted only about two years, but it yielded some definitive moments in the creation of the Doug mystique.
Emerson found his first success acting and directing on the New York stage. Under Griffith’s supervision he started filmmaking in 1914, with an adaptation of his own successful play, The Conspiracy. I haven’t seen this or most of his other early work, but his 1915 Ibsen adaptation Ghosts, codirected with George Nichols, betrays little of the dynamism that would run through his Fairbanks projects (although The Social Secretary of 1916, without Doug, is lively enough). Emerson continued to direct films and New York stage productions until his death in 1936, at the age of fifty-eight.
Loos was a tiny prodigy. She sold her first scripts at age nineteen, with the third, The New York Hat (1913), directed by Griffith, earning her twenty-five dollars. (Her punctilious account book is reprinted in her 1974 autobiography Kiss Hollywood Goodbye.) After writing scores of shorts, she moved into features in 1916, when, she claims, Emerson discovered her script for His Picture in the Papers. Clearing the project with Griffith and casting Doug Fairbanks, the team proceeded. This, Fairbanks’ third feature, proved a great success and solidified important aspects of his star persona.
 Loos married Emerson, whom she recalled as having “perfected that charisma, which even a bad actor has, of being able to charm his off-stage public.” (4) He called her Bug, she called him Mr. E., and they became a Hollywood couple. They kept themselves before the public eye with interviews and books like How to Write Photo Plays (1920) and Breaking into the Movies (1921). These are full of information about the filmmaking practices of the day.
Loos married Emerson, whom she recalled as having “perfected that charisma, which even a bad actor has, of being able to charm his off-stage public.” (4) He called her Bug, she called him Mr. E., and they became a Hollywood couple. They kept themselves before the public eye with interviews and books like How to Write Photo Plays (1920) and Breaking into the Movies (1921). These are full of information about the filmmaking practices of the day.
Why did Emerson and Loos split from Fairbanks? Loos says that that Doug had become somewhat jealous of her notoriety. (5) Further, the couple yearned to return to New York. There Loos would hobnob with the Algonquin club crowd and write Gentlemen Prefer Blondes, a successful serial, book, play, and silent film. Eventually she would write plays and return to Hollywood as an MGM screenwriter.
Although they remained married and collaborated on plays and films, the pair eventually lived apart, the better to ease Emerson’s philandering. “Mr. E.’s devotion was largely affected by the amount of money I earned,” Loos recalled. (6) By her own testimony, she earned plenty. She writes in 1921:
The highest paid workers in the movies today are the continuity writers, who put the stories into scenario form and write the “titles” or written inserts. The income of some of these writers runs into hundreds of thousands of dollars a year . . . . Scenario writing does not require great genius. (7)
Loos is largely credited with bringing the witty intertitle into its own. Expository “inserts” were often neutral descriptions of the action or pseudo-literary ruminations. Loos created intertitles that were amusing in themselves. When Jeff, the hero of Wild and Woolly, comes to Bitter Creek he’s delighted to find a rugged life matching the one he mimicked in his East Coast mansion. So naturally Loos’ title reads, “All the discomforts of home.”
She wedged in puns, satiric jabs, and asides to the audience. The vegetarianism portrayed in His Picture in the Papers makes for anemic romance. Loos’ title prepares us:
The young suitor and Christine kiss by tapping each other’s cheek with their fingertips.
Later the intertitle stresses the more robust wooing program launched by Doug.
By the time Loos and Emerson left Fairbanks, the look and feel of their contributions had been mastered by others, notably director Allan Dwan, and smart-alec intertitles continued to grace Fairbanks’ modern comedies. Throughout the 1920s, most comedies would strive, not always successfully, for the cleverness Loos brought to the task. My own favorite in her vein comes in the Lloyd vehicle For Heaven’s Sake (1926). Harold is a millionaire courting a girl working in her father’s mission house in the slums, and one of the titles refers to “The man with a mansion and the miss with a mission.” Such niceties largely vanished when movies started to talk.
Cutting edge
We can learn a lot about the history of Hollywood from these films too. In the 1910s, narrative techniques were being put in place: the goal-oriented hero, the multiple lines of action, the need to prepare what will happen later, the use of motifs as running gags. At the start of The Matrimaniac, we see Doug sneaking into a garage and letting the air out of a car’s tires. Only later, after he has eloped with the daughter of the household, do we realize that this was a way to keep her father from pursuing them. In the course of the same film, the elopement is aided by passersby, and Doug keeps scribbling IOUs to pay them. At the end, the parson who has helped the couple the most is rewarded by the biggest payoff, with Doug shoveling bills at him.
The same years saw the consolidation of the “American style” of staging, shooting, and cutting scenes. (For more on this trend, see our earlier entries here and here.) Fairbanks’ films from 1916 to 1920 display a growing mastery of continuity techniques; the style coalesces under our eyes.
The system depended on breaking up master shots into many closer views. This practice was less common among European directors of the time, who might supply inserts of printed matter like letters but did not usually dissect the scene into shots of different scales. In His Picture in the Papers, for instance, we get a master shot (nearer than it would be in a European picture) of Melville paying court to Christine, followed immediately by closer views that show their expressions.
This is a minimal case. Not only are the shots all taken from the same side of the line of action (the famous 180-system) but they are taken from approximately the same angle. Filmmakers sometimes varied the angle more, usually to indicate a character’s point of view but sometimes to bring out different aspects of the action. (See here for examples from William S. Hart.)
Very quickly directors realized that you didn’t need a master shot if you planned your shots carefully. In Flirting with Fate, the artist Augy is chatting with Gladys, while her mother and her rich suitor watch from another part of the room. No long shot presents both pairs.
The mother summons Gladys, and when she and Augy rise, director Christy Cabanne cuts to another shot of them, moving into the frame.
This is a very rare option in most national cinemas of the period, which would simply frame the couple in a way that allowed them to rise into the top of the same shot. Now Gladys hurries out, crossing the frame line. This exit matches her entrance on frame left, meeting her mother.
Such a scene is obvious by today’s standards, but a revelation at the time—a way of lending even static dialogue scenes a throbbing rhythm that absorbed viewers. Around the world, notably in the Soviet Union, young directors saw this as the cutting-edge approach to visual storytelling. The new style was as probably as exciting to them as the powers of the Internet are in our time.
Because of analytical editing, the cutting pace of American films of the late 1910s is remarkable, and the Fairbanks films, with their strenuous tempo, are fair examples; the average shot length in these films ranges between 4 seconds and 6.6 seconds. With so many shots, production procedures emerged to keep track of them. To a certain extent shots were written into the scenarios Loos refers to, but directors also broke the action up spontaneously during filming. The cameraman, and later a “script girl,” would log the shots during shooting so that they could be assembled correctly in the editing phase.
Directors were still refining the system, though, as we can see from an awkward passage of shot/ reverse shot in A Modern Musketeer.
The eyelines are a bit out of whack, but odder still are the identical backgrounds of the two shots. Evidently director Allan Dwan made these shots quickly and closer to the canyon rim, in the expectation that nobody would notice the disparity.
Point-of-view shots were easier to manage, and they could intensify the drama. Later in A Modern Musketeer, the rapacious Chin-de-dah tells the white tourists he’s getting married. To whom? asks Elsie. Instead of answering, “You,” he holds up his knife.
Sometimes you suspect that filmmakers were multiplying shots just for the fun of it. The early Fairbanks films are vigorous to the point of choppiness; action scenes spray out a hail of images, some offering merely glimpses of what’s happening. Wild and Woolly is especially frantic, with the final sequences of kidnapping, gunplay, and a ride to the rescue breathless in their pace. In the course of it, Emerson realizes that fast action needs some overlapping cuts to assure clarity. Doug bursts through a locked door in one shot, and from another angle, we see the door start to open again.
Only a few frames are repeated, but the movement gains a percussive force. Doubtless the Russians studied cuts like this; Eisenstein made the overlapping cut part of his signature style.
By contrast, The Mark of Zorro and its successors have calmer pacing. Doug’s acting got more restrained too, with his bounciness largely confined to the action scenes. Already in 1920, high-end pictures were finding a more academic look, a polished and measured style. Dialogue titles became more numerous, and big sets and other production values were highlighted.
I’ve been able to sample only a few points of interest in the early Fairbanks output. I haven’t talked about Fairbanks’ foray into Sennett-style farce, the cocaine-fueled Mystery of the Leaping Fish (1916), or the bold experimentation of the cinematography in the dream sequence of When the Clouds Roll By. My point is just to note that these films radiate exuberance—not only in their hero but in their very texture. Scene by scene, shot by shot, Doug’s energy is caught by an efficient, pulsating style that was an engaging variant of what would soon become the lingua franca of cinematic storytelling.
For other reading on Fairbanks, you can consult Alastair Cooke’s Douglas Fairbanks: The Making of a Screen Character (New York: Museum of Modern Art, 1940), one of the earliest and still most thought-provoking studies; John C. Tibbetts and James M. Welsh’s His Majesty the American: The Films of Douglas Fairbanks, Sr. (South Brunswick, NJ: A. S. Barnes, 1977), which is wide-ranging and strong on the early films; Booton Herndon’s Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks (New York: Norton, 1977); and Douglas Fairbanks: In His Own Words (Lincoln, NE: iUniverse, 2006), a collection of interviews and essays signed (but probably mostly not written) by the star. I’ve also been enlightened by Lea Jacobs’ essay “The Talmadge Sisters,” forthcoming in Star Decades: The 1920s, ed. Patrice Petro (Brunswick: Rutgers University Press, forthcoming). Online, there is much information at the Douglas Fairbanks Museum site.
(1) Kristin Thompson, “Fairbanks without the Mustache: A Case for the Early Films,” in Sulla via di Hollywood, ed. Paolo Cherchi Usai and Lorenzo Codelli (Pordenone: Biblioteca dell’Immagine, 1988), 156-193; David Bordwell, Narration in the Fiction Film (Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1985), 166-168, 201-204.
(2) This set is very well chosen, but there are enough other films surviving from this period to warrant another box. It could include The Lamb (1915), Double Trouble (1915), The Good Bad Man (1916), Manhattan Madness (1916), The Americano (1916), Down to Earth (1917), The Man from Painted Post (1917), His Majesty the American (1919), and The Half Breed (1916), in which Fairbanks plays a biracial hero. On the matter of race, the films in the collection aren’t free of condescension and stereotyping, but there are also moments of affection between Fairbanks and Native Americans. He had extraordinarily dark skin, a fact he apparently took in his stride.
(3) I believe that this print is from a different version than the one I’ve known before; a few shots seem to show slightly different angles. (Perhaps the earlier one was from a foreign negative?) An informative page of the Flicker Alley booklet signals the provenance of the prints. While I’m on the subject, I should mention that occasionally the framing seems a bit cropped, but that could be due to the source material.
(4) Loos, Kiss Hollywood Goodbye (New York: Ballantine, 1974), 2.
(5) Loos’ account of the break with Fairbanks can be found in her memoir, A Girl Like I (New York, 1966), 178. You have to admire a book that ends with the line, “Miss Loos, you sure are flypaper for pimps!”
(6) Loos, Kiss Hollywood Goodbye, 14.
(7) Emerson and Loos, Breaking into the Movies (Philadelphia: Jacobs, 1921), 43.
When the Clouds Roll By.
PS 30 Nov: Internets problems and a memory lapse kept me from mentioning two other important books on Anita Loos: Gary Carey’s lively biography Anita Loos (Knopf, 1988) and Anita Loos Rediscovered: Film Treatments and Fiction, ed. and annotated by Cari Beauchamp and Mary Anita Loos (University of California Press, 2003). Both Carey and Beauchamp echo Loos’ claims that the couple split from Fairbanks because he was somewhat envious of the attention they received, while Carey adds that Fairbanks wanted to break out of the “boobish” parts Loos wrote for him (p. 50).
PPS 8 Dec: Mea culpa again. I overlooked Richard Schickel’s book-length essay, His Picture in the Papers: A Speculation on Celebrity in America, Based on the Life of Douglas Fairbanks, Sr. (New York: Charterhouse, 1973). It’s a lively and thoughtful argument that Doug was one of the very first modern celebrities, and one who enjoyed his role as such.