Archive for October 2009
Between you, me, and the bedpost

Imitation of Life.
DB here:
I do not like finding phallic symbols in movies.
I grant you that there are some films that deliberately evoke the love wand: Tex Avery cartoons, Frank Tashlin and Jerry Lewis movies. Surely the Wolf in Avery’s Red Hot Riding Hood (1943) has more than a Platonic interest in Red’s stage show.

But some critics/ academics look way too hard. For them, as a literature professor of mine put it back in the mid-1960s, phallic symbols are everywhere in art. And I learned fast that he meant everywhere, from the Odyssey to Emily Dickinson. I changed sections.
Films, of course, are full of images that encourage the hunt for avatars of the skin flute. So for forty years, I’ve argued against interpretations of a scene that depend on reading you-know-what into anything that resembles a pole, post, or pylon—any vaguely tubular shape, slender or squat, organic or mechanical. It is a duffer’s mistake to think that film shots including swords, logs, telephone poles, pine trees, skyscrapers, Greek columns, fountain pens, picket fences, shovels, rocket ships, and Pontiac fins always pay homage to the trouser snake.
Except, I must admit, bedposts.
I don’t think I’ve ever slept in a bed with bedposts, not even in those cozy B & Bs that smother you with affection and sugar-sprinkled muffins. But the American cinema likes bedposts. Red-blooded American women in classic movies often have beds braced or decorated with bedposts.
Sometimes those bedposts do some alarming things.
Exhibit A: Start, as we often do (but probably shouldn’t), with D. W. Griffith. In The Birth of a Nation, Elsie Stoneman has just spent a romantic afternoon with Ben Cameron, aka The Little Colonel.

She races into her bedroom, obviously smitten.

What does she do? She hops to the bed and leans dreamily against the fancy tapering bedpost. Now Griffith gives us the closest image of her that we’ve seen so far in the movie.

And since Griffith never passes up a chance to crosscut between anything and anything else, we get another shot of Ben, perhaps looking off toward Elsie’s house. (We have to say perhaps because Griffith is not terribly concerned with consistent eyelines.) It operates as a typical Griffith signal that one character is thinking about another.

And as if aware that Ben is thinking of her, Elsie rewards her bedpost accordingly.

Should you doubt that these bedpost calisthenics are connected with the thought of a guy, I submit Exhibit B. In Bringing Up Baby, Susan Vance (Katharine Hepburn) is taken with David Huxley (Cary Grant). While he showers, she wraps herself around the only thing in the room taller than she is.


One can easily see why a glimpse of Cary Grant stepping out of the shower could make somebody clutch a support , but wouldn’t a chair have done as well?
Exhibit C: Douglas Sirk has done interesting bedpost work in Imitiation of Life (surmounting this entry), but surely his triumph is Magnificent Obsession (1954). A blind Helen Phillips (Jane Wyman) has just learned that no operation is likely to recover her sight. Helen rises from her chair, and we hear a wordless choir along with a piano theme evocative of Rob (Rock Hudson), the mysterious man in her life. As if drawn by magnetism, she makes her way through the darkness to a totemic mass, sort of Elsie Stoneman’s bedpost on Viagra. She moves with the solemnity of a priestess paying homage to an angry god.

Actually, this thing isn’t exactly a bedpost; it’s a strange thrusting protrusion from a love seat that functions as a room divider. But it’s clearly in the bedpost tradition—as we see when, like Elsie, Helen embraces it and leans her head against it.


Soon Rob enters, framed by the post, and in no time the couple are in a clinch.


If forced to interpret these items, I’d probably say that Griffith may have included The Bedpost in a moment of frank eroticism, Hawks knew the cliché and exploited it for an actor’s bit of business, and Sirk, sophisticated Euro émigré, used it ironically. But of course these interpretations are open to dispute. I expect someone to start a dissertation on the matter immediately.
I don’t know of comparable scenes in which men, thinking of women, hug bedposts or crawl into big cavities. Bedpost worship can obviously be interpreted as another sign of Hollywood’s bias toward patriarchal values. But its blatancy and more or less witting silliness also respond to that quality that delighted Parker Tyler about Hollywood movies—the way that flagrant symbolism is flung onto the screen but toyed with, to tease us. For Tyler, the “only indubitable reading of a given movie” was
its value as a charade, a fluid guessing game where the only “winning answer” was not the right one but any amusingly relevant and suggestive one: an answer which led to interesting speculations about society, about mankind’s perennial, profuse, and typically serio-comic ability to deceive itself.
Sometimes, then, a bedpost is just a bedpost. But probably not in the movies.
The quotation comes from Parker Tyler’s Three Faces of the Film, rev. ed. (South Brunswick, NJ: Barnes, 1967), 11.
My frame enlargements from a 16mm print of Magnificent Obsession aren’t good enough in the scene I mentioned, so I’ve been obliged to draw my images from the Criterion DVD. That version crops the frame to 2.0:1, which has seemed too radical for many observers, me included. Should it instead be 1.66 or 1.85? The aspect-ratio debate has played out in extensive detail here and here.
Thanks to Lea Jacobs and Jeff Smith for some DVD loans. Jeff also encouraged me to keep this discussion in good taste.

Queen Christina.
Don’t knock the blockbusters

Promoting Pirates of the Caribbean in Japan (By tralala.online)
Kristin here:
When was the last time you heard someone complaining about the high cost of the latest Toyota prototype? Probably not recently, since car manufacturers don’t tend to boast about how much it costs them to design a new model. In fact, I couldn’t find any information on how much the development of automobile prototypes costs. Some new models catch on, some don’t. Presumably some don’t make a profit for their makers. The same tends to be true for other big-ticket items.
In a way, a film’s negative is like a prototype. It costs a lot for a mainstream commercial film to be made, tens or hundreds of millions of dollars in many cases, before the first distribution print is struck and the first ticket sold. Yet once that prototype exists, any number of distribution prints can be struck, and a film may make back many times its negative cost.
[Added October 28: A friend of mine privy to information about car manufacturing informs me that an ordinary prototype runs $50 to 250 million. A radically new product like an electric car could run over a billion. And car companies do keep those figures secret, so it’s no wonder I couldn’t find them.
Coincidentally, $50 to 250 million is pretty much the range of budgets for mainstream commercial Hollywood features these days.
My friend told me other things about car manufacturing that make it sound as though the comparison between the two industries is a pretty reasonable one. For example, car companies can save money by releasing new, slightly modified versions of a popular model, such as the Honda Civic, rather than designing a new model from the ground up. Sort of like sequels in the film industry. More surprisingly, when car manufacturers (and some companies in other industries) make their products by outsourcing some of the components, they call it the “Hollywood model.”]
For some reason, the cost of making that negative is often public knowledge. To some extent, at least, since we all know that the budget as acknowledged by a studio may be considerably less than the actual costs. The notion that a movie set its company back by $200 million is to some extent a selling point. I’m sure that back in 1922 Universal wasn’t happy that Erich von Stroheim’s Foolish Wives ended up costing more than a million dollars. Still, they turned it to their advantage by advertising it as the first million-dollar movie, and studios have been using the same tactic ever since.
The producers and makers of other kinds of artworks don’t tend to make such information public. How much does it cost to put on a symphonic concert or publish a book? We may hear about big advances paid to an author, but that’s basically a lump-sum against future royalties, and the author doesn’t get any more until–if ever–the advance is paid off. But how much do editorial supervision, printing, and binding set a publisher back? What kind of money goes into the creation of a large stone sculpture?
Journalists looking for a hook for an article about movies find a sturdy one in the idea that today’s film budgets are bloated. They point to classic movies of decades past that cost only a few million to make and then compare these to the loud, overblown summer tentpoles of today, with their multi-hundred-million-dollar costs. Of course this overlooks the inflation of the dollar over the years. In the 1950s the average family income was about $5000 and an average house cost under $20,000. A penny bought a gumball and could be used in parking meters. Just about everything costs a lot more now.
To be sure, other factors have raised the budgets of films well beyond what they would be through inflation alone. The key factors have been star salaries and computer-generated special effects. The latter can account for half the cost of an effects-heavy film. Beyond the negative cost, typical budgets for prints and advertising have skyrocketed.
Some people seem to see an innate immorality in today’s biggest budgets, as well as an almost inevitable lack of quality in the films that result. Here’s one of the first results of a search on “big budget movies,” from Dmitry Sheynin on suite101.com. He even makes the car comparison:
The film industry has had a good summer this year – action sequences were bigger than ever, and expensive displays of pyrotechnics and CGI showcased new and exciting ways to destroy cinematic credibility.
With the economic crisis forcing many companies to scale down or even discontinue some of their more opulent product lines (think GM), it’s comforting to know Hollywood studios are still spending inordinate sums of money producing bad movies.
I think that’s fairly typical of the grousing you find on the internet and in print. No doubt Hollywood produces many bad movies. But actually, it is comforting to know that Hollywood is still spending great sums of money, ordinate or in-, if you think of the welfare of the country as a whole.
Every now and then I’ve pondered the possibility that American movies must be one of the products, if not the product, that has the most favorable balance of trade. While the US doesn’t have quite the stranglehold on world film markets that it used to, most significant Hollywood films get exported to numerous countries. Conversely, very few films from abroad are imported, and those that come in, especially the foreign-language ones, play in far fewer theaters and sell far fewer tickets than do domestic films. In 2006, according to US census figures, foreign films took in $216 million in the U.S., while domestic films sold $7.1 billion worth of tickets. So that’s 3% of the U.S. market for imported films, which is the figure I’ve heard pretty consistently for decades.
(In passing, I note from the same report that theaters made 66% of their income on tickets, meaning that we moviegoers spend about a third of our cash on all that stuff in the lobby.)
Turns out my ponderings have been correct. On the Motion Picture Association of America’s “Research & Statistics” page, there appears the claim, “We are the only American industry to run a positive balance of trade in every country in which we do business.” (“The industry” includes both film and television.) In April the MPAA put out its latest annual report, “The Economic Impact of the Motion Picture & Television Industry on the United States.” The combined trade surplus in the moving-picture industry for 2007 was $13.6 billion, or 10% of the US trade surplus in private sector services. According to the report, “The motion picture and television surplus was larger than the combined surplus of the telecommunications, management and consulting, legal, and medical services sectors, and larger than sectors like computer and information services and insurance services.”
Lest anyone think these figures are mere industry propaganda, the MPAA’s information, though made public, is gathered for the benefit of the film studios, which collectively own the association. Screen Digest, a highly respected trade publication, summarized some of the report’s material in its September issue (“Film and TV Are Key to US Economy,” p. 265).
For better or worse, most films that are really successful abroad are big-budget items, with lots of expensive special effects and (usually) top stars. Back in 1997 people were aghast at the first $200 million movie, Titanic—until it brought in nearly $2 billion around the world. Here, in unadjusted dollars, are the top foreign earners for the past nine years (not including domestic box-office):
2008 Indiana Jones and the Kingdom of the Crystal Skull $469,534,914
2007 Pirates of the Caribbean: At World’s End $651,576,067
2006 Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man’s Chest $642,863,913
2005 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire $605,908,000
2004 Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban $546,093,000
2003 The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King $742,083,616
2002 Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets $616,655,000
2001 Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone $657,158,000
2000 Mission: Impossible II $330,978,216
Add in the DVDs and ancillary products, and the balance of trade gets even more favorable.
Yes, it may sound absurd that it requires $200 million to make a movie, especially one that gets mediocre reviews from critics and fans. Still, from a business point of view, it makes sense and it’s good for the country. It’s especially important in a period of financial crisis, when the movie industry’s income seems considerably less affected than many others. Our overall trade deficit is falling, since Americans are saving more and buying less from abroad. This year the film and television industry’s share of the surplus will presumably grow.
Apart from the balance of trade, according to the MPAA report, in 2007 the moving-image industry also employed 2.5 million people, paid $41.1 billion in wages, spent $38.2 billion at vendors and suppliers, and handed over $13 billion in federal and local taxes.
If you think the trade deficit doesn’t affect you, think again the next time you travel abroad and curse the exchange rate with the euro or the yen.
No doubt there’s a great deal of waste and slippery dealing involved in those huge budgets, but there are definite advantages that don’t get considered often enough.
I do see a lot of foreign cars on the roads.
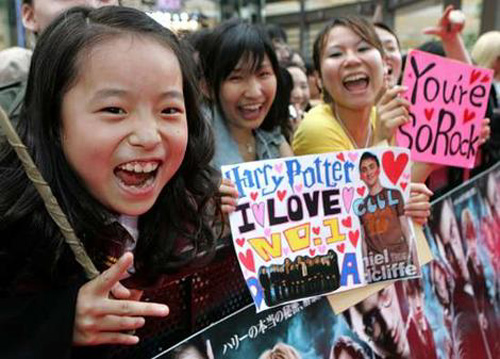
[October 23: Coincidentally, two days ago Steven Saito posted a story on how foreign-language films that have achieved blockbuster status in the rest of the world don’t stand much of a chance of getting into the American market. He mentions the “Christmas Vacation” series that I referred to in an earlier post.]
Wrapping up the ROW

Paparazzi swarm over the nominees for the Dragons and Tigers Award at the Vancouver International Film Festival.
Kristin here:
Some final films from VIFF
So far Central American countries have produced fewer films than their neighbors to the north and south. So I couldn’t pass up The Wind and the Water, the first fiction feature made in Panama. Made by a collective of fifteen young indigenous people from the Kuna Yala archipelego under the leadership of MIT graduate and first-time director Vero Bollow, it’s a tale of threats to the paradisiacal island by developers who want to build a giant hotel there. It also reflects temptations for young people to desert their traditional lives on the islands for the attractions of nearby Panama City.
The contrast between the islands emerges through a simple tale. Machi, a young man from the islands, goes to the city for schooling and finds it grim and threatening. Rosy, a transplanted native who grew up there, aspires to be a model.

She returns to the islands for her grandfather’s funeral. Confronted with crude latrines and fish-head stews, she is initially miserable but gradually falls under the spell of the area’s beauty. Meanwhile her father works for the group planning to move the islands’ population to a new suburb and build their resort.
The plot is based loosely on that population’s vigorous efforts—successful so far—to fend off efforts of outsiders to gain control of the islands. I was reminded while watching it of the many classic documentaries of the 1930s and 1940s, like Song of Ceylon, shot by Americans and Europeans in exotic locales. For decades film scholars deplored the fact that the people who formed the subjects of such films were being portrayed by outsiders. The Wind and the Water, though a fiction film, has a strongly documentary thread running through it, but this time it is the local population making a film about their own situation.
 Bollow (right), who initially left MIT to live in Panama and bring digital technology to indigenous people, wrote the script along with the fifteen team members. She attended Vancouver and answered questions, but members of the team will be traveling with the film to other festivals.
Bollow (right), who initially left MIT to live in Panama and bring digital technology to indigenous people, wrote the script along with the fifteen team members. She attended Vancouver and answered questions, but members of the team will be traveling with the film to other festivals.
In some ways, Ozcan Alper’s debut feature, Autumn, is a classic art-house film. Yusuf, a student radical, is released after ten years in prison because he has a fatal lung disease. He returns to his home. He returns to his rural home in the eastern Turkish mountains and settles in with his widowed mother, keeping his illness secret. He tutors a local boy in math and perhaps falls in love with a melancholy prostitute struggling to support her child.
Many of the scenes consist of the hero lying or sitting in the yard, contemplating the surrounding mountains as autumn slowly changes them. David found the lack of dramatic action and the slow pace of the scenes to be overly familiar conventions of art cinema. No doubt the hero’s goals are de-dramatized, as when he promises a bicycle to the student should he succeed in mother or when very late in the film he decides to help the prostitute. There is one central motif that becomes overly emphatic. When Yusuf first notices the prostitute, she is buying a Russian novel; they simultaneously sit alone watching the same broadcast of Uncle Vanya; eventually she tells Yusuf that he’s like a character out of Russian literature. The film’s tone successfully suggests this comparison without our needing to have it made explicit.

To me, the success of the film arises from the director’s integration of the landscape into the story. The prominence of the rugged landscape and the care with which the story is linked to the fall of leaves and the creeping of snow down the mountainsides lifts this above standard art-house fare. In this case, the fading of the year, beautifully brought into a central role by the cinematography, becomes linked more subtly to the hero’s plight.
Kill Daddy Goodnight, an Austrian film by veteran director Michael Glawogger, starts with a promising premise. The protagonist Ratz hates his father, a cold and critical government minister, and creates a videogame, “Kill Daddy Goodnight,” to wreak a fantasy revenge. Summoned by Mimi, a friend with whom he may or may not be in love, he abruptly flies to New York. She wants him to renovate the basement hideaway of her grandfather, a fugitive Nazi war criminal. Initially revolted, over the course of his work he comes to like the old man. Ratz also manages to find a sleazy internet entrepreneur willing to offer “Kill Daddy Goodnight” on his website, where it becomes an immediate success. Interspersed with this plot are scenes of an unidentified man (below) recording testimony against and visiting his childhood friend, who had worked for the Nazis during the war and killed his father.

So far, so good. But the film’s already complex plot is overburdened by strong hints of Ratz’s incestuous desire for his sister, a thread that comes to little. Mimi’s motivations are confusing, and it’s hard to sympathize with any of the characters. Perhaps that was the intention, but my sense was that the two intriguing plotlines, which could have fit neatly together, were diffused by distractions and uncertainties.
I didn’t get to many documentaries, but being a lover of Vivaldi’s vocal music, I had to see Argippo Resurrected. It’s the fascinating tale of how Czech conductor and musicologist Ondrej Macek ingeniously tracked down the lost 1730 opera, which had originally been composed for Prague. He then staged the piece in one of the two perfectly preserved court theaters of the era, the Castle Theatre at Cesky Krumlov, two hours outside of Prague, near the Austrian border.

The other is at Drottningholm, outside Stockholm, where in 1999 David and I had the privilege of seeing The Garden, a new opera about Linnaeus. (It was the first premiere at the theater since it was sealed in the 18th century.) The original candles have prudently been replaced by electric replicas of one candlepower each, flickering realistically. The Cesky Krumlov theater still uses real candles to light both the stage and the musicians’ stands. I guess this says something about fire codes in Eastern Europe. I for one would be happy to risk it in order to have a thoroughly authentic experience, especially if a Vivaldi opera was playing.
It’s a complicated story to fit into 62 minutes. Director Dan Krames took a clever and effective approach, starting backwards. He shows the theater first, with its wooden framework, sets, and stage machinery. He then goes on to introduce some of the musicians and singers, in the process explaining the concept of authentic performance style to those who may not be familiar with it. We also get to see some short excerpts from rehearsals, so that we come to know the opera a little. Only then does Krames proceed to the tale of Macek’s search for the original manuscript and his laborious piecing-together of the individual arias. Macek makes an engaging subject, though he is so self-deprecating about his discovery that the film has to include another musicologist to explain just how extraordinary the accomplishment was.
Finally Macek takes us on a tour of Venice, showing the few surviving places associated with Vivaldi, whose life is little documented. Along the way, there are further excerpts from rehearsal for the production shown, featuring a collection of excellent singers. Krames told me that Argippo Resurrected should be released on DVD in about a year. In the meantime, a live recording of Macek’s production is available as a 2-CD set.
Some final photos
Film festivals aren’t just for watching movies, of course. They’re for seeing old friends, meeting new ones, and sharing meals—including the festival’s wonderful hand-made waffles—to talk about what we’ve seen. As usual, David had his camera in hand nearly all the time, as the accompanying images show.

Theresa Ho, Eunhee Cha, and Tony Rayns: Three key players in the Vancouver Festival.


Chris Chong (director of Karaoke) and Liu Jiayin (Oxhide II).


Bob Davis, of American Cinematographer, and Noel Vera, Critic after Dark.

Canadian corner: Lisa Roosen-Runge, Shelly Kraicer, and Peter Rist.

Get your Terimayo, Oroshi, and Okonomi here: Japadog, a Vancouver Institution.
Wantons and wontons

Oxhide II.
DB here, with more from the Vancouver film fest:
Two of the more innovative films I saw evoked film history—one explicitly, the other obliquely. Raya Martin’s Independencia is part of a planned series devoted to the history of the Philippines, told from the bottom up. In this first installment, villagers flee into the jungle to hide from the American “liberation” of their islands. The film centers on a mother and son who, joined by a woman the son finds, create a new family. After years, the son and the woman have a child, but their new life is threatened by the encroachment of the invaders.

What sets Independencia apart is Martin’s effort to create the look and feel of a 1930s fiction feature. He shot the movie wholly in a studio, and the evidently faked backdrops are counterbalanced by gorgeously controlled lighting effects, and even dashes of color. Since virtually no Filipino films survive from this period, Martin gives us less a pastiche than a possibility, a sort of hypothetical archival film. The fact that the film makes aggressive use of Dolby sound, especially during a tremendous storm sequence, only adds to the sense of history being reimagined for today.
More traditional, at first glance, is Puccini and the Girl, a historical drama by Paolo Benenuti and Paolo Baroni. Facts of the case: In 1909, a maid in Puccini’s Tuscan villa, accused of being his concubine, committed suicide. But an autopsy revealed that she was a virgin.
The film’s reconstruction of what happened behind the scenes, tracing the veins of jealousy and deceit running through the household, relies on recent research into the tragedy.
At the same time, we have an homage to silent cinema. In most scenes we hear no dialogue: actors whisper at a distance from us, or simply conduct themselves without speaking. What words we do hear are recited pro forma (the Mass) or sung (in a waterside tavern, or in nondiegetic accompaniment). There is only one line of conversation, and that is given greater saliency by being a cry from the heart.

So we’re largely confronted with a silent film, accompanied by music and sound effects. To add to the estranging effect, characters communicate chiefly through letters and telegrams—exactly as in the films of the period. We hear the letters’ text read aloud, but the sense of stately compositions propelled by written commentary, distinctive features of 1910s cinema, remains. An unwitting homage, perhaps, but one that pleased this fan of classic tableau cinema.
Independencia was part of the Dragons and Tigers thread, one of the hallmarks of the Vancouver event. Year after year it gives an unequaled view of current Asian cinema. This year’s program, assembled by Tony Rayns and Shelly Kraicer, was at least as fine as ever. Eight films compete for the $10,000 prize given to first or second features. The winning film, Eighteen by Jang Kun-jae, centered on the familiar situation of teenage lovers separated by parents and school pressures. I didn’t see all the competitors, but my own favorite was Chris Chong’s Karaoke, a Malaysian story of a young man coming to terms with his mother’s decision to sell her karaoke bar. The first ten minutes are quite creative, disorienting the audience through complicated sound mixing, while the boy’s community, devoted to the production of palm oil, is presented with a documentary directness.
Outside the competition, I saw several Asian films of consequence. I’ve already discussed Yang Heng’s Sun Spots and Bong Joon-ho’s Mother. Ho Yuhang’s At the End of Daybreak marks a shift from his lyrical first feature, Rain Dogs, which I reviewed at Vancouver in 2006. A plot situation close to that of Eighteen is treated in much darker tones. A young man falls in love with a high-school girl, but he’s driven to murder by her growing indifference to him. The familiar elements of furtive sex, drinking parties, and demands from the girl’s family for reparations are given a noirish treatent. Ho’s admiration for American crime novels shows in his increasingly bleak handling of the affair. Here the femme fatale is a high-school girl, and the entrapped male’s revenge is complicated by an unexpected erection.
 Also under the influence of classic crime films was Yang Ik-June’s Breathless from Korea (right). It shows a brutal debt collector coming to terms with his childhood. Under a harsh surface realism, the film has the contours of the familiar redemption of a hard case, including the decision to reform that comes a tad too late. (Whenever a crook vows that this will be the last time he pulls a job, wait for the ironic retribution.) I thought that the character parallels (two scenes of murdered mothers) were somewhat too neat, but the director plays the anti-hero with conviction and deadpan humor, and Kim Kkobbi supplies an exhilarating turn as the tough high-school girl who becomes his companion.
Also under the influence of classic crime films was Yang Ik-June’s Breathless from Korea (right). It shows a brutal debt collector coming to terms with his childhood. Under a harsh surface realism, the film has the contours of the familiar redemption of a hard case, including the decision to reform that comes a tad too late. (Whenever a crook vows that this will be the last time he pulls a job, wait for the ironic retribution.) I thought that the character parallels (two scenes of murdered mothers) were somewhat too neat, but the director plays the anti-hero with conviction and deadpan humor, and Kim Kkobbi supplies an exhilarating turn as the tough high-school girl who becomes his companion.
Bong Joon-ho has been something of a leitmotif on this site lately, with my comments on Influenza and Mother. Under the rubric “Bong Joon-Ho & Co.,” Dragons and Tigers screened a collection of shorts paying tribute to the Korean Academy of Film Arts. Most were from the 2000s, but Kim Eui-suk’s Chang-soo Gets the Job, dated from 1984. Focusing on a gang of teenage purse snatchers, Kim’s film was a little rough technically, but it built its story deftly. The quality of the rest was quite strong, with the grisly and wacky Anatomy Class (2000, Zung So-yun) being a high point. Meanwhile, Bong’s Incoherence (1994) shows that his urge to deflate official hypocrisy, seen in Memories of Murder and The Host, was already present in his student days.

My admiration for Hirokazu Kore-eda runs high, as I indicated in my discussion of Still Walking at last year’s VIFF. But Air Doll, while full of vagrant pleasures, left me unsatisfied. The Kafkaesque premise, derived from a manga, is that an inflatable saucy-French-maid dolly comes to life, endowed with speech and movement but retaining her seams and air valve (both of which will figure in the plot). Her sad-sack owner doesn’t notice the transformation, but while he’s at work, she takes a job at a video store and wanders the city.
The aim, I think, is to defamiliarize ordinary city life by seeing it through Nazomi’s eyes. The fact that a sex effigy is the most innocent character in the movie is part of the point. Makeup, money, and fashion start to seem extensions of sad, solitary eroticism, and the line between mainstream movies and porn gets blurred. But all the thematic elements didn’t blend very well, and at moments, as during the music montages showing people’s desperate loneliness, I worried that for once Kore-eda had slipped into conventional sentimentality. The tone also shifts, with a climax that revises the big scene of In the Realm of the Senses. Kore-eda deserves credit for his unflagging effort to try something fresh with every project, but here, it seemed to me, that the film was defeated by an overcute conceit and underdeveloped execution.
The most exciting Asian film I saw at VIFF was Liu Jiayin’s Oxhide II. Her first feature, Oxhide, was screened at Vancouver in 2005. (Full disclosure: I was on the jury that awarded that film the D & T prize.) This one seemed to me even better.
To say that this 132-minute film is about a family making dumplings is accurate but misleading. To add that the action consumes only nine shots makes it sound like an arid exercise. In fact, it’s a consistently warm, engaging—I don’t hesitate to say entertaining—film that is also a demonstration of how a simple form, patiently pursued, can yield unpredictable rewards.
In the first Oxhide, we saw the comedy and tensions of Liu’s life with her parents, who run a leatherwork shop. By the time she shot part two, they had already lost their business, but the sequel presupposes that the shop is still going, albeit coming to a critical point. So there’s a quasi-documentary aspect, as the family’s financial strains, discussed cryptically at various points, hover over the mundane process of wonton cookery. Yet although everything looks spontaneous, it was all completely staged—written out in detail, rehearsed over months, reworked in test footage, and eventually played out in “real time.”
And in real space. The first shot, which consumes twenty minutes, shows Liu’s father pummeling a hide in his vise and eventually clearing the table for serious food preparation.

Actually, the film’s subject is that table. On its surface, a meal is prepared; around it, the family gathers; we even see what happens underneath. We watch father and mother chop scallions, mince pork, twist and yank dough, pinch the dumpling wrappers around the filling. We watch the daughter try to match her parents’ dexterity. This is a movie about housework as handiwork, and family routines and frictions.
For minutes on end, we see only hands and arms; Liu’s 2.35 frame often chops off faces. Liu employed a construction-paper mask to create the CinemaScope format within HD video. Why the wide frame? Most filmmakers use it for expansive spectacle, she remarks; but “I wanted to see less.” And the horizontal stretch further emphasizes the table.

As if this weren’t rigorous enough, Liu has filmed the table from a strictly patterned arc of camera positions, dividing the space into 45-degree segments. These unfold in a clockwise sequence around the table. What could seem an arbitrary structural gimmick is justified by the fact that each setup proves ideally suited to each stage of the process. When father and mother team up to start the meal, the angle gives us two centers of interest. And Liu feels free to “spoil” her mathematical structure by varying the height and angle of her camera. Plates, bowls, and an articulated lamp become massive outcroppings in this micro-landscape.

Oxhide II is unpretentiously inventive, quietly virtuosic. Evidently it took a Chinese filmmaker (whose day job is writing TV dramas) to blend domestic life with the rigor of Structural Film. Liu displays the fine-grained resources yielded by several cinema techniques, from framing and staging to lighting and sound. The finished dumplings get constantly rearranged on the cutting board. Each family member has a different technique for pulling off bits of dough, and each gesture yields its own distinctive snap.
I had to think, almost with pity, of all those US indie filmmakers who believe they have to cultivate CGI and slacker acting, to seduce investors and strain for outrageous sex and edgy violence. Liu made this no-budget, low-key masterpiece over years in a single room, and with her parents. That’s a new definition of cool.
Liu promises us another installment. In the meantime, every festival that’s serious about the art of cinema should pledge to show Oxhide II.

Puccini and the Girl.
PS 12 October: Thanks to Matthew Flanagan for correcting an embarrassing typo.
PS 15 October: Thanks to Ben Slater for correcting yet another one!













