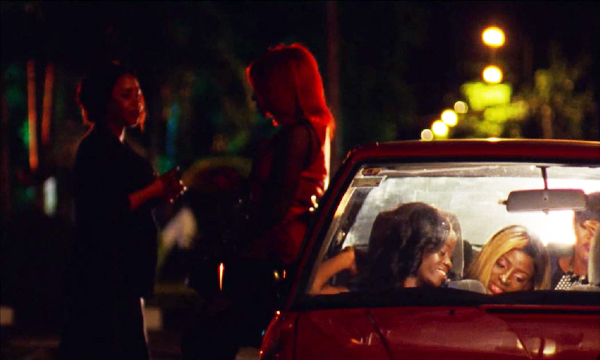Vancouver: Continuing our world tour
Tuesday | October 6, 2020 open printable version
open printable version
Eyimofe (2020)
Kristin here:
Turning back from documentaries to international art cinema, I’m recommending three films, two from Eastern Europe and one from Nigeria.
Servants (2020)
Ivan Ostrochovsky, an established Slovak producer of documentaries, whose first feature Goat (2015) was successful on the festival circuit, has followed it up with a second. Servants showed in the Encounters program at Berlin and earned enthusiastic reviews (Variety, Screen Daily).
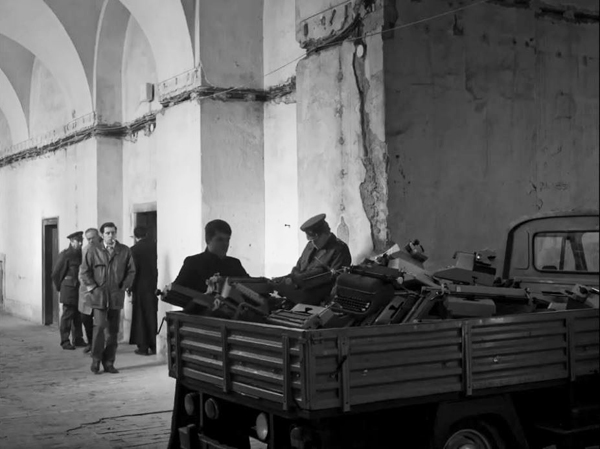
The film opens with a flashforward as a body is dumped on a dark country road–a scene that will later be replayed when we have more information as to who the victim is. Suddenly a title, “143 days earlier,” appears, and the plot focuses on two beginning seminary students, Juraj and Michal. Briefly we seem to following their personal stories, but their introduction to the seminary routine serves largely as exposition for us. Signs of Communist repression of Catholicism begin to surface. A defiant note anonymously posted leads to a confiscation of all the students’ typewriters (above) in a search for clues as to its author.
The organization behind the repression is an actual historical agency, “Pacem in Terris,” which spied on and controlled the Catholic Church, from 1971 to the early 1980s. (The film is set in 1980.) Its goal was to seek out any signs of political activity, i.e., rebellion, among the clergy and seminarians. Juraj and eventually Michal join a small clandestine group of students working against Pacem in Terris. They become the targets of a ruthless agent, “Doctor Ivan,” (seen at the right below). He is the man responsible for the body-dumping in the opening.
Servants, impressively shot in black-and-white, has been called a film noir, and it certainly has all the sinister tone, the chiaroscuro lighting, and the ill-fated heroes of that genre, mixed with the trappings of art cinema.
Ivanovsky demonstrates how much suspense and dread can be packed into a mere eighty minutes.
On the Quiet (2019)
Another short feature that packs a lot of drama into its 81 minutes is Hungarian director Zoltán Negy’s first feature, On the Quiet. It deals with the touchy subject of alleged sexual abuse of a minor. The film’s smart script, co-written by Negy, is credited as having been developed at the “My First Script Workshop” of the Zagreb Film Festival. As I have suggested elsewhere, such workshops run by festivals have come to play a major role in making such sophisticated storytelling possible.
The main strength of the script is how it maintains an utterly balanced ambiguity about the allegations at its core. The beginning introduces the protagonist, Dávid, first violinist in a student orchestra in a prestigious music school. The teacher-conductor, Mr. Frigyes, employs eccentric techniques with the players. When Dávid fails to perform his solo part adequately in rehearsal, Frigyes tells the other students to gather round to massage his shoulders. This apparently helps him improve.
Soon Frigyes is giving private lessons to 14-year-old Nóri, a pretty, inexperienced but talented cellist. The first lesson we witness has him relaxing her by having them toss a ball back and forth. He touches her elbow and shoulder to adjust her posture. That is all that we witness. Yet soon Nóri complains to Dávid that the teacher has done “weird” things to her, but she won’t specify except to say they were “intimate.” Disturbed by this, Dávid gives her his phone to secretly record a lesson with Frigyes. The resulting dialogue could equally be the teacher directing the girl’s cello technique or instructions about sexual caresses. Dávid’s girlfriend points out to him that Frigyes uses his touchy-feely approach with all the students, but he persists in trying to discover the truth.
The situation escalates as Dávid informs a female counselor, who interviews Nóri and her mother. The girl denies that anything untoward happened. Still, the gossip spreads and the situation eventually threatens Frigyes’s position at the school. Did he abuse the girl? Did he simply not realize how his hands-on guidance could make the girl uncomfortable? Is she naively over-reacting to teaching methods that don’t seem to bother the other students?
I have seen one review that simply declares that the teacher is a perverted abuser, but the film seems far more subtle to me. Without ever implying that Nóri’s complaints should be dismissed, the film explores the effects of the spreading rumor on all those involved. It does show that no real investigation of the claims, which would be the logical way to proceed, ever takes place. In short, it is a careful presentation of its sensitive subject.
The film is well directed, though far from flashy. It does have the occasional striking shot, as when Dávid ponders the situation one evening (above) or sits talking with Nóri on a playground merry-go-round in an overhead shot (see bottom) that hides their expressions and suggests his confusion.
An interview with Negy about the film suggests that he is a thoughtful as well as a promising director–and one with three more film scripts underway.
Eyimofe (2020)
From the early 1990s, Nigeria has built up a thriving production of low-budget, DIY and professional films. At first distributed on VHS tape and then on digital disk, these have had enormous success at home and among the African diaspora. Kunle Afolayan formed a company that commanded government support and product placement to finance October 1 (2014), which played at film festivals, mostly within Africa. More recently, Kemi Adetiba’s The Wedding Party (2016) premiered at the Toronto International Film Festival, and Kathryn Fasegha’s 2 Weeks in Lagos premiered at the 2019 Cannes festival, where it was somewhat overshadowed by Mati Diop’s Atlantics, playing in competition.
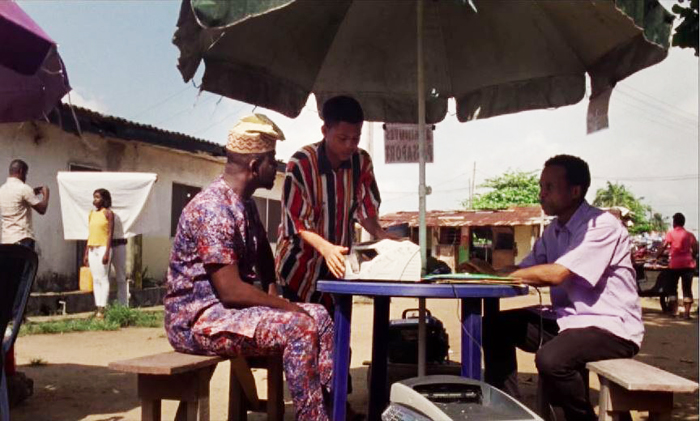
Now comes Eyimofe (This Is My Desire, in English, but much of the coverage on the internet uses the Yoruba title). It is directed by twins crediting themselves as Arie and Chuko, though their family name is Esiri. They have created an formally and stylistically impressive film that gives fascinating insights into the society of the sprawling conurbation of Lagos, an area with an estimated population of 21 million.
Arie Esiri studied Screenwriting and Directing at Columbia University’s School of the Arts, while Chuko Esiri earned an MFA, also in Screenwriting and Directing, from New York University’s Tisch School of the Arts. They wisely shot Eyimofe on 35mm, and the lush visuals exploit the bright colors of Sub-Saharan African clothing (see top of entry) and furnishings. Cinematographer Arseni Khachaturan adds bright colored light, especially at night and in shops, to create a gorgeous look (above and below).
The plot is split into two parts via titles: “Spain” and “Italy.” In each part, the main character is struggling to migrate. Mofe, an electrician, is gradually collecting the documents and money he needs for his move to Spain, where he will adopt the name Sanchez. Rosa, working both as a beautician and cocktail waitress, has similar aspirations to relocate to Italy, taking her younger sister Grace along. Both protagonists must scrape up money to pay for the passport, visa, fake letters promising employment, and other expenses. There are many complications, including a death in Mofe’s family and an unexpected revelation of the lengths to which Rosa and Grace will go to secure their passage.
The two stories are largely separate. There are moments when the characters pass each other briefly, and Grace even chats with Mofe at a little repair stand he sets up. Yet none of these chance encounters involves any causal connections between the two plots.
Early in the film Mofe visits an open-air “office” where a man who specializes in getting passports and visas–for a hefty fee (see top, where Mofe is on the right). In the background we glimpse a woman getting a passport photo taken against a white cloth. Late, near the beginning of the “Italy” section, we meet Rosa, having her passport photo taken in front of a similar backdrop (below). She’s in a different passport shop, however, suggesting that such informal establishments, vital for aspiring emigrants to cut through the red tape and delays of government procedures, are common in Lagos. It’s also the first of several parallels between her story and that of Mofe, clearly intended to suggest how common such struggles to leave for Europe are.
Unlike Mofe, Rosa aspires to a fun, modern social life, buying fancy clothes while sleeping with her landlord (who happens to be Mofe’s landlord as well) and then starting an affair with a wealthy Lebanese-American businessman. Her nightlife offers the occasion for flashy images, including the positively Godardian composition of her in a car with her friends (at the top of this section). As with Mofe, an unexpected death helps derail her plans, and we learn just how far she and Grace had been willing to go in their hopes for a better life abroad.
Eyimofe is a powerful film and well worth seeking out at a festival or on streaming. It’s having its UK premiere at the London Film Festival, which starts tomorrow. For a brief discussion by the directors about the film’s background, financing, and festival life, listen to this BBC radio interview. For a detailed description of the film’s success during its screenings during the Berlin festival from a Nigerian point of view, see here.
As a remarkably rich and successful festival draws toward its end, special thanks to Alan Franey, PoChu AuYeung, Jane Harrison, Curtis Woloschuk, and their colleagues for their help during it.
On the Quiet (2019).