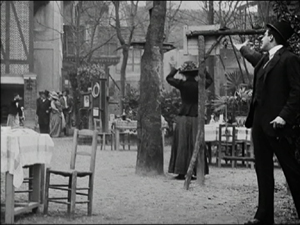Archive for the 'Directors: Capellani' Category
Silent films, old and new
Blancanieves
Kristin here:
February and March have been good to silent cinema. Time for a round-up of some highlights as we impatiently anticipate Il Cinema Ritrovato, coming up in a little over two months.
Publications on Albert Capellani
In reporting on the 2010 and 2011 programs of Il Cinema Ritrovato, I highlighted one of the festival’s major revelations, that of the silent films of Albert Capellani. These generous doses of Capellani’s splendid films were put together by Mariann Lewinsky, who realized his importance after she included some of his shorts in her annual “Cento Anni Fa” programs. In my entries I argued that Capellani was revealed as one of the early cinema’s great masters. (The 2010 entry is here, and the 2011 one here.)
Not surprisingly, during the intervening years, scholars have been busy researching Capellani’s films and career. March 6 to 24 saw a major retrospective at the Cinémathèque Française. (Information on the program is still available online, as is a detailed press release.) Shortly before it began, the first biography appeared: Christine Leteux’s Albert Capellani: Cineaste du Romanesque, with a foreword by Kevin Brownlow.
Leteux discovered Capellani in May of 2012, thanks to seeing Notre-Dame de Paris and Les Misérables at the Forum des Images in Paris. Setting out to learn more about the filmmaker, she realized how thoroughly his memory had nearly vanished from film history. She sought out and received the cooperation of his grandson, Bernard Basset-Capellani, whom she describes as “intarissable” (inexhaustible) on the subject.
The result is a solid, traditional biography, with chapters mostly organized around the companies for which Capellani worked (Pathe, SCAGL, World, Mutual, and so on) and some of his key films (Les Misérables, The Red Lantern). The prose style is easily readable French, at least to someone like me with an average knowledge of the language. For an interview with Leteux concerning the book, see here.
The book is on sale at the Cinémathèque’s shop, which unfortunately does not sell online. It was supposed to be available on Amazon.fr, but so far is not. The easiest way for those outside France to order it is through three third-party book-sellers on amazon.fr, all offering it at the cover price of 14.90 €. Leteux’s book is a vital source for anyone interested in early cinema.
I was pleased to see that the last chapter ends with some quotations from my second entry on Capellani, ending with “With the end of the main retrospective, however, it is safe to say that from now on anyone who claims to know early film history will need to be familiar with Capellani’s work.”
The book includes a filmography and list of films available on DVD. These include a new one, a restoration of The Red Lantern by our friends at the Cinematek in Brussels, available on Amazon.fr or directly from the Cinematek’s shop.
The French-language historical journal on cinema, 1895, timed its March, 2013 issue to coincide with the Cinémathèque’s retrospective. It is entirely devoted to Capellani. I have not had a chance to see it yet, but the table of contents is available here. The only online purchasing source for individual issues I have found is here; the page gives a lengthy summary of the contents.
Mariann continues to search for more surviving prints for restoration and eventual inclusion in future editions of Il Cinema Ritrovato. She has sent me some tantalizing news about recent discoveries and restorations. There will be a third Capellani season in 2014. This will probably include some of the director’s American films: Social Hypocrites (now restored), Flash of the Emerald (the one surviving reel), Inside of the Cup (surviving but so far with no projection print), Eye for Eye (two surviving reals), Sisters, and the French film Le Nabab. Other possible restorations include House of Mirth, La belle limonadiere, and Oh Boy!
A description of the 2013 Ritrovato festival is available here.
Nanook and friends
Early this year we posted our annual list of the ten best films of ninety years ago. It featured the classic early documentary, Robert Flaherty’s Nanook of the North. In March our friends at Flicker Alley released a two-disc Blu-ray edition of Nanook paired with the 1934 Danish feature, The Wedding of Palo (Palos Brudefærd). The latter is one of those titles that one occasionally encounters on the fringes of older historical surveys, but it has been difficult indeed to see. This new print is a 2012 restoration from a George Eastman House original 35mm nitrate copy.
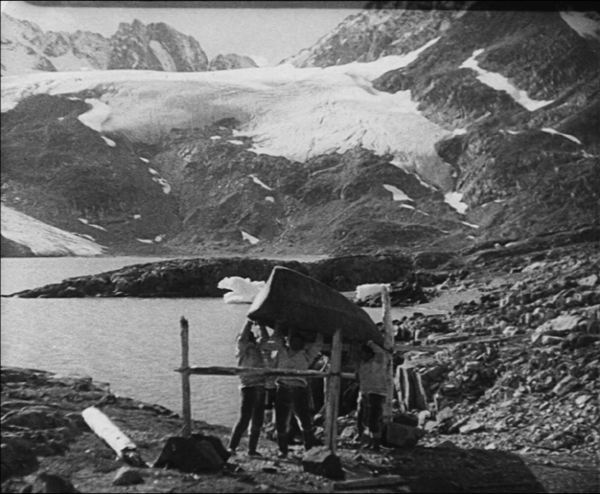
 Nanook is familiar enough, but The Wedding of Palo is not. It was made by the Danish explorer and anthropologist Knud Rasmussen, who appears in a brief introductory passage. Clearly he was influenced by Flaherty’s work. He combines a simple fictional narrative with documentary scenes of traditional Inuit life in eastern Greenland. The basic story involves the heroine Navarona, whose brothers are reluctant to lose their housekeeper by allowing her to marry. Two men of the tribe court her and come into violent jealous conflict. Interjected are sequences of a salmon hunt, a festival, a traditional song duel between the two rivals, and a polar-bear hunt. The staged dialogue scenes involve sound recording, with no subtitles but the occasional brief intertitle to translate.
Nanook is familiar enough, but The Wedding of Palo is not. It was made by the Danish explorer and anthropologist Knud Rasmussen, who appears in a brief introductory passage. Clearly he was influenced by Flaherty’s work. He combines a simple fictional narrative with documentary scenes of traditional Inuit life in eastern Greenland. The basic story involves the heroine Navarona, whose brothers are reluctant to lose their housekeeper by allowing her to marry. Two men of the tribe court her and come into violent jealous conflict. Interjected are sequences of a salmon hunt, a festival, a traditional song duel between the two rivals, and a polar-bear hunt. The staged dialogue scenes involve sound recording, with no subtitles but the occasional brief intertitle to translate.
As in Nanook, the non-professional actors are remarkably natural, especially the “actress” portraying the heroine. There is a cute young boy brought in at intervals for comic appeal, and the members of the village seem always to be laughing and enjoying a suspiciously carefree life. The film has the advantage of more spectacular scenery than that in Flaherty’s film, with huge mountains and glaciers in place of the vast ice-covered vistas (see bottom image).
As usual, the Flicker Alley team has gone beyond the call of duty with this release. It includes not only the two features, but six bonus films, as described in the press release:
Nanook Revisited (Saumialuk) by Claude Massot was made in the same locations used by Flaherty. It shows how Inuit life changed in the intervening decades, how Flaherty consciously depicted a culture which was then already vanishing, and how Nanook is used today to teach the Inuit their heritage. Nanook Revisited was produced in 1988 on standard definition video for French television. Dwellings of the Far North (1928) is the igloo-building sequence of Nanook re-edited and re-titled as an educational film; Arctic Hunt (1913) and extended excerpts from Primitive Love (1927) are by Arctic explorer Frank E. Kleinschmidt; Eskimo Hunters of Northwest Alaska (1949) by Louis deRochemont shows many activities seen in Nanook thirty years after, and Face of the High Arctic (1959) depicts the ecology of the region, produced by the National Film Board of Canada.
Altogether, the films run an impressive 281 minutes. There’s also a booklet with excerpts from Flaherty’s book, My Eskimo Friends, an essay by Lawrence Millman, “Knud Rasmussen and The Wedding of Palo,” and notes on the films.
Snow White and the Seven (?) Bullfighting Dwarves
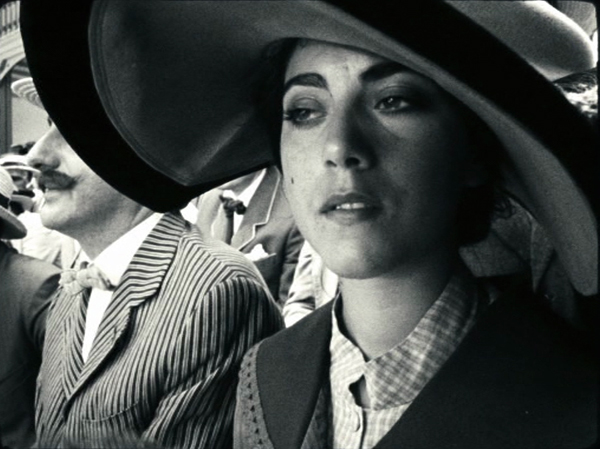
In 2011, a French film, The Artist, gained huge attention in the infotainment media as a modern version of silent cinema, winning yet another Best Picture Oscar for the Weinstein brothers. It was a reasonably successful imitation of mid- to late 1920s cinema during the transition to sound. Now a much better modern silent film has arrived, Pablo Berger’s Blancanieves, a loose version of the Snow White story transposed to 1920s Spain. A famous bullfighter is paralyzed after being gored in the ring. His wife dies in childbirth and his scheming nurse marries him. She keeps his daughter, Carmen, away from her father by setting her to work as a downtrodden servant in his country estate. Upon her father’s death, the evil wife schemes to have her killed, and she escapes to the protection of a troupe of six bullfighting dwarves who, possessing uncertain arithmetic skills, bill themselves as seven bullfighting dwarves.
While The Artist was a fairly good imitation of 1920s Hollywood filmmaking, Blancanieves is a pastiche of the 1928-29 era of European silent cinema. It draws on what I have termed the International Style of filmmaking, a late 1920s blend of influences from the French Impressionism, German Expressionism, and Soviet Montage movements. One could almost pass it off as a genuine film of the era.
At times there are subjective effects à la Impressionism. A superimposition conveys Carmen’s memories of her father’s crucial instructions to her, and superimposed images of hands waving handkerchiefs present the enthusiam of the crowd’s plea for the bull to be pardoned.
This was also the period in which the power of the wide angle lens, particularly in close-ups and in low-angle shots, was exploited, initially in Soviet cinema and then all over Europe. Blancanieves is full of such shots, as in the frame at the top of this entry and in these two shots from the opening scene:
There are also montage sequences, building up to flurries of very short shots. This accelerated-editing technique is typical of both Soviet and French filmmaking of the era.
The too-frequent use of handheld camera in Blancanieves detracts somewhat from the feeling of authenticity. In the late 1920s, cameras were too heavy to be handheld. They could be strapped to the body of the cinematographer with harnesses, but that creates a subtly different look. And during the late 1920s, shots with the camera holding on a character while the background spins around behind him or her would have been achieved by placing both camera and actor on a large turntable. (This effect apparently was pioneered in Germany in the mid-1920s). But the occasional dramatic lighting effects, particularly in the climactic scene, are distinctly reminiscent of German cinema.
In general, the narrative is charming and amusing. The heroine’s pet rooster provides exactly the sort of comic relief that is common in films of the 1920s, and the story has an effective fairy-tale quality. I found the ending a bit disappointing and certainly not typical of the films of the 1920s. Still, Berger has clearly watched an enormous number of 1920s European films and absorbed their styles. He can imitate the International Style remarkably well, telling a tale that is appropriate to the 1920s and yet has a touch of humor that doesn’t belittle the silent era.
Blancanieves was released in the US on March 29 and is currently making the rounds of art-houses and festivals.
Other entries discussing the International Style and wide-angle filming at the end of the silent era can be found here and here.
The Wedding of Palo
Capellani trionfante
Quatre-vingt-treize (1914)
Kristin here:
The early films of Albert Capellani are probably the most significant of all the discoveries of the Hundred Years Ago series.
Mariann Lewinsky
During the recent Il Cinema Ritrovato, I was somewhat surprised at the relatively small audiences for the programs that included films by Albert Capellani. Those films formed the second half of a large Capellani retrospective that began during the 2010 festival. Last year’s program was a revelation to me, and this year’s only confirmed my sense that here is a truly major discovery from the period before World War I. No doubt the addition of a fourth venue and the appeal of the Boris Barnet and early Howard Hawks retrospectives drew some attendees away.
As I wrote in my first Capellani entry, his significance has only slowly become apparent over several of the festivals. Initially his films were few and scattered through the annual “Cento Anni Fa” seasons of movies made one hundred years earlier. (The first “Cento Anni Fa” program in 2003 was curated by Tom Gunning; those since have been curated by Mariann Lewinsky.)
My first entry was handicapped by the fact that almost none of the films was available on DVD, and few of them had ever been accessible for researchers to view in archives–Germinal being the main exception. For illustrations, I mostly resorted to online versions of a few of the films, mediocre in visual quality and covered with bugs and time read-outs. The situation has changed enormously in the intervening year. Many more films have been restored; many of the archival notes at the beginning of this year’s prints were dated 2011. Moreover, in May Pathé brought out the Coffret Albert Capellani, a four-disc set with seven of the best-preserved films of 1906, as well as L’Assomoir and three major features from 1913 and 1914. Filling in the gaps to a considerable extent is the Albert Capellani: Un Cinema di Grandeur disc, from the Cineteca di Bologna, released just in time for the festival; it contains twelve films from 1905 to 1911. Between them these releases contain 23 films, plus some fragments. (The contents are more extensive than it might appear, since the three features alone add up to about seven hours.) Booklets accompanying the DVDs provide much up-to-date information on Capellani. It’s hard to think of an early filmmaker whose work has gone from such scarcity to such abundance in a single year. Once again, a driving force behind this dramatic improvement has been Mariann, working with La Fondation Jerôme-Seydoux-Pathé and the archives that provided print material.
I have taken advantage of this new availability to return to my earlier entry and add illustrations to descriptions of such important films as L’Arlésienne and L’Épouvante, which I could only summarize verbally when I first wrote it. This entry takes up where that one left off, with comments on several of the newly revealed films, or in one case, a new version.
For a list of all the Capellani films so far shown at Bologna and their availability on DVD, see the end of this entry.
An artist of the 19th Century meets a new art form
Those festival guests who missed the Capellani films missed, in my opinion, the rewriting of early film history. He is not simply another important silent filmmaker to be placed in the pantheon. Film by film, this year and last, I kept comparing what I was watching with what D. W. Griffith had made that same year. In each case, Capellani’s film seemed more sophisticated, more engaging, and more polished. Overall Capellani may not have been a better director than Griffith, but for the period of the French films, I believe it would not be exaggerating to say that he was: L’Arlésienne (1908) compared with anything Griffith did that year or L’Assomoir (1909) versus The Lonely Villa or even The Country Doctor. Capellani’s L’Épouvante (1911) was shown again this year; I had to shake my head in amazement that it was made the same year as another woman-in-danger film, The Lonedale Operator. Nothing in Griffith’s pre-war career comes close to Les Misérables or Germinal.
Both Griffith and Capellani came from the theatre, though the French director had already had a much more successful career there than had the American. Both had a strong bent toward melodrama and historical epics. But their styles developed along different lines. Undoubtedly Griffith’s pioneering work in editing sets him apart; Capellani never ventured far in that area. Capellani’s strengths were in the tableau style, with lengthy takes and intricately staged action. (For David’s thoughts on the tableau style, see here and here.) Rather, his strengths were in his elaborate staging of scenes, whether with one actor or a crowd. Perhaps because of his theatrical success, from early on Pathé must have given him generous budgets, for his settings are more opulent than Griffith’s, and he frequently went on location to the spectacular and picturesque landscapes and buildings of France. For example, he could simply take his team into old streets in Paris and create a more realistic impression of the city in the French Revolutionary era than Griffith could manage with the sets of Orphans of the Storm eight years later. (See left, Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge, 1914; note how close Capellani places the camera to the wall at the left, exaggerating at once the sense of depth and of narrowness.)
There is no doubt that in the long run, Griffith’s editing-based approach won out and helped establish the norms that remain with us to this day. It has been all too easy to trace the history of cinema as, at least implicitly, a history of innovations in editing. The great directors were those who fit into that specific history. Although Griffith never entirely mastered the classical Hollywood style the way Allan Dwan or Rex Ingram or Maurice Tourneur did, the continuity editing system undoubtedly grew in part out of techniques he popularized. In an historiographic approach based on editing, those who did not contribute to its development are likely to be passed over. Capellani uses every technique but editing with great artistry, and hence his films may be easy to dismiss as theatrical or old-fashioned. Moreover, many of them are based on 19th-Century classics, especially by Zola and Dumas, even when they deal with an older period, notably the French Revolution in his last two surviving French features, Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge and Quatre-Vingt-Treize.
Yes, as Mariann wrote in last year’s catalogue, “Capellani’s profile made him the target of a film historical trend–now long discredited–which criticised ‘the theatrical’ and promoted ‘the filmic.’ This is perhaps why he was so underestimated.” I am not sure that the contrast between theatrical and filmic cinema has entirely disappeared even today, but if we assume that all film techniques are equal, we can better appreciate Capellani in the context of his era.
I admit that, to a film historian or buff who learned early cinema from seeing Griffith and Chaplin and perhaps Hart and Feuillade, Capellani’s films may at first take some getting used to before their virtues become apparent. A feeling for Victorian narrative art, both written and visual, would help. At first, the acting might seem histrionic, and there are probably few, if any other directors’ films that so well preserve the stage conventions of the previous century. But for the most part, the acting in Capellani’s films is quite brilliant. The lack of editing might be a hurdle for some. Capellani also entirely avoided dialogue titles, and the expository titles are few. Characters are constantly writing and reading letters, which substitute for intertitles. It’s a convention one must simply accept, and it forces the viewer to concentrate fiercely on the actors’ faces and gestures, which carry the narrative information. For me, all this simply adds up to gripping filmmaking.
Take L’Assomoir, the earliest undeniable masterpiece from among the films so far shown at Bologna (though L’Homme aux gants blancs and L’Arlésienne come close). It is full of lengthy takes with intricate choreography. In all his films, Capellani clearly gave precise movements and business to each actor present, no matter how insignificant, and their faces, stances, and gestures, often fairly broad, make up for the almost entire lack of cut-ins. Take the scene where Gervaise and her new fiancé Copeau celebrate their engagement in an open-air café, with the proceedings interrupted at intervals by Gervaise’s former lover Lantier and the vengeful Virginie, with whom Lantier has taken up. The scene is done in a single two-minute shot, with the fluid action moving forward and back, in and out.
The ten frames below show phases of the action:
(1) Lantier in the foreground and Virginie in the middle ground watch the engagement party guests arrive. (2) Virginie speaks to Gervaise as Copeau comes forward.
(3) The guests begin to dance, with an organ-grinder coming in from the right. (4) The dancers move out left, and Copeau and Virginie begin to dance.
(5) They move out left with the organ-grinder, leaving Gervaise alone. (6) A comic friend who is continually eating comes back in to speak to Gervaise and then leaves.
(7) Lantier comes in from the right and starts bullying Gervaise. (8) Another friend comes in and drives him away out right.
(9) The dancers and organ-grinder return, with Virginie still dancing with Copeau. (10) The scene ends as Gervaise sits disconsolately while Virginie moves to Lantier and the pair watch Gervaise menacingly from the extreme right edge of the frame.
Similarly complex scenes, notably a celebration of Gervaise’s birthday, follow, culminating in a final shot that runs 6:45 minutes, out of a 35:46 minute film! (There is a pair of titles in Flemish and French that interrupt the shot early on, but the take was clearly continuous, and the titles seem likely to have been added by the exhibitor in whose collection the sole known surviving print was discovered.)
As Mariann also points out, one can find “filmic” elements in Capellani, including “the sheer photographic beauty of exterior shots, which is not to be found in the work of any of his contemporaries.” The frame at the top of this entry, made in 1914, is striking enough. (Mont St. Michel appears only in this fashion, as a tiny shape in the backgrounds of a few shots to establish that the characters have landed on the Normandy coast, but otherwise does not figure in the film.) But I suspect few would guess that the shot illustrated at the bottom was made as early as 1906.
The temptation is to go on and on about Germinal and make a long entry even longer. But Germinal has been the most familiar of Capellani’s films, and I mentioned some writings on it in my first entry. I’ll just make a few remarks about it here.
First, Capellani does a remarkably good job of capturing the naturalism of the Zola novel, as the first frame below suggests. Second, the scenes in the mine convincingly convey a sense of cramped working spaces, despite the need to shoot on sets (second frame below).
The film also makes highly effective use of the giant slag heaps behind the coal fields, placing them in the backgrounds of shots in various locales:
Clearly the resemblance of these neatly squared-off heaps to pyramids did not escape Capellani. (Compare the Red Pyramid at Dashur, above.) I think he intended this to be noticed and to be part of a motif linked to the decor of the mine owner’s study:
Like many rich men in the movies of this era, the owner is characterized as a collector of antiquities and of modern statuary with ancient motifs. (One film shown this year, I forget which, showed a rich man buying such pieces.) A case in the hallway beyond the study presumably houses his real ancient pieces, while his desk sports a small modern statue of a samurai, and the mantelpiece holds a modern Egyptianizing bust of a woman. Capellani was probably intentionally comparing the mine owner to a pharaoh and his workers to the “slaves” who built the pyramids. (This was the view of the time, though the pyramids were in fact built with paid labor.) Such a conceptual use of motifs again marks the sophistication Capellani’s films had reached by the “anna mirabilis” of 1913.
A major step forward since last year is the fact that we now have a reasonably complete print of L’Homme aux gants blancs. As it demonstrates, Capellani can cut in on those rare occasions when it’s necessary (first frame below). Here we need to see the detail of the seamstress fixing a loose button on the new gloves, not just for its own sake but because those gloves will later be lost, found by a thief, and deliberately dropped beside the body of a woman whom the thief kills. The seamstress’ identification of the repaired glove leads to the arrest of the wrong man. In the final shot (second below), the devil-may-care thief, witnessing the arrest, enjoys the irony by holding the door open for a police inspector and handing him his dropped cane. The ending is grim, since the paddy-wagon departs, leaving us to assume that the wrong man will be punished.
I can’t mention all the films shown this year, but two I particularly enjoyed were La Bohème (1911) and Le Signalement (1912), neither of which I can illustrate.
Firstly, this year Capellani’s brother Paul, whom we have seen in smaller roles in previous years, emerged as a fine actor, with perhaps his best work being as Rodolphe in La Bohème. (He played the same role opposite Alice Brady in Capellani’s American feature based on the same story, La Vie de Bohème, in 1916; there the more restrained acting style favored in the U.S. by that point makes his performance less dynamic and affecting.) The familiar tale is compressed but movingly told.
Le Signalement (“The Description”) in some ways echoes the remarkable dramatic twist of the previous year’s L’Épouvante. There a burglar ends by gaining our sympathy, and the suspense during the later part of the film centers not around the frightened heroine but around whether the terrified man will fall to his death. The heroine’s compassion makes for a moving resolution. In Le Signalement, Capellani raises the stakes. A shoemaker and his daughter (granddaughter?) Jeanette, played by the excellent child actor Maria Fromet, live in a French village. The police circulate a flyer describing a child murderer who has escaped from a nearby insane asylum. While delivering some boots, the cobbler is lured to linger in a tavern, and the murderer comes to the house. In characteristic fashion, Capellani lets most of the length of the killer’s time in the house play out in a single take into depth; the camera faces diagonally across the room toward the open door, the only place where help might appear.
When the escapee arrives, Jeannette innocently invites him in and offers him some food, including a dangerous-looking knife to cut a piece of pie. Tempted to kill and yet overwhelmed by the child’s kindness, the man sits and eats. Capellani ups the ante when Jeannette lifts a crying baby, whose presence we had not previously noticed, out of a basket to comfort it, even handing it to the man to rock. During all this we are left in suspense as to whether he will give in to his murderous obsession or resist it. At last the pair hear the police outside, and Jeannette realizes that her visitor is the killer–yet she helps him to escape out the window. Again we are torn, not wanting the child’s generous gesture to be thwarted and yet not wanting a child murderer to run loose! The plot solves the dilemma in a neat and dramatic fashion. Overall, like L’Homme aux gants blanc and L’Épouvante, Le Signalement packs conflicting emotions into a single reel.
Such density of narration is one characteristic of Capellani’s work. As Mariann wrote in the program last year: “Capellani’s speciality as a director is the broad scope of his narratives, connecting different locations and characters, which invests even short films with grandeur and space, to such an extent that the film lengths, given in either metres or minutes, often seem unbelievable. What? Can L’Épouvante really only be 11 minutes long? And Pauvre mère and Mortelle Idylle only 6 minutes each?”
Two final French features
Apparently Capellani made eight films in 1914, but as far as I know, only two survive. Both happen to deal with the French Revolution, and both are based on 19th-Century novels: Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge (Dumas) and Quatre-Vingt-Treize (Hugo).
Last year I suggested that Le Chevalier might be a bit of a let-down after the heights of Les Misérables and Germinal. But it would be hard to match Germinal, and I have to admit that upon seeing Le Chevalier again on DVD, it kind of grew on me. The main problem, I think, is that Capellani doesn’t take much trouble to give the characters traits and make them sympathetic. They seem more like game pieces in service to the plot. But as always the staging and acting are marvelous, and both locations and sets, as I suggested above, give a vivid sense of revolutionary Paris.
Oddly, though, for the first time there are signs that Capellani is being influenced by cinematic trends of the day and is trying to expand his style in a somewhat tentative way. Clearly, like so many filmmakers, he has seen Cabiria and been impressed by its lumbering tracking shots. The tribunal near the end where the young lovers, Maurice and Geneviève, are condemned uses such a tracking movement well, pulling out from the lovers and the court to include the crowd that welcomes the death sentences:
In a few scenes Capellani also explores offscreen space in a way that I haven’t seen in his other films. Most dramatically, when Maurice sneaks up to the house where he hopes to see Geneviève, he appears small in the distance, disappears out the bottom of the high-angle framing, and suddenly reappears very close in the foreground, having somehow climbed up to a window:
In one scene Capellani even cuts in for a closer view and a different angle during a letter-writing scene. It’s a bit clumsy, with a mismatch on the man’s position–though not one that is worse than many attempted matches in European cinema of the 1910s:
The cut-in isn’t really necessary, though, and one would expect Capellani not to use it. This is one of the few moments in all the films shown where briefly Capellani seems truly old-fashioned, catching up with a technique that had already been in use for a few years. Here I wish he had stuck to his accustomed long shots, for it’s a sign of things to come. The next year Capellani would be working in the U.S. and making a smooth transition into continuity editing.
Capellani’s last film in France was Quatre-Vingt-Treize. With the outbreak of World War I, the subject matter, French fighting against French during the Revolution, was considered too provocative in a fervently patriotic context, and the film was banned. Capellani did not finish it but went immediately to the U.S. After the war, it was completed by his fellow theatre/film director André Antoine and finally released in 1921. There is no sign of any of the footage being by a different hand or done at a later time. It appears that Antoine simply edited the footage, perhaps to a script or shot list from the director, since the result on the screen is pure Capellani. It eschews the mild experiments of Le Chevalier and returns to a concentration on acting and a wonderful use of locations. At one point, in a single take, a troupe of Revolutionary soldiers marches past in a woodland setting. After they exit, there is a brief pause, and a man rises up from behind the foreground rocks in the path, signaling. Suddenly counter-revolutionary soldiers pop up all over the frame from the undergrowth and follow their foes stealthily in a seemingly unending stream:
In this film the characters are assigned more traits than in Le Chevalier, and the result, even at 165 minutes, is a rattling good tale.
(I mentioned that Capellani avoided dialogue intertitles. This films has some, but it may be that Antoine added those on his own.)
Despite dealing with the same historical period, the two films say nothing about Capellani’s politics, since in Quatre-Vingt-Treize the sympathies are clearly with the Revolutionaries, and in Le Chevalier, they lie with the group, including the title character, who are plotting to rescue Marie Antoinette from prison.
The American period
Given Capellani’s expertise in and long use of the tableau style of filmmaking, it is remarkable how easily he adapted to Hollywood. Only a few of his films from the early years in Hollywood survive, and His La Vie de Bohème (1916), a pleasant, well-made film, is not nearly as lively and absorbing as the French version, La Bohème (1912). I enjoyed the other features shown, Camille (1915, starring Clara Kimball Young) and The Virtuous Model (1919, starring Dolores Cassinelli), but I couldn’t help missing the French Capellani. It is hard to imagine how his career would have developed had he stayed in France. Perhaps, like Victor Sjöström and Ernst Lubitsch, he could have waited until after the war to move smoothly from the tableau style to adopt continuity editing. Perhaps, like them, he could have remained one of the top filmmakers of the silent period. (He returned from Hollywood to France after directing the 1922 Marion Davies vehicle The Young Diana. He did not direct again and died in 1931.) Good though the Hollywood features are, however, for me they inspire none of the sense of discovery and excitement that the films of the 1908 to 1914 period do.
Wishful thinking
By the 2011 festival, most of the known Capellani films have been restored. Some have improved before our eyes. In 2008 and again in 2010, the older restoration of L’homme aux gants blancs (1908) was shown. The newer, more complete restoration combines images derived from a 35mm print and a 28 mm one. A new restoration of Germinal with toning based on original color indications was shown this year.
There were also some fragments, which were saved for the seventh and final program in the series, “Borders and Blind Dates (A Workshop).” There is a version of Le Belle et la bête, for example, that is badly deteriorated, even within most of the footage retained by the restorers. What little remains suggests that the film must have been quite charming; the fragment is included among the extras on the Cineteca di Bologna DVD. There were also some films that were considered as possible Capellanis. According to the booklet accompanying the same DVD, Capellani is thought to have made anywhere from 70 to 80 films from 1905 to 1912. The number is uncertain, due to problems of attribution. Of these, about half survive, less than a third of them from the 1910-1912 period.
La loi du pardon, a 1906 melodrama of the type Capellani frequently made, is listed in the festival catalogue as “Ferdinand Zecca? Albert Capellani?” It could be Capellani, but to me most of his films of the 1906-07 years, though excellent, are not distinctive enough to be attributed to him without any documentation. Manon Lescaut (1912 or 1914; it is listed as both in the program on pages 128 and 129) was more tantalizing. An adaptation from a classic French novel, made by Pathe’s prestigious S.C.A.G.L. unit, would seem exactly Capellani’s sort of project. The first scene, set in an open-air café, seemed plausible as his work, but the rest of the film has little or nothing of his style about it. Instead there is a lack of long-held, intricately staged shots, one completely unnecessary cut-in, and too many old-fashioned painted sets. Compared to the location work in Germinal or just about any of the big films from the immediate pre-war years, these looked crude. Plus, as Caspar Tyberg pointed out to me, the action was staged more quickly than one would expect from Capellani, who often lets situations develop gradually, with many details in the gestures and facial expressions. There are some of his films in archives but apparently as yet unrestored. (According to the booklet accompanying the Coffret Albert Capellani, the Cinémathèque Française has a negative of a 1909 version of Manon Lescaut.) Otherwise I fear we must count on future discoveries in the archives for more Capellani films. Surely some will be forthcoming, now that archivists are aware of the importance of this newly revealed master. “Cento Anni Fa” will move on into 1912, 1913, and 1914, and perhaps the Capellani retrospective will resurface occasionally.
With the end of the main retrospective, however, it is safe to say that from now on anyone who claims to know early film history will need to be familiar with Capellani’s work. If you live outside Europe and don’t already have a multi-region DVD player, this might be the time to invest in one. It would be worth it just to see these new DVDs.
Capellani films shown at Bologna and their availability on DVD
Symbols used in the list:
* A film on the Coffret Albert Capellani, (La Cinémathèque Française, La Fondation Jérôme Seydoux-Pathé), Pathé, two four discs with booklet, Region 2 Pal. 36-page booklet in French. There is a bare-bones filmography, with titles and dates, on page 35, but this no doubt will be revised as research continues.
** A film on Albert Capellani: Un Cinema di Grandeur 1905-1911 (La Fondation Jérôme Seydoux-Pathé, the Cineteca Bologna) Il Cinema Ritrovato, 1 disc with booklet, Region 2 Pal. Intertitles in various languages; optional subtitles in Italian, French, and English. 55-page booklet in Italian, French, and English.
+ The titles I would most like to see on a future DVD!
In last year’s entry, I expressed the hope that some films from previous years could be repeated. Whether or not that hope influenced the programming, some were.
[Added July 19: Mariann tells me that she is now convinced that La Loi du pardon is genuinely a Capellani film. I find that quite plausible.]
2005
*Le Chemineau (1905)
2006
**La Fille du sonneur (1906)
2007
*Les Deux soeurs (1907)
*Le Pied de mouton (1907)
**Amour d’esclave (1907)
2008
Don Juan (1908)
La Vestale (1908)
*Mortelle idylle (1908)
Corso tragique (1908)
Samson (1908)
**L’Homme aux gants blancs (1908)
Marie Stuart (1908)
2009
*L’Assomoir (1909)
**La Mort du Duc d’Enghien (1909)
2010
Dans l’Hellade (1909)
**Le Pain des petits oiseaux (1911)
*La Fille du sonneur (1906) (Repeated from 2006)
Notre-Dame de Paris (1911)
+Les Miserables (1912)
**Le Chemineau (1905) (Repeated from 2005)
*La Femme du lutteur (1906)
**L’Arlésienne (1908)
Eternal amour (1914)
**L’homme au gants blancs (1908) (Repeated from 2008)
**L’Épouvante (1911)
*Pauvre mère (1906)
**L’Intrigante (1910-11)
La Mariée du château maudit (1910)
**Cendrillon ou la pantoufle merveilleuse (1907)
Samson (1908) (Repeated from 2008)
*Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge (1914)
*Drame passionel (1906)
**Le Pied de mouton (1907) (Repeated from 2007)
**La Mort du Duc d’Enghien (1909) (Repeated from 2009)
La Fin de Robespierre (1912)
+La Glu (1913)
The Red Lantern (USA, 1919)
*Mortelle idylle (1906)
+L’Évade des Tuileries (1910)
2011
La Belle au bois dormant (1908)
Le Courrier de Lyon ou l’attaque de la malle poste (1911)
+La Bohème (1912)
La Vie de Bohème (USA, 1916)
*Quatre-vingt-treize (1914, released 1921)
**[Amour d’esclave (1907) Not shown for lack of time]
+Le Signalement (1912)
*L’Âge du Coeur (1906)
**Les Deux soeur (1907) (Repeated from 2007)
Camille (USA, 1915)
*Germinal (1913)
**L’Homme aux gants blancs (1908, more complete restoration)
Le Visiteur (1911)
Marie Stuart (1908) (Repeated from 2008)
Le Luthier de Crémone (1909)
The Feast of Life (USA, 1916)
**La Belle et la bête (1908, fragment) In “Extras” on DVD
Foulard magique (1908, fragment)
Béatrix Cenci (1909, incomplete)
**La Loi du pardon (1909) By Capellani or Ferdinand Zecca
La Legend de Polichinelle (1907)
[August 13, 2012: Roland-François Lack has recently added a post on Capellani on his website, The Cine-Tourist. He gives an extraordinarily detailed run-down of the Parisian (and Vincennes) locales used by Capellani (such as the one below), with many frames from the films and both current and vintage photos of the places, as well as a few maps and some engravings and other graphics. Well worth a look!]
La Fille du sonneur (1906)
Capellani ritrovato
Aladin ou la lampe merveilleuse.
Kristin here–
[Note, July 11, 2011. The release of a considerable number of Capellani films on DVD since the 2010 festival has allowed me to add some frames to my examples below. The frames from L’Arlésienne, L’Épouvante, and Pauvre mère are new, and the one from Cendrillon has been replaced by a better copy. For more on the DVD, see the entry on the second half of the retrospective.]
Back in the 1980s and early 1990s, researchers into silent cinema became used to the discovery of little-known auteurs. The 1910s proved an exceptionally rich source of directors beyond the familiar names of Griffith, Ince, Chaplin, Feuillade, Lubitsch, Stiller, and Sjöström.
In 1986 Le Giornate del Cinema Muto’s epic retrospective of pre-1919 Scandinavian cinema revealed the Swedish master Georg af Klercker. In 1989, a similarly ambitious presentation of pre-Revolutionary Russian films brought the work of Evgeni Bauer to light. In 1990, the “Before Caligari” year added Franz Hofer to the list of obscure directors at last receiving their due. After that quick series of revelations, there has been a dearth of such significant revelations until, some would argue, now.
This year Bologna’s Il Cinema Ritrovato presented 24 films directed by Albert Capellani (1874-1931), previously known mainly to specialists for two films, his magisterial adaptations of Hugo in the four-part serial Les Misérables (1912) and of Zola in Germinal (1913). The retrospective has been  arranged by Mariann Lewinsky, who, as in previous years, has also been responsible for this year’s “Cento anni fa” program, covering the output of 1910. (The “Cento anni fa” series began in 2003, with Tom Gunning as programmer, and Mariann took over that duty in 2004.)
arranged by Mariann Lewinsky, who, as in previous years, has also been responsible for this year’s “Cento anni fa” program, covering the output of 1910. (The “Cento anni fa” series began in 2003, with Tom Gunning as programmer, and Mariann took over that duty in 2004.)
A gradual rediscovery
When Georges Sadoul wrote his multi-volume Histoire général du cinéma, the second part (1948) mentioned Capellani a few times. With the lack of available prints of the films, however, he was limited to treating the director primarily as the head of S.C.A.G.L., the prestige production unit launched by Pathé in 1908. Richard Abel’s The Ciné Goes to Town: French Cinema 1896-1914 (1994) devotes considerably more space to Capellani. Dick was able to view and analyze seven of the shorts and four features but was hampered by the incompleteness of some of these and the lack of such key films as L’Arlésienne (1908). As Mariann points out in her program notes, Capellani’s significance has been commented on by several scholars, including our colleagues Ben Brewster and Lea Jacobs. (Ben’s detailed analysis of the acting in Germinal is here, including a citation to a 1993 article on the film by Michel Marie).
Mariann, however, has recently been instrumental in bringing Capellani’s films to broader attention. The decision to mount retrospectives of his work has spurred archives to restore several which had been unavailable or lost, and more prints will presumably be ready for next year.
Capellani has actually been creeping up on us in Bologna for some time now. In 2006, Mariann’s programs from 100 years ago had reached 1906–the year when Capellani’s career really got started, though at least one of his films appeared in 1905. We saw only one from 1906, La Fille du sonneur. I can’t say that I remember anything about it. In the 1907 program, Les Deux soeurs, Le Pied de mouton, and Amour d’esclave. Again, I probably would have to say that I don’t recall these films, except that I vaguely recognized Le Pied de mouton, a fairy tale about a young man who receives a magic object in the form of a large sheep’s foot, when it was shown again this year.
By 2008, however, a pattern had started to emerge, and Mariann showed seven Capellani films, with six of them forming one program devoted solely to the director’s work, “Albert Capellani and the Politics of Quality”: La Vestale, Mortelle idylle, Corso tragique, Samson, L’Homme aux gants blancs, and Marie Stuart. The seventh, Don Juan, appeared in the “Men of 1908” program.In visiting archives and choosing films Mariann often saw prints without credits and from unknown directors, so the pattern only gradually became clear. In the 2008 catalogue she reflected on her realization that Capellani was showing up regularly in her choices for the annual centennial celebrations: “When organising the 1907 programme, however, in the light of Amour d’esclave, a gorgeous mise-en-scène of classical antiquity, I asked myself for the first time, ‘Who made this sophisticated film?'”
She speculated that the relative neglect of Capellani perhaps came from the Surrealists’ campaign against highbrow filmmaking during the 1910s and 1920s:
From his very first film on–the memorable Le chemineau of 1905, based on an episode from Victor Hugo’s Les Misérables–Albert Capellani transports the contents and qualities of bourgeois culture to the cinema. He films Zola, Hugo and Daudet–his Arlésienne of 1908 has unfortunately been lost. His many fairy tale films (scène des contes), biblical and historical scenes reveal him as a great art director, who also adopted the latest developments in modern dance and worked with its stars Stacia Napierkowska and Mistinguiette. Highly versatile, he had an unerring sense of the best approach to a given genre.
Fortunately, L’Arlésienne has subsequently been discovered by Lobster Films, just in time to be presented this year.
The 2009 program contained only two Capellani films, but one was the extraordinary Zola adaptation L’Assommoir. This had been known only from fragments until a complete copy was found in Belgium. It displays an unusual degree of realism that fits the naturalist subject matter and also contains complex and deft staging that moves numerous characters around a scene in a way that shifts the spectator’s attention among them exactly as the flow of the narrative requires. The other, La Mort du Duc d’Enghien, was shown again this year. It’s a rare case of an historical drama of the period that manages to arouse a genuine sympathy for its main character, a young nobleman unjustly arrested and executed upon Napoleon Bonaparte’s orders. More on it later. The 2009 catalogue announced that in the following year, Capellani would graduate from the annual “Cento anni fa” programs to his own retrospective.
This year’s films
This first full-fledged Capellani retrospective gave a generous though not complete overview of his surviving films from early 1906 to 1914—a few bearing 2010 restoration dates. Capellani also worked in the United States from 1915 to 1922, and the program included The Red Lantern, a 1919 feature starring Nazimova. This, Mariann’s notes assure us, is “a taster for next year’s festival,” which will include further restorations from the French period, as well as more features from his American career. (It would be good to see the other Capellani films shown in previous years repeated, now that we have a sense of his work more generally.)
Ideally our examples here should include frames from the films shown at this year’s festival, but none of them is out on DVD. The Brewster article linked above has a generous selection of well-reproduced frames from a 35mm print of Germinal. As far as I know, the only Capellani film available on DVD is Aladin ou la lampe merveilleuse, on the third volume of Kino International’s “The Movies Begin” set. I’m sure it was included there not because it was a Capellani but because it survives in beautiful condition and is an epic with elaborate hand-coloring. I’ve included frames at the top and bottom of this entry, despite the fact that it has not been shown at Bologna. The smaller frames illustrating a few of films shown at Il Cinema Ritrovato come from the Gaumont Pathé Archives website (registration required). This site is the best online source of information on the director’s films, including complete video versions in a few cases. These are, however, quite small screens, and they display the double branding of a prominent timer and a bug of a Pathé rooster superimposed over much of the frame.
Capellani had worked in the theater as a director and actor until Pathé recruited him in 1905. In a sense, he became a specialist in literary adaptations, especially after his appointment in 1908 as artistic director of S.C.A.G.L. Yet the films being shown this year include pure melodrama (such as Pauvre mère, “Poor mother,” 1906), crime-suspense films (L’Épouvante, “The Terror,” 1911), classic fairy-tales (Cendrillon, 1907), and historical/biblical costume pictures (Samson, 1908).
With his theatrical background, it is not surprising that Capellani was able to cast many old colleagues in his films, notably Henry Krauss, who played Quasimodo in Notre-Dame de Paris (1911) and Jean Valjean in Les Misérables (1912). Wherever his actors came from, however, Capellani was a master at directing performances. In many cases the acting makes characters who would seem completely conventional figures in most films of the day into people with whom the audience can empathize.
The staging in Capellani’s shots is inevitably impeccable. The progression of the story is clear even in shots with numerous characters on camera. More of his stage experience coming out, one might say, but he also adapts his technique to the visual pyramid of space tapering toward the camera’s lens.
L’Évadé des Tuileries (1910), for example, deals with the Count du Champcenetz, the governor of the Tuileries during the French Revolution, who initially tries to alert the royal family to their impending arrest and subsequently flees for his life from the revolutionary forces that invade the palace. In the most spectacular shot, he rushes in, exhausted and wounded, to speak to the king as the members of the royal family gradually enter and guards surround them. Champcenetz collapses and slides partway under a chair at the foreground right as the revolutionaries burst into the room. The business of the ensuing struggle, the departure of the combatants with the royals under arrest, and a short burst of looting leaves a still scene with the dead and wounded on the floor. Suddenly an arm moves at the far lower right corner of the frame, and we become aware that Champcenetz has survived.
David has praised the sustained tableau staging in depth of the 1910s, in the films of Feuillade, Sjöström, Hofer, and others, but here is Capellani doing it all in 1910—and this is not the first of his films to display such control of the complex arrangement of actors in space.
None of this is to suggest that Capellani’s films are “stagey.” He is quite capable of a cinematic flourish for purposes of dramatic effectiveness. L’Arlésienne, shot largely on location in the old town of Arles, includes a shot of the young couple atop a tower that looks over the cityscape. The camera begins on the spire, panning right until the couple appear in medium shot, with the town beyond them and the parapet. They wander out right, and the camera pans around the parapet, only catching up with the couple when they are roughly 180 degrees opposite to where the camera started:
It is hard to believe that in London L’Arlésienne played on the same program as L’assassinat du Duc de Guise, which, sophisticated as it is in some ways, seems seems downright old-fashioned when contrasted with Capellani’s film.
Even flashier is L’Épouvante, which seems at first a simple story of a young woman in danger as she retires for the night, unaware that a burglar had stolen her jewelry just before she came in and is now hiding under the bed. She lights a cigarette and carelessly tosses the match on the floor. The camera tracks slowly back from the bed to bring the burglar into view; he registers fear that the match is still alight and might set the rug on fire. He reaches to snuff it out, and a sudden cut places us at a high angle above the heroine as she looks down and sees the hand appearing from beneath her bed. A return to the long shot displays her reaction:
Up to this point our sympathy has been entirely with the heroine. But once she escapes the room and locks the burglar in, his struggle to escape before the police find him takes up much of the remaining action and gradually gains him our sympathy as well. Trapped multiple stories up, he climbs to the roof, only to have to retreat as the pursuers rush up and search there. Moving downward, the burglar ends up hanging by an ominously bending gutter.
Only the heroine is left in her flat to discover his plight, and she lowers some drapes for him to climb up. In a touchingly awkward scene, the man is relieved but unable to express his gratitude except by returning the stolen jewelry and silently exiting, while she makes no attempt to stop him. In a way, L’Épouvante reminded us of Suspense, Lois Weber and Phillips Smalley’s remarkable 1913 film of a woman besieged in her house by a burglar, but the unexpected shift of emotional dynamics between the two characters in Capelanni’s film makes it equally memorable.
Capellani’s pictorial sense in real locations has been widely remarked upon. Even in La Mariée du château maudit (1910), a relatively slight tale of spooky doings in a deserted castle where a wedding party plays hide-and-seek, becomes impressive in part because of its use of an extensive set of actual ruins. There’s also a remarkable moment after the bride accidentally becomes locked in a room with a skeleton dressed in a bridal gown. She reads an old book telling of the young woman’s fate, and two successive bits of the story appear as matte shots on the right and left leaves of the open book. (Working at Pathé, Capellani could use impressive special effects, as the dream image in the Aladin frame at the top demonstrates.)
The sets are masterful as well. I was particularly struck by Jean Valjean’s desk in the second episode of Les Misérables (1912). It creates an effect of forced perspective that is like German Expressionist eight years ahead of its time. Valjean has escaped from prison and become a mayor and successful small-factory owner. Javert, formerly a guard at the prison and now a local police officer, suspects Valjean of being the fugitive. Now he comes to Valjean’s office to introduce himself.
Valjean sits at the left behind an enormous desk which dominates the left and center of the screen; its size is exaggerated by rows and stacks of thick volumes ranged across its top. About a third of the screen is empty at the right, where Javert enters at the rear and walks only partway forward. The effect is to make Javert appear smaller than he really is, with the low camera height that Pathé films were using by this point exaggerating the effect; during part of the scene he is also partially blocked by the desk. The suggestion is that he has no ability to follow up his suspicions of such a powerful man.
In a subsequent scene, when Valjean brings the ailing worker Fantine to his office, the desk has been moved away from the camera, which frames the scene from further to the right. The result is a far more open space at the right, while Valjean brings forward a chair for Fantine that puts her in front of the desk. Unlike Javert, she is not dwarfed by the desk, which, once Valjean comes to lean over her, is barely visible. Instead, the right half of the screen is left unoccupied so that a flashback can fill it.
In the scene like the one with Javert, a German Expressionist film would have exaggerated the size of the desk even further and perhaps tilted the floor up at the rear, but the effect is clear and dramatic enough as it is. Again, it is not an effect one would expect to find in a film of the early 1910s. There is also a contrast between the massive desk and the relatively small, insubstantial table that Javert uses as a desk in the setting of the police headquarters
Even the most conventional films receive what I began to recognize as Capellani touches, often to bring a moment of realism into a fantasy or melodramatic setting. In Cendrillon, the gardener who carries in a huge pumpkin to be turned into the heroine’s magic coach exits wiping the sweat from his head with a handkerchief (below left). The little girl who falls out of a window to her death in Pauvre mère leaves a large, dramatic splotch of blood on the sidewalk when her lifeless body is lifted—a realistically gory touch of a sort which I don’t recall seeing in any other film of this era (below right). When the hero finds the magic lamp in Aladin ou la lampe merveilleuse, he blows dust off it and turns it over to shake out further dirt (see bottom).
Another sort of touch appears in La Mort du Duc D’Enghien, a carefully executed motif of a sort one doesn’t often see in films of this type. The hero is arrested while at a hunting lodge, and throughout he wears a distinctive hat that’s probably part of a hunting outfit. He throws it defiantly to the floor during the courtroom scene in which he is unjustly condemned; he throws it down again in his cell, this time to indicate despair and exhaustion; in the final execution scene, he tosses it aside as part of his brave resignation, facing the firing squad with open arms and without a blindfold. These moments aren’t stressed, and one could understand the plot perfectly well without noticing the repetition. Still, the motif helps characterize D’Enghien quickly in this relatively short film and indicates the care with which Capellani was crafting even his one-reelers.
Mariann was somewhat apologetic about La Glu, a 1913 feature, since it centers around a femme fatale who victimizes three men in the course of the narrative. The title is the heroine’s nickname, and it means what it sounds like, “glue,” and particularly sticky substances like bird-lime that are used to ensnare. But the audience thoroughly enjoyed this distinctly absurd but entertaining and fast-paced tale of a heartless, mercenary woman, played with relish by Mistinguett, and the men foolish enough to fall for her. After all, there are plenty of depictions of love-’em-and-leave-’em men from this period, so why not turn the tables? At least one flagrant coincidence brings all of them to the south of France, where the heroine goes for a vacation, and Capellani contrasts the early scenes of high-society Paris with the stark seascapes in and around a fishing village. Though another literary adaptation (from a novel and play by Jean Richepin), this film certainly stands out among the pre-war features and demonstrates once more Capellani’s versatile ability with a range of genres.
After all these treats, the last French feature on offer, Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge (1914), proved a slight let-down. Capellani had a penchant for substituting letters and other texts for intertitles, but this film pushes the device to the point where sometimes it seemed as if every other shot was an insert. The plot, dealing with a scheme to rescue the imprisoned Marie Antoinette, was also frustratingly complicated and not presented with the admirable clarity that characterizes most of the other films. As I’ve mentioned, Capellani was often able to generate an empathy with the characters which is rare for films of this period, but as a result of the constant plot twists, the Chevalier and his endangered mistress remain rather remote figures. There are some effective moments, though. One exterior view of the protagonist’s home places a door at the upper center, approached by a symmetrical pair of staircases running to the right and left and forming a pyramid shape. A foreground pond elaborates the space still further, so that when a crowd tries to break in, the staging utilizes the frame vertically and horizontally, with intricate movements of individuals to avoid the water.
Ahead of his time–up to a point
As I remarked in an entry on last year’s festival, L’assommoir struck me as looking like it had been made in 1912 or 1913 rather than 1909. Now it becomes clear that many of Capellani’s films give this sense of trying things that other filmmakers would begin doing routinely a few years later. In some cases, like L’Arlésienne, it’s a focus on acting of a sort that we associate with Griffith’s films like The Mothering Heart or The Painted Lady. In others, it’s the motifs or the subtle changes of framing or the eye for landscapes. Although the editing is not usually flashy, Capellani is good at keeping spatial relationships clear, as the series of shots depicting Valjean’s escape from prison in the first part of Les misérables demonstrates. As Mariann wrote, he seemed able to adapt to any genre. I’m not a particular fan of the historical films so common during this period, but Capellani manages to humanize most of his.
It was only with Le Chevalier de Maison-Rouge that the sense of Capellani being ahead of most of the directors of his time largely disappeared, though it seems premature to judge from a single 1914 film. Perhaps during the immediate pre-war era, and especially the creatively fecund year of 1913, the exploration of the cinema by an increasing number of masters created a spurt that he did not participate in. And perhaps more films from 1913 and 1914 will appear in next year’s retrospective and give us a better sense of how his career developed in that crucial period. It will also be interesting to trace his assimilation of the developing classical Hollywood norms once he moved to the U.S. By 1919 and The Red Lantern, he clearly had absorbed the norms thoroughly, and his style had become indistinguishable from that of his American colleagues.
Added July 13: Roland-François Lack has kindly written to point out that another Capellani film exists on DVD. (Thanks, Roland-François!) His 1908 version of the French tale Peau d’âne was included as a supplement on the  collector’s edition of Jacques Demy’s film of the same name. It is also included in the “Intégrale Jacques Demy” 12-disc set. These DVDs are Region 2 (Europe) and won’t work on other region-coded players.
collector’s edition of Jacques Demy’s film of the same name. It is also included in the “Intégrale Jacques Demy” 12-disc set. These DVDs are Region 2 (Europe) and won’t work on other region-coded players.
The source of the print isn’t clear on the disc. (It’s another one that hasn’t been shown at Bologna.) Probably Pathé’s own archive, since there’s a little rooster-shaped bug superimposed at the lower left in every shot.
It’s a fairly contrasty print with replaced intertitles in French only. It also seems to be running at 24 fps or something close to it. The action zips right along, which is a pity. There’s a lot of carefully executed pantomime-style acting. It’s impossible to catch all the gestures, especially since there are often three or four actors going at it at the same time. It would actually be a good film for teaching about the acting styles of this period if one could just slow it down.
I wouldn’t have spotted this as a Capellani film if I hadn’t known its source when I watched it. Still, it has some of the traits we’ve recently come to associate with him. The meeting between the heroine and Prince Charming takes place in a carefully chosen setting with a reflecting pond in the foreground. It looks like the film was shot on a hazy day, but it looks as though the camera may be set up to shoot with the sunlight at the characters’ backs.
The film also has the director’s typical elaborate interior sets juxtaposed with a dramatic use of real exteriors. The frame at the left below shows the fairy appearing for the first time to the princess. It’s not easy to see, but the busy interior includes a deep, diagonal space with several arches decorated with portraits that are painted, frames and all on the square pillars. Once the heroine disguises herself and flees to avoid her suitors, Capellani goes on location, using an impressive château and streets that look like they are in the same vicinity.
I hope that some of the more realistic films will soon appear on DVD. Lobster in particular could make their newly restored L’Arlésienne available.
Back in Bologna
The newly restored version of The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly on the Piazza Maggiore.
Kristin here-
This year, the main complaint about Il Cinema Ritrovato, the annual festival held by the Cineteca Bologna, is that there’s too much to see. With three venues playing films against each other, plus the 10 pm screenings each evening in the Piazza Maggiore, there’s no way to see everything. Some people complain that the conflicts are becoming worse-but I remember these same complaints about the over-abundance of films coming in previous years as well. Yes, it’s frustrating at times, but being offered more films than one can watch is a problem a lot of people would love to have. Basically one either chooses a couple of threads to follow through or just goes to whatever appeals in any given time slot.
According to the 2009 festival’s newsletter, there were 810 attendees, including 557 from outside Italy.
This year there have been several main focuses: a retrospective of Frank Capra’s silent and early sound films; a portion of the Cinémathèque de Toulouse’s program of Jewish-themed Russian and Soviet cinema from the 1910s to the late 1940s; a selection of color films from the early years of the twentieth century to the 1960s; a survey of the work of Vittorio Cottafavi; the annual “100 years” program, this time from 1909; the sea films of Jean Epstein; the silent Maciste films; and many other items.
Even between the two of us, we could not take in nearly all of the riches on offer, so here’s some of what I managed to see, with David’s report to follow.
An annual hundredth birthday
Each year the festival has a thread of programs of films from one hundred years earlier. This tradition started in 2003, when Tom Gunning was asked to put together groups of films from 1903. Thereafter Mariann Lewinsky took over as programmer for these threads. In recent years, her choices have been supplemented by small groups of films chosen by individual national film archives. This year Tom programmed the 1909 Griffiths and a group of other U. S. titles.
Maybe it’s just my impression, but the hundred-year packages seem to gain in prominence and popularity each year. Presumably in response to such popularity, the festival has just released a DVD with a selection of 22 shorts from this year’s 1909 program: Cento anni fa: Il cinema Europeo del 1909/European cinema in 1909 (running two hours and twenty minutes and presented below by Mariann). It contains only about a fifth of the roughly 100 films screened, but many of the others are available in online archives. DVDs of previous years’ programs are in the works, with 1907 soon to come. The DVD and other publications of the festival are available here.
I managed to see most of the 1909 programs but obviously can mention only a sampling. Undoubtedly the highlight for me and others I talked to was Albert Capellani’s L’Assommoir, notable for its skillful and intricate staging and splendid performances. It looked more like a film from 1912 or 1913. During the comedy, Un chien jaloux (a Gaumont one-reeler by an unknown director, left), pianist Donald Sosin had the audience in stitches by providing barks, whines, and growls as appropriate. (It’s included on the DVD, alas, without the sound effects.)
highlight for me and others I talked to was Albert Capellani’s L’Assommoir, notable for its skillful and intricate staging and splendid performances. It looked more like a film from 1912 or 1913. During the comedy, Un chien jaloux (a Gaumont one-reeler by an unknown director, left), pianist Donald Sosin had the audience in stitches by providing barks, whines, and growls as appropriate. (It’s included on the DVD, alas, without the sound effects.)
French director Alfred Machin contributed two excellent dramatic films, both involving windmills: Le Moulin maudit (also on the DVD) and, in the program of early color films, L’Ame des moulins. Comedy stars were represented by two Cretinetti films and a strange Max Linder film in which he becomes Amoreux de la femme à barbe (“Infatuated with the Bearded Lady”).
There were a great many documentaries giving glimpses into the world of 1909. Airplanes were much in  evidence, as were detailed depictions of industries in colonized countries. Mariann confessed herself to be fascinated by the random, unplanned events that intrude into both non-fiction and fiction films of this early period-particularly those shot in the street. As usual with early films, passers-by frequently come to a standstill and gawk at the camera. As she pointed out, the frequent intrusion of dogs into the frame reflected the reality of the time, when numerous homeless animals inhabited cities. We all became very aware of these animals, which David dubbed “Lewinsky dogs.” At the right, a little one that half-enters the end of one shot of a typical chase film, Les tribulations d’un charcutier (director unknown; also on the DVD).
evidence, as were detailed depictions of industries in colonized countries. Mariann confessed herself to be fascinated by the random, unplanned events that intrude into both non-fiction and fiction films of this early period-particularly those shot in the street. As usual with early films, passers-by frequently come to a standstill and gawk at the camera. As she pointed out, the frequent intrusion of dogs into the frame reflected the reality of the time, when numerous homeless animals inhabited cities. We all became very aware of these animals, which David dubbed “Lewinsky dogs.” At the right, a little one that half-enters the end of one shot of a typical chase film, Les tribulations d’un charcutier (director unknown; also on the DVD).
Mariann watched a great number of 1909 films in order to make her selection. Her experience convinced her of what many of us feel, that this was a turning point for the development of film art, though perhaps not as dramatic a one as 1913. Apart from L’Assommoir, Griffith’s The Country Doctor could be pointed to as evidence that the year saw films of a greater complexity and beauty than had previously been released. Griffith may no longer be quite the lone giant of the pre-1920 era that film historians have portrayed. Still, there are touches in The Country Doctor that no other director could have conceived, such as the early shot of the central family strolling through a field of tall grass that hides everything except the doctor’s top hat floating above the stalks.
Reaching 1909 raises the question as to how long these 100-year anniversary programs can continue and what form they should take. With fiction films getting longer in years to come, particularly in Europe, there emerges a problem of including enough of them to give a sense of a single year without having the programs expand even more. Perhaps non-fiction films will figure as an increasing proportion of this thread-with more Lewinsky dogs inadvertently captured for posterity.
A garland of color films
Two programs of early color films demonstrated the various processes: hand-coloring with stencils, tinting, toning, and attempts at photographic color. The only really successful of the latter were two 1912 shorts using the Gaumont system, which provided images in sharp, reasonably true color.
I caught only a few of the features in the color thread. Victor Schertzinger’s Redskin (1929), in two-strip Technicolor, was a beautiful print. Despite its implausibly happy ending, this story was a sophisticated look not only at racial tensions between whites and Indians but also at equally divisive tensions among Indian tribes. Like the other occasional films of the early decades that show the action from the Indians’ standpoint (Griffith’s The Red Man’s View figured in the 1909 program) are remarkably sympathetic to their culture. The color portrays not only the beautiful desert landscapes of the American Southwest but also Navaho blankets and Pueblo sand paintings.
Toward the end of the week, when people asked me what my favorites had been so far, I forgot to mention Pandora and the Flying Dutchman, which had played way back on the opening Saturday. It has a reputation as a bizarre film, and I wasn’t expecting much beyond some glowing color images of two beautiful stars, Ava Gardner and James Mason. But I was pleasantly surprised by its well-handled fantasy tale of the Flying Dutchman visiting a contemporary Spanish seaside resort and finding his true love. In particular a lengthy flashback to the Dutchman’s original crime has a degree of stylization and intensity that allow it to avoid seeming absurd. The tale has an other-worldly quality that recalls some of Powell and Pressburger’s films-enhanced by the presence of cinematographer Jack Cardiff handling the Technicolor.
Unfortunately Track of the Cat (William A. Wellman, 1954) failed to similarly avoid a sense of the absurd in its overheated Tennessee William pastiche set on an isolated farm in the West. Lumbering dialogue lays out explicitly all the tensions among the members of the central family, exacerbated by the depredations of an elusive puma and a visit by the younger brother’s potential fiancée. The reason for its presence in the festival, though, was its color scheme. Wellman set out to make a “black and white film in color,” as the program describes it. Both the snowy landscapes and the interiors are dominated by white, black, and flesh tones, with the sole exception-the Robert Mitchum character’s bright red coat-disappearing from the action partway through.
Not only silents need restoring
Martin Scorsese’s influence hovers over the festival and the Cineteca Bologna. One of the two screening rooms in the Cineteca’s building is the Scorsese (the other being the Mastroianni). In recent years, films from the institution that Scorsese founded, the World Film Foundation, have been screened here. The WFF is dedicated to restoring and preserving films from countries whose archives might lack the resources to handle such major projects. This year’s presentations were Fred Zinnemann and Emilio Gómez Muriel’s Redes (The Wave, 1936), Shadi Abdel Salam’s Al Momia (known in English as The Night of Counting the Years, 1969), and Edward Yang’s A Brighter Summer Day (1991). The foundation also aided in the editing of Ingmar Bergman’s home movies into Images from the Playground (Stig Borkman, 2009).
I had seen The Night of Counting the Years in one of the faded 16mm copies that have long been the only form in which this Egyptian classic was available. The new copy is a vast improvement, finally revealing why this is considered perhaps the great Egyptian film. It is based around a true story from 1881, when a powerful tribe on the west bank at Luxor discovered a cave containing a huge cache of royal mummies and funerary goods that had been hidden away by ancient priests to preserve them after the extensive robbing of their original tombs. The tribe started selling items gradually on the illicit antiquities market, but one of its members revealed the location of the cache to the authorities, allowing them to salvage most of the mummies and their grave goods. The film was beautifully shot on location in the desert and temples of the west bank and provides a meditation on why the young man might have acted against the apparent best interests of himself and his family.
A 1991 Edward Yang film might not seem an obvious candidate for restoration, yet the complete version of A Brighter Summer Day was barely rescued from oblivion. The original negative does not exist, and the print materials on the shorter version were discovered to be moldy. Rescuing these and combining footage from both versions has resulted in a pristine new print of Yang’s greatest achievement. An in-depth look at Taiwanese society a decade after Chiang Kai-chek took over the island, it follows a middle-class boy drawn gradually into gang violence. The new version, which premiered at Cannes earlier this year, looked great on the big screen in the Arlecchino.
This and that
A brief tribute to Harry d’Abbadie d’Arrast included Laughter, the director’s first sound film. A romantic comedy, it stars Frederick March as a witty young composer aspiring to marry a wealthy society woman against her father’s wishes. The film has touches of Holiday and Design for Living, both films yet to be made. Laughter confirms d’Abbadie Arrast’s reputation as a good but lesser filmmaker in the Lubitsch mold.
 We all have reason to celebrate the fact that Georges Méliès’ films went into the European public domain this year. (The films have long been in the public domain in the U.S.) With obstacles to programming out of the way, the festival presented a program in homage, featuring twenty shorts presented by Serge Bromberg, who helped put together the extensive Méliès collection that came out in the U.S. and won the 2008 award for best DVD set here at the Cinema Ritrovato. (It came out in France earlier this year.) While all the films shown are on the DVDs, it was a treat to see them on the big screen. Bromberg provided a lively, if not entirely authentic, running commentary to “explain” the action of the final film, La Fée Carabosse.
We all have reason to celebrate the fact that Georges Méliès’ films went into the European public domain this year. (The films have long been in the public domain in the U.S.) With obstacles to programming out of the way, the festival presented a program in homage, featuring twenty shorts presented by Serge Bromberg, who helped put together the extensive Méliès collection that came out in the U.S. and won the 2008 award for best DVD set here at the Cinema Ritrovato. (It came out in France earlier this year.) While all the films shown are on the DVDs, it was a treat to see them on the big screen. Bromberg provided a lively, if not entirely authentic, running commentary to “explain” the action of the final film, La Fée Carabosse.
Demonstrating that history repeats itself, Belgian film scholar Eric De Kuyper programmed a selection of titles dealing with financial speculation and crisis. These included perhaps the best of several items from Louis Feuillade shown during the week, Le Trust ou les batailles de l’argent (1911). It stars René Navarre, who would soon play Fantômas, as an unscrupulous detective, and the action is more in the thriller mode than a serious depiction of French finances. Also included was a 1916 German feature, Die Börsenkönigin (“The Queen of the Stock Exchange”), with a fine performance by Asta Nielsen as a woman more successful in finance than in love.
More to come from David, on Capra, DVD awards, and personalities glimpsed by a roving camera.
For our previous Cinema Ritrovato entries, see here for 2008 and here, here, and here for 2007. For a thorough discussion of dogs in early film, with comments by Mariann Lewinsky, see Luke McKernan‘s authoritative entry here. On the occasion of Edward Yang’s death in 2007, David offered an homage to him and A Brighter Summer Day here.