Archive for the 'Directors: Forsyth' Category
Watch those hands; or, Burt, Jean-Luc, and Bill come to Cinephile Summer Camp
Nouvelle Vague (1990).
DB here:
At this year’s Summer Film College in Antwerp, Peter Bosma pointed out that the event seems to be a unique mixture.
Films are screened from morn to midnight: this time, 38 films across 6 days and two half-days. But it’s not exactly a film festival, as there are no new releases.
 So is it like Bologna’s Cinema Ritrovato? Not exactly. While the shows included some restored titles (notably the Belgian Cinematek’s pretty makeover of Pollyanna, 1920), the films were mostly original prints with an occasional DCP.
So is it like Bologna’s Cinema Ritrovato? Not exactly. While the shows included some restored titles (notably the Belgian Cinematek’s pretty makeover of Pollyanna, 1920), the films were mostly original prints with an occasional DCP.
Moreover, the films cluster around two or three major themes. This year we had Late Godard (fourteen titles, counting episodes of Histoire(s) du cinema) and the career of Burt Lancaster (eleven). In addition, there were nightly showcases called “Masterworks in Context,” which included one surprise film, title undisclosed. But unike most movie marathons, the Summer Film College introduces screenings with lectures and discussions. This year there were fourteen sessions, each running about ninety minutes. These are serious, intensely informative talks—very far from the usual brief introductions one gets at festivals or in art house warm-ups.
So is it an educational enterprise? Definitely, but without assignments, tests, or grades. It’s designed to serve Flemish-speaking professors and students, but also civilians who are just interested in a weeklong package of film and film talk. The event helps forge a community of film appreciation.
Finally, there’s often a guest filmmaker on hand, usually related to the main threads. This time it was Bill Forsyth, who directed Burt in Local Hero. That film was screened, along with Bill’s wonderful Housekeeping.
So what would you call the College? I once called it Cinephile Summer Camp, and that still seems accurate in evoking the sense of fun and camaraderie that pervade the place. We don’t all get mosquito bites, but after a week you come to enjoy seeing familiar faces and talking with them about what they’re seeing. Just as when you go to summer camp, you get to stay up late. But at no summer camp I ever attended did we drink so much beer.
JLG/SJ/DB
The principal speakers were Tom Paulus and Anke Brouwers, who covered Burt, and Steven Jacobs on Late Godard. The Masterworks in Context shows were introduced by several guest speakers, including Lisa Colpaert (excellent on I Walked with a Zombie) and Vito Adriaensens (covering both Murder! and Vampyr). For Pollyanna, Bruno Mestdagh of the Cinematek staff explained the process of restoration. I played utility infielder, offering one talk on Burt and three on JLG.
How often do you get to see 35mm prints of Une femme mariée, Passion, Je vous salue Marie, Détective, JLG/JLG, Eloge de l’amour, and Nouvelle Vague? The Godard series, which ended with a 3D show of Adieu au langage, was a high point of my summer viewing. Back home I had prepared by rewatching all Godard’s features from Sauve qui peut (la vie) onward, but my video homework didn’t prepare me for the way the big screen amps up their prickly, seductive power.
I don’t speak or read Dutch, so I missed many subtleties in Steven Jacobs’ talks, but thanks to Power Point I could figure out the main points. Few lecturers can pack so much information and ideas into ninety minutes.
We had no way of knowing how familiar the audience was with Godard, early or middle or late, so Steven started with an orienting talk on JLG’s pre-1980 work (above). He swiftly reviewed key aspects of Godard’s New Wave period, traced his shift toward “a critical cinema” between 1967-1969, and explored the move into his Marxist phase. Along the way, he stressed the way cultural developments like auteur theory, Pop Art, Maoism, Brechtian theatre, and semiotics shaped Godard’s films. Particularly acute was his discussion of the “one image after another” sequence in Ici et ailleurs (1975). In all, the talk was an ideal prelude to Une femme mariée, which pointed up so many motifs of the later work: the focus on the couple, the emphasis on media-based images, and the persisting shadow of the Holocaust.
Steven is an art historian at University of Ghent; he earlier appeared on this blog as co-author of the imaginative book The Dark Galleries. After tracing Godard’s return to mainstream cinema and his move to Rolle, Switzerland, Steven focused on that splendid example of JLG the painter, Passion. Steven has written eloquently on the film in his Framing Pictures, and here he widened his focus to discuss its relation to other films centered on the tableau vivant, like Pasolini’s La Ricotta and Ruiz’s Hypothesis of the Stolen Painting.
You’d expect that Steven would have a field day with Histoire(s) du cinema, and he did. Unlike most Godardophiles, I’m not wild about this series of video essays. I can’t take them as serious studies in film history, and too often I sense he’s just playing around. (Enough with the stroboscopic flashes, okay?) But Steven obliged me to rethink them by showing how they fit into the Postmodern art scene, especially the video art movement after the 1970s. He pointed out the central importance of the Hitchcock episode and the series’ constant concern with the Holocaust, often in dialogue with Shoah. Citing Godard’s claim that video taught him to see cinema in a new way, Steven suggests that the format also created a tenor of paradoxical melancholy. It’s as if JLG’s experiments with this new technology drove him to celebrate the death of the cinema he knew.
My three talks on Late Godard tried to ask something that I didn’t find many traces of in the literature. What are these films doing with (or against) narrative? I think that the focus on JLG as “film essayist” has sometimes obscured the fact that he has long insisted that he needs stories. Yet he seems to have no interest in the craft of storytelling as we understand it. He avoids dense exposition, careful foreshadowing, well-timed revelations, and cumulative climaxes. He tends to spoil the narrative expectations he sets up.
As a result, his plots—for his films have them—are distressingly opaque. Exactly what happens in a Late JLG film is often difficult to determine. I’m always surprised when discussions of these late films provide capsule plot summaries, for the very difficulty of arriving at these should claim our attention. As just one instance, many critics seeing Adieu au langage for the first time thought the film centered on one couple. It centers on two. But the fact of that mistake ought to interest us enormously: What in the film’s presentation made it difficult to follow the basic situation? Are there strategies Godard follows in creating his apparently willful obscurity?
Godard’s unique strategies of storytelling are carried down into felicities of visual and verbal style. Again, I think that critics haven’t sufficiently acknowledged just how strange and opaque the surfaces of these movies are. For one thing, characters are unidentifiable from scene to scene, thanks to camera setups that cut off their faces, wrap them in shadow, or leave them offscreen altogether.
I’ve touched on these matters earlier (here and here), but just as a quick example, consider this shot from the opening of Nouvelle Vague. It has to be one of the most oblique introductions to a protagonist we can find in cinema.
Corporate owner Elena Torlato Favrini strides out of her mansion past her chauffeur while taking a transatlantic call. Any other director would favor us with a close view of her, perhaps tracking as she cuts a swath through her entourage. Instead we get a shot framing her chauffeur climbing out of their Mercedes.
As he crosses in front of the car, we hear her on her cellphone. She can be glimpsed fleetingly in the background, through the car window.
She approaches us, becoming briefly visible as she passes the car, but when she stops, she’s decapitated. We don’t get anything like a good look at her, and the locked-down camera refuses to reframe her. Instead, the framing emphasizes her slipping on her gloves.
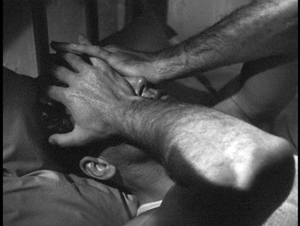
The gesture ties into other imagery in the film. A little before this shot, there’s an isolated shot that establishes hands as a major motif in the film. But we should also notice that this fairly abstract shot also presents the gesture of Elena slipping on a glove. Or rather, it almost presents it, as the shot is abruptly chopped off just as the gesture begins.
So slipping on the glove, started in an earlier shot, is finished at the Mercedes. But just as important, the visual idea of a hand gesture broken by a cut resurfaces at the climax. When Richard Lennox helps Elena out of the water, the action is also incomplete. Only five frames show him grabbing her arm before a cut interrupts the action.
Another filmmaker would have held the image on that triumphant grip, but Godard denies us this little burst of satisfaction. Of the five frames in this bit of the shot, there is just one frame showing Richard’s hand seizing her. Godard again spoils a solid narrative effect. But he does narrative in his own way, with the broken-off gestures counterpointed by the hands that do meet at other points in the film.
Every scene in Nouvelle Vague, and most scenes in Late JLG, seem to me to be built on one or more fine-grained pictorial and auditory ideas like these. Those ideas can seem perverse, as in the chauffeur scene: why let us see his face but play down Elena’s? He’s not a major character; we don’t even learn his name until the film’s final moments. Unhappily, this peculiar instant of comparison is lessened in the 1.66 version of the film available on DVD. That image suppresses the driver’s face no less than Elena’s, losing Godard’s peculiar version of “gradation of emphasis.”
All the more reason to try to see these films in their full-frame glory, as I’ve argued before.
BL (Beautiful Loser)/AB/TP
Criss Cross (1949).
With big tousled hair, unadulterated sinew, and teeth gleaming like a Pontiac grille, Burt Lancaster came to fame in the late 1940s. He belonged to a new cohort of actors quite different from the 1930s Debonairs (William Powell, Melvyn Douglas, Cary Grant) and the Bashful Boys (Cooper, Fonda, Stewart). Yet the new lads were also at variance with the rugged Ordinary Joes (Cagney, Bogart, Tracy, Gable).
 For one thing, Lancaster, Victor Mature, Robert Ryan, Robert Mitchum, Kirk Douglas, and Charlton Heston were brawny—monsters, in a way. They often took off their shirts. One publicity still for River of No Return shows Mitchum more unclothed than Monroe. Three of them played prizefighters, and Mitchum, himself a boxer, had the broken nose of a brawler.
For one thing, Lancaster, Victor Mature, Robert Ryan, Robert Mitchum, Kirk Douglas, and Charlton Heston were brawny—monsters, in a way. They often took off their shirts. One publicity still for River of No Return shows Mitchum more unclothed than Monroe. Three of them played prizefighters, and Mitchum, himself a boxer, had the broken nose of a brawler.
Of the group, Burt had probably the strongest A-list career overall. He fostered a great variety of projects. Who else of his generation appeared in films by Visconti and Malle? What other unflinching liberal was prepared to play a US general bent on a coup (Seven Days in May) or a conspirator behind the Kennedy assassination (Executive Action) or an obstinate officer fighting in Vietnam (Go Tell the Spartans)? He portrayed a renegade officer demanding the revelation of the brutal policy behind the Vietnam War (Twilight’s Last Gleaming). His closest rival and frequent costar Kirk Douglas didn’t enjoy such a vigorous and prestigious twilight. Only Brando kept beating him to the prize: Burt wanted to play the lead in Streetcar Named Desire and The Godfather. Unpredictably, he wanted as well to play the gay prisoner in Kiss of the Spider Woman.
I had had only slight interest in Burt as a star before this edition of the Summer School. But listening to the talks, seeing the films, and preparing my contribution made me realize how extraordinary an actor he was, and how important in Hollywood postwar history. Burt was well-served by the fine lectures offered by Tom Paulus and Anke Brouwers.
Anke provided an in-depth survey of how Burt and the Brawny Gang brought to a new level the culture of male athleticism—on display in Fairbanks and Valentino, developed further in the body-building craze of the 1930s, and culminating in what one 1954 magazine article called Hollywood’s “Age of the Chest.” She brought in forgotten pin-up boys like Guy Madison and pointed out how Burt and his peers paved the way for Rock Hudson and Tony Curtis. Anke went on to specify Burt’s beefcake persona, established in The Flame and the Arrow (1950) and locked into place in The Crimson Pirate (1952), which we saw. In her followup talk next day, she surveyed Burt’s place in the industry. He was one of the few stars to supervise a successful independent production company, Hecht Hill Lancaster (earlier, Norma Productions and Hecht Lancaster).
Tom moved on to consider Burt’s star charisma. He traced how Burt adjusted his authoritative image to different roles—the con man, the confident leader, the embittered idealist. Tom was especially good at analyzing Burt’s acting technique, tying it to particular trends in theatre and film of the time and pointing up the physicality of his performance of specific, precise tasks. Given the standard situation of rigging a bomb, he contrasted Burt’s meticulous finger work in The Train (1964) with that of Kirk going through the motions in The Heroes of Telemark. Tom even spared some time for Burt’s diction—a quality that really popped out when we watched Elmer Gantry (1960).
In a later lecture, Tom surveyed “Late Burt,” and his relation to political cinema of the 1960s and 1970s. He followed that with a revealing account of Burt’s relation to the trend of “Mexican Westerns” launched in the 1950s. Another arc in Burt’s career: from Vera Cruz (1954) to Ulzana’s Raid (1972), with The Professionals (1966) in between. That we saw in another gorgeous print.
I could go on a lot more about Tom and Anke’s lectures, but I don’t want to give away too much. The talks contained so much original research and discerning analysis of both the films and trends within film history that I’m hoping Tom and Anke will lay these ideas out at book length. Part “star study,” part film criticism, part industry history, their lectures were exhilarating.
My own contribution was minimal, a talk on First-Phase Burt. The Brawny guys were well-suited to the trend toward hard-boiled movies, those crime pictures we later decided to call “noirs.” Those weren’t usually suitable for older players (though there were some makeovers, such as Dick Powell and Fred MacMurray). To fill these roles came Alan Ladd, Glenn Ford, Dana Andrews, and Richard Widmark, along with the beefcakes. At the same time, “independent” producers within the studios began contracting their own new talent and loaning it out. Burt was signed by Hal Wallis at Paramount, who also had Kirk Douglas, Wendell Corey, and Lizabeth Scott in his stable. Films like Desert Fury (1947) and Sorry, Wrong Number (1948) were Wallis package projects.
Hired straight from the stage with no film experience, Burt debuted as the Swede in The Killers (1946), on loanout to Mark Hellinger at Universal International. Burt benefited from a galvanizing entrance. Lying on a bed in the dark, refusing to flee the hitmen on his trail, Burt is a shadowed, curiously languid torso in a tight undershirt.
Only after a beat do we see something else: massive hands rubbing a weary head. Soon that head is revealed.
As the killers burst in, the whole image comes together.
Has a Hollywood beginner ever been given such a gift as this opening?
With this onscreen wattage, it’s all the more striking that this young discovery is curiously absent from his early films. He’s onscreen for only a third of The Killers’ running time, and not even half of Brute Force (1947) and Sorry, Wrong Number. The film Wallis wanted to be his debut, Desert Fury (1947), gives him only twenty-three minutes out of ninety, and in the second male lead at that. All My Sons (1948) puts him in an ensemble drama. I Walk Alone (1948), the Norma production Kiss the Blood Off My Hands (1948), and another Universal project, Criss Cross (1949) start to make him a proper, central protagonist. By then, he is ready to become the star attraction of the swashbuckling films.
Moreover, in his early phase, he mostly plays losers. Not the brightest guy in the room, he’s easily suckered by a femme fatale in The Killers and Criss Cross. He makes amateurish mistakes at crime (Sorry, Wrong Number) and, coming out of prison, he is the last to realize the rackets have gone corporate (I Walk Alone). At the start of Kiss the Blood he punches a man too hard and kills him. He’s caught and whipped and imprisoned, and when he comes out he stumbles back into crime again. He’s shrewd enough to set up a prison break in Brute Force, but so doggedly determined is he to reunite with his girl on the outside that he launches a suicidal bloodbath.
When he finally catches on to his fate, we get expressions ranging from stupefaction to anguish (The Killers, Criss Cross).
He even cries (All My Sons, Kiss the Blood).
Loser or winner, when he is onscreen, he has the outlandish physical presence of the born star. Most obvious is a physique (Kiss the Blood, Brute Force).
Even his back, featured with a prominence we get with few other actors, is straining against a drenched prison uniform (Brute Force) or a tailored suit (Criss Cross).
The face was a cameraman’s dream; it could be craggy or somber, thoughtful or tormented (The Killers, Brute Force x2, Criss Cross).
He can be stiff-armed and zombielike coming out of prison in Kiss the Blood, but he can also gamely cock his elbows, ready to spring, like Cagney and Cary Grant (I Walk Alone).
The enormous hands, which look likely to crush a skull (Criss Cross) or rip apart a phone cord (Sorry, Wrong Number), could be surprisingly delicate, tentatively touching his girlfriend’s wheelchair or laying down plans like playing cards (Brute Force).
In The Killers he makes skillful use of those hands, pocketing his busted one or spreading out the scarf given him by the treacherous Kitty.
Easily taken in by Kitty’s plan, he seems to have a qualm when his gripping embrace relaxes and the fingers splay in hesitation.
This sort of handwork would become crucial, as Tom pointed out, to Burt’s performance style, particularly in The Birdman of Alcatraz.
“I’d never looked in eyes as chilling as Lancaster’s,” Norman Mailer once said. You can see what he meant.
Again, though, the actor is in control. Some years back I wrote that eyes by themselves aren’t very expressive: the eyelids, eyebrows, and mouth tell us more. I still think that’s right, but Burt manages to convey the sense of the beast at bay with remarkable control of just the eyeballs. He seems to be looking for an escape hatch without moving his head an inch.
While Burt was playing losers, his counterpart Kirk Douglas was often playing heels—cynical manipulators who stomp on everybody else, as in I Walk Alone. Sometimes Kirk learns his errors (Young Man with a Horn, 1950) but several roles of the period, in Out of the Past, Champion, and Ace in the Hole, make him a glib villain or tawdry antihero. Somewhat later Burt explored this characterization too, notably in Vera Cruz, Elmer Gantry, and The Rainmaker (1956). How did he shift from the beautiful loser to the fast-talking con artist?
I think there are hints from the start. In The Killers, after he’s washed up as a fighter, the Swede goes in for street crime. When he confronts his old friend the cop, Lancaster brings those arms and hands into play. In his enormous unstructured topcoat, he lifts his fists up to his waist. It’s both the businessman’s getting-down-to-brass-tacks sweep, but also a kind of puffing up, exposing that massive frontal expanse. Little Sam Levene can grasp his lapels, but he doesn’t stand a chance against this.
Burt uses the same imperious gesture when, in Sorry, Wrong Number, he’s trying to bully a company employee into joining a crooked deal.
In these noir movies, his intimidation of others won’t put him ahead of the game. But perhaps these arm movements begin to sketch a more flamboyant loser like Gantry. By striking what actors used to call an “attitude,” Burt could start to build an entire character: a hell-for-leather charlatan.
Seeing the films, listening to Tom and Anke, and studying Lancaster’s work on my own brought home to me again the importance of the details of performance and the presence of a star. These movies would be utterly different if Mitchum or William Holden played the Burt parts. Our actors don’t wear masks or Hazmat suits. We’re powerfully affected by what they bring to the character in voice, body, face, and gesture—the expressive dimensions of cinematic presence.
BL/JLG/BF
College coordinators Lisa Colpaert and Bart Versteirt, flanking Bill Forsyth.
What do Burt and JLG have in common? For one thing, some images from Criss Cross in Histoire(s) du cinema 1a (see above). For another, Bill Forsyth.
With the success of Gregory’s Girl (1981), Bill was invited by David Puttnam, then at Columbia, to make a Scottish movie with a couple of American actors. The result, Bill says, now looks to be a “soft-core environmental movie.” Local Hero (1983) remains much loved, and for good reason. It makes nearly all of today’s multiplex raunch look adolescent. It has a tone of civility, an embrace of eccentricity, and a genuine interest in people reminiscent of Ealing comedies. For me it’s a masterpiece of sweet, light-hearted art.
Local Hero feels loose and leisurely, but it’s actually a very economical movie. The first few minutes should be studied by screenwriters interested in tight exposition and fast attachment to a protagonist. It’s peppered with sidelights on its central drama, such as the Russian’s song about how “even the Lone Star State gets lonesome.” That neatly sums up the situation of the yuppie sad sack MacIntyre (“I’m more of a Telex man”) learning about village life. As usual, I was moved by Mark Knopfler’s plangent score, the electronic overtones meshing with the pulsations of the Northern Lights.
Burt’s role is that of CEO deus ex machina. Having assigned Mac to buy a Scottish seacoast town for an oil refinery, Mr. Happer eventually descends in his chopper and decides to establish a laboratory there instead. Burt’s crisp delivery and tight fingerwork are still on display at age seventy. The other actors don’t use their hands as much as he does–partly so they’re not distracting us from him, I suspect, but also because newer-style Hollywood acting doesn’t encourage it. In any case, as usual Burt uses his acrobat’s sense of physicality to intensify his performance. Even clasping his hands behind his back tells about the character’s authoritative dignity.
Bill learned that Burt regretted not doing more comedy, so he wrote the mogul’s part with him in mind. Burt signed on eagerly. He showed up on the set with a full beard, hoping Bill would let him keep it; they compromised on a mustache.
Bill had worked mainly with teenage actors on That Sinking Feeling (1979) and Gregory’s Girl, so Burt was really the first adult performer he ever directed. Across their three weeks together, Burt demanded nothing, except that he wanted to loop his dialogue. Bill preferred not to loop, and as it turned out only one scene needed to be rerecorded.
Burt and Bill skipped lunch in order to prepare the next scene, becoming “lunch bums.” Bill remembers Burt hanging out with the other actors and chatting with extras. He freely made fun of Bill’s accent: “”He speaks no known language.” He told Bill: “I don’t know what you’re saying, but I know what you mean.”
Bill talked as well about his own career. Starting out in the days before home video, he learned dialogue and pacing by audio taping classic films. (Sounds like a good idea to me.) He became a performer’s director. “The only thing I’ve ever said to a cameraman is: ‘Accommodate the actors.” He quoted Burt approvingly: “The space in front of the camera is the actor’s space.”
What’s the connection to JLG? It turns out that Godard was the director Bill most admired in his salad days. During the 60s he sated himself on art cinema, especially New Wave imports. When he saw Pierrot le fou, he left the theatre stunned. Godard became “the master. He still is, for me.”
Accordingly, Bill’s earliest cinema efforts were in an avant-garde vein. One piece, puckishly called Film Language, started with ten minutes of black leader while a text by Beckett was read out. Another, Waterloo, included a vast ten-minute shot in which the camera left one household, climbed into a car, rode a great distance, and ended up in another home. The film played at the Edinburgh film festival to an audience of 200. By the end three viewers were left. “I’d moved my first audience.”
Bill remarked that he sometimes regrets not sticking with experimental media. Today, he says, he might be a video-installation artist. A teasing idea. But we should be grateful that we got his features. I don’t know if Jean-Luc would agree, but I bet Burt would.
Thanks to Bart Versteirt, Lisa Colpaert, and their colleagues for a great week. Thanks as well to the participants, whose willingness to take on anything we threw at them was very encouraging. And a farewell to two friends who have projected films at every Summer Film College I’ve attended over the last sixteen years: Esther Dijkstra and Joost De Keijser. They have helped make the event the splendid enterprise it is.
Peter Bosma’s informative book Film Programming: Curating for Cinemas, Festivals, Archives is available here.
A detailed “index of references” for Histoire(s) du cinema is provided by Céline Scemama.
Our first encounter with Bill Forsyth was at Ebertfest. For more on actors’ handiwork, try this entry.
An eager crowd of campers awaits Adieu au langage.
The show goes on
DB here:
Kristin and I had hoped to blog directly from this year’s edition of Ebertfest (formerly Roger Ebert’s Festival of Overlooked and Forgotten Films), but our blogging software failed us. We could post text but no pictures, and where’s the fun in that? Fortunately, the event was widely covered. The schedule, with very full film notes, is here. You can get a sense of what was happening by checking Jim Emerson at scanners and Peter Sobczynski at Hollywood Bitchslap and Kim Voynar at Cinematical and Lisa Rosman at A Broad View and P. L Kerpius at Scarlett Cinema and Andrew Wells at A Penny in the Well and many others. There is some coverage at the News Gazette, although the most informative stories from the paper aren’t on the net. Then there’s Roger’s own blog, Ebertfest in Exile, which in one entry goes off on an unexpected trajectory….toward Joe vs. the Volcano.
Now that we can again illustrate our entry, we offer you an ex post facto blog, like last year’s, which makes up in bulk for its tardiness. I hope to follow soon with a picture gallery.
This year’s Ebertfest lacked an essential ingredient: Roger Ebert. But Chaz Ebert took over hosting duties superbly, aided by the terrific organizational skills of Nate Kohn and Mary Susan Britt. At every screening, one person or another paid tribute to Roger’s gifts to film culture—his writing, of course, but also his tireless championing of deserving movies that should be brought to wider audiences.
The format of Ebertfest offers something for everyone. Traditionally, the opening night is an older film screened in classic 70mm, a format that’s almost vanished. Past years have included shows of Lawrence of Arabia, Play Time, and My Fair Lady. 70mm looks gorgeous on the vast screen of the Virginia Theatre. This year the film was Kenneth Branagh’s Hamlet, at four hours the most complete version of the play ever put on film. It looked grand.
 Another slot is reserved for a silent movie, often accompanied by the Alloy Orchestra. (Part of their armory, including bells, springs, and a thunderstrip, can be found on the left.) Having programmed The Black Pirate, The General, and The Eagle in earlier years, Roger picked von Sternberg’s sumptuous Underworld (1927), which Kristin introduced and led a discussion about. The Alloy boys’ scores are getting more nuanced by the year, and this one did as much justice to von Sternberg’s quiet passages as to the gunplay.
Another slot is reserved for a silent movie, often accompanied by the Alloy Orchestra. (Part of their armory, including bells, springs, and a thunderstrip, can be found on the left.) Having programmed The Black Pirate, The General, and The Eagle in earlier years, Roger picked von Sternberg’s sumptuous Underworld (1927), which Kristin introduced and led a discussion about. The Alloy boys’ scores are getting more nuanced by the year, and this one did as much justice to von Sternberg’s quiet passages as to the gunplay.
Yet another Ebertfest mainstay is a children’s show on Saturday morning, and last year’s wonderful Holes was followed by an unexpected pick—Ang Lee’s Hulk, with the director in attendance. The place was packed, Lee was his charming self, a trio serenaded him, and the audience left well-pleased.
Prime spots are reserved for less-known films, with an emphasis on independent and personal cinema. We saw Tom DiCillo’s Delirious, Sally Potter’s Yes, Joe Greco’s Canvas, and Jeff Nichols’ Shotgun Stories. A highlight for me was Eran Kolirin’s The Band’s Visit, which I’d missed elsewhere. This unassuming, warm, funny movie recalled Tati and 1960s Czech films like Intimate Lighting. Then there was The Cell by Tarsim Singh at a late-night screening, with John Turturro’s Romance and Cigarettes to wrap things up on Sunday. For kaleidoscopic commentary on all these, see the above-mentioned weblogs.
Princely contradictions
I hadn’t seen Hamlet in 70mm in its initial 1996-1997 run, and at first the idea of taking this fairly intimate piece to a wide-film format seemed counterintuitive. But on the Virginia screen the film lost none of the play’s intensity and it gained a welcome monumentality. The central set, the Danish throne room as a gigantic hall of mirrors flanked by a warren of corridors and fissured by secret passageways, is made for the wide image.
Scale of time also matters. By playing the full version, Branagh can give full weight to the father/ son parallels that riddle the play. If Olivier’s Hamlet was about a son’s love for his mother, Branagh makes the play about the strife between fathers and sons, with women caught in the middle. Hamlet Sr./ Hamlet Jr., Claudius/ Hamlet, Jr., Polonius/ Laertes, old Norway/ Fortinbras, and even the Player’s speech about the murder of Priam: the parallels are in Shakespeare’s text but played out at proper length they snap into sharp relief. Once Laertes is off to Paris, Polonius makes sure he’s spied on, just as Claudius orders Rosenkrantz and Guildenstern to watch Hamlet. In his turn, Hamlet assigns Horatio surveillance duty during the play-within-a-play (a piece of action nicely caught in the opera glasses that Branagh’s choice of period allows). Branagh’s decision to emphasize the military politics around Fortinbras’ march into Denmark helps justify the 70mm format and his decision to set the action in late nineteenth-century Europe; it also allows him to expand, through crosscutting set up early in the movie, the plot of another son at odds with his father.
Sex is important in this game. Branagh presents flashbacks to Hamlet and Ophelia in bed together, accentuating the prince’s later indifference and motivating her despair at his rejection. Not that the fathers don’t clock some mattress time too. Claudius the urbane politician becomes an infatuated newlywed, and Derek Jacobi gives to my mind a definitive performance. Even Polonius, usually treated as a pompous ass, smokes worldly little cigars and has a drab tucked into his bed, so that his advice to Laertes and Ophelia about proper conduct becomes not only patronizing but hypocritical.
 During the Q & A, Timothy Spall and Rufus Sewall emphasized something that Branagh explains on the DVD set: the need to create ensemble performances out of footage shot at different times. Sewall (a dark and scary Fortinbras) was filmed in a few days, before full-blown production, with his bits cut into the film at intervals. Robin Williams, as Osric, was also filmed out of continuity; there are scarcely any shots of him in the same frame as other players.
During the Q & A, Timothy Spall and Rufus Sewall emphasized something that Branagh explains on the DVD set: the need to create ensemble performances out of footage shot at different times. Sewall (a dark and scary Fortinbras) was filmed in a few days, before full-blown production, with his bits cut into the film at intervals. Robin Williams, as Osric, was also filmed out of continuity; there are scarcely any shots of him in the same frame as other players.
Spall, a temporizing Rosenkrantz, was present for much more of the filming and was eloquent in explaining how shooting in long, wheeling takes demanded great precision from the actors—hitting marks, using body language, and timing speeches carefully.
Branagh put the bulky 70mm camera on a dolly, then reinforced the studio floors so that no tracks or boards were necessary; the camera could glide anywhere. “Walk and talk” technique, which I’ve blogged about before, comes home to roost in a Shakespeare film; Branagh wanted continuous shots so that the audiences could follow the flow of the speeches, and it works very well.
In fact, Branagh’s editing varies in a patterned way across the play. Acts I and III are briskly cut, averaging about 5 seconds per shot. Acts II and IV rely on much longer takes, typified by the tracking-shot arabesques, and they average 10-11 seconds per shot. And Act V? Here, as you might expect, Branagh pushes the pace to suit the converging plotlines and the burst of poisonings at the climax: the average shot runs about 3 seconds. This seesawing rhythm helps sustain viewer interest across four hours, and it shows an unusually geometrical approach to a movie’s overall architecture.
In his program review, Roger points out that the play remains deeply mysterious, even in a production as lucid and buoyant as Branagh’s. Hamlet is of course one of the most fascinatingly inconsistent characters in literature. I’ve read the play probably a dozen times and seen many film versions of it, and I’m inclined to think that in Hamlet Shakespeare is experimenting with how indeterminate a character can be and still be intelligible to us. It’s not that he’s indecisive; we have to decide what he truly is, and Shakespeare makes our task very hard.
All the other characters in the play are complicated but consistent. Only Hamlet seems to reinvent himself at every entrance. He tells us that he will put on an “antic disposition,” but before he’s gotten very far with his fake madness, he tells Rosenkrantz and Guildenstern of his strategy, knowing that they are likely to report it to Claudius. This has the effect of letting Hamlet behave any way he wants, sincere or duplicitous, calculating or mad. When he’s around others, he’s always “on,” and this makes his true nature and purposes difficult to divine.
 I liked Branagh’s idea of having Hamlet consulting a book on demonology, for in a revenge tragedy the protagonist has to be sure that the aggrieved spirit urging revenge isn’t a demon in disguise. More generally, the Victorian milieu lets Branagh give us a truly bookish Hamlet, one who retreats to his stuffed library when overcome by the strife unfolding in the vast throne room. At the same time, that library contains players’ masks and a curious miniature theatre that Hamlet toys with thoughtfully. He lives among books, but also among images of pretense and deceit.
I liked Branagh’s idea of having Hamlet consulting a book on demonology, for in a revenge tragedy the protagonist has to be sure that the aggrieved spirit urging revenge isn’t a demon in disguise. More generally, the Victorian milieu lets Branagh give us a truly bookish Hamlet, one who retreats to his stuffed library when overcome by the strife unfolding in the vast throne room. At the same time, that library contains players’ masks and a curious miniature theatre that Hamlet toys with thoughtfully. He lives among books, but also among images of pretense and deceit.
The questions tease you right to the end. Hamlet finds Laertes’ plunge into Ophelia’s grave overdramatic, but he goes on to declare that he himself loved her with the strength of forty brothers. Before the climactic duel, Hamlet apologizes to Laertes (“I have shot my arrow o’er the house/ And hurt my brother”), but it seems almost bad faith, given all the misery he has helped cause. Is this a morally obtuse sincerity, or another masquerade? It’s this Hamlet, reliably unpredictable, that Branagh’s manic-depressive performance brings home so forcefully.
The unwitting wisdom of the suits
It’s common to say now that the 1970s was the last great era in American cinema, followed by the degradations of the blockbuster 80s, but that remains little more than PR. Putting aside the “revolution” of the 1970s, which seems to me overrated, I’ll just offer the opinion that the 1980s brought us many worthy films, some of them quite daring. For example, one of the sweetest “little movies” of the era is Bill Forsyth’s Local Hero (1983).
It’s a comedy, at once dry and warm, about an oil executive sent to buy a small Scottish town and beachfront in preparation for the installation of a pumping rig and refinery. Forsyth’s script reverses the cliché. The townsfolk, far from clinging to their beloved tradition, are in fact anxious to sell and look forward to being rich. The young executive, Mac, doesn’t try to drive a hard bargain but settles into the rhythm of a life different from that he has known. His boss, a passionate amateur astronomer, surprises everyone with his final decision about the deal. You might call Local Hero one of the first films about the clash of global capitalism and community values, but though that’s accurate, the schematic formula doesn’t capture the understated humor and humanity of Forsyth’s treatment.
Forsyth is at Ebertfest for a screening of his no less brilliant Housekeeping; see Jim Emerson’s eloquent and poised review here. But I wanted to ask about Local Hero. The Scottish village is rendered with the affectionate good humor we find in Ealing comedies, and Forsyth mentioned that after he’d made the film he discovered an Alexander Mackendrick movie, The Maggie (1955), that prefigured his. For me, there were echoes of Jacques Tati in the long-shots and sound gags, and Forsyth confirmed that one of the formative films in his youth was M. Hulot’s Holiday, screened by an indulgent school head.
 Forsyth talked about certain choices he made. The Mark Knopfler score, bringing together Scottish tunes and a Texas twang, helped open out the film in a way that a more conventional lyrical score would not. Forsythe talked as well about the final shot, one of the most satisfying I’ve ever seen. The original cut ended with Mac returning to his Houston apartment and staring out at the dark urban landscape—beautiful in its own way, but very different from the majesty of the Scottish shore. There the original film ended, but the Warners executives, although liking the film, wanted a more upbeat ending. Couldn’t the hero go back to Scotland and find happiness, you know, like in Brigadoon? They even offered money for a reshoot to provide a happy wrapup. Forsyth didn’t want that, of course, but he had less than a day to find an ending.
Forsyth talked about certain choices he made. The Mark Knopfler score, bringing together Scottish tunes and a Texas twang, helped open out the film in a way that a more conventional lyrical score would not. Forsythe talked as well about the final shot, one of the most satisfying I’ve ever seen. The original cut ended with Mac returning to his Houston apartment and staring out at the dark urban landscape—beautiful in its own way, but very different from the majesty of the Scottish shore. There the original film ended, but the Warners executives, although liking the film, wanted a more upbeat ending. Couldn’t the hero go back to Scotland and find happiness, you know, like in Brigadoon? They even offered money for a reshoot to provide a happy wrapup. Forsyth didn’t want that, of course, but he had less than a day to find an ending.
The movie makes a running gag of the red phone booth through which Mac communicates with Houston. Forsyth remembered that he had a tail-end of a long shot of the town, with the booth standing out sharply. He had just enough footage for a fairly lengthy shot. So he decided to end the film with that image, and he simply added the sound of the phone ringing.
With this ending, the audience gets to be smart and hopeful. We realize that our displaced local hero is phoning the town he loves, and perhaps he will announce his return. This final grace note provides a lilt that the grim ending would not. Sometimes, you want to thank the suits—not for their bloody-mindedness, but for the occasions when their formulaic demands give the filmmaker a chance to rediscover fresh and felicitous possibilities in the material.
Salvation through self-punishment
Another outstanding film of the 1980s is Paul Schrader’s Mishima: A Life in Four Chapters (1985), which he brought to Ebertfest in a sparkling print. Schrader is one of two American film critics who became major directors (Peter Bogdanovich is the other), and there’s little doubt that he’s the most cerebral and theoretically inclined of that group known as the Movie Brats. Even if he hadn’t written milestone screenplays (Taxi Driver, Raging Bull) and made provocative films (Blue Collar, Hard Core, Affliction), he would be remembered for his critical writing. A trailblazing essay on Joseph H. Lewis, “Notes on Film Noir,” the essay on the yakuza film, and the book Transcendental Style in Film (1972) made Schrader a distinctive voice in American film culture. Fortunately you can now read his entire oeuvre online at paulschrader.org.
While the youthful Schrader expresses admiration for Bonnie and Clyde and The Wild Bunch, he’s no cheerleader for the New Hollywood. It’s bracing to watch him tear Easy Rider and Alice’s Restaurant limb from limb. The website displays each article in situ, on its original page of print. Since he wrote for many alternative weeklies, ads for bongs and day-glo paint lie alongside Schrader’s reflections on Bresson and Boetticher.
Although I also admire Patty Hearst, Mishima is my favorite Schrader-directed project. I think it’s one of the most artistically courageous films in American cinema. Putting the dialogue almost entirely in Japanese and focusing on a writer few Americans know, it compounds its difficulty with a daunting structure. On one axis, we get four chapters: Beauty, Art, Action, Harmony of Pen and Sword. On another axis, there are three interwoven strands: an account of the final day of Mishima’s life, when he seized control of a general’s office in order to address the garrison; a chronological biography, from his childhood to his adulthood; and stylized, efflorescent scenes taken from three Mishima novels. All these strands knot in the film’s final moments, when Mishima commits seppuku in the office and we see the culmination of the action shown in the novels’ tableaus. A “cross-hatched” structure, Schrader calls it.
The three strands are kept distinct through some technical markers: black and white for the biographical scenes, cinema-verite color for the 1970 attack on the garrison, and stylized color and setting for the extracts from the novels. Schrader explained that he had originally wanted to use video for the novel scenes, but his brilliant production designer Ishioka Eiko told him that the results might not be effective. Instead, she supplied designs of a dreamy radiance.
At the same time, both the biographical scenes and the tableaux take us through different eras of Japanese history, but in a way that sharpens comparisons among them. In the 1930s the boy Mishima glimpses a female impersonator at the kabuki theatre, but in his novel of the period, Runaway Horses, the young men formulate their plan to restore the emperor through an attack on corrupting capitalists. The sets for Kyoko’s House have, Eiko explained, ugly design because in the 1950s the Japanese were copying ugly American designs (though the results look pretty ravishing onscreen).
Schrader wanted to avoid the classic plot trajectory of a hero overcoming obstacles. He sought instead to present the way that a person’s life “becomes more and more fascinating, but you never really understand it.” The shuffling of chronology let him juxtapose different aspects of Mishima’s nature. The man wasn’t exactly contradictory, Schrader says, but rather “compartmentalized”: He could keep his aesthetics, his homosexuality, his militarism, and his childhood distinct, and the film aims to show these different facets of his career.
 Nevertheless, I’d argue, the film has a marked trajectory. “Perfection of the life or of the art?” Yeats asked. Schrader’s Mishima wants both, together. He seeks to fuse physicality (eroticism, violence, endurance of pain) with spirituality (given as the realm of art). The emblematic image is the poem written in a splash of blood. He finally realizes that for him this fusion can come only in death, because his life has come to embody, literally incarnate, his literary themes and techniques.
Nevertheless, I’d argue, the film has a marked trajectory. “Perfection of the life or of the art?” Yeats asked. Schrader’s Mishima wants both, together. He seeks to fuse physicality (eroticism, violence, endurance of pain) with spirituality (given as the realm of art). The emblematic image is the poem written in a splash of blood. He finally realizes that for him this fusion can come only in death, because his life has come to embody, literally incarnate, his literary themes and techniques.
Schrader’s film enacts the blending of art and life in its very imagery. At the climax, in the biographical strand Mishima climbs into a jet and the black-and-white imagery gains radiant color as he stares into the sun. The shift brings the biography up to 1970, and so provides a transition to the color footage of the writer’s last day, but it also recalls the opening credits, with the sun rising, and the closing shot of the cadet Isao about to slash himself.
Schrader regrets the transition showing Isao running to the beach, because the imagery shifts from Ishioka’s stylized world to something more realistic (albeit with glowing amber rocks). So for the upcoming Criterion DVD release he has fiddled with the final shots so that the sun and sky look far more abstract. Evidently he wants the world of art and the world of life to remain stubbornly apart—denying to his film what his protagonist yearned for.
You might object that the film’s formal intricacy and specialized themes make for a fairly chilly experience. It isn’t a wildly emotional movie, that’s true; it has some of that ceremonial, contemplative quality you get from a Philip Glass opera, which provides a theatre of pictorial attitudes rather than action. (For an example, see coverage of the current Met production of Glass’s Satyagraha.) No coincidence that Glass provided the score for the film, which he wrote without seeing any footage and which Schrader cut and shuffled to provide cues. Glass obligingly rescored the film to fit the musical collage Schrader wanted.
The film provides a visceral and a sensuous experience, but it doesn’t carry you off on waves of emotion. It will never be popular on a massive scale, because it makes almost no concessions to what people like in biopics. But if you can adjust yourself to a solemn celebration of blood and beauty, Mishima offers unparalleled rewards.
More from Schrader
“Inspiration is just another word for problem-solving.”
Schrader’s intellect never lets up. What other filmmaker could produce such a thoroughly informed academic case as he does in the 2006 “Canon Fodder” (available on his site)? One on one, I peppered him with questions and he answered with seriousness and subtlety. Two themes ran through his comments: his approach to direction and his view that cinema is dead.
On his directing: Until his last project, he embraced the “well-made film.” He shoots with a single camera, and plans his takes cut to cut. (That is, not a lot of coverage from many angles that will be winnowed out during editing.) He doesn’t storyboard because he wants to develop the staging organically on site. He visits the set, tries out blocking with the actors and DP, then decides on the spot about the breakdown into shots. For the Temple of the Golden Pavilion scenes of Mishima, like the one above, he and cinematographer John Bailey played “dueling viewfinders,” pacing around the actors to test points of view and then settling on tracking shots which incorporated the best angles.
But for his latest project, Adam Resurrected (2008), Schrader switched to a rougher style. Now, he says, he uses two cameras and he likes the bouncing and swaying frame yielded by the Bungee Cam. “I’m sick of the well-made film.”
On new media: Schrader’s stylistic turnabout comes from his conviction that cinema, “the dominant art form of the twentieth century,” is coming to an end. Today’s audience demands new forms of moving-image media. Thanks to television, young people have seen every conceivable story, so narrative is “exhausted” as an expressive resource. They expect their media products to be free, available on demand, and interactive. The result is a challenge to traditional media on every front: financial, cultural, and artistic.
Schrader looks to the Internet as not just an intriguing option but film’s destiny. So while he is planning a traditional “three-act” film, he also has written a screenplay for a 75-minute Net movie. In his essay, “Canon Fodder,” he predicted the end of traditional cinema but thought that he could keep going before the revolution. Now, he says, the sun is setting faster than he expected and if he wants to make more films he has to adjust.
I’m no prophet, but I don’t share his beliefs about the imminent collapse of traditional cinema. I also think that Web-based films, with viewers tempted to browse and graze and fast-forward, will limit aesthetic options. The computer monitor is not as hospitable to contemplative cinema, which demands that the audience patiently submit to unfolding time. When I worried at a panel that an Ozu or a Bresson could not have originated in the age of YouTube, he told me, “Get over it, David!” Though we disagree, talking with him was terrifically stimulating. I left with the hunch that Schrader will continue to devise some characteristic provocations for new media, for which we should be thankful.
Envoi
Dusty Cohl was one of the mainstays of Ebertfest, as well as the founder of the Toronto Film Festival and a shot in the arm to world film culture. He died last fall. He was honored by several events at this year’s festival, notably the biographical film, Citizen Cohl: The Untold Story, by Barry Averich (The Last Mogul). On my first visit to Ebertfest, the tough, salty guy with the quick grin and the cowboy hat immediately made me feel welcome, and he did the same when Kristin came along the following year. Everyone whose life he touched was grateful for Dusty’s generosity of mind and spirit.