Archive for the 'Film comments' Category
Welcoming Jews as heroes in an alternate 1924 Vienna
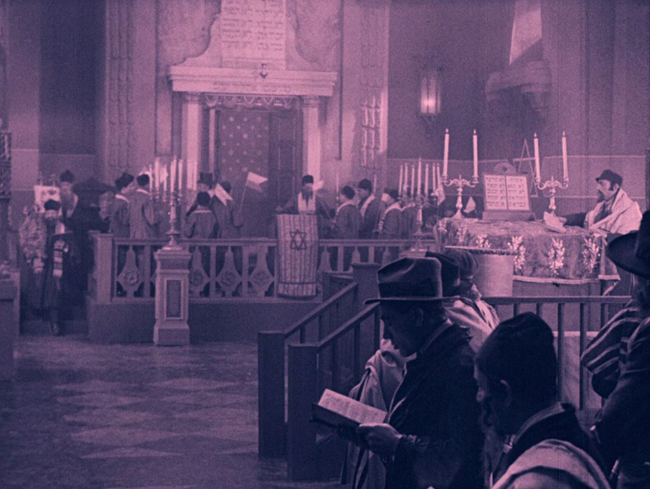
The City without Jews (1924).
Kristin here:
Once again Flicker Alley has released a restoration of a film that few have ever heard of. But we all should have heard about this one. And we should have wanted to see it. Now we can.
The City without Jews (Die Stadt ohne Juden) is an Austrian silent film released in 1924 and directed by H. K. Breslauer. It falls into the brief cycle of films about Jews released in the first half of the 1920s. I’ve written about this briefly in regard to Flicker Alley’s earlier Blu-ray of another film in this cycle, E. A. Dupont’s Das alte Gesetz (1923). The other notable Jewish-themed films are the Expressionist classic Der Golem: Wie er in der Welt kam (Paul Wegener and Carl Boese, 1920) and Carl Dreyer’s first German film, Die Gezeichneten (“The Stigmatized Ones,” called in Danish Elsker hverandre, or “Love One Another,” 1922). Thus The City without Jews is, as far as I know, the last entry in this cycle.
The Russian Revolution and civil war had driven many “Eastern Jews” into Europe, and they, created an anti-immigrant sentiment that grew into a more generalized intolerance toward the more assimilated Jews already in these countries. The earlier films had made little reference to the current growth of antisemitism in Europe and particularly in Germany and Austria. Der Golem was a period fantasy, Dreyer’s film dealt with pogroms in 1905 Russia, and Das alte Gesetz was a drama largely about conservative attitudes toward assimilation within the Jewish community.
Beslauer’s film was based on a satirical novel of the same name (1922) by Hugo Bettauer. It has proven his most famous novel, though undoubtedly in film circles he is best known as the author of Der freudlose Gasse, the source for G. W. Pabst’s 1925 classic of New Objectivity. Bettauer was a controversial figure, given the rising right-wing extremism in the mid-1920s. Perhaps spurred by the release of the film, a dental technician and member of the National Socialist Party assassinated Bettauer in early 1925; the assassin was sentenced to 18 months in a mental clinic and then walked free.
Despite an initial success in Vienna, The City without Jews was shown only a few times abroad, in various censored or abridged versions. The last known screening was in the Netherlands in 1933, as a anti-Nazi film. Portions of an incomplete print of that version, added to reels found in 2015 in a Parisian flea market, formed the basis of the current restoration. Given its sources, the result can hardly be identical to the original, but it plays very smoothly, and there are no noticeable remnants of gaps or re-editing. An account of the restoration is offered by Anna Dobringer as one of several brief essays in the booklet accompanying the dual DVD/Blu-ray release by Flicker Alley.
A satirical, serious picture of antisemitism
Of the four Jewish-themed films mentioned above, The City without Jews is the only overtly political one. Beslauer’s film, the action takes place in “Utopia,” a thinly disguised Vienna (where the film was shot), and many of the main characters are the Councillors and Chancellor.
The film starts by emphasizing that assimilated Jews already established in Utopia worship alongside the recent Eastern Jews, as suggested by the two foreground figures in the opening synagogue scene (see top). The government finds it convenient to blame various problems, such as rising prices and unemployment, as well as the fall of the country’s currency, on the Jewish population. With mounting popular unrest, the Chancellor accedes to the idea of expelling all Jews from the city.
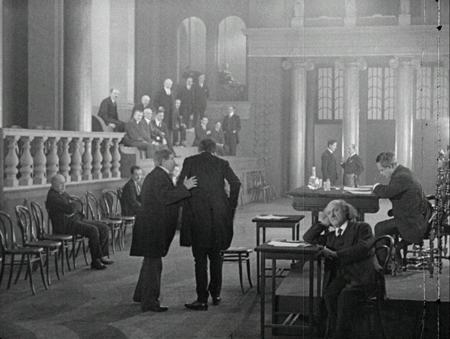
The result is a rather uneasy balance in the early portions of the film between satirical views of the local politicians, officials, and businessmen, and the very real sufferings of the Jews and their Christian supporters and spouses. (The film is a quite polished and expensive production, as the legislative chamber, above, shows.) The Christian officials are treated as caricatures, rather similar to the way officials are portrayed in Soviet films of the second half of the 1920s–which Breslauer, of course, could not have seen.
The scenes of the entire Jewish population being expelled, on the other hand, is treated quite seriously and fairly realistically. Scenes of families being dragged out of their homes are not at all humorous, and the departure en masse by train calls to mind methods that were to be used in reality little over a decade later–though here the trains are ordinary passenger ones rather than cattle-cars.
A rather odd premise which the film emphasizes is the impact that the expulsion has on marriages between Jews and Christians. No fewer than five mixed couples of various classes are made prominent, and all are ripped apart. One involves a rabid anti-Semite, portrayed as a drunken dolt. His daughter has married a Jewish man, and they have a daughter. The scene of the husband’s departure shows the anti-Semite (in dark coat at the center below) grieving along with his daughter as they watch the little girl saying good-bye to her father.
The author and filmmakers seem to understand well the familiar phenomenon of the bigot who is only brought to sympathize when people who are discriminated against turn out to be members of their own family.
Pure satire takes over
Once the Jews are gone, the satirical approach fully takes over. It turns out that the Jews had been the foundation of everything good and strong in the Utopian society. Businesses collapse, the currency falls, foreign countries boycott Utopia, and foreign banks (being controlled by Jews) refuse to loan the failing government money. The Chancellor and his allies lament that they no longer can blame the Jews for these problems.
More amusingly, the culture falls apart. High society people who had only dressed elegantly because Jews did decide that they don’t need to buy the latest fashions. One powerful businessman who runs an expensive ladies’ clothes emporium discovers that his establishment is no longer profitable (below left). Austrian men abandon their dignified suits and revert to their casual clothes and giant tankards of beer (right). The sophistication associated with the Jews has disappeared. (All this forgets the recently arrived Eastern Jews, with the action concentrating on the very much assimilated ones.)
Among the five Jewish-Christian couples separated by the expulsion is Leo Strakosch, who is engaged to the daughter of one of the local Councillors. He emerges as the film’s protagonist, returning to Utopia in the persona of a Parisian painter and Roman Catholic. His disguise makes him look like a thinner version of Dr. Mabuse (top of this section), and one suspects that Lang’s two-part film, released in 1922, had not gone unnoticed.
Like Mabuse, Leo manipulates the dire political situation, campaigning for a repeal of the expulsion order and a return of the Jews as the only way to save Utopia’s situation. He does so, of course, in a good cause. Ultimately the decision concerning the repeal hangs on a single vote lacking for the two-thirds majority needed to rescind the order.
Leo gets one of the Councillors drunk and sends him away during the vote, thus causing the repeal to succeed.
The result is a huge success. Jews return, sales and the currency rise, mixed couples are re-united, and the government now credits the returning Jews with the restoration of the country’s health. Strakosch, now out of his disguise, is greeted as the first returnee by cheering crowds and bouquets.
Expressionism as revenge
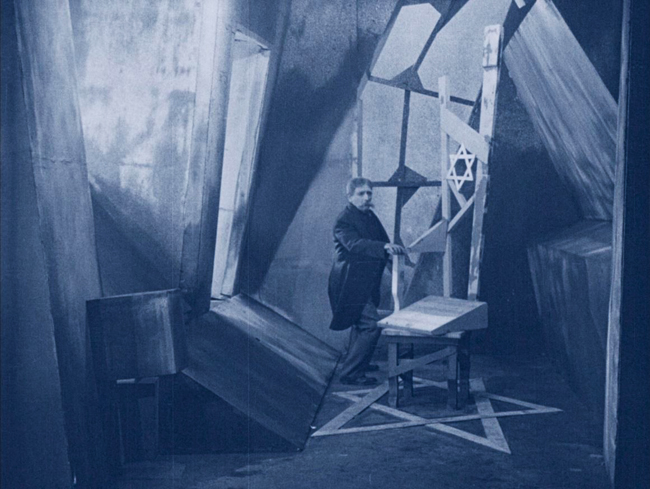
The drunken Councillor whose lacking vote caused the return of the Jews ends up in a scene that quite explicitly imitates the end of The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari. He dreams of being imprisoned in a cell with Jewish stars built into the scenery (see bottom). He recoils in horror at the sight. This is followed by a shot of a doctor (above) who declares, “A strange case of delirium, my dear colleague. The man imagines himself to be a Zionist.” I dearly hoped that he would go on to say, “I think I know how to cure him now,” but it was not to be. Obviously the diagnosis is completely wrong, since the Councillor is terrified by the Jewish imagery in his cell. But of course, Dr. Caligari’s diagnosis may have been wrong as well.
The film is accompanied by a charming score, provided by pianist Donald Sosin and violinist Alicia Svigals. For a list of bonus materials, click on the link at the top of this post.
The City without Jews has fallen into the state of an obscure film, no doubt, but it deserves more attention now than it received at the time of its release. It has become a cliché to point out that a film of the past speaks to our current world situation. Still, this film does.
Thanks to Jeffery Massino and the team at Flicker Alley!
PLANET HONG KONG comes to . . . Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Film Critics Society has just published a Chinese long-form translation of the second edition of my Planet Hong Kong: Popular Cinema and the Art of Entertainment. It can be ordered from the HKFCS bookshop. Sample pages and further information can be found here. I’m grateful to Li Cheuk To, Alvin Tse, and their colleagues for preparing and checking the text and finding nice pictures.
That second English-language edition dates back to 2011–a distant past in terms of the rapid changes in world cinema. So for this translation, I wrote a postscript last year, and at the suggestion of Cheuk To I’m posting it here. The book is dedicated to Ho Waileng.
Revisiting Planet Hong Kong
Raymond Chow Man-Wai and Louis Cha Jin Yong both died in 2018. Journalists seeking a strong hook might take these unhappy departures as emblematic of changes in Hong Kong film culture—marking the “end of an era,” as we say. But Chow retired from the scene in 2007, and Cha finished revising his classics at about the same time. They stand, of course, as towering figures in Chinese cinema, but from my perspective today’s Hong Kong film is for the most part continuing processes that started quite far back. In other words, and much to my regret, the golden era ended some time ago.
I wrote the first edition of Planet Hong Kong in the late 1990s. As I explain in the book, I had been watching some Hong Kong films since the 1970s and got interested in the 1980s creative developments. By 1995, when I first visited the territory, those developments were already fading, though that wasn’t obvious to me. The local market was becoming unstable, regional tastes and investment sources were shifting, and the mainland economy was expanding. That age, undeniably golden, was ending.
When I interviewed local executives for the book, some said that they thought Hong Kong could become the “Hollywood of China.” Perhaps, they thought, all the experienced talents and financial and technical resources of the territory would be much sought after as China opened up its market.
By the time I came to revise the book in the early 2000s, such idealism had waned. As you’ll see in the pages that follow, it became obvious that Chinese authorities had shrewdly manipulated the market and the infrastructure to build up a powerful domestic industry. The rise of that industry, along with the waning of Hong Kong film, led to the biggest growth of a national film business ever seen in history. And those processes would assimilate Hong Kong creative talent on the mainland’s terms.
Now, as the 2010s come to an end, it seems that all the trends that I traced in the 2011 edition have continued, even accelerated. From 263.8 million viewers in 2010, mainland attendance has risen to over 1.6 billion in 2017. In 2010, the mainland claimed theatrical revenue of US$1.5 billion; in 2017 those were $8.27 billion. According to official figures, 970 feature films were produced in 2017. Although most of those were not released theatrically, it still remains a colossal achievement.
Over the same period, Hong Kong cinema continued in stasis. Production hovered between 42 and 64 annual releases. Theatrical admissions were likewise fairly flat, at an average of 25 million a year. Box-office revenues in 2010 came to US$179.4 million, and moved to $237.9 million in 2017. This is a substantial increase, but rising ticket prices (seen in every film culture) is likely one cause. Part of the rise, which occurred in the mid-2000s, is probably due to the emergence of 3D exhibition, which yields premium ticket pricing. And the greater part of that box office did not accrue to local films.
Certainly Hong Kong professionals at all levels were important resources for the growing mainland industry. Stars were and still are sought for major roles, and figures from decades ago, such as Chow Yun-fat, Tony Leung Chiu-wai, Shu Qi, and Andy Lau Tak-wah, can still draw audiences. Directors Tsui Hark, Jackie Chan, Stephen Chow Sing-chee, Peter Chan Ho-sun, Chang Pou-soi, Wong Jing, Johnnie To Kei-fung, and Stanley Tong Gwai-Lai found success in China, mostly with coproductions. The biggest coup of the era, Wolf Warrior 2 (2017; above) with its 154 million admissions, came from Wu Jing, a veteran actor and martial artist in Hong Kong films. Just as important, Edko, Emperor Motion Picture Group, and other local companies gained from producing movies for the mainland audience.
More broadly, the mainland box office was keeping Hong Kong film alive. A “local” film was likely to have mainland investment, and when it played there it had a good chance of making much more money than at home. SPL 2: A Time for Consequences (2015) took in less than US$2 million in Hong Kong but won over $90 million in China. Wong Jing’s From Vegas to Macau 2 of the same year captured $154 million there, as opposed to $3.6 million in Hong Kong. Through the 2010s, even a moderate success on the mainland could recoup far more money than it could in the tiny local market. To some extent the growing market to the north replaced the regional South Asian market that had sustained Hong Kong film in earlier decades. (How that market was lost is traced in Chapter 3.)
China cultivated homegrown directors as well, especially those who adapted conventions of Hong Kong and South Korean romantic drama and comedy to the local milieu. For any year, then, the top twenty films at the Chinese box office typically consisted of a mix. There would be imports (nearly all from Hollywood), domestic films by prestige directors (Zhang Yimou, Feng Xiaogang et al.), local genre films by younger hands, and two or three big box-office attractions steered by Hong Kong directors.
Coproductions that found mega-success in China didn’t register as strongly in Hong Kong. Tsui’s Flying Swords of Dragon Gate (2011), Jackie Chan’s CZ12 (2012), Peter Chan’s American Dreams in China (2013), Raman Hui’s Monster Hunt (2015), and Tsui’s Journey to the West: The Demons Strike Back (2017) all failed to crack the local top ten. Stephen Chow seems to have lost his hometown following: Journey to the West: Conquering the Demons (2013) failed to score big there, while The Mermaid (2016) did, but in seventh place, below Marvel superheroes and the local thriller Cold War 2.
Not that the territory’s audience was particularly loyal to locally-sourced product either. The waning attendance I noted in Chapter 10 persisted. For the period 2010 to 2018, no more than two local films won a place in any year’s top ten. For three of those years, none did. In 2018, Project Gutenberg ranked number 12, the only local film to appear among the top thirty contenders.
Granted, in most countries, especially small ones, domestic films don’t get big box-office returns. Hollywood films dominate, with only one or two local productions finding a place on the year’s top ten. Still, those of us who remember when Hong Kong films ruled the local market have to see the stagnation as saddening. Nonetheless, with China offering many more opportunities for investment and rewards, it’s remarkable that there remains a local industry at all—and one turning out four or five dozen features a year.
Those films have tended to follow the templates established decades ago: romantic comedies, domestic dramas, films of social comment, and urban action pictures. Filmmakers have updated those genres with digital production and mostly skillful use of modern technologies of color control, computer effects, and elaborate camera movements, including the use of drones for aerial shots. But anyone familiar with classic Hong Kong film will recognize the persistence of traditional plots and story premises. Golden Job (2018) brings back the rascals from the Young and Dangerous series to execute a heist, under circumstances that strain their brotherhood. Project Gutenberg (2018) revisits the Chow Yun-fat mythos with a counterfeiting story (shades of A Better Tomorrow) that allows him to wear white suits, brandish guns in both fists, and participate in a twisty plot that owes something to the 1990s narrative stratagems I discuss in Chapter 9.
The continuity should hardly be surprising, because a great many veteran creators are still active. Producer Raymond Wong Pak-ming, who co-founded Cinema City and went on to create Mandarin Films and Pegasus Motion Pictures, continues to release films. Yuen Woo-ping was a choreographer and director in the 1970s and achieved worldwide fame with The Matrix (1999) and Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon (2000); he recently directed Master Z: The Ip Man Legacy (2018). Ann Hui, Tsui Hark, and many other directors from the 1970s remain top figures in a film culture that offers many opportunities to venerated talents.
Although I’ve long admired Hong Kong films in many genres, readers of of Planet Hong Kong know that I believe that the action film—as wuxia pian, kung-fu movie, or cops-and-robbers thriller—was the area of its most long-lasting contribution. The tradition of powerful physical action, gracefully executed and forcefully staged and cut, was a genuine contribution to the history of film as an art form.
For that reason it’s a pleasure to report that the “ordinary” action pictures of the last decade have by and large maintained that tradition. Donnie Yen Ji-dan, an actor who chooses intelligent projects, endowed films like Kung Fu Jungle (2014), the Ip Man vehicles (2008-2019), and Chasing the Dragon (2017) with vivid, exciting sequences. He and other filmmakers seem to have abandoned the looser camerawork of the early 2000s and returned to precision shooting: fixed camera, instantly legible compositions, and a flow of movement across shots that can accelerate, slow, or halt, all in the service of impact on the viewer.
Still, in the hands of a skillful craftsman any technique can work. Benny Chan Muk-sing’s White Storm (2013), a full-bore male melodrama in the John Woo manner, mixes run-and-gun handheld style with a revival of the forceful compositions and crisp editing of the heroic-bloodshed days. Cheang Pou-soi’s Motorway (2012) invests a simple plot with excitement through nearly abstract shots of cars gliding through streets and alleys, augmented by stretches of ominous silence.
Similarly, I see the positive legacy of the Infernal Affairs series (2002-2003) in franchises like Overheard (2009-2014) and Cold War (2012, 2016). While not as tightly contained as the trilogy, these films benefit from plotting that is less episodic and more finely woven than we find in the policiers of the 1980s. They also judiciously insert florid action sequences, creating a sort of middle ground between the bureaucratic intrigue of Infernal Affairs and the more extroverted spectacle of something like Police Story (1985)—or, come to think of it, any of Jackie Chan’s Police Story titles.
There’s much to be said about Tsui Hark’s PRC adventure sagas as well, particularly in their use of 3D. (The Taking of Tiger Mountain, 2014 above, is a mind-bending use of that technology.) But for my purposes here I’d like to focus on two other major talents that I analyzed in the second edition. Both made outstanding contributions to the action picture in the years since the second edition was published.
Wong Kar-wai’s The Grandmaster (2013), despite being circulated in varying versions, remains for me a powerful achievement. It carries on Wong’s persistent experimentation with decentered narrative, following not only Master Ip Man but also his chief rival Razor and Gong Er, daughter of Ip’s one-time adversary. As I suggest in a blog entry this diffuse treatment of the major characters may bear the traces of a multiple-protagonist plot reminiscent of Days of Being Wild. In addition, through strategic flashbacks and shifts from character to character, this “chaptered” film evokes the interrupted and embedded story lines of other Wong films.
Stylistically, The Grandmaster makes fresh use of distended time and slow-motion imagery; these are conventions of the kung-fu genre as well as a signature of Wong’s work. More unusual is what I call in the blog entry the “mosaic” texture he builds up through close-ups that can be put in various places in one scene or another, or even one version or another. In general, I think that Wong alters the thematics of the martial-arts film by emphasizing Gong Er’s tragic dilemma: defeating the man who killed her father both sustains and erases her family’s legacy. And, as we might expect with Wong, the film strikingly parallels martial-arts prowess with impulses toward romantic love.
Another major film of 2013, Johnnie To Kei-Fung’s Drug War, is no less characteristic of its creator. (I analyze it in another blog entry.) A cat-and-mouse intrigue between crooks and cops, it depends heavily on our filling in gaps and reading characters’ minds. Police officer Zhang tries to penetrate a drug-smuggling outfit, and he devises a perfect To/Wai Ka-fai strategy: He sets up two meetings with two kingpins who don’t know each other. At each meeting Zhang impersonates the other guy. This game of shifting identities, of symmetry and doubling among roles, is a common narrative device of the Milkyway films, but in Drug War it’s given new urgency and a great deal of suspense. One economical shot brings the two unsuspecting gangsters together in the same frame as they leave and enter elevators.
At the same time, the informant Timmy is playing his own game—one that it may take a couple of viewings to decipher. As in The Mission (1999), many scenes of Drug War consist of men looking at each other, trying to divine hidden intentions—here, framed in the simplest possible shots, mere faces seen inside adjacent cars. Timmy’s eventual double-cross culminates in one of the cruelest shootouts to be found anywhere in To’s work; its bleakness recalls the end of Expect the Unexpected (1998). Throughout his career, To’s originality and craftsmanship in this rich genre have made him one of the great contemporary directors.
Wong completed only The Grandmaster in the years I’m considering, but To remained quite productive. Romancing in Thin Air (2011) and Don’t Go Breaking My Heart 2 (2013) returned to the mode of white-collar romance that Milkyway had made its own, while The Blind Detective (2013) combined that eccentric tone with an off-center cop premise recalling Mad Detective (2007). Life without Principle (2011; discussed in this entry) was a striking use of multiple-character plotting to make incisive points about the financial crisis.
Office (2015), an adaptation of Sylvia Chang’s popular play, was at once a flamboyant musical and an experiment in 3D. In Three (2016) To took up the challenge of a tightly circumscribed time and space, tracing the raid on a hospital ordered by a triad who’s there in police custody. Milkyway produced films by others, notably Motorway and Trivisa (2016), an opportunity for three first-time filmmakers to collaborate on a feature with three intersecting story lines. This last effort was in keeping with To’s dedication to creating programs and award competitions for newcomers to the industry. He remained one of Hong Kong’s most imaginative and tireless creators.
I should mention one more tendency, and it’s an encouraging one. Both editions of Planet Hong Kong pointed out that the Hong Kong people, contrary to the stereotype, actually cared a great deal about politics, especially after 1989. Recent years have seen a resurgence in films explicitly about activism in the territory. An early example is Matthew Tome’s documentary Lessons in Dissent (2014), a stirring account of struggles over educational policy and voting rights, featuring the most heroic 15-year-old I’ve ever seen. The 2014 Umbrella Revolution brought forth Evans Chan’s Raise the Umbrellas (2016) and Yellowing (2016; below) by Chan Tse Woon of Ying e chi There was also the ambitious speculative fiction Ten Years (2015), an ensemble of stories forecasting political repression in 2025. It’s very encouraging to see these efforts to insist on free speech and social criticism.
Finally, it’s worth pointing out how much classic Hong Kong film anticipated developments in Hollywood. The comic-book franchises that found new popularity with X-Men (2000) and Spider-Man (2002) and the Dark Knight trilogy (2005-2012) feature chivalric warriors with extraordinary fighting skills and weaponry. Like the knights-errant of wuxia fiction and film, these superheroes can leap high in the air and subdue villains with secret fighting techniques. Some, like Iron Man, have an equivalent of “palm power.”
Sometimes the American films have acknowledged their sources in Asian martial arts traditions, as when Batman trains as a ninja (Batman Begins, 2005) and Doctor Strange studies under a sifu in his 2016 film. The combat scenes, full of flips and somersaults, owe a great deal to the acrobatic traditions on display in Hong Kong cinema. If the result lacks the precision and visceral punch we find in classic Hong Kong films, it’s still worth noting that Westerners have learned that kung-fu, fights in mid-air, and elegant swordplay look cool on the screen. Hollywood should thank Hong Kong for helping invigorate the American action film.
A few words about what the original book tried to accomplish. At the most basic level, I wanted to understand Hong Kong cinema as an industry, an artistic tradition, and a cultural force. At the same time, I wanted to study it as an example of a popular cinema, one that developed strategies of storytelling and style and emotional appeal that were accessible to millions of people around the world. I wanted to analyze its unique contributions to the development of film art, so that meant I had to do some comparative work, situating Hong Kong film in relation to other traditions—most notably, that of Hollywood. At another level, I was interested in particular genres, especially the action film, and directors. As a result, parts of the book—mostly the “interludes”—are devoted to a particular filmmaker or group of filmmakers. And while I expected that many readers would already be Hong Kong film fans, I wanted to persuade skeptical readers that this national cinema was worth respect. This overall project I tried to amplify in the second edition you’re now reading.
Since the last edition, I have not followed Hong Kong cinema as intensively as I would have liked. Other projects have diverted me. But I have never lost my admiration for this cinema, this culture, and this citizenry. Watching Hong Kong films and visiting the territory have added a new dimension to my life.
From my first stay in 1995, when Li Cheuk-to introduced himself to me during the festival, through many visits over the decades, I have always treasured my friends there. So many people helped me in my research—people attached to the festival, to the archive, to the industry—that to list them all would add too much to this already overlong postscript. But they are mentioned throughout the book, and I hope they know how much I appreciate their generosity over the years. I’ll be happy if anything I’ve done here and elsewhere, in other writing and teaching, have helped film lovers better appreciate the astonishing contributions of Hong Kong film to world cinema artistry.
Among those valued friends was the kind and dedicated Ho Waileng. A tireless worker for the festival, she also translated the first version of Planet Hong Kong into Chinese. She remains in the hearts of everyone who knew her.
P.S. 10 August 2020: We in the US are now accustomed to being shocked but not surprised. I woke up to learn that Jimmy Lai, maverick mogul and publisher of Apple Daily, and many of his colleagues were arrested under the new “national security” law. It’s ironic that President Trump, who has reportedly sought to jail our journalists, moved quickly to place sanctions on Hong Kong earlier this year. The latest crackdown may be a response to the U.S. condemnation of the bill’s restrictions on free speech. (I discussed them here.) An arrest warrant is out for an American citizen living in the U.S. because he advocates democracy for Hong Kong. A coalition of Democratic and Republican senators and representatives have sponsored legislation to widen refugee status for Hong Kongers. Another irony: It’s called the Hong Kong Safe Harbor Act.
Ho Waileng at Angkor Wat, 2006. Photo by Li Cheuk To.
Is there a blog in this class? 2020
Picnic at Hanging Rock (1975).
Kristin here:
Recently our blog reached its 1000th entry, a fact we celebrated with a retrospective entry. That’s a lot of entries. How to find something that might be of interest or use to you? If you know what you’re looking for, the site’s search engine works quite well, I find. We’ve added categories at the right to guide people with specific interests.
“Is there a blog in this class?” is designed to assist teachers who might want to consult the blog or assign entries to the students. I started it the year after we posted the first entry and has continued annually, with entries posted roughly a month before university and college semesters begin. We do have some readers who have followed “Observations on Film Art” from that point, but most have come later to it. We hope this series might also be useful in guiding them to interesting content from from the past year. The series can be found here: 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019.
Last year I started listing new entries in our video-essay series on The Criterion Channel, which is in a sense an extension of this blog and has the same title.
I’ll go chapter by chapter through Film Art: An Introduction, though some chapters have no relevant entry this year.
Chapter 1 Film as Art: Creativity, Technology, and Business
In this chapter we emphasize how technological choices affect film style. My entry “THE LIGHTHOUSE: A period film with period style” (above) discusses how the filmmakers uses lenses, film-stock, and lighting equipment to simulate the look of a silent-era film.
We also discuss the film industry in this chapter of Film Art. I wrote on how annual box-office figures can be deceptive about trends in studios’ income: “So was there an actual box-office slump in 2019?”
David commented on how the move to streaming films has affected viewing habits and film scholarship: “When media become manageable. Streaming, film research, and the Celestial Multiplex.”
Chapter 2 The Concept of Form in Film
This is the chapter where we discuss different levels of meaning. David’s entry “Hunting Deplorables, gathering themes” deals with interpretation, using The Hunt as its main example.
Chapter 3 Narrative Form
David wrote some analytical essays on individual films this year: “Not just a Christmas movie: DIE HARD on the big screen,” “Un-Marry me a little: MARRIAGE STORY and LITTLE WOMEN,” and “When Hollywood ruminates: Calm after THE MORTAL STORM.” Above, a scene from Marriage Story that would nicely illustrate the functions of a motif and the ways narration can use it for a revelation.
Chapter 4 The Shot: Mise-en-Scene
Criterion Channel #31 Here I examine the subtleties of the three-point lighting system in “Comedy, Suspense, and Three-Point Lighting in TO BE OR NOT TO BE.”
Criterion Channel #33 Jeff Smith on how different aspects of mise-en-scene are used to create a woman’s viewpoint: “Feminist Mise-en-scène in MY BRILLIANT CAREER.”
Chapter 5 The Shot: Cinematography
Criterion Channel #35 I look at how camera techniques turn a horror-story adaptation into an art film: “In the Service of Horror–The Lyrical Cinematography of PICNIC AT HANGING ROCK.”
Criterion Channel #32 In relation to this chapter’s section on framing, I discuss the functions of offscreen space at the beginnings of scenes in “Withholding and Revealing in AN ANGEL AT MY TABLE.”
In Criterion Channel #30, Jeff Smith analyzes “The Long Take in SHOCK CORRIDOR.”
If you’re teaching a film noir or the whole noir trend, have a look at David’s piece on cinematography in Trapped: “TRAPPED: Low-budget flash is good for you.”
Chapter 6 The Shot: Editing
In “Who will match the Watchmen?” David examines editing strategies in the HBO series, The Watchmen. He traces how the filmmakers used match cutting to mimic the time-jumping transitions in the graphic novel.
David analyzes a sneaky technique combining editing, framing, and figure movement in King Hu’s The Valiant Ones: “Sometimes a swordfight …”
Criterion Channel #37 Yasujiro Ozu created his own unique style of editing; David analyzes how he uses it in a poignant silent comedy: “Ozu’s Space Adventures: Editing in PASSING FANCY.”
Chapter 7 Sound in the Cinema
On the occasion of the prolific and beloved composer Ennio Morricone’s death, Jeff Smith provides an in-depth analysis of Morricone’s approach and style, with many excerpts that let you revisit some of his classic themes: “The poet of dynamic immobility: Ennio Morricone: A guest blog by Jeff Smith.”
Criterion Channel #36 Focusing on a single Morricone film, Jeff picks out “Musical Motifs in THE BATTLE OF ALGIERS.”
Chapter 9 Film Genres
Jeff Smith has explored Tarantino’s genre-mixing strategies in “When worlds collide: Mixing the show-biz tale with true crime in ONCE UPON A TIME IN . . . HOLLYWOOD.” This was our most popular entry of 2019. Jeff shows how Once Upon a Time. . . in Hollywood is tied to 1960s film and music cultures here and in his follow-up entry “Twice upon a time in . . . Hollywood: Jeff Smith revisits Tarantino’s retro opus.” These pieces could also be used in teaching Chapter 12’s section on contemporary Hollywood.
Criterion Channel #34 David examines how an unconventional use of style can transform a familiar genre like the horror film: “VAMPYR: The Genre Film as Experimental Film.”
Ch 12 Historical Changes in Film Art: Conventions and Choices, Traditions and Trends
My annual look at the famous and lesser-known classics of ninety years ago: “The ten best films of … 1929.”
David analyzes the sophisticated classical style of the 1917 adaptation of Wilkie Collins’ mystery thriller The Woman in White in “Hollywood starts here, or hereabouts.”
In the last year Flicker Alley has continued to release Blu-rays of crucial classics of the silent cinema. I review releases of Fridrikh Ermler’s Fragment of an Empire (above) and Marcel L’Herbier’s L’Argent, important late entries in the Soviet Montage and French Impressionist movements, in “Two more classics from Flicker Alley.” The company has also at last made Pudovkin’s “Bolshevik Trilogy,” Mother, The End of St. Petersburg, and Storm over Asia, available in decent copies: “Flicker Alley fills the Pudovkin gap.”
We tend to slant these annual updates to Film Art, since that’s where the blog started. Certainly many of the entries listed above are also relevant to Film History: An Introduction. Here are some further possibilities.
Joe Anderson’s Spring Night Summer Night is a hard film to classify, but it could be something to consider in teaching the indie section of Chapter 22 of Film History. See my analysis with some background production information in “‘Student Film,’ exploitation film, indie classic.”
David’s analysis of Roy Andersson’s About Endlessness (2019, below) fits into the category of “The Arresting Image” in Chapter 25: “The raptures of rigor: Roy Andersson’s ABOUT ENDLESSNESS in Venice 2019.” Andersson won the Silver Lion as best director at the festival.
You no doubt recall the controversy that erupted when Scorsese complained about blockbusters dominating American distribution and exhibition. David’s remarks on it in “Captain Cinephilia: Scorsese strikes back,” could work into either Chapter 28 or 30–or both.
I haven’t included all of our film-festival reports. Last year we attended five festivals, a record for us, little dreaming that the following year we would not be able to visit any. For brief comments on the films we saw or just a vicarious experience of a festival in these locked-down days, see these links, in chronological order: Wisconsin, Il Cinema Ritrovato in Bologna ( here, here, and here), Venice (here, here, here, here, here, and here), Vancouver (here, here, and here), and Torino (here, here, and here).
Finally, all teachers and lovers of cinema should be aware of the riches offered by The Walker Art Center Dialogues, a collection of recorded interviews with major filmmakers. These include a conversation between David and Robert Altman.
Thanks to everyone who enabled us to write these entries over the last year: the teams at the Wisconsin Film Festival, Il Cinema Ritrovato of Bologna, the Venice International Film Festival. the Vancouver International Film Festival, the Torino Film Festival, Jeff Masino and the staff at Flicker Alley, and of course the dedicated team at Criterion, especially Peter Becker, Kim Hendrickson, Grant Delin, and their colleagues. And thanks to our readers for staying with us through a year of cinematic discoveries.
Little Women (2019).
The poet of dynamic immobility: Ennio Morricone: A guest post by Jeff Smith
Ennio Morricone holding his principal instrument, the trumpet, in a picture taken in the 1970s. Photo by Roberto Masotti.
DB here: For our blog entry #1001, who better to memorialize Morricone than our stalwart collaborator Jeff Smith? He has provided many music-sensitive analyses of films both recent and classic. Our most popular entries from last year were his two looks (here and here) at the music and musical culture behind Once Upon a Time. . . . in Hollywood. Herewith his warm appreciation of a maestro.
Jeff here:
On July 6, 2020, the legendary composer Ennio Morricone passed away in Rome at the age of 91. As expected, several encomia were published reflecting upon Morricone’s musical genius. Of particular note were reflections by two writers for Variety, film critic Owen Gleiberman and film music historian Jon Burlingame.
The tributes highlighted many notable features of Morricone’s film work: his gift for melody, his sense of humor, his eclecticism, and his amazing productivity. Having written more than 500 film and television scores, Morricone’s compositional output was jaw-dropping. After all, even Josef Haydn wrote only 106 symphonies.
Throughout my own career as a film scholar, I frequently engaged with Morricone’s music. In preparation for the writing of my dissertation, I did an independent study with David on Hollywood film music. My final project? A detailed analysis of the score for Sergio Leone’s The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, complete with handwritten transcriptions of every musical theme and motif I could identify.
I vividly remember the satisfaction I felt in being able to play the main title from start to finish on the piano. It is one thing to read music and play it. It is another to take what you hear and try to put it in some reproducible form on paper. Playing back Morricone’s famous theme, I felt I’d gained insight into the mind of the great composer. That work eventually became the basis for chapter six in my first book, The Sounds of Commerce.
My fascination with Morricone’s work has continued to the present day. Last summer, I wrote a review of Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words, a book of interviews conducted by Alessandro De Rosa. This past April the Criterion Channel posted my most recent “Observations on Film Art,” which examines musical motifs in Morricone’s score for The Battle of Algiers.
That’s close to thirty years of near-obsessive fascination with Morricone’s music and his compositional style. In what follows, I share some additional thoughts on the Maestro’s legacy, offering some insight on the reasons for his seemingly inexhaustible creativity.
The Sicilian defense
The first section of Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words is all about the maestro’s love of chess. Although the composer would describe himself as a hobbyist, his chess skills surpassed those of most amateurs. Morricone played against Boris Spassky, Garry Kasparov, and other Grand Masters. When asked about his passion for the game, Morricone explains that he sees important parallels between music composition and chess. Both activities involve mathematical relations. These relations are further expressed in axes of verticality, horizontality, and graphics.
This initial discussion of chess struck me as a key to understanding Morricone’s creative process. The game of chess is often analogized as a battle where stratagems and tactics are deployed in an effort to outmaneuver – and thus, defeat – one’s opponent. That comparison undoubtedly rings true. Yet when one looks at the board before the game starts, it also represents something simpler: a field of open possibilities. Not every move is permissible, of course. But when you consider possible combinations of moves, the permutations can number in the millions. And even though the rules of chess constrain the patterns of moves that can be made, all of these possibilities are generated by the dispositions of up to 32 pieces on a field of 64 squares.
Morricone seems to approach the blank space of staff paper as though it were a chessboard at the start of the game. A chess player works with sixteen pieces that can be used in various combinations. A composer works with the twelve tones of the chromatic scale to create intervals and chords. As with the chessboard, there are millions of different permutations in the way these twelve tones can be arranged. More importantly, since each note in the scale can be varied by pitch class, duration, articulation, dynamics, and instrumental color, the options seem endless.
Yet while the “terror of the white page” can be an obstacle to the creative process, that has never appeared to be the case with Morricone. Why? I think it is because the composer found a method of composition that reduced the apparently infinite possibilities to the level of the merely multitudinous.
In Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words, the composer characterized himself as a student of the Second School of Vienna. Unlike Arnold Schoenberg and Anton Webern, who were part of the first Viennese School, Morricone tried to transpose the former’s twelve-tone technique into a seven-tone system while retaining the latter’s commitment to the rules of serialism that ordered all other musical parameters. For Morricone, this system had the advantage of enabling him to write tonal music without having to slavishly adhere to its characteristic tensions and resolutions. By adopting Webern’s principles of serialism, the notes, according to Morricone, “are freed from their reciprocal constraints.”
Over time, Morricone learned how to adapt this simplified version of twelve-tone serialism to the needs of each film score he wrote. In some cases, he would work within a pentatonic system. In others, he might base his compositions on a row of six or eight tones. In still others, he might jettison the system altogether.
This simplified serial technique provided Morricone with a compositional framework that was extraordinarily generative. Once the composer has determined the tone row and the ordering of other musical parameters, he simply spins off hundreds of variations that are then fitted to the film’s dramatic situations. The smaller tone row still acts as a guarantor of harmonic unity. Morricone describes it as the music’s DNA, something like an identifying marker in every musical “cell.” Specific changes in rhythm, tempo, orchestration, volume, and tessitura all provide means of refreshing the basic musical schema.
Indeed, Morricone’s compositional system proved so procreant that he sometimes wrote three or four versions of a score’s theme in order to give the director some options to choose from. In Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words, he offers an example with the police triumph theme in The Untouchables. The theme was the last one written for the score, and Morricone prepared three pieces that were recorded with two pianists. He then sent them off for director Brian De Palma’s consideration. De Palma didn’t like any of them. Back to the drawing board,
Morricone wrote three more pieces and shared them with De Palma. In a phone call, the director told Morricone that he still wasn’t convinced. Morricone completed three additional pieces and sent them. This time, though, he included a brief that summarized the strengths and weaknesses of all nine proposals. Morricone himself recommended against variant number six, claiming it was most triumphant and therefore the least convincing. Concluding his story, Morricone asks, “Guess which one he chose?”
After I sniggered at the composer’s dig at De Palma’s musical sensibilities, the larger implications of Morricone’s anecdote began to sink in. My mind was well and truly blown. If Morricone had written eight other themes in lieu of the one that was ultimately chosen, how much music had he actually written for The Untouchables? And if this, as Morricone indicates, was not an isolated case, how many unused cues are likely sitting in boxes somewhere in Rome simply waiting to be discovered? As noted earlier, Morricone had written music for more than five hundred films and television shows. Were the aggregated number of unused cues and alternate versions of themes the equivalent of another one or two hundred scores? And if we trust Morricone’s judgment, some of these versions are actually better than the ones we already know.
All of this is a reminder that Morricone’s output is astonishing. This is evident both in terms of the size of his corpus and the sustained quality of his work over a period of almost sixty years.
Much of that productivity, I think, was fueled by Morricone’s transposition of serialist concepts to the film score. Like the rules of chess, which prohibit certain moves, Morricone’s use of simplified tone rows gave him a set of “rules” that fruitfully limited certain options in terms of melody and harmony, but still preserved the usual range of choices for other musical parameters. It also shaped our sense of Morricone’s style by favoring certain compositional devices over others. Pedal points and ostinati are completely permissible in Morricone’s system. But a rapid chromatic run of the type used in classical Hollywood “hurries” would be out of bounds.
Such a rapid chromatic run is also ill-suited to Morricone’s aesthetic for another reason; it is a musical gesture that implies directional movement. Instead Morricone strives to produce a sensation of “dynamic immobility” in his work, the musical equivalent of the swirls, eddies, and ripples we associate with lake water. The sense of immobility derives from Morricone’s interest in writing tonal music outside of the strict rules governing the Western tonal system. One hears chord changes. But you couldn’t describe any particular change as a modulation insofar as there is no definite key to ground these harmonic relations. Consequently, you discern harmonic change, but without the sense of teleological movement toward a cadence as a definite endpoint.
If Morricone’s approach to harmony strives for a feeling of moving stasis, what then accounts for the music’s dynamism? For Morricone, it is the constant change evident in the other musical parameters: texture, pitch, dynamics, and timbre.
Listen again to the cue from The Untouchables. Do you notice the sorts of surges and swells produced by its chord changes? Does it sound like it moves to a definite endpoint? Or does one instead get the feeling of an endlessly deferred resolution? If those surges and swells produce the latter, that’s Morricone’s “dynamic immobility” in situ.
Morricone’s creative spark seems all the more remarkable when one considers that he worked in a production environment guided by the notion that “I don’t need it good; I need it Tuesday.” That Morricone flourished within this milieu for more than five decades eventually made him “untouchable.”
Roll over Beethoven and tell Tchaikovsky the news
A Fistful of Dollars (1964).
In The Sounds of Commerce, I argued that the 1960s proved to be an important period in the history of the Hollywood film score as the dominance of its neoromantic style began to wane. Driven partly by the popularity of theme songs and soundtrack albums, composers infused the classical Hollywood score with elements of both jazz and pop music. To be sure, those styles all had their place in Hollywood films. Characters performed Tin Pan Alley songs in musicals. Dance bands played jazz as part of the nightlife featured in gangster films and films noirs. And one even heard the occasional bit of Gershwin-style orchestral jazz pop up in a score. The changes I discerned in sixties film scores were more a matter of degree than of kind.
What prompted the change? Besides the emergence of new ancillary markets for film music, Hollywood also saw a generational shift take place throughout the industry, including film composers. Sadly, some of the greatest proponents of the classical Hollywood style, such as Herbert Stothart, Erich Wolfgang Korngold, and Victor Young, were dead before 1960. Others, like Roy Webb, Max Steiner, and Miklós Rózsa, remained active, but they saw fewer assignments come their way.
Taking their place was a new breed more attuned to changes in the jazz and pop idioms. Instead of aping Gershwin, these new composers were more likely to draw upon swing music or West Coast jazz. Similarly, several film composers also began to incorporate elements of pop music’s newest sensation: rock and roll. In an interview I did with Henry Mancini, he described his famous “Peter Gunn” theme as a rock tune due to its “straight eight” rhythms and its twangy guitar line. Not coincidentally, John Barry’s arrangement of the James Bond theme foregrounded Vic Flick’s guitar in a similar way. The middle section of the tune features a swinging, Dizzy Gillespie-ish break. But that guitar sound stood out, much closer to Carl Perkins than to Wes Montgomery.
During the 1960s, no film composer was as thoroughly steeped in the rock idiom as Ennio Morricone. Yet, unlike Mancini and Barry, who were drawn toward rockabilly in their use of electric guitar, Morricone cribbed from the slightly more modern sounds of early sixties surf-rock. Morricone tells Alessandro De Rosa that he used the electric guitar long before he wrote the scores of his spaghetti Westerns, albeit not as a solo instrument. Yet he opted to feature the electric guitar in the main theme of A Fistful of Dollars because he liked “its tough and sharp timbre,” which he felt was perfect for the atmosphere of the film.
De Rosa also notes that the Shadows’ surf music was extremely popular on Italian record charts in the early sixties, especially their Western-themed classic “Apache.” The distinctive twang of Hank Marvin’s Fender Stratocaster was widely imitated by Italian beat bands. By the time A Fistful of Dollars was in production, the Shadows’ influence had seeped into Italian popular music culture. When they topped the Italian charts in 1963 with “Geronimo,” another paean to the American west, it probably seemed quite natural to make the Stratocaster’s sound the centerpiece of Leone’s groundbreaking film.
Morricone made the electric guitar the star of many more spaghetti Western scores. But none so prominently as the “Man With the Harmonica” theme of Once Upon a Time in the West. Famously, the film features no main title in the opening credits, “scoring” the scene instead with the sounds of the wind, a creaking mill, the clanging of a metal gate, and an especially persistent horsefly (among other things). Morricone’s score doesn’t come into Leone’s film until about the twenty-minute mark. But when it does it makes quite an entrance.
Frank and his gang have just slaughtered the McBain family. The only survivor is a red-headed boy who comes running out of the house after hearing gunshots. As he comes into a close-up, Bruno Battisti D’Amario’s guitar starts blasting through the theater speakers. The sound is loud and distorted, cutting through the silence like an axe through a chicken’s neck.
In his instructions to D’Amario, Morricone insisted that the theme was meant to “wound the audience’s ears like a blade” the first time we hear it. As a coup de théâtre, it is brutally effective. I’ve seen it more than twenty times, and the moment never fails to give me chills. Here we see Morricone experimenting with the timbre of the guitar by heightening the effects of high volume and high voltage to overdrive the power valves of the amplifier. The effect was such that some critics even described Morricone’s score for Once Upon a Time in the West as a sort of “post-Hendrix” rock. The comparison was undoubtedly flattering. No musician had done more to explore the timbral possibilities of the electric guitar than Jimi Hendrix.
Morricone experimented in other ways that seemed to merge elements of avant-garde classical music with more vernacular forms. Consider his “Harmonica” motif in Once Upon a Time in the West alongside Henry Mancini’s main title for Wait Until Dark, which was released about a year before Leone’s epic. Both film scores explore microtonal effects, albeit in quite different ways.
In Mancini’s case, he asked the studio to give him two pianos that were tuned a quarter tone apart. He then asked his two performers to play the chords of an accompaniment figure in rapid succession.
The dissonance produced through this effect is unlike any produced in atonal writing. There the composer deliberately emphasizes intervals that create a sense of disharmony, such as minor seconds, major sevenths, and tritones. Yet Mancini’s microtonal experiment does something else entirely. Our ears tell us we should be hearing the same chord, but the repetition on the detuned pianos sounds a bit off. Mancini’s score evokes a kind of dislocation well suited to Wait Until Dark’s generic trappings as a psychological thriller. The effects, though, were even more pronounced for the two pianists who played on the main title. Pearl Kaufman and Jimmy Rowles both reported having to take frequent breaks during the recording sessions. The sort of “swimming” effect produced by the detuned pianos gave them a feeling of vertigo and nausea commonly found in motion sickness.
Morricone’s approach to microtonal harmonies proves to be much more elemental: the wavering sounds of two notes played on the harmonica, ostensibly a half step apart. Anyone who has played a harmonica knows it requires great breath control. Inhale and you make one pitch. Exhale and you make another. Beyond that, skilled performers can also bend pitch on a harmonica by changing their embouchure. Harmonica players can also use their hands as dampers, altering the sound in much the same way a wah-wah mute alters the tone of a trumpet.
All of these techniques give the harmonica player a number of means to bend pitch. Morricone takes full advantage of them with the “Harmonica” motif in Once Upon a Time in the West.
Listening to this passage, one can hear how Franco De Gemini’s mouth harp straddles the fence between sounding bluesy and sounding strident. Morricone viewed the half-step relation in the motif as a key element in building musical tension since it is heard in the flashback that explains Harmonica’s life-long quest for revenge. Yet De Gemini’s subtly wavering pitch seems to capture the full range of microinterval variants that fall between the D# and E that comprise the last two notes of the motif.
Both composers’ explorations of microtonal effects prove effective. But the precision of the quarter tone difference in Mancini’s detuned pianos gives the music a mechanistic quality that seems cold and brittle. By contrast, the harmonica’s fluid pitch-bending in Once Upon a Time in the West is looser, freer, more improvisatory – all of which fits the types of vernacular music played on harmonica.
This effect was enhanced by Morricone’s recording techniques. He first recorded the orchestra and then recorded De Gemini’s harmonic track individually. Although the latter recording was less precise, Morricone said that “the tension generated by the performance made his harmonica float over the orchestra. Now on the beat, then behind it, this time ahead….in short, it was almost as though it was fluctuating.”
Morricone’s compositional and recording techniques in Once Upon a Time in the West might seem less daring than Mancini’s more avant-garde experiment in Wait Until Dark. Yet Morricone’s music gains something in its more organic placement within Leone’s film. The harmonica’s wavering pitch is akin to the sorts of portamenti and string-bending frequently heard from saxophones, guitars, and basses in a multitude of rock and roll songs produced throughout the idiom’s history. And the harmonica as an object has long been a common feature of the Western’s iconography. In this way, Morricone’s experimentation is grounded in the dramatic, stylistic, and symbolic structures of Leone’s epic.
A horse of a different tone color
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly (1966).
Unquestionably, Morricone’s most audible innovations came through his approach to orchestration. As nearly every obituary noted, his unusual combinations of instruments became a hallmark of the Morricone sound. In a summary of the signature elements found in the score for The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, The Economist declared:
And then there is the freewheeling range of sounds with which he chose to make that music: the whistling, the yodeling, the gunfire and the squeaky ocarina, an ancient Italian wind instrument that looks like a sweet potato and is better known to a younger generation as the soundtrack of a Nintendo video game.
As I suggested above, Morricone was part of a cohort that moved outside the neo-Romantic style of film composition associated with the studio era. Unconventional orchestrations were an important part of that push.
Several factors provided impetus for this change. One was the embrace of jazz and pop styles. Incorporating those elements often meant writing for the instruments typically associated with those idioms. Mancini, John Barry, Frank De Vol, and Nelson Riddle all were prominent exponents of this approach during the 1960s. Indeed, many of Mancini’s orchestrations simply add strings to the usual forces of a jazz big band.
A second factor was the breakdown of the studio system in the 1950s. The majors’ retrenchment saw them making fewer films and reducing their overhead costs. They sold off parts of their backlots and leased their soundstages to independent producers or television crews. They also tried to shed labor costs, including those associated with maintaining an in-house orchestra.
This was bad news for musicians, who suddenly found themselves working in a gig economy as independent contractors. But it was good news for composers who now could write music for something other than a standard chamber orchestra. (During the Golden Age, studio bosses would sometimes chafe at the notion of hiring extra musicians, since they were already keeping as many as fifty regularly on call.)
With more flexible options when it came to musical labor, composers began to experiment with more unusual combinations. Whereas the typical studio orchestra employed one or two keyboardists, Bernard Herrmann arranged one cue in Journey to the Center of the Earth for nine organs. Three organists played electronic organs and one played a cathedral organ.
In many ways, Herrmann’s experiments with orchestration provide an interesting foil for Morricone’s own flights of fancy. For two of the scores Herrmann wrote for Alfred Hitchcock, he self-consciously limited his palette to the sounds of a single section of the orchestra. On Psycho, Herrmann wrote only for strings, claiming that the more monochrome sound was fitting for a black and white film. Yet, within that uniformity, Herrmann wrought an extraordinary range of subtle differences in timbre through the use of pizzicato, mutes, and unusual bowing techniques. The famous bird shrieks produced by the violins during the shower murder recall the avant-primitivism of Stravinsky’s Rite of Spring. But Herrmann achieved this effect only with strings rather than a full orchestra.
Herrmann did something similar in his unused score for Torn Curtain, which was written for sixteen French horns, nine trombones, two tubas, twelve flutes, two sets of timpani, eight cellos, and eight basses. For Torn Curtain, Herrmann’s restriction of his palette was inspired by the setting rather than the cinematography. By emphasizing the low brass and lower-pitched strings, the composer sought to find a sonic equivalent to the drab cheerlessness of life behind the Iron Curtain. Alas, Hitchcock rejected the score under pressure from Universal to produce a saleable music tie-in. The studio wanted something like the Beatles. What they got from Herrmann was more like John Philip Sousa on an acid trip.
If Herrmann’s orchestrations were the musical equivalent of a Mark Rothko painting, exploring a range of subtle shadings within a single color, Morricone’s were closer to the collage principles of Robert Rauschenberg. Just as Rauschenberg’s work juxtaposed unconventional materials and objects within a single canvas, Morricone enjoyed the wild, discordant collisions that could come by combining oddball instruments with one another. The composer is often described as a postmodernist because of his “everything but the kitchen sink” approach to orchestration. No doubt this is one of the reasons his work was so appealing to “downtown” musical avant-gardists like John Zorn.
Consider, for example, the way Morricone uses vocal textures throughout his score for The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. It features Edda Dell’Orso’s gorgeous soprano, natch. But it also features a variety of other vocal sounds, some of which border on the “unmusical.” These include the famous “coyote incipit” that has become something of a meme for the spaghetti Western more generally.
There are also plenty of other chants, grunts, and yelps that add their flavors to the musical stew. Morricone even had his singers vocalize through various trumpet mutes to produce the “wah-wah-wah” that is a motivic counterpart to the coyote incipit.
Morricone also made marvelous use of library effects to incorporate the sonic iconography of the Western into his score. We hear gunfire, whipcracks, and ricocheting bullets as elements of rhythmic punctuation throughout the music of The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. (Since cowboy yells and whipcracks both appear in the opening theme of Rawhide, perhaps both of these tactics are a sly reference to star Clint Eastwood’s television career.) Even these audacious touches are supplemented by simple, but effective solutions to musical problems. In need of a rhythmic pulse underneath the melody, Morricone coaxed Bruno D’Amario to tap the pickup on his electric guitar.
All of this suggests something very Cagean in Morricone’s approach to orchestration. It is though he took the idea of Cage’s “prepared piano” in which different objects could be laid on the strings of piano’s soundboard, and applied it to the full orchestra.
What is the sound of one wing flapping?
The Mission (1986).
Although Morricone’s spaghetti Western scores displayed his boldest experiments in orchestration, his interest in unusual sonorities continued throughout his career. Some choices are a bit more conventional than others. But they always strike me as inherently right. The oboe seems like a fairly idiosyncratic instrument for an 18th-century Jesuit missionary. Surprisingly, though, its melancholic yet dulcet melismas are a perfect complement to the big sound of The Mission’s double chorus, the latter itself inspired by the luminous sacred music of Palestrina.
Or think of Morricone’s use of the panpipe. He seems attracted to its airy timbre, using it in several scores throughout his career. Yet, comparing its appearance in both Once Upon a Time in America and Casualties of War shows that the panpipe’s sound resists any easy associations. In Leone’s gangster epic, the panpipe is introduced in “Cockeye’s Theme” in a scene where Noodles buys a one-way ticket to Buffalo. After completing his purchase, his attention is drawn to a large poster encouraging tourists to visit Coney Island. The music suggests Noodles’ memories of childhood and his grief after hearing the news that his three childhood friends all died in a battle with federal agents.
It comes back, though, at the moment when Dominic is killed by Bugsy, a rival gang member. As Morricone noted, Leone identified this scene “as a definite point of no return in the story, the watershed marking the end of youth.”
In contrast, for De Palma’s combat film, Morricone used two panpipes in the theme he wrote for the young Vietnamese woman who is abducted, raped, and killed by US soldiers. Here the motivation was something that struck Morricone in the staging of her death.
She buckles her legs like a dying bird, before tumbling down from the high ground. I imagined a theme based on just a few notes for two panpipes, which by ping-ponging their sound, evoke the slowing fluttering of a bird’s wings shortly before death.
At first blush, Morricone’s description of the scene sounds like “Mickey-Mousing” where the music accents a character’s actions, movements, or gestures. But what Morricone actually gives us turns out to be much more sophisticated. A classical Hollywood composer like Max Steiner might have caught the girl’s collapse through a downward glissando or a rapid, descending scale run. Instead Morricone gives us a different musical gesture – the alternation of two notes on the panpipe – to suggest an action not visible onscreen: a dying bird’s fluttering wings.
As is evident in the clip, we hear the two panpipes play over the image of the young woman’s broken body. Yet Morricone associatively links it to the birdlike movement seen about a minute earlier: the buckling of her knees as she falls.
A moment such as this one nicely captures Morricone’s gift for storytelling. Many of Morricone’s fans treat his scores as absolute music, often listening to them repeatedly without ever watching the films they accompany. But Morricone also had a gift for translating a film’s larger themes and meanings into musical forms.
Morricone achieved fame for his beautiful melodies, rich harmonies, and surprising orchestrations. None of that would be very meaningful, though, if these elements weren’t firmly rooted in the composer’s extraordinary dramatic sense.
The greatest?
The Hateful Eight (2015).
At the end of Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words, Alessandro De Rosa asks the composer if there was a specific moment when he realized he’d become one of the greatest, most influential composers of the century. Morricone gets flustered by the question, claiming such judgments are premature. In music, it takes hundreds of years to determine whether one’s work endures. He then adds a polite, but banal conclusion, saying it is wonderful to be appreciated and even better to have one’s music reach so many people.
Still disarmed by the question, Morricone continues hesitatingly:
The greatest of the century? It is difficult to reply….Oh dear…. where did you hear this?
De Rosa responds, “It was just to provoke your vanity…” Acknowledging the trap set before him, Morricone smiles and replies, “You don’t say….I figured!”
Morricone’s humility might be a tacit recognition that he’s had the great fortune to write music for the movies–one of the greatest engines for pleasure that the world has ever seen. A great film surely benefits from a great score. Yet it can seem that the composer is just along for the ride.
Still, Morricone understood that his music was often better than the films it accompanied. As he well knew, fortune gives with one hand and takes with the other. Morricone wrote music for masterpieces like Days of Heaven. He also worked on schlockfests like The Exorcist II: The Heretic.
Perhaps more than other craft positions, the lot of a film composer can seem unique. Music exists as its own formal system. But film scores are always written in the service of something else and judged accordingly. Directors often hope in vain that a composer can salvage a bad scene. Yet composers themselves will say they’re not miracle workers. And even when the score can stand on its own, some pugnacious critic will ask, “Should it?”
When I was doing the initial research for my dissertation during the early nineties, I recall some film music critics dividing the field into craft workers and stylists. The paradigm case for the former was a composer like Jerry Goldsmith, who subordinated his personality to the dramatic requirements of the work. Goldsmith could write a bittersweet jazz melody for Chinatown, a stirring horn call for the war epic Patton, cartoonish “Mickey-mousing” for the comic fantasy Gremlins, and outré dodecaphonic themes for sci-fi adventures like Planet of the Apes and Alien. Binge-watch all five films and it would seem hard to believe the music was all the work of a single person.
Stylists, on the other hand, were composers who had created such a distinctive sound that their music could not be mistaken for that of another. All three of the composers featured in my book seemed to fit that rubric – Henry Mancini, John Barry, and Ennio Morricone – a factor that likely contributed to the popularity of their scores in ancillary markets.
Looking back almost thirty years later, the label of stylist fits the work of Mancini and Barry quite well. In fact, I have anecdotal proof of the latter in my first viewing of Michael Apted’s espionage thriller Enigma. Halfway through film, I wondered to myself who had written the score since it sounded a lot like John Barry. Checking the poster afterward, my hunch was confirmed; it was John Barry!
For Morricone, though, the “stylist” label seems misapplied. At the time, this was due to the fact that he was so strongly associated with the spaghetti Western. He had written music for more than thirty films in the cycle and had come to define it in the public imagination. It is telling that the scores written for other spaghetti Westerns by Luis Bacalov or Riz Ortolani sound like Morricone facsimiles.
Identifying Morricone so closely with the spaghetti Western, though, ignores the inspired music he wrote for so many other genres: horror films, gangster films, thrillers, historical epics, political satires, and even the occasional romantic drama.
Take five Morricone classics not so randomly selected: Teorema, Investigation of a Citizen Above Suspicion, Cinema Paradiso, Tie Me Up! Tie Me Down!, and The Hateful Eight. Could any other composer have written the notes that we hear? Probably not. They all seem to bear the distinctive Morricone signature. Yet they are also so unlike one another that it seems unfair to suggest that he didn’t mold his sound to the specific needs of each film. For Morricone, we have to throw out the “either/or” implied by the rubric. He’s both a craft worker and a stylist.
If that seems like a copout on my part, it’s one I will happily embrace. For me, like many others evaluating Morricone’s legacy after his death, his music is both cerebral and visceral. It warms the heart and tickles the brain, sometimes simultaneously. And that seems rare for much 20th-century concert music, which even at its best, can feel quite cold and analytical.
Thirty years later, Morricone’s music still enthralls me in a way that’s unlike that of any other film composer, especially when the score is heard coming from the big screen. I’ve had the great pleasure of screening a 35mm print of The Untouchables the past two years. Hearing Morricone’s main title played back in Dolby Stereo with a proper subwoofer, I still get goosebumps. I even anticipate the massive bass drum hit that punctuates the rhythms played by brushes on the snare. If the stinging guitar chord that introduces Frank was intended to sound like a stab, that bass drum sound is the musical equivalent of a gut-punch.
Ciao, Maestro! You will be missed. Yet your music will live on, perhaps even for centuries. For my part, you’ve given me hundreds of joyful moments at the cinema and a lifetime of wonderful memories.
Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words can be found here. If you want to learn more about his music, this is a great place to start. It includes reproductions of Morricone’s handwritten musical notation. It also includes a thorough survey of both Morricone’s film scores and his concert works.
My review of Ennio Morricone: In His Own Words is here. A brief discussion of Morricone’s score for The Hateful Eight can be found in my 2016 Oscar preview. Incidentally, Tarantino used Bernard Herrmann’s rejected score for Torn Curtain for the excerpt from Rick Dalton’s action film The 14 Fists of McCluskey in Once Upon a Time . . . in Hollywood. The cue can be found here and the scene from Tarantino’s film is here.
My chapter on Morricone’s spaghetti Western scores can be found in The Sounds of Commerce.
Henry Mancini discusses his score for Wait Until Dark in his autobiography, Did They Mention the Music? Bernard Herrmann’s score for Psycho has been analyzed by several film music scholars. Among the best is Fred Steiner’s “Bernard Herrmann’s ‘Black-and-White’ Music for Hitchcock’s Psycho,” anthologized in Elmer Bernstein’s Film Music Notebook: A Complete Collection of the Quarterly Journal, 1974-1978. Details of Herrmann’s orchestrations for his rejected score for Torn Curtain can be found in the liner notes of conductor Joel McNeely’s recording. They’ve been posted here.
The chess portrait above is by Riccardo Musacchio.
Morricone waits backstage at a 2010 concert of his work at the Royal Albert Hall in London. Photo by Roberto Musacchio.