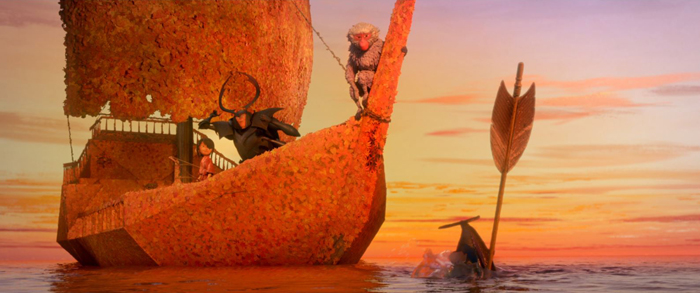Archive for the 'Film comments' Category
The ten best films of … 1933
Dragnet Girl (1933).
Kristin here –
Due to health problems, we have been reposting older entries lately and will continue to do so. Still, I could not skip this year’s contribution to the inexplicably popular series of ten-best lists for ninety years ago. Previous lists can be found here: 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929, 1930, 1931,and 1932.
Last year’s list was easy to fill with marvelous films. Surprisingly, 1933 proved to be a thin year for masterpieces. The major auteurs of Hollywood and France created relatively minor films and German filmmakers were busy finding safe places to live and work. In short, there were some obvious films to head the list, but there are some titles here that I would include in a stronger year.
Fortunately one of the greatest filmmakers hit his stride in 1933. Yasujiro Ozu made three films that could be among the top ten. I usually don’t put two films by the same director on these lists, but I’m including two of his (sorry, Woman of Tokyo). Earlier Ozu films that featured on these lists can be found in the 1930, 1931, and 1932.
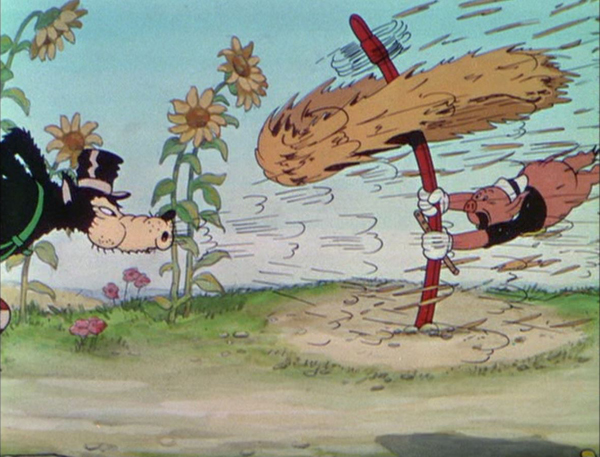
Dragnet Girl
2023 has been the 120th anniversary of Ozu’s birth and the 60th anniversary of his death. Retrospectives and exhibitions internationally have no doubt widened fans’ awareness of his earlier films. For decades almost none of his films made before Late Spring (1949) were much known outside Japan. Ozu’s gentle family dramas were so familiar that few would have believed that he began with genre films: student comedies, family comedies, salaryman comedies, and even gangster films. Now, fortunately, his entire surviving output is available on DVDs and Blu-rays, though sometimes not in versions with English subtitles.
The Criterion Collection’s Eclipse series brought the best of the very early films to DVD, including the two Ozu films on this list.
Film buffs familiar only with Ozu’s late films might well ask, could Ozu make a good gangster film? Actually, he could make a great one. Dragnet Girl is one of his early masterpieces.
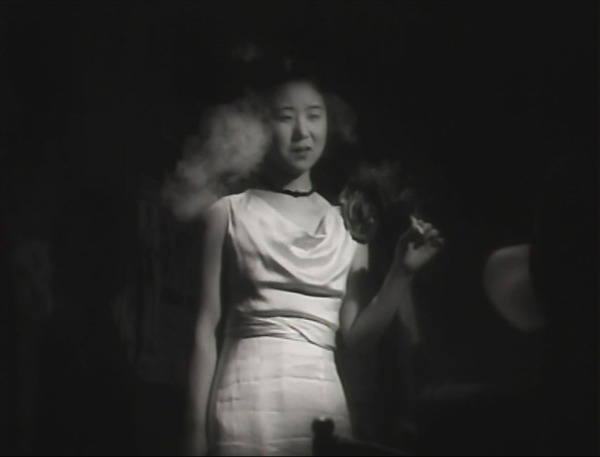
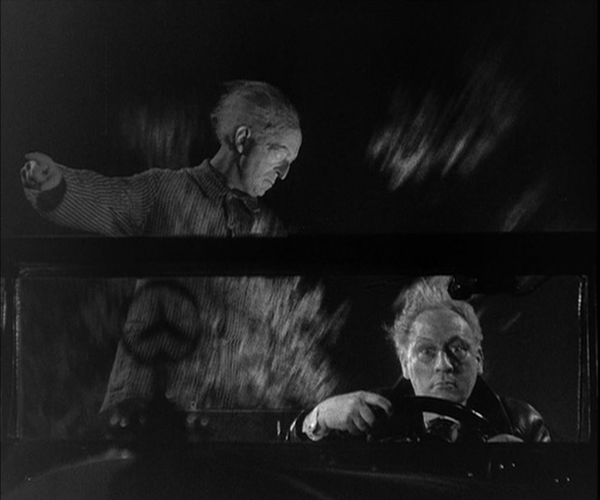
Ex-boxer Joji is a small-time thug, living of his mistress, Tokiko. An aspiring young boxer and wannabe gangster, Hiroshi, idolizes Joji and spurns his sister Kazuko’s pleas to stay in school. Joji falls for Kazuko, and Tokiko finds that she likes the girl and wants to emulate her by persuading Joji that they should leave their lives of crime. But there’s one last job …
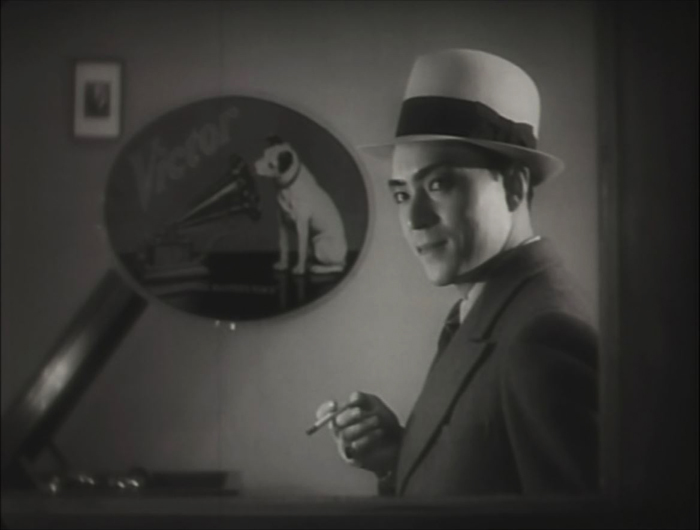
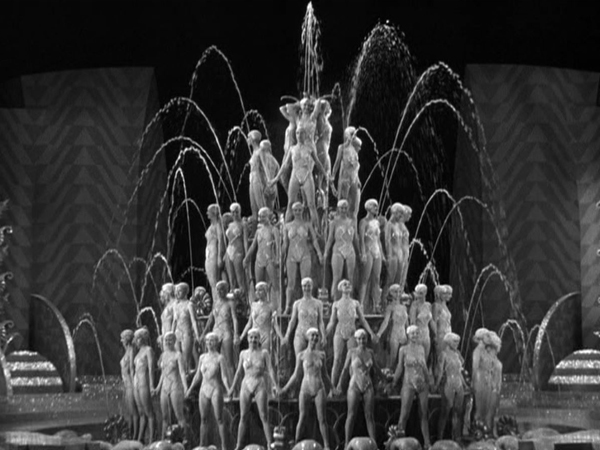
The style is quite noir, and Ozu has fun playing with the various Nipper figures and decals in the music shop where Kazuko works (see top). And Kinuyo Tanaka, best known in the West for tragic roles in Mizoguchi films, does quite well as a gangster’s moll (above).
Dragnet Girl is available on DVD in the Criterion Collection’s “Silent Ozu–Three Crime Dramas” and streams on The Criterion Channel.
Passing Fancy
As part of the slow discovery of Ozu’s work outside Japan, Western audiences finally got a glimpse of his early work when I Was Born, But … became available. As wrote last year, it “may be the one where he achieved the perfect balance of humor and poignancy that characterizes so many of his best films.” Or maybe it was Passing Fancy that struck that balance perfectly.
In a way, Passing Fancy reverses the premise of I Was Born, But …. In the earlier film, two boys become petulant and rebellious when they realize that their respected father is a mediocre salaryman taking orders from a wealthy boss and even playing the clown to entertain party guests for the boss. The parents realize the sadness of their situation but manage to handle the boys with understanding.
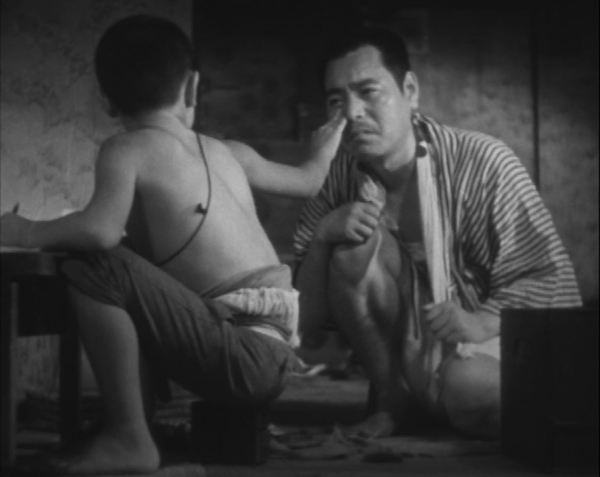
In Passing Fancy, the father, Kihachi, is an illiterature, carefree worker who approaches his duties as a single father to his bright son Tomio. Tomio acts as the parent, dragging his father out of bed, dressing him, and seeing him off to work. Tomio strives for an education, insisting on doing his homework when Kihachi tells him to go out and play. The two get into a serious argument, and their reconciliation (above) is one of Ozu’s most poignant of many poignant scenes.
As David says in his book on Ozu, Passing Fancy is more focused around complex characterization than his other early films. The secondary characters include Harue, an unemployed young woman, whom Kihachi briefly believes he can woo despite being considerably older (the “passing fancy” of the title). There is Kihachi’s cynical friend Jiro, who accuses Harue of being a gold-digger and rejects her growing love for him. The plot focuses on the characters and their changing attitudes, especially Kihachi’s alternation between fits of fatherly responsibility and selfishly neglectful behavior.
Passing Fancy is available on DVD in the Criterion Collection’s “Silent Ozu-Three Family Comedies” and streams on The Criterion Channel. The same link leads to David’s discussion on editing in Passing Fancy in our “Observations on Film Art” series. A PDF of his book, Ozu and the Poetics of Cinema, is available for free here.
Design for Living
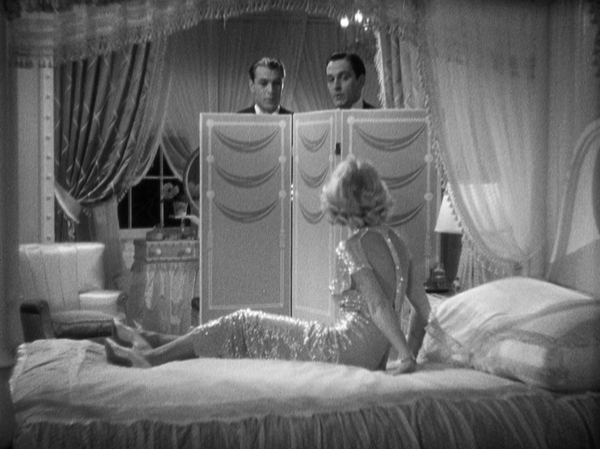
Ernst Lubitsch’s Trouble in Paradise (1932) is generally considered one of his very best films. It tends to put Design for Living in its shadow. Still, this Ben Hecht adaptation of a Noel Coward romantic comedy is nearly as good, with three marvelous stars–Gary Cooper, Frederic March, and Miriam Hopkins–and enough witty dialogue for three features.
It’s also as risqué as anything Lubitsch did, narrowly missing the introduction of the Code in 1934. The three leads, Tom Chambers, a painter (Cooper), George Curtis, a playwright (March), and Gilda Farrell, a commercial artist (Hopkins) meet on a train in France and soon move in together. They swear a gentlemen’s agreement that there will be, as Gilda forthrightly says, “No sex.” This doesn’t work out, as Gilda has affairs with both, one after the other. Eventually they reunite and swear another gentlemen’s agreement–which clearly is leading to a menage à trois.
Design for Living is interesting to contemplate in relation to the Code’s dictates that characters who transgress moral or legal strictures must be punished by the film’s end. Most obviously here the three characters end up settling into a comfy romantic trio. Beyond that, though, Gilda’s desire to become a mother of the arts by guiding the pair’s unsuccessful careers has paid off spectacularly by the end. Her pitiless criticisms of their work (“Rotten!”) goad both of them to fame and fortune. The only one punished by the end is the wealthy advertising executive Max Plunkett (Edward Everett Horton), whose brief, straitlaced marriage to Gilda ends disastrously. The Lubitsch Touch indeed.
Design for Living is available on DVD or Blu-ray from The Criterion Collection and streams on the Channel.
The Testament of Dr. Mabuse
As is well known, Fritz Lang, despite not being Jewish, left Germany for France and ultimately Hollywood in 1933 when Hitler came to power. His last German film until he returned in the late 1950s was The Testament of Dr. Mabuse. The film was banned immediately, with the German version having its premiere in Budapest. A French version, also directed by Lang but with different actors, circulated in Europe and the US, and various recut versions were circulated thereafter.
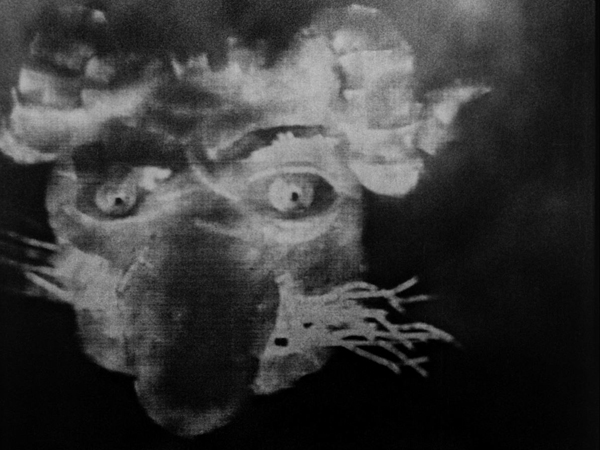
A sequel to the two-part serial Dr. Mabuse, der Spieler (which was on my top-ten list for 1922), Testament took a very different approach to its titular villain. Now Mabuse has become insane and is incarcerated in a mental institution. There he obsessively scribbles down plans for a universal reign of crime. To escape the institution, his spirit enters the body of Dr. Baum, his psychiatrist (above), who becomes his surrogate in leading the gangsters who carry out Mabuse’s plans.
The sequel is not quite up to the original, in large part because the menacing Rudolph Klein-Rogge, who played Mabuse in that film, is barely present here. We see him briefly in his cell and occasional in some sort of spirit form, but Dr. Baum is not nearly as fascinating as a surrogate Mabuse.
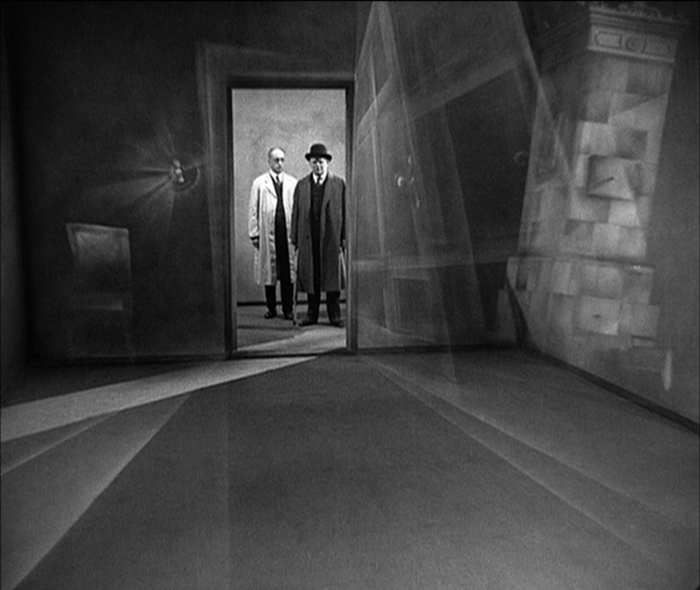
Stylistically, however, Testament is pure Lang, with high long shots along dark, deserted streets, art-deco interiors, and a spectacular fire at a gas factory. There’s also a justly famous scene of an assassination from one car to another on a crowded street. Lang also seems to bid good-bye to Expressionism, with a subjective shot from the point of view of an asylum patient (see bottom).
The Testament of Dr. Mabuse is available on DVD from The Criterion Collection and streams on the Channel. The DVD set includes the French version and a restoration of the German version missing three minutes of the original running time.
Zero for Conduct
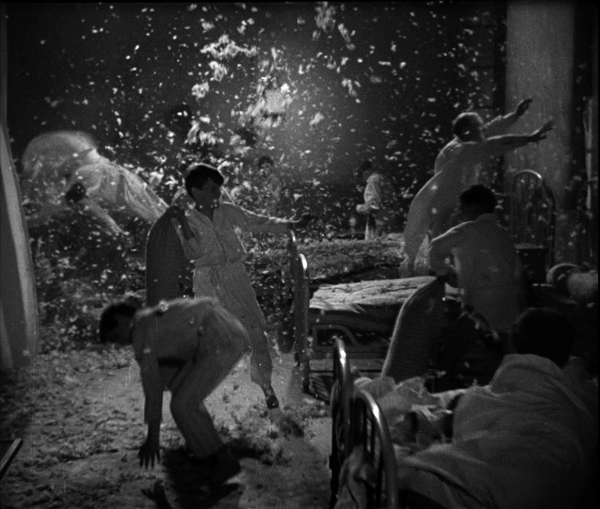
Zero for Conduct has been another victim of censorship. Jean Vigo’s depiction of the miseries in a school for mainly working-class boys and especially the rebellion that some of the foment was too much for the authorities. It was only discovered after World War II, being released in the USA in 1947 and being taken up by cinephiles and the New Wave filmmakers in France.
I first saw the film as a graduate student. It was a muddy, gray print that did not reveal to me what all the fuss was about. Modern restoration has revealed the details and the luminosity of the cinematography by Boris Kaufman, as in the nighttime dormitory rebellion (above).
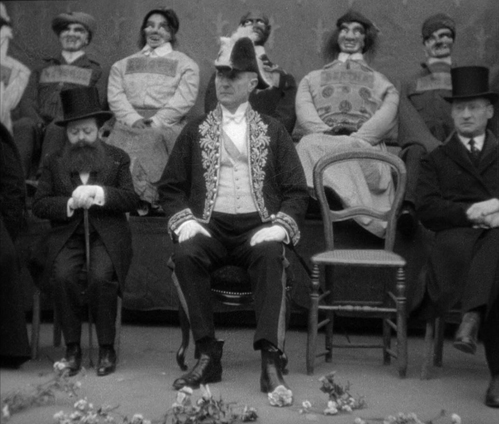
Vigo is sometimes referred to as a surrealist director. There are moments in Zero for Conduct that could be described as surrealist, as when the one kind teacher Huguet, draws a carticature while doing a hand-stand or the life-sized dummies that represent the attendees at the school fête where the rebellion breaks out. On the whole, however, the odd touches seem more to represent the way the children see the world, for the film is told largely from their vantage points.
Zero for Conduct is available in its restored version on DVD or Blu-ray in the set “The Complete Jean Vigo” from The Criterion Collection and streams on the Criterion Channel.
A Night on Bald Mountain
It’s not often that a completely new animation technique is introduced, but it happened in 1933. Claire Parker and Alexander Alexeieff had invented the pin board or pin screen method. It involved a perforated board three by four feet, with hundreds of thousands of headless pins stuck through it. By pushing pins forward selectively and casting a raking light across the board, they could create images that resemble moving engravings.
A Night on Bald Mountain is set to Mussorgsky’s tone poem. There is no narrative, only a series of unconnected, disturbing images pass quickly across the screen, often morphing from one shape to the next. The result, as the above images suggests, is eerie indeed.
Given the labor-intensive work required on each film, the pair produced a small number of animated shorts across decades, supporting themselves by making many advertising shorts. The Wikipedia entry on Alexeieff has an excellent summary of the couple’s career and an extensive filmography.
Most prints of A Night on Bald Mountain are too dark. A restored version is included in Flicker Alley’s essential DVD/Blu-ray collection, “Early Women Filmmakers: An International Anthology.” It streams on The Criterion Channel.
Footlight Parade
1933 was a remarkable year for the series of Warner Bros. musicals famous for their numbers staged and choreographed by Busby Berkeley. No fewer than three major titles were released that year: 42nd Street, Gold Diggers of 1933, and Footlight Parade. I can’t put all three on the list, and I suspect the general opinion is that Footlight Parade is the best of the entire series.
It’s far livelier than the others, with the crazy premise that a company forms a service delivering live stage prologues to movie theaters. The result is a frantic race to get from one theater to the next. It has James Cagney, whose fast patter and unique, jittery dancing style injects an energy that offsets the bland Dick Powell. It has a string of big numbers, from “Honeymoon Hotel” to “By a Waterfall” to “Shanghai Lil,” all showing Berkeley at his flamboyant best.
Footlight Parade is available in Blu-ray and other formats from Warner Bros. The image above was taken from a DVD in “The Busby Berkeley Collection,” a bargain boxed setwith five films and a documentary.
Duck Soup
Speaking of surrealism, the Marx Brothers ended their five-film contract at Paramount with what is widely considered their best film, Duck Soup, directed by Leo McCarey.
At Paramount, the brothers were allowed to create messy scenarios without the logic and unity dictated for most Hollywood films–including those made at MGM under the dictates of Irving Thalberg. The result is a series of comic set pieces loosely held together by a plot involving the tensions between two Ruritanian countiries, Fredonia and Sylvania.
The most famous of these set pieces is the mirror scene, where Pinky (Harpo), dressed as Firefly (Groucho), struggles to hide the absence of a broken mirror by mimicking his actions perfectly. Rather than confronting Pinky, Firefly devises ever more elaborate movements to reveal the ruse, inevitably copied flawlessly by Pinky (above). Other comic highlights that have nothing to do with the plot involve Pinky and Chicolini (Chico) running a peanut stand and carrying on a feud with the neighboring lemonade stand run by the master of the slow-burn, Edgar Kennedy.
This feud foreshadows the battle scene at the climax of the film. Staged entirely in the Fredonia headquarters, the action becomes increasingly nonsensical, with Firefly’s military outfits changing at frequent intervals and madcap dispatches coming in from the front.
Duck Soup also has the advantage of not including either of the hitherto obligatory harp and piano solos by Harpo and Chico. There are no such “serious” interludes or subplots involving young lovers, as there would be in A Night at the Opera and other later films. It’s the Marxes’ only film with unadulterated crazy humor throughout.
Duck Soup is available on Blu-ray and other formats here. The same range of formats are available for “The Marx Brothers Silver Screen Collection,” which contains their five Paramount films.
King Kong
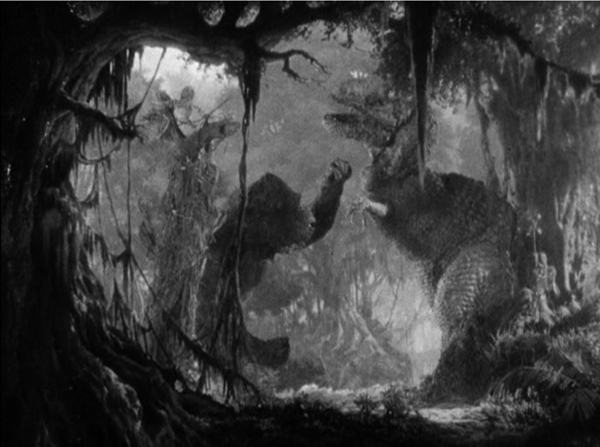
King Kong was released only a few years after Universal had seemingly identified ed the horror genre with vampires, sub-human monsters, and old dark haunted houses. Kong was different, a monster that could be sympathized with. Viewers could attribute human feelings to Kong as he saves Ann Darrow from a tyrannosaurus (above). As documentary filmmaker Carl Denham remarks, the giant gorilla’s affection for Ann turns the plot into a beauty-and-the-beast tale.
The film also added a touch of novelty by having Kong climb the Empire State Building, which had been opened to the public only two years earlier.
The impact of the film was no doubt enhanced by Max Steiner’s revolutionary musical track. It used leit motifs and a large orchestra, and the music played for a larger portion of the film than was usual in early sound films.
King Kong also expanded the methods of special effects available to filmmakers with its extensive use of Willis H. O’Brien’s puppet animation for Kong and the dinosaurs of Scull Island. (As I discussed in a previous post, O’Brien’s puppet animation was used extensively eight years earlier in the 1925 version of The Lost World.)
King Kong is available on Blu-ray from Warners. My image is from the out-of-print “Two-disc Special Edition” on DVD.
The Three Little Pigs
Despite being a major force in the American film industry by this point, Walt Disney has been little-represented in my lists. So far only The Skeleton Dance (1929), the first of the Silly Symphonies, has represented his output. The Three Little Pigs wasn’t a technical milestone in Hollywood animation. The first three-strip Technicolor short was Disney’s bland Flowers and Trees, which won the 1932 Oscar for an animated film (the first years this category was included). The Three Little Pigs won for 1933. In 1994 a large group of professional animators voted it number eleven on a list of the fifty greatest animated shorts. (An interesting list available here.)
Obviously people like the film a lot. It grossed ten times its production cost. It’s considered a classic. It has all the advantages of the best Disney shorts–beautiful color, fast action, and a catchy song, “Who’s Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf?” It’s also quite funny. The framed pictures on the walls of the three pigs’ houses are easy to miss, but they characterize each pig cleverly.
The Three Little Pigs is available from multiple sources. My frame was taken from the “Walt Disney Treasures: Silly Symphonies” DVD set. The “Treasures” series, recognizable by its aluminum cases, is out of print and hard to find, though there are a few copies available on eBay. (The same version has been posted on YouTube, but beware, it is distinctly out of focus.)
The Testament of Dr. Mabuse (1933).
DIE HARD revived: An entry revisited
Die Hard (1988).
David’s health situation has made it difficult for our household to maintain this blog. We don’t want it to fade away, though, so we’ve decided to select previous entries from our backlist to republish. These are items that chime with current developments or that we think might languish undiscovered among our 1094 entries over now 17 years (!). We hope that we will introduce new readers to our efforts and remind loyal readers of entries they may have once enjoyed.
Today’s revival responds to the return of Die Hard to theater screens in time for Christmas. Since our original posting in 2019 (“Not just a Christmas movie”), this supreme action picture has further cemented its reputation as a yuletide favorite (although it was originally released in July). Happy holidays from the Nakatomi Corporation!
DB here:
It’s been quite a fall season for UW–Madison film culture. There were visits from avant-garde legend Larry Gottheim, New York Times co-chief film critic Manohla Dargis, Schawn Belston (Senior VP of Mastering at Disney), and Julia Reichert, whose American Factory is now routinely turning up on ten-best lists. The semester’s first screening at our Cinematheque was Kiril Mkhanosvsky’s Give Me Liberty, a Milwaukee movie also gracing year-end best lists. Our programs included restored films by African pioneer Paulin Soumanou Vieyra, retrospectives of Reichert and Kiarostami, a 3D double feature of Revenge of the Creature and Parasite (no, the other one), a program of early women directors in America, a selection of films conserved by the Chicago Film Society, and a miscellany ranging from Olivia and Near Dark to Tropical Malady and Red Rock West.
Travels to festivals, partly covered in our blog entries, forced us to miss too many of these shows. But we couldn’t miss the final one: Die Hard (1988).
It’s a film I’ve admired since I first saw it in summer of 1988. I’ve taught it in many classes, but never written about it. Seeing it again, in a pretty 35mm print from the Chicago Film Society, has made me want to say a few things as my final blog entry for this busy year.
The man between
Think-piece pundits like to say that Hollywood movies are about good guys versus bad guys. But usually things are more complicated. Very often the good guy is an outsider caught between two large-scale forces, good or bad or both–the cattle ranchers versus the townspeople, or the mob versus the cops. Often the protagonist is an outlier, forced to solve the problem using means that respectable social forces can’t.
Call it the problem of the House Democrats. When the lawbreaker can’t be brought to justice, how do you make him pay? The answer is one that William S. Hart movies provided in the 1910s. We need a “good bad man,” a rogue agent who knows the scheme from the inside but is willing to do the right thing. Which means that he has to be flawed too, a little or a lot, and that he can eventually reform.
In Die Hard, the forces of law and order line up as the Los Angeles police and the FBI. The threat is Hans Gruber’s gang, posing as terrorists but actually planning to rob the Nakatomi Corporation of $640 million in bearer bonds and kill lots of hostages in the process. The naive TV broadcasters support both, recycling official scenarios of how hostage-taking works and reinforcing the gang’s masquerade as a terrorist group.
The contrasts are marked. The forces of order are American, in alliance with a Japanese company, while the attackers are Europeans. At the start, we hear American music (the rap played by the limo driver Argyle), but Hans hums Beethoven. The cops’ technology notably fails, as when the assault vehicle and a helicopter are consumed by firepower. But the gang’s hi-tech expert Theo can crack the vault, assisted by Hans’ plan to push the Feds to cut the building power.
Above all, the forces of social order are strikingly inept, while the gang is ruthlessly efficient. Unlike the police, who “run the terrorist playbook,” Hans boasts that he has left nothing to chance. The cops can’t imagine an adversary that exploits the official by-the-book procedures. As for the business types, Takagi’s calm bluff and Ellis’s freewheeling jargon can’t cope with a gang leader who doesn’t get the Art of the Deal.
Clearly, America and Japan need help. That appears in the form of John McClane, the cop from the East Coast trapped in Nakatomi Plaza.
McClane is the man between, spatially and strategically. He witnesses the action from inside the skyscraper, and bit by bit he figures out the gang’s real scenario. And he’s caught between both forces. The gang tries to find and kill him, while the cops refuse to recognize him as an ally. Confronting Karl’s brother early on teaches McClane that he can’t play by procedure. (“There are rules for policemen,” says a thug who doesn’t believe in rules.) The LAPD’s ineptitude shows that McClane can’t expect help on that front. So he must become almost as reckless as his adversary, though in a virtuous cause. This principally means blowing stuff up.
McClane isn’t totally without resources. He has as helpers Al, the desk cop who comes on the scene and sustains his morale, and Argyle, who’s there to play a crucial role at the climax. But mostly he’s alone in facing problems. He needs weapons. He needs shoes. He needs to protect the hostages, most of all his wife Holly, who has climbed up the corporate ladder. (In another movie, she would be the in-between protagonist.) To keep Holly from becoming a bargaining chip, McClane needs to hide his identity. And he needs to figure out the gang’s ultimate plan, of seeding the rooftop with explosives that will destroy the building and cover their escape.
John’s solutions are notably low-tech. While the police and the gang depend on advanced firepower and computer finagling, McClane lashes an explosive to a desk chair and uses a fire hose as a rope. He has to improvise shoes by taping a maxi-pad to a bleeding foot. No holster for your automatic? How about some Christmas wrapping tape? And don’t forget to taunt your adversaries with Yankee wisecracks.
In the course of this drama, the very physical McClane becomes a model for his allies. Holly punches the reporter who revealed John’s identity, and Argyle cold-cocks Theo at the point of getaway. Most dramatically Al kills the revived Karl when he’s about to plug McClane. The people in between take up arms.
McClane and his allies solve the House Democrats’ problem. Law can’t be lawless, even in protecting itself. Business, always aiming at the bottom line, has to give up principles. (“Pearl Harbor didn’t work out, so we got you with tape decks.”) These forces of social order are inefficient, trusting, and superficial. They can’t stand up to sheer brutal onslaught. In a crisis they will fold, or simply choose the nuclear option: agents Johnson and Johnson are ready to lose a big chunk of hostages.
McClane is a mediating figure that permits the film to show you can be strategically lawless for the sake of lawfulness. The fly in the ointment, the monkey in the wrench, screws up plans on both sides, but for the benefit of everyone else.
The Big Dumb Action Picture isn’t so dumb
This thick array of thematic parallels would be interesting in itself, but it gets worked out through precise storytelling. There was a time when critics knocked action movies as simply ragbag assortments of fights, chases, and explosions. Die Hard, I think, changed ideas of just how well-wrought an action picture could be. About 53 minutes of it consist of physical action (including people sneaking around), leaving almost 70 minutes for other stuff: suspense, changing goals, surprise information, attention to parallel plotlines, and little moments like the thief pilfering candy just before an ambush.
The film typifies tidy classical Hollywood construction, beginning with an arrival (the jet) and ending with a departure (the McClanes in a limo). In between we get a big dose of the classic double plotline, romance and work. Holly’s job at Nakatomi threatens their marriage, and John takes on a temp job, that of fighting the gang, which also endangers the couple’s efforts to reconcile.
For every Superman, there’s a Kryptonite, and here the protagonist’s flaws include his fear of heights (set up in the second shot, reiterated throughout) and, more importantly, his resistance to Holly’s independence. By the end, he’s learned a lesson. The film’s streak of male sentimentality allows John to ask his wife’s forgiveness for blocking her career ambition. She’s ready to compromise too, reassuming his last name when she meets Al. The characters we care about change, at least a little. That could be the motto of most classical Hollywood plots.
As usual, we get crosscutting among several lines of action. John’s arrival is crosscut with Holly at work fending off Ellis, and in the rest of the film the gang’s stratagems are intercut with the cops’ plans and McClane’s efforts. At various points, five or six actions are alternating with one another.
All these escalating situations cluster into distinct parts, the four that Kristin has argued for as typical of Hollywood architecture.
The Setup runs about 33 minutes, culminating in the murder of Takagi and Hans’s promise that he can open the vault.
The Complicating Action, a counter-setup, coalesces around John’s goals of communicating with outsiders, avoiding capture, and attacking the thieves when he can. Through many chases and fights, the gang seeks to block all these efforts. The lines converge when John shoots Marco and tosses his body onto Al’s car. He gains the bag with the detonators, giving him the upper hand. Then the TV reporter gets involved, the cops arrive, and John is ordered to wait. Things seem to be stabilized.
After this midpoint, the Development supplies what Kristin calls “action, suspense, and delay.” Officer Dwayne Robinson arrives, pitting himself against Al and McClane. We can regard the police assault, Ellis’s clumsy attempt to broker a deal, and the arrival of the FBI men as a series of delays that endanger the stability of the standoff. At the end of this section, John meets Hans (posing as an escaped hostage): now both men know each other. And in the firefight that follows, John loses the detonators. Hans declares, “We’re back in business,” and the original plan can go forward.
The last twenty-five minutes constitute the Climax, launched by McClane’s “darkest moment.” He seems utterly beaten. Picking glass shards out of his feet, he gives Al a message for Holly over the CB radio. Al tells of his own burden, the accidental shooting of a child. The stakes are now very high.
Rapid crosscutting shows John finding the bombs on the roof and fighting with Karl, while the FBI helicopter attacks the building and Hans discovers that Holly is John’s wife. John stampedes the hostages down the stairs off the roof and escapes the strafing from the chopper before it blows. Argyle dispatches Theo, while John finds the surviving gang members in the atrium and shoots Hans, who falls to his death.
In the Epilogue, Al and John meet, Al dispatches Karl, Holly socks the newsman, and John and Holly drive off with Argyle.
These parts present a tight, logically building plot composed of swiftly changing situations. Along the way we encounter a great many motifs that create echoes or contrasts. Everyone notices the Rolex, at first a symbol of Holly’s talents but also of corporate swagger; only by unfastening it can they let Hans drop from the window. When Argyle floats the possibility that Holly will rush back into John’s arms for a movie ending, John murmurs: “I can live with that.” Agent Johnson speaks the same line, but for him it means an acceptable level of civilian casualties.
Holly’s unmarried name, Gennero, shows how a motif can develop in relation to the drama. At first it’s a sign of pride in her own identity (typical corporation, Nakatomi has misspelled it on the touch screen). Her name-change triggers the couple’s quarrel, but it has another narrative use: It conceals John’s identity from Hans. And at the end he introduces her to Al as Gennero but she reasserts her love by correcting him: “Holly McClane.”
Then there are differences of class and country. Hans reads Forbes, but McClane the US boomer references Roy Rogers and Jeopardy. (Hans is so unplugged from pop culture he thinks John Wayne was in High Noon.) Argyle the former cab driver and Al the cop know the downside of city life, but so does John the New York detective, who adapts Roy’s trademark phrase to the mean streets: “Yippee-ki-yay, motherfucker.”
Even a conventional Hollywood gesture, that of attacking a picture of a loved one, acquires a nifty plot function. Annoyed at John, Holly slaps down the family portrait on her shelf. Good thing too, because otherwise Hans would have seen it during the invasion. We’re reminded of that picture when in a moment of quiet John looks at the same snapshot in his wallet. Only after Hans has encountered John is he able to flip the portrait back up and realize that Holly is the “someone you do care about.”
There are lots more felicities like these–so many that I’d consider Die Hard a “hyperclassical film,” a movie that’s more classically constructed than it needs to be. It spills out all these links and echoes in a fever of virtuosity. Hard to believe that the makers started shooting without a finished script.
Intensified continuity, personalized
Die Hard is a good example of a stylistic approach I’ve called “intensified continuity.” It’s a modification of the classical method of staging, shooting, and cutting scenes. Here director John McTiernan and DP Jan de Bont tweak that approach in distinctive and powerful ways. You can find examples all the way through the movie, but I’ll draw most of my illustrations from the first hour, when the stylistic premises get laid out for us.
Cutting speeds accelerated sharply in Hollywood films from the 1960s onward, and for its time, Die Hard was a rapidly-cut movie. The average shot runs just under five seconds, about what you’d get in a 1920s silent film. By today’s standards, which fall more in the 3-4 second range (even for movies outside the action genre), it’s a bit sedate.
One factor that increases the cutting pace is a greater reliance on singles and close-ups. These are tighter than we’d expect in most studio films of the classic era.
Even in close-up, the shots aren’t snipped free of their surroundings, thanks to the wide frame and layers of focus–both important in the film’s overall style, as we’ll see.
Likewise, intensified continuity exploits a greater range of lens lengths than we’d find in studio films of the classic era. We get wide-angle shots like those above along with telephoto shots throughout. Here the long lens is used to pile up people around Holly, and an even longer lens shows her optical viewpoint on the bandits in the office.
And there’s a free-roaming camera, thanks chiefly to Steadicam technology. But interestingly, Die Hard avoids some of today’s most common camera movements, such as shooting a fixed conversation with a sidewise or circular tracking shot. These would become more common in the 1990s.
McTiernan thought a lot about his camera movements, as he explains in interviews and the commentary track on the DVD. He wanted to shape spectators’ attention, to use camera movement to nudge things into view. “The audience’s eye wants to go with you.” Accordingly, more than in many contemporary films, Die Hard‘s camera movements have a shape: they end on a point of information.
Sometimes it’s just a quick pan, doing duty for a cut. At other times, the reframing is a gentle nudge that prepares for a new scenic element, as when Holly enters her office.
In shooting Predator (1987), McTiernan wanted to cut moving shots together, but his editor resisted. For Die Hard, he refilmed his camera movements at different rates so that two would match. A good example is when Karl’s brother strides carefully into an area under construction. The camera tracks with him, but when he turns to find the source of a whining noise, the arcing movement at the end of one shot is picked up in the next as the framing circles to reveal the saw.
That reveal is given, characteristically, in rack focus. I could have added rack focus as another featured technique of intensified continuity. McTiernan and de Bont take it very far, making Die Hard one of the great rack-focus movies. The image is constantly shifting focus to guide our attention to the changing layers of the scene.
This neat, compact presentation not only preserves the commitment to long-lens close-ups we find in intensified continuity. The technique also gives each rack focus the snapping force of a cut. (And you don’t need to build big sets.) Needless to say, the rack-focusing wouldn’t work if McTiernan hadn’t committed himself to staging his action in depth. More on this below.
Staging in ‘Scope
Die Hard finds ingenious ways to “let the audience’s eye go with you” in the widescreen format. Sometimes it’s a matter of classic edge framing. Thanks to a low angle, John and Holly converse along a wide-angle diagonal.
Sometimes McTiernan reverts to a technique not enough directors use nowadays: blocking and revealing. In classic cinema that was usually a technique reserved for long shots, when actors could move aside as part of ensemble. Die Hard applies blocking and revealing to the tight framings of intensified continuity.
A thug in an elevator checks his weapon, pivots for an instant, and then moves aside to show the elevator arriving at the target floor.
Here again a rack focus helps. The moment reiterates the importance of the thirtieth floor in the skyscraper’s geography.
When Hans finds the body of Karl’s brother, we can study his expression. He flips the victim’s head to reveal a gunman, who looks to Hans before he says his line.
In a neat touch, the thug’s mouth isn’t shown. Today a director would probably show his whole face, but, really, who cares? The careful framing keeps him a secondary character, and a future target of McClane. And no need to rack focus on him, which would give him unwonted importance. All we need to remember him is that he’s the thug with long hair.
I can’t refrain from using one audacious example from late in the film. John and Hans have met, and Hans has revealed himself by targeting John with the pistol McClane has given him. In reverse shot, John reveals that it has no bullets and grabs it away from Hans.
But the pistol, and that gesture, have concealed the elevator behind them. When the pistol is knocked down, the elevator light pops on in the background. Our attention snaps to it, aided by that characteristic ping we hear throughout the movie (another motif).
The crisp turn of events, given visually and sonically, gets ampified by the acting. McClane’s cockiness turns to panic and Hans gets the upper hand. (“Think I’m fucking stupid, Hans?” Ping. “You vere saying?”)
The most bravura rack-focus comes during the climax, when the firehose reel whizzes down behind McClane and he realizes that he’s being dragged through the shattered window.
The coordination of the long lens, camera movement, staging, and racking focus is especially rich when Hans drifts among the hostages searching for the man in charge. He recites Takagi’s life history as he passes from one possibility to another (including, comically, Ellis).
At the climax of the passage, McTiernan’s staging-in-layers sets up Takagi, Karl, and Holly before Takagi takes charge. Briefly blocked by Hans, he admits his identity by stepping out from behind and into focus.
McTiernan isn’t done. A reverse shot of Hans finishing his spiel (“…and father of five”) punctuates the suspense. McTiernan buttons up this passage by returning to his “moving master” shot and having Karl shove Takagi out.
That clears the way for us to see Holly’s reaction. A beat dwells on her as she shifts her eyes to Hans, foreshadowing her conflict with him at the climax.
This sort of layering of faces popping in and out of visibility has precedents in earlier cinema, chiefly of the “tableau” period of the 1910s. McTiernan has, I think, spontaneously rediscovered for modern times what William C. de Mille was up to in the party scene in The Heir to the Hoorah (1916). (For more on that, go here.)
Of course McTiernan also has to work with the 2.35:1 anamorphic format, which enables him to spread his layers out more. That format also allows some remarkable compositions, such as the one surmounting today’s entry. The cut to the shot of John in Holly’s office uses the abstract splash painting (seen here for the first time) as a visual analogy for the explosion of gunfire offscreen at the same time.
McTiernan and de Bont constantly find striking but cogent images, thanks to lighting as well as color and format. Here’s McClane on top of an elevator peering through the perforated grille; his POV is a striking but still informative composition. the cut between the two provides a little punch of contrasting light and shade.
There are felicities like these feathered all through this remarkable movie, but the momentum of storytelling never flags. This remains a masterpiece of Hollywood filmmaking.
Thanks to our readers for following us this year. Kristin will be weighing in soon with her annual list of best films from ninety years ago. In the meantime, HO-HO-HO.
Madison owes an enormous debt to our Cinematheque team: programmers Jim Healy, Mike King, Ben Reiser, and Zach Zahos, as well as veteran projectionist Roch Gersbach. Santa should reward them. You can too by visiting the Cinematheque’s Podcast, Cinematalk. There you’ll find conversations with Manohla Dargis, Schawn Belston, and James Runde.
For lots of background on the making of this film and the four sequels, there’s Die Hard: The Ultimate Visual History by Ronald Mottram and David S. Cohen. At rogerebert.com, Matt Zoller Seitz has a discerning appreciation on the occasion of the film’s twenty-fifth anniversary.
Jake Tapper has provided the definitive analysis of Die Hard as a bona fide Christmas movie.
McTiernan (with whom I share an alma mater) provides very good DVD commentaries (even for Basic). Prison also seems to have given him some pronounced political views. Alas, the website he created as a platform for them is apparently no longer available. Word is that McTiernan is preparing a new film, Tau Ceti 4, with Uma Thurman. A videogame promo is purportedly signed by him.
Of other McTiernan films, I also much admire The Hunt for Red October (1990). The Thomas Crown Affair (1999) seems to me better directed than the original, and The 13th Warrior (1999), despite being taken out of his hands, remains a pretty interesting film. (Name another Hollywood movie in which a Muslim poet visiting Northern Europe is justly appalled at its barbarism.) Nomads (1986) also has its good points.
I discuss the issues of narrative and style raised here at greater length in The Way Hollywood Tells It: Story and Style in Modern Movies. You can also search “intensified continuity” for blog entries hereabouts. On CinemaScope aesthetics, see this entry and this video.
Die Hard (1988).
Thank you, Lignan
DB here:
On 2 November, Lignan University of Hong Kong conferred upon me an honorary doctorate. My health situation kept me from attending, but I sent a statement of thanks. I’m grateful for the honor, and for Professor Darrell Davis for reading it at the ceremony (pictured above). Here it is.
I am deeply proud to receive an honorary doctorate from Lingnan University. It is one of the jewels in the crown of Hong Kong higher education. I have enjoyed my many visits to the campus and have made many friends during that time. Conversations with them have inspired me to improve my work.
I fell in love with Hong Kong film before I came to love Hong Kong. In the 1970s I was deeply moved by Bruce Lee’s films beyond their obvious visceral appeal, they showed a young Chinese man standing up for justice and righteousness. I now realize that Bruce Lee embodied the dignity and compassion for others that remain central to the spirit of Hong Kong itself. In the years that followed, my appreciation of Hong Kong cinema grew, and I was inspired to express my ideas in a book on it. As I became more acquainted with its many fine filmmakers and the craftspeople who supported them, I came to realize that the same spirit has continued in this film culture.
My admiration for Lingnan, therefore, is part of my overall respect for the excellence of Hong Kong cinema and of the community it represents.
I regret that my health situation does not allow me to participate more fully on today’s occasion, but remain assured that my heart is with Lingnan University, its students and faculty, as well as the people of Hong Kong.
My thanks to the University, to Professor Davis and Profesor Emilie Yeh Yueh-yu (below), and to Ginn Fung Kai Chun and Amy Pang Wing Si for their kind assistance.
“Best Picture” ≠ “Live Action”
Wreck-It Ralph (2012).
Kristin here:
Way back in 2006, I posted a long piece on the increasing prominence of animated features being released each year. This was in the infancy of the blog, and the entry shows it–few photos, inserted as thumbnails. We only gradually worked up to our format of posting plenty of illustrations. By contrast this current contribution offers plenty of visual pleasure.
Basically I argued three points. First, that by their nature animated films would tend to be among the highest-quality films in any given year, despite their relatively small number in those days.
My argument laid out some reasons for this high quality. First, the fact that animated films were perforce thoroughly planned in pre-production, meaning that every detail was carefully considered. This means that relatively few inadequate scenes are reworked in production. Live-action films these days tend to be heavily dependent on shooting lots of coverage and making many decisions in the editing stage. Not true of animated films. Similarly, the soundtrack is recorded in advance and the images animated to sync with it. Hence the sound is meticulously planned. The voice actors record their voices and leave, usually not hanging around to try and change their scenes during shooting or fluffing lines and thus requiring multiple retakes of scenes.
My second point addressed the opinion, widely circulating in the trade press, that the spread of animation, and particularly digital animation, was a mistake. I quoted a recent Screen International article: “Much has been made this year of the seeming over-saturation of studios’ computer-generated titles, with critics and analysts pointing to growing movie-goer apathy.” I pointed out that such a claim didn’t fit the facts: “As a proportion among the total number of films made, CGI’s box-office successes seem fairly high compared to live-action films.”
My third point was that American distributors did not know how to market films from abroad, so that Ghibli and Aardman titles did not get nearly the audiences they deserved. Since then the distributor GKIDS has shown that it’s possible, at least for a relatively small company, successfully to release such films. They currently offer films with eleven best-animated feature Oscar nominations (with one win, Spirited Away), having gained distribution rights to Ghibli films, previously controlled by Disney.
Since I wrote that entry, the number of animated films, mostly digital, released yearly has sharply increased. And the disproportionate number of those animated films that appear among the top hits of the year continues to demonstrate that people are not apathetic. The spread of streaming services, combined with the decline of theatrical attendance during the pandemic, make it difficult to judge the success of films. Going back to 2019, where it’s a bit easier to judge, the top ten films included two animated successes, Toy Story 4 and Frozen II. An additional two were in the top twenty, How to Train Your Dragon: The Hidden World and The Secret Life of Pets 2. Animated films did not make up 20% of all films released, but that’s the portion of the top twenty they occupied.
I followed up that entry with one that found additional evidence that animated features were doing well, including the fact that Ice Age: The Meltdown was, though not the top box-office film of 2006, the most profitable film of that year.
So many developments have occurred in the world of feature animation since that first post that I decided to write an update.
The neighborhood is getting crowded
To some extent today’s update was inspired by a recent online post concerning new competition for Disney, which had absorbed Pixar and easily led the box-office race for years, with Dreamworks a second-run. Current developments led Alexandra Canal to point out some interesting figures. In 2022, Disney’s box-office total was $1.93 billion in ticket sales, for 26% of market share. Universal, number two, generated $1.64 million, for 22%, and Sony’s box-office coming in at a mere $834.8 million, or 11%. But things are changing. Other studios’ investments in building animation wings have started to challenge Disney’s dominance of the market for these films.
So far in 2023, as of July 1, Universal has The Super Mario Bros. (released April 5) at number one on the top-grossing list and over $1.3 billion worldwide. Sony has Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse (June 2) at number four and approaching $620 million worldwide. By contrast, Disney has had two flops in recent memory: Lightyear (which I found mildly entertaining but not what I expect from Pixar) under-performed last summer, and Disney’s own Strange World (November 23) ended up with less than $74 million. Disney’s film in the top ten is the live-action version of The Little Mermaid (May 26), at number five with just over half a billion.
It will probably take several years for the long-term effects of streaming and the theatrical distribution recovery (if any) will have on Disney’s dominance. Still, it seems that the other Hollywood studios’ move toward creating their own animated departments is succeeding to some extent. The trend toward a greater variety of animated films may last.
Best Animated Feature or Best Picture? Which will win?
For this entry I have picked a rather arbitrary method of comparing quality animated films with quality live-action ones. I’m going to look at the Best Animated Films Oscar winners and nominees in comparison to the Best Picture ones.
Every now and then someone points out that such excellent animated films are now being turned out regularly that it would be logical to nominate the best of them for Oscars in the Best Picture category. There has never been a rule against such a crossover. So far it has only happened three times: Beauty and the Beast (1991, before the Best Animated Feature category existed), Up (2009), and Toy Story 3 (2010). None won, though they did take home Oscars in their own race. Other categories are technically open to animated films. Seven have been nominated for best screenplay, all Pixar films, with none winning.
A somewhat comparable situation has happened in the Foreign Language category. We tend to forget, but ten foreign-language films have been nominated for Best Picture: Grand Illusion (1938), Z (1969), The Emigrants (1972), Cries and Whispers (1973), Il Postino (1975), Life Is Beautiful (1998), Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon (2000), Babel and Letters from Iwo Jima (both 2006), Amour (2012), Roma (2018), Parasite (2019), Minari (2020), Drive My Car (2021), and All Quiet on the Western Front (2022). Oddly enough (maybe there was some change of rules), starting in 1998 with Life Is Beautiful, six of these also got nominated for Best Foreign Language film: Life Is Beautiful, Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, Amour, Roma, Parasite, Drive My Car, and All Quiet on the Western Front. All of them won in the Foreign-Language category, but only one, Parasite, won Best Picture as well. Presumably if a film was good enough to be nominated for best picture, it certainly would be good enough to win the Foreign-Language Oscar.
The same was true for animated films. Up and Toy Story 3 were nominated in both categories and won just the animation awards. (The animated feature award was started in 2002 for films released in 2001, so Beauty and the Beast could not do the same.)
Now we turn to another way of looking at the Best Picture and Best Animated Feature categories. If one is on Facebook, as I am, or, presumably, other social-media sites, as I am not, in many years one reads many vociferous complaints about the quality of the Best Picture winners. Since online people love lists, there are plenty of people weighing in on the ten worst films to have won that prize. These ten are usually fairly recent, since these online commentators usually don’t watch older films. Occasionally someone mentions Cavalcade (1933), but those are the real cinephiles.
I’m going to compare the Best Picture and Animated Feature nominees and winners, starting in 2002, when the latter category originated (for films released the previous year). The questions are, are some of the animated nominees and/or winners better than the live-action films that won Best Picture in the same year, and if so, how often does this happen? This is not, of course, to say that the Oscars are a true reflection of the cream of the crop, especially in the live-action Best Picture category. The best animated films (at least, English-language) tend to rise to the surface in terms of nominations because there simply are so few of them in comparison.
Logically, having chosen the Oscars as a means of comparison, I should compare all the excellent nominated animated films with all the excellent nominated live-action films. After all, the film or films deserving to win seldom do so. Maybe some of them are better than the animation winner. I’m not going to include all the nominees, because first, it would make this entry more lengthy and convoluted than it already is. Second, I haven’t seen all the nominees in either category, though I have seen a higher portion of the animated ones. Still, I shall mention in parentheses live-action titles that in my opinion were more deserving of the Best Picture Oscar than the actual winner.
I have seen all the animated winners and all of the live-action ones apart from Crash. Thanks to the reviewers and friends who warned me off the latter. (To be honest, I turned Chicago off about twenty minutes in.)
The Face-off
So let’s go year by year and see how the Best Picture fares against the Best Animated Feature–or in some cases multiple nominees in that category.
Going by release years rather than the years when the awards were given, we start with 2001. A Beautiful Mind was the winner. I’ve actually seen it on a list of worst-ever Best Pictures, but I think it’s a fairly good film. Shrek, the animated champ that year, was much admired, but I was disappointed by it. Monsters, Inc., however, was up against Shrek, and in my opinion deserved to win. It’s arguably better than A Beautiful Mind.
There’s no contest for 2002. Even today, awarding a foreign-language film the best-animated prize is nearly impossible–or indeed, a non-Hollywood one. (Non-American winners come from the UK and Australia.) To be sure, many Academy voters probably saw the dubbed version of Spirited Away. Nevertheless, the obvious sheer brilliance of Miyazaki’s film (above) won the day. Indeed, with Godard gone, Miyazaki may be our greatest living filmmaker–though no one can see enough films from around the world to make such a judgment.
2002 was the first year in which there were enough eligible animated features that five rather than three films were nominated, something that wouldn’t happen again until 2009. Nevertheless, the animated competition was pretty lackluster: Ice Age, Lilo and Stitch, Spirit: Stallion of the Cimarron, and Treasure Planet. Spirited Away, arguably one of the greatest films of our current century, is miles beyond Chicago. If there is any evidence that the animated films can top the live-action ones, this year provided it.
Unlike our Supreme Court and other federal judges, I shall recuse myself from judging the 2003 contest. Having written a book on the subject of The Lord of the Rings film franchise and having had extraordinarily generous cooperation from the filmmakers, I can’t really be objective. Quite possibly Finding Nemo is better than The Return of the King,
2004 saw a return to only three animated features–a situation that would last until 2007. Three nominations were enough, however, since The Incredibles was up against Crash, a film high on many lists of the worst-ever winners. I doubt many would dispute my claim that The Incredibles won this face-off by a mile. (Again, I haven’t seen Crash or some of the other nominees, but I very much suspect that Spielberg’s Munich should have won.)
I am less confident in calling the 2005 winner. Million Dollar Baby is a decent film, though I wish Eastwood had not injected the heavy-handed point that Maggie wins Frankie’s heart because she’s a substitute for the daughter who has willfully disappeared from his life. Frankie losing his prejudice against training women boxers would be more powerful if it was simply based on her skill and determination. Still, I hesitate to say that the animation winner, Wallace & Gromit: The Curse of the Were-Rabbit (above), is better. (One of the English-language imports that have won.) I am a huge Aardman fan, but Wallace and Gromit work better in the shorts (especially the sublime The Wrong Trousers). Of the other two nominees in the category, Tim Burton’s Corpse Bride isn’t a contender, but one could make a case for Howl’s Moving Castle (Miyazaki again) as the film of the year.
Scorsese’s The Departed is a more complicated case in the 2006 face-off. Those of us who know the Hong Kong film it’s based on, Andrew Lau and Alan Mak’s Internal Affairs (2002), know how very much Scorsese used from the original. Plus who can forgive that final shot? Being a George Miller fan, I was quite disappointed by Happy Feet (the second English-language import to win). Rather bland, I thought, and certainly no Babe: Pig in the City (1998). I think Cars should have won best animated feature, and it outdoes The Departed as well. For some reason a lot of people don’t like Cars all that much compared to other Pixar films, which I don’t understand. Certainly Cars 2 is awful and Cars 3 pleasant enough. But the original is terrific.
The 2007 contest must be a draw. It’s hard to choose between the Coen Brothers’ No Country for Old Men and Rataouille, the animated winner. (If Paul Thomas Anderson’s There Will Be Blood has won best picture, I would give it the edge over the Pixar film. It’s another of the great films of the current century.)
It’s safer to say that in 2008 WALL-E tops Danny Boyle and Loveleen Tandan’s Slumdog Millionaire. The first half hour of WALL-E, set on Earth, is perhaps the best thing Pixar has done. It falls apart a bit once the hero and Eve get onto the giant spaceship to which humanity has fled once the Earth became uninhabitable. It turns into a prolonged chase that isn’t nearly as interesting as the incredibly clever exploration of the detritus of civilization that WALL-E diligently searches through in that first half-hour. Still, for that half-hour, I give it the edge against Slumdog Millionaire.
In 2009, there were for the second time five animated nominees. The category would return to three in 2010, but thereafter there have always been five. Kathryn Bigelow’s The Hurt Locker was probably one of the stronger films to win best picture in the period I’m covering. Still, can it really be said to be better than both Pixar’s Up (the winner) and Wes Anderson’s Fantastic Mr. Fox? And possibly Coraline or The Secret of Kells, Laika’s and Cartoon Saloon’s first entries into the fray respectively. (One benefit of writing this entry is that I watched for the first time all three of Tomm Moore’s lovely nominated Irish films, including The Song of the Sea and Wolfwalkers.)
My case is pretty strong in 2010. With only three nominees, the animated winner, Toy Story 3, easily tops Tom Hooper’s The King’s Speech. (We should remember we’re in the period when Harvey Weinstein was bludgeoning his company’s films into the winner’s circle.) Some would say How to Train Your Dragon would as well. (Among the live-action nominees, I would vote for Inglourious Basterds, but it would be a miracle if the Academy members chose such a film.)
With 2011 we reach another case where the best-picture winner is widely decried as among the worst to pick up the trophy: Michel Hazanavicius’ The Artist. The line-up of animated entries was pretty weak apart from Rango, directed by, of all people, Gore Verbinski. This brilliant outlier within the animation industry (produced by Nickelodeon), is a sort of cross between Chinatown and Once upon a Time in the West. That’s Rango with the villainous-tortoise mayor, above; the latter is a combination of Noah Cross in Chinatown and Mr. Choo-choo in Once upon a Time in the West.
Rango seems to have largely slipped from people’s memories, perhaps partly because it’s not a Disney or Pixar film that you buy on disc for your kids and have around forever. I don’t know what kids would make of Rango, but it’s definitely more aimed at adults. And hilariously imaginative.
2012 was a banner year for great animated films. The Oscar winner, Pixar’s Brave, was the first of six films in a row from Pixar and Disney, both at that point under the leadership of John Lasseter. I don’t find Brave among the best of these, but it’s OK and it no doubt benefited from all the fuss about it having Pixar’s first female protagonist. For me, there were no fewer than three wonderful nominees that were better: Laika’s Paranorman, Aardman’s The Pirates!: In an Adventure with Scientists! (the British title, changed to the much more boring The Pirates! Band of Misfits for North American release), and Disney’s Wreck-it Ralph. All three offer a flood of clever jokes and original concepts that could only be understood by adults. In Wreck-It-Ralph there’s the AA-style meeting of video-game villains that Ralph attends (top). Or in The Pirates!, the Pirate of the Year awards ceremony that puts the rival contestants in split-screen à la the Oscars show (second from top).
Any of them beats the “best picture,” Ben Affleck’s Argo. Remember that? (I haven’t seen all its live-action rivals, but Lincoln and Amour would have been creditable winners.)
Steve McQueen’s 12 Years a Slave fully deserved to win Best Picture. There’s certainly nothing to rival it in the somewhat set of nominations in the animation category. I did not find the winner, Disney’s Frozen, particularly interesting. It seems to be geared to appeal to small children. Miyazaki’s The Wind Rises was the only plausible nominee to go up against Sir Steve’s film, but I’m not going to make that argument. (It’s a real pity that Gravity was in the competition this year, since it truly is a great film and also deserved to win.)
Moving on to 2014, the live-action winner was Iñárritu’s Birdman or (The Unexpected Virtue of Innocence). The list of animated nominees was not as strong as some years, but I think Birdman is overrated, and Disney’s Big Hero 6 tops it. (I’ve only seen some of the live-action nominees, but The Grand Budapest Hotel and some of the others were pretty strong contenders.)
In 2015 the winners in the two categories were Tom McCarthy’s Spotlight and Pixar’s Inside Out. I don’t really have a preference. (Here’s another case, similar to Inglourious Basterds, of a marvelous but violent, over-the-top masterpiece deserved Best Picture: Mad Max: Fury Road. It pretty much swept the technical awards to end up with six, but Spotlight won only two–picture and screenplay. Go figure.)
I remember watching Barry Jenkins’ Moonlight in a theater in 2016. I sat there thinking that this film was made by a talented young man who someday might win an Oscar. To me, his The Underground Railroad was a more impressive achievement and deserved a slew of Emmys. Three excellent animated films were nominated in 2016: Disney’s Zootopia, Laika’s Kubo and the Two Strings (bottom), and Disney’s Moana. I was convinced that Kubo would finally win Laika it’s first, well-deserved Oscar. Zootopia won over what I think is a slightly better film, Moana, but one can’t really complain in this case. (My preferences for Best Picture would have been Arrival and La La Land.)
The situation was reversed in 2017. Much though I like many of Guillermo del Tor’s films, I’d have to give Pixar’s Coco the edge over The Shape of Water (talk about a Mexican stand-off!). (The true masterpieces among the nominees that year were Nolan’s Dunkirk and Paul Thomas Anderson’s Phantom Thread. At least, as so many of my friends have said, Three Billboards outside Ebbing, Missouri didn’t win.)
Now we come to the notorious year of 2018, when Peter Farrelly’s (!) Green Book won best picture against competition that included Spike Lee’s BlacKkKlansman and Curaón’s Roma. This incomprehensible choice throws an even greater light on the high quality of the animated race that year. Three masterpieces were among the five nominees: Sony’s Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse, which won, Wes Anderson’s Isle of Dogs (above), and Disney’s Ralph Breaks the Internet. Any one of these rolls right over Green Book. Incredibles 2 is pretty good as well. I enoyed the fifth nominee, Mamoru Hosoda’s Mirai, but it hadn’t a chance against these three.
2019 is easy. Bong Joon Ho’s Parasite beats everything, even Pixar’s Toy Story 4. Probably a lot of people agreed with my assessment that the franchise was showing a bit of wear and tear, though not nearly as much as last year’s Lightyear. (Again, it’s a pity that two other masterpieces nominated that year couldn’t also win: Little Women and Once upon a Time in Hollywood.)
For 2020, when theater-going was difficult if not impossible, studios delayed many films or sent them straight to streaming. The result was a somewhat uninspired lineup of animated nominees. Soul almost inevitably won. I must admit that I preferred Pixar’s films as they were until recently–adventures of various sorts, whether involving actual superheroes, groups of toys, or an old man flying his house to South America to learn how to be sociable again. These had psychological depth, but they didn’t make it explicit by making emotions into characters or sending them to heaven. So Nomadland comes out ahead this time. (I would have preferred two other nominees, The Father or The Trial of the Chicago 7.)
In 2021 I found Sian Heder’s Coda as heartwarming as anyone, but Oscars are purportedly for picking great films that we assume till be watched in the future as classics. Not that they get it right very often, but, well, Oscar-bait ain’t what it used to be. The Danish animated documentary Flee leaves us with a tear in the eye as well, but the Academy stuck to its long habit of rewarding Pixar and/or Disney films and made Encanto its top animated film. This film had many good moments, but it annoyed me every time it got into a lively scene. Suddenly the characters (and virtual camera) started zipping about through the settings. Those settings were gorgeous, but we didn’t get a chance to look at them. Just compare it with Moana, which also had scenery worth lingering over while still managing to drip with exuberance. (For the live-action champ, I would have gone for Nightmare Alley, The Power of the Dog, or West Side Story. It was a pretty good year.)
There was, however, one animated feature nominated that year: the unmissable The Mitchells vs. the Machines–though many may have missed it when during the pandemic it skipped theatrical and went straight to Netflix. It was produced by Phil Lord and Chris Miller, who also did Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse for Sony Pictures Animation, and although a very different film, it has all the energy, imagination, and craziness of that film. It also plays out the potentially apocalyptic rebellion against humans by AI and the robots run by it. The premise is that an angry computing system being replaced by a new generation sends robots to put all humans in plastic cubes and fire them into space–including its own inventor. The dysfunctional Mitchells are humanity’s only hope. The funniest and most telling scene is when they stop at a mall and all the products in the stores, which have chips installed holding a kill order to destroy the family, start attacking them. This culminates in a bunch of Furbies going after them, led by the world’s largest Furby (above).
What happened in the 2022 category is sort of like what happened in 2002, when Spirited Away won. An outlier from outside the traditional Hollywood studio structure (Netflix) was nominated among a somewhat weak group of animated films and won the day. I settled down to watch the broadcast of the ceremony wondering if Academy members would recognize what a remarkable film Guillermo Del Toro’s Pinocchio is and not just reflexively vote for the Pixar film. That was Turning Red, which got a lot of attention for daring to show a teenager hitting puberty and experiencing her first period. I didn’t think it was a very good film and confirmed my sense that Pixar has declined in recent years. It’s probably better than The Good Dinosaur and now Lightyear, which is not saying much. (Carolyn Giardina’s recent “Elemental Steps into the Ring in Major Box Office Test for Pixar,” astutely sums up reasons for the aesthetic decline of Pixar–and, one might add Disney Animation.)
I know a lot of people for some reason are enthralled by Everything, Everywhere, All at Once, which won the 2022 Best Picture. I found it mildly entertaining but at least it gave Michelle Yeoh a career win for Best Actress. Pinocchio is miles beyond it. (Everything won against a slew of superior films. In alphabetical order: The Banshees of Inisherin, The Fabelsmans, Tár, and Women Talking.)
Totting up the live-action vs. animation winners in this face-off, we find one recusal, one draw, five decisions in favor of the live-action winners and fourteen for the animated winner or one or more of the animated nominees. As I mentioned at the start, the figures would be quite different if I had compared all the Oscar-worthy animation awards with all the Oscar-worthy Best Picture nominees. Still, in general this comparison may suggest that animated films are unfairly treated as one of the minor categories that people don’t pay much attention to.
I’m not suggesting that the Academy change their categories or rules. There’s probably no way to boost the prestige of the Animated Feature nominees.
The point here has simply been to add some evidence to my claim that a higher percentage of animated films tend to be excellent in a way that compares favorably with the live-action films nominated in the more prestigious category. Despite this, animated films are simply not taken seriously by most people, inclined cinephiles. They are still viewed as children’s fare, despite the successful appeal to adults built into many of the titles I’ve singled out here. They are also mostly comic to some extent and often involve fantasy, while Oscar bait leans toward drama and, with rare exceptions, away from fantasy/science fiction.
The conclusion is that if you think, for whatever reason, that live-action Oscar winners and films in general have declined in the past few decades, check out some ‘toons.
Kubo and the Two Strings (2016).