Archive for the 'Film criticism' Category
Little things
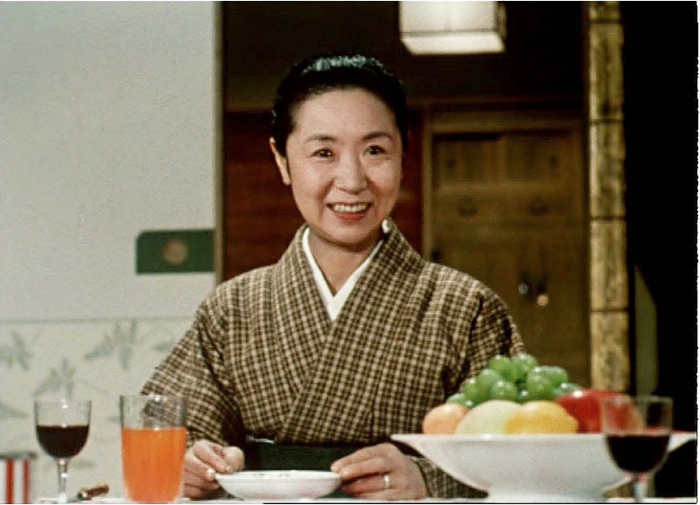
Equinox Flower (Ozu, 1958).
DB here:
Academic critics and fans share a passion for looking closely at the movies we admire. A lot of film critics enjoy spiraling out from the film to ponder Big Ideas, which is okay, I guess. But I confess I particularly enjoy digging in for trouvailles (great word), lucky discoveries that passed me by on earlier encounters.
Across my career, many of the directors I admire seem to have tucked in little things just for me (or you). They don’t necessarily carry meanings; they’re quietly decorative, subtly off-center to the narrative. Tati slipped peculiar items into the corners of the frame. Sturges offered gags that only people with his sense of humor will find funny. A successful crowdsourcing enterprise exposed Welles’ homages to early film. Above all, Ozu nudged me toward red teakettles and surprising details. Who else lines up the levels of beverages in a table setting, and then matches that plane to the edge of a fruit bowl?
If you care enough about my movie, the director seems to say, I’ll reward you with a trouvaille. Here are two I found recently.
Showing the stitches
Sometimes a trouvaille is a felicity of craft. The director quietly shows off his virtuosity to those in the know. While studying Pulp Fiction for a book I’m finishing, I noticed that Tarantino sets up the ending in a sidelong way.
You’ll remember that the opening shows Honey Bunny and Pumpkin discussing how a restaurant is one of the safest robbery targets. Abruptly they launch an assault on the diner. Then they drop out of the film for a couple of hours.
Very likely we’ve forgotten about them when Jules and Vincent settle down for breakfast in a diner. After discussing the virtues of pork products and the prospects for Jules’ future, Vincent rises to go to the toilet. As he pauses, it’s possible, but not easy, to discern the larcenous couple out of focus in their booth behind him. Given their peripheral status and the centrality of Travolta’s performance, I suspect that almost no one notices them on a first viewing.
Soon after Vincent has left, we’ll hear a repetition of the final bits of the couple’s conversation and we’ll see a replay of their leaping up to announce the robbery. Tarantino has rewarded the sharp-eyed viewer with a slight anticipation of the replay, and a hint at how his film will fold back on its opening sequence.
But this echo is matched by a “pre-echo” during the opening sequence. As Pumpkin and Honey Bunny plan their heist, a close view of her includes a bulky man in a t-shirt walking into the distance.
At this point, a first-time viewer hasn’t been introduced to Vincent, so the t-shirt guy is just part of the scenery. Only in retrospect do we realize that here Tarantino is anticipating, and overlapping, the portion of the robbery that we’ll see in the final moments of the film.
Here the critic/fan is invited to appreciate how carefully made the film is. It’s a quality we don’t sufficiently recognize in Tarantino: a delight in fine-grained formal niceties.
Easter Egg, avant la lettre
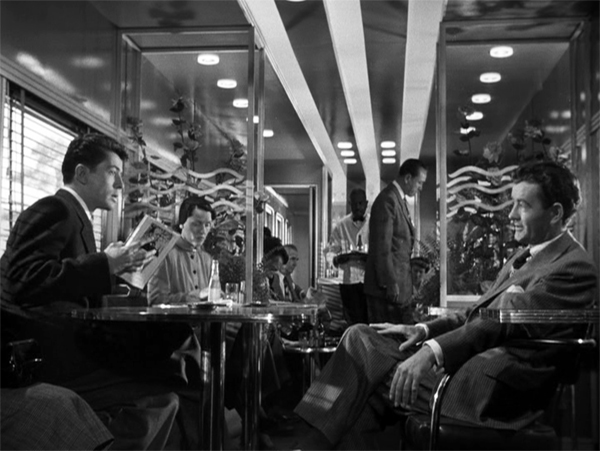
In Hitchcock’s Strangers on a Train (1950), tennis pro Guy Haines is introduced (implausibly) reading a book on his trip. Soon he’s accosted by the spoiled, marginally nuts Bruno Anthony, and the plot gets under way. Only a fan, or a critic, will want to know: What’s Guy reading?
It’s not easy to tell. We don’t get a close-up of the book. The best we can tell, from above, is that it’s a hardcover, with a photo on the back of the dust jacket. Later, after Guy and Bruno have shared a meal in a compartment, we can glimpse the spine.
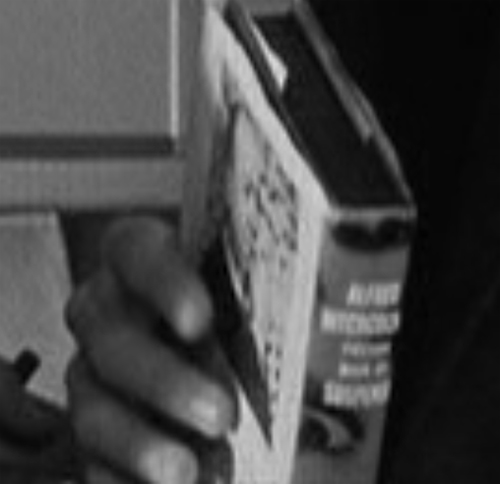
Blown up, thanks to the glory of Blu-ray, the spine looks like this.
A little research reveals that the volume is Hitchcock’s collection of stories published in 1947 by Simon and Schuster.
Several anthologies were published under Hitchcock’s name from the 1940s onward, but most were in paperback. This was a more prestigious item, and I suspect it helped the branding effort that was underway during his Hollywood career. The picture on the back is of Hitchcock, of course. (My copy lacks a dust jacket, so I can’t supply that.) But the resonance comes from the fact that I was reading this very book as part of preparation for my own study of 1940s mystery culture.
It’s not exactly product placement; the book’s presence is too fleeting to register with audiences, surely. Including the book seems more in the nature of a private joke among Hitch and his team. Guy is a man of good taste, reading a book by the man directing the film he’s in.
Today we’re familiar with Easter Eggs, those bonus materials that establish a complicity between filmmmaker and viewer. Is this an early example? It could be a prize for fan connoisseurship. The book isn’t emphasized, being buried in the mise-en-scene, and so it encourages the devout to poke and probe. It also points outside the film to the production context. Still, how many 1950 viewers, lacking our ability to freeze and magnify the frame, could have spotted it? Perhaps only the devotion of a modern fan, aided by new technology, can bring this trouvaille to light. An incipient Easter Egg, then, awaiting digital technology to be discovered?
Once we’re down this rabbit hole, let’s scramble further. What stories might Guy be reading? There are two hints. We have the placement of the jacket flap in the shot above, and an earlier shot showing the book open.
As best I can tell, the story Guy’s reading is likely to be “Yours Truly, Jack the Ripper.” It tells of a psychiatrist who meets an Englishman called “Guy Hollis.” Sir Guy believes that Jack the Ripper has migrated to the US and is at large in Chicago. With the aid of the psychiatrist, Sir Guy finds him. Apart from the name Guy, the correspondence to Strangers it would seem to involve a peculiar bond between two men, one of whom is a psychopathic killer.
But there’s another, stranger affinity.
The author of “Yours Truly, Jack the Ripper” is Robert Bloch., whose novel Psycho would furnish Sir Alfred his 1960 film. Coincidence? In the land of trouvailles, are there any coincidences?
Fans have raked over these movies assiduously, so I can’t imagine I’m the first to notice these fine touches. No matter. When you discover them on your own, you still feel a tiny thrill of communicating with the filmmaker, behind the backs of all those folks who didn’t notice. Ozu, I often feel, is making movies especially addressed to me. It’s an illusion, of course, but I refuse to give it up.
Thanks to the University of Wisconsin–Madison Filmies listserv for helping me understand what counts as Easter Eggs, and for a reality check on my sanity.
This site includes lots more on Hitchcock, Ozu, Sturges, and Tarantino. My book on Ozu is available from the University of Michigan. It takes time to download, so be patient.
P.S. 15 August 2021: As I thought, I’m not the first. A mere twenty-one years ago, Dana Polan in his monograph on Pulp Fiction (British Film Institute) noticed the pre-echo of Vincent headed toward the toilet. Good going, Dana! Film analysis wins again.
Days of Youth (Ozu, 1929).
Learning to watch a film, while watching a film
The Hand That Rocks the Cradle (1992).
DB here:
“Every film trains its spectator,” I wrote a long time ago. In other words: A movie teaches us how to watch it.
But how can we give that idea some heft? How do movies do it? And what are we doing?
Many menus
Tinker, Tailor, Soldier, Spy (2011).
In my research, I’ve found the idea of norms a useful guide to understanding how filmmakers work and how we follow stories on the screen. A norm isn’t a law or even a rule; it’s, as they say in Pirates of the Caribbean, more of a guideline. But it’s a pretty strong guideline. Norms exert pressure on filmmakers, and they steer viewers in specific directions.
Genre conventions offer a good example. The norms of the espionage film include certain sorts of characters (secret agents, helpers, traitors, moles, master minds, innocent bystanders) and situations (tailing targets, pursuits, betrayal, codebreaking, and the like). The genre also has some characteristic storytelling methods, like titles specifying time and place, or POV shots through binoculars and gunsights.
But there are other sorts of norms than genre-driven ones. There are broader narrative norms, like Hollywood’s “three-act” (actually four-part) plot structure, or the ticking-clock climax (as common in romcoms and family dramas as in action films). There are also stylistic norms, such as the shoulder-level camera height and classic continuity editing, the strategy of carving a scene into shots that match eyelines, movements, and other visual information.
Thinking along these lines leads you to some realizations. First, any film will instantiate many types of norms (genre, narrative, stylistic, et al.). Second, norms are likely to vary across history and filmmaking cultures. The norms of Hollywood are not the same as the norms of American Structural Film. There are interesting questions to be asked about how widespread certain norms are, and how they vary in different contexts.
Third, some norms are quite rigid, as in sonnet form or in the commercial breaks mandated by network TV series. Other norms are flexible and roomy (as guidelines tend to be). There are plenty of mismatched over-the-shoulder cuts in most movies we see, and nobody but me seems bothered.
More broadly, norms exist as options within a range of more or less acceptable alternatives. Norms form something of a menu. In the spy film, the woman who helps the hero might be trustworthy, or not. The apparent master mind could turn out to be taking orders from somebody higher up, perhaps somebody supposedly on your side. One scene might avoid continuity editing and instead be presented in a single long take.
Norms provide alternatives, but they weight them. Certain options are more likely to be chosen than others; they are defaults. (Facing a menu: “The chicken soup is always safe.”) An action film might present a fight or a chase in a single take (Widows, Atomic Blonde), but it would be unusual if every scene in the film were played out this way. Not forbidden, but rare. Avoiding the default option makes the alternative stand out as a vivid, willed choice.
Very often, critics take most of the norms involved for granted and focus on the unusual choices that the filmmakers have made. One of our most popular entries, the entry on Tinker, Tailor, Soldier, Spy, discusses how the film creates a demanding espionage movie by its manipulations of story order, characterization, character parallels, and viewpoint. It isn’t a radically “abnormal” film, but it treats the genre norms in fresh ways that challenge the viewer.
Because, after all, viewers have some sense of norms too. Norms are part of the tacit contract that binds the audience to creators. And the viewer, like the critic, looks out for new wrinkles and revisions or rejections of the norm–in other words, originality.
Picking from the menu
Norms of genre, narrative, and style are shared among many films in a tradition or at a certain moment. We can think of them as “extrinsic norms,” the more or less bounded menu of options available to any filmmaker. By knowing the relevant extrinsic norms, we’re able to begin letting the movie teach us how to watch it.
The process starts early. Publicity, critical commentary, streaming recommendations, and other institutional factors point up genre norms, and sometimes frame the film in additional ways–as an entry in a current social controversy (In the Heights, The Underground Railroad), or as the work of an auteur. You probably already have some expectations about Wes Anderson’s The French Dispatch.
Then, as we get into the film, norms quickly click into place. The film signals its commitment to genre conventions, plot patterning, and style. At this point, the film’s “teaching” consists largely of just activating what we already know. To learn anything, you have to know a lot already. If the movie begins with a character recalling the past, we immediately understand that the relevant extrinsic norm isn’t at that point a 1-2-3 progression of story events, but rather the more uncommon norm of flashback construction, which rearranges chronology for purposes of mystery or suspense. Within that flashback, though, it’s likely that the 1-2-3 default will operate.
As the film goes on, it continues to signal its commitment to extrinsic norms. An action scene might be accompanied by a thunderous musical score, or it might not; either way, we can roll with the result. The characters might let us into their thinking, through voice-over or dream sequences, or we might, as in Tinker, Tailor, be confronted with an unusually opaque protagonist whose motives are cloudy. The extrinsic norms get, so to speak, narrowed and specified by the moment-by-moment working out of the film. Items from the menu are picked for this particular meal.
That process creates what we can call “intrinsic norms,” the emerging guidelines for the film’s design. In most cases, the film’s intrinsic norms will be replications or mild revisions of extrinsic ones. For all its distinctiveness, in most respects Tinker, Tailor adheres to the conventions of the spy story. And as we get accustomed to the film’s norms, we focus more on the unfolding action. We’ve become expert film watchers. We learn quickly, and our “overlearned” skills of comprehension allow us to ignore the norms and, as we stay, get into the story.
Narration, the patterned flow of story information, is crucial to this quick pickup. Even if the film’s world is new to us, the narration helps us to adjust through its own intrinsic norms. The primary default would seem to be “moving spotlight” narration. Here a “limited omniscience” attaches us to one character, then another, within a scene or from scene to scene. We come to expect some (not total) access to what every character is up to.
In Curtis Hanson’s Hand That Rocks the Cradle, we’re initially attached to the pregnant Claire Bartel, who has moved to Seattle with her husband Michael and daughter Emma. When Claire is molested by her gynecologist Dr. Mott, she reports him. The scandal drives him to suicide, and his distraught wife miscarries. She vows vengeance on Claire. Thereafter, the plot shuttles us among the activities of Claire, Mrs. Mott, Michael, the household handyman Solomon, and family friends like Michael’s former girlfriend Marlene. The result is a typical “hierarchy of knowledge”–here, with Claire usually at the bottom and Mrs. Mott near the top. We don’t know everything (characters still harbor secrets, and the narration has some of its own), but we typically know more about motives, plans, and ongoing action than any one character does.
More rarely, instead of a moving spotlight, the film may limit us to only one character’s range of knowledge. Again, scene after scene will reiterate the “lesson” of this singular narrational norm. That repetition will make variations in the norm stand out more strongly. Hitchcock’s North by Northwest is almost completely restricted to Roger Thornhill, but it “doses” that attachment with brief asides giving us key information he doesn’t have. Rear Window and The Wrong Man, largely confined to a single character’s experience, do something similar at crucial points.
Sometimes, however, a film’s opening boldly announces that it has an unusual intrinsic norm. Thanks to framing, cutting, performance, and sound, nearly all of Bresson’s A Man Escaped rigorously restricts us to the experience of one political prisoner. We don’t get access to the jailers planning his fate, or to men in other cells–except when he communicates with them or participates in communal activities, like washing up or emptying slop buckets.
The apparent exception: The film’s opening announces its intrinsic norm in an almost abstract way. First, we get firm restriction. There are fairly standard cues for Fontaine’s effort to escape from the police car that’s carrying him. Through his optical POV, we see him grab his chance when the driver stops for a passing tram.
The film’s title and the initial situation let us lock onto one extrinsic norm of the prison genre: the protagonist will try to escape. Knowing that we know this, Bresson can risk a remarkable revision of a stylistic norm.
Fontaine bolts, but Bresson’s visual narration doesn’t follow him. The camera stays stubbornly in the car with the other prisoner while Fontaine’s aborted escape is “dedramatized,” barely visible in the background and shoved to the far right frame edge. He is run down and brought back to be handcuffed and beaten.
The shot announces the premise of spatial confinement that will dominate the rest of the film. The narration “knows” Fontaine can’t escape and waits patiently for him to be dragged back. In effect, the idea of “restricted narration” has been decoupled from the character we’ll be restricted to. This is the film’s first, most unpredictable lesson in stylistic claustrophobia.
Got a light?
Most intrinsic norms aren’t laid out as boldly as the opening of A Man Escaped, but ingenious filmmakers may provide some variants. Take a fairly conventional piece of action in a suspense movie. A miscreant needs to plant evidence that incriminates some innocent soul.
In Strangers on a Train, that evidence is a cigarette lighter. Tennis star Guy Haines shares a meal with pampered sociopath Bruno Antony, whose tie sports colorful lobsters. Bruno steals Guy’s distinctive cigarette lighter.
Bruno has proposed that they exchange murders: He will kill Guy’s wife Miriam, who’s resisting divorce, and Guy will kill Bruno’s father. Bruno cheerfully strangles Miriam at a carnival, aided by the lighter.
When Guy doesn’t go through with his side of the deal, Bruno resolves to return to the scene of Miriam’s death and leave the lighter to incriminate Guy. The film’s climax consists of the two men fighting on a merry-go-round gone berserk. Although Bruno dies asserting Guy’s guilt, the lighter is revealed in his hand. Guy is exonerated.
Once the lighter is introduced in the early scenes, it comes to dominate the last stretch of the film. In scene after scene, Hitchcock emphasizes Bruno’s possession of it. Sometimes it’s only mentioned in dialogue, but often we get a close-up of it as Bruno looks at it thoughtfully–here, brazenly, while Guy’s girlfriend Ann is calling on him.
When Bruno picks up a cheroot or a cigarette, we expect to see the lighter.
One of the film’s most famous set-pieces involves Bruno straining to retrieve the lighter after it has fallen through a sidewalk grating.
Bruno has dropped it before, during Miriam’s murder, but then he notices and retrieves it. It’s as if this error has shown him how he might frame Guy if necessary. The image of the lighter in the grass previews for us what he plans to do with it later.
What does the lighter have to do with norms? Most obviously, Strangers on a Train teaches us to watch for its significance as a plot element. It’s not only a potential threat, but also Bruno’s intimate bond to Guy, as if Bruno has replaced Ann, who gave Guy the lighter. The film also invokes a normalized pattern of action–a character has an object he has stolen and will plant to make trouble–and treats it in a repeated pattern of visual narration. The character looks at the object; cut to the object; cut back to the character in possession of the object, waiting to use it at the right moment. Our ongoing understanding of the lighter depends on the norm-driven presentation of it.
Once we’re fully trained, Hitchcock no longer needs to show us the lighter at all. En route to the carnival to plant the lighter, Bruno lights a cigarette with the lighter, although his hands conceal it. But then the train passenger beside him asks for a light.
In order to hide the lighter, Bruno laboriously pockets it and fetches out a book of matches.
If we saw only this scene, we might not have realized what’s going on, but it comes long after the narrational norm has been established. We can fill out the pattern and make the right inference. Bruno wants no witness to see this lighter.
The hand that cradles the rock
In The Hand That Rocks the Cradle, under the name Peyton Flanders, Mrs. Mott becomes nanny to Claire’s daughter and infant son. Pretending to be a friendly helper, she subverts Claire’s daily routines and her trusting relationship with Michael. As in most domestic thrillers, the accoutrements of upper-middle-class lifestyle–a baby monitor, a Fed Ex parcel, expensive cigarette lighters, asthma inhalers, wind chimes–get swept up in the suspense. Peyton weaponizes these conveniences, and through a somewhat unusual narrational norm the film trains us to give her almost magical powers.
We get Peyton’s early days in household filtered through her point of view. Classic POV cutting is activated during her job interview. She notices that Claire’s pin-like earring drops off and she hands it back to her.
Attachment to Peyton gets more intense when she sees the baby monitor and then fixates on the baby.
We’re then initiated into her tactics, and to the film’s way of presenting them. Serving supper, Claire doesn’t notice that her earring drops off again. Peyton does.
Breaking with her POV, the narration shifts to Claire and Michael talking about hiring her. But this cutaway to them has skipped over a crucial bit of action: Peyton has picked up the earring. Unlike Hitchcock, director Curtis Hanson doesn’t give us a close-up of the important object in the antagonist’s hand. In a long shot we simply see Peyton studying her fingers. Some of us will infer what she’s up to; the rest of us will have to wait for the payoff.
After another cutaway to the couple, Peyton “discovers” the earring in the baby’s crib. Her show of concern for his safety seals the hiring deal and begins her long campaign to prove that Claire is an unfit mother.
This elliptical presentation of Peyton’s subterfuges rules the middle section of the film. Selective POV shots suggest what she might do, but we aren’t shown her doing it–only the results. For instance, Claire lays out a red dress for a night out. Peyton sees it, then sees some perfume bottles.
Cut to Claire and then to an arriving guest, and presto. When she returns to the mirror, her dress is suddenly revealed as having a stain.
Later, Claire agrees to send off Michael’s grant application during her round of errands. Once she gets to the Fed Ex office, she will discover the missing envelope. Before that, though, we get another variant of the intrinsic norm showing Peyton’s trickery.
In the greenhouse, while Claire is watering plants, Peyton spots the envelope in her bag. We don’t see her take it, and there’s even a hint that she hasn’t done so. A nifty shot lets us glimpse her yanking her arm away as Claire approaches. It’s not clear that she has anything in her hand.
In what follows, the narration confirms Peyton’s theft while building up the threat level.
If she’s caught, this woman will not go away quietly.
While cozying up to the children–Peyton cuddles with Emma and even secretly breast-feeds baby Joe–Peyton eliminates all of Claire’s allies. By now we know her strategy, so after she suggests to Claire that the handyman Solomon has been molesting little Emma, all the narration needs is to show us Claire discovering a pair of Emma’s underwear in his toolbox. As with Bruno’s pocketing the lighter in Strangers on a Train, we’re now prepared to fill in even more of what’s not shown: here, Peyton framing Solomon.
Michael, a furtive smoker, sometimes shares a cigarette with Marlene. So it’s easy for Peyton to plant Marlene’s lighter in Michael’s sport coat for Claire to discover. Again, the moment of the theft has given her quasi-magical powers. She sees Marlene’s lighter in her handbag in the front seat.
Again thanks to a cutaway, we don’t see her take it. Indeed, it’s hard to see how she could have; she comes out of the back seat with an armload of plants.
But later Marlene will tell Michael (i.e., us) that she’s lost her lighter, and a dry cleaner will find it and show it to Claire.
The attacks have escalated, with Claire now suspecting Michael of infidelity. She confronts him without knowing that Michael has invited friends to a surprise party for her. Her angry accusations are overheard by the guests, and this public display of her anxieties takes her to a new low.
Peyton’s revenge plan is almost wholly consummated, so we stop getting the elliptical POV treatment of her thefts. Instead, the plot shifts to investigations: first Marlene discovers Peyton’s real identity, with unhappy results, and at the climax Claire does. Her POV exploration of the empty Mott house counterbalances Peyton’s early probing of Claire’s household. When she sees Mrs. Ott’s breast pump–another domestic object now invested with dread–she realizes why baby Joe no longer wants her milk.
This is the point, fairly common in the thriller, when the targeted victim turns and fights back.
In The Hand That Rocks the Cradle, a familiar action scheme–someone swipes something and plants it elsewhere–is handled through an unusual narrational norm. The scenes showing Peyton’s pilfering skip a step, and they momentarily let us think like her, nuts though she is. Thanks to editing that deletes one stage of the standard shot pattern, the film trains us to see how banal domestic items, deployed as weapons, can destroy a family. In the course of learning this, maybe the movie makes us feel smart.
Arguably, we’re able to fill in the POV pattern in The Hand That Rocks the Cradle because we’ve learned from encounters with movies that used the standard action scheme, including Strangers on a Train. This is one reason film style has a history. Dissolves get replaced by fades, exposition becomes more roundabout, endings become more open. As audiences learn technical devices, intrinsic norms recast extrinsic ones and some movies become more elliptical, or ambiguous, or misleading. All I’d suggest is that we get accustomed to such changes because films teach us how to understand them. And we enjoy it.
The passage about training us comes from my Narration in the Fiction Film (University of Wisconsin Press, 1985), 45. I discuss norms in blog entries on Summer 85, on Moonrise Kingdom, on Nightmare Alley, and elsewhere. A book I’m finishing applies the concept to novels as well as films.
The example of mismatched reverse angles comes from The Irishman (2019) In the first cut, Frank is starting to settle his coat collar, but in the second, his arms are down and the collar is smooth. In a later portion of that second shot, Hoffa gestures freely with his right hand, but in the over-the-shoulder reverse, his arm is at his side and it’s Frank who gets to make a similar gesture. To be fair, I should say that I found some striking reverse-angle mismatches in Strangers on a Train too.
For more on conventions of the domestic thriller, go to the essay “Murder Culture.”
Radomir D. Kokeš offers an analysis of how Kristin and I have used the concept of norm. We are grateful for his careful discussion of our work and his exposition of the achievement of literary theorist Jan Mukarovský. See “Norms, Forms and Roles: Notes on the Concept of Norm (not just) in Neoformalist Poetics of Cinema,” in Panoptikum (December 2019), available here.
Strangers on a Train (1951).
Five critics, one of them a killer
Goodfellas (1990).
DB here:
Fourteen months of being house-bound gave me plenty of chance to catch up on my reading. But the reading was almost all devoted to the book I was writing on mystery plots in fiction, film, and other media. Now that it has been catapulted out to unwary publisher’s readers, it’s time for me to catch up on some 2020 books I like. In this batch, all have a connection to film criticism, and murder, attempted or consummated, creeps into more than one.
Movies for Muggles
Somebody ought to write a history of the one-movie monograph. Early on there were picture books, and roadshow attractions often produced pretty laminated books as souvenirs, filled with PR stories and color images. My vote for the first analytical monograph would be the very ambitious Tu n’as rien vu à Hiroshima! (1962). In the early 1970s, American academic presses began offering critical studies of single films; an early example was the FilmGuide series edited by Harry Geduld and Ron Gottesman. (My favorite entry was Jim Naremore‘s study of Psycho.) Since then many publishers have pursued the format, usually as part of a series.
Now we have 21st Century Film Essentials, newly launched at the University of Texas Press. The first two entries are pretty canon-busting. Dana Polan writes on The Lego Movie, and Patrick Keating on Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban. I haven’t seen Polan’s book, but Keating directly takes up the challenge of the series.
As a franchise film, as a work of digital cinema, as a work of collaborative authorship, and above all as a thoroughly engaging demonstration of the art of storytelling, Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban is an essential work of twentieth-first century cinema.
 I confess I was skeptical, and still am a little. But Keating’s meticulous analysis and interpretation of the film does convince me that this is a ripe example of modern “hyperclassical” cinema. By that I mean a dense, “through-composed” revision of traditional narrative strategies and film techniques, working smoothly together to create effects at many levels. A hyperclassical film is more thoroughly classical than it “needs to be.” In other words, here’s another counterexample to the notion that “post-classical Hollywood” shows a collapse of traditional norms.
I confess I was skeptical, and still am a little. But Keating’s meticulous analysis and interpretation of the film does convince me that this is a ripe example of modern “hyperclassical” cinema. By that I mean a dense, “through-composed” revision of traditional narrative strategies and film techniques, working smoothly together to create effects at many levels. A hyperclassical film is more thoroughly classical than it “needs to be.” In other words, here’s another counterexample to the notion that “post-classical Hollywood” shows a collapse of traditional norms.
Keating’s argument for the film’s richness, I think, revolves around two central concepts. First is that of narrative viewpoint. Virtually all of Azkaban, unlike the earlier entries in the franchise, is filtered through the consciousness of Harry. We’re attached to him as he experiences the action. That doesn’t, Keating hastens to add, make the film radically subjective; indeed, there are relatively few shots from Harry’s optical viewpoint. Attaching the unfolding plot to a character doesn’t rule out a wider perspective, if only because cinema puts him within a wider frame of a shot or an edited sequence. There’s always the possibility of our registering action or other characters’ reactions. The end of the Quidditch flight is thick with these impacted viewpoints, and elsewhere Cuarón’s constantly moving camera nudges us toward implications that supplement, or sometimes contradict, what Harry is concentrating on.
Keating’s other main concept is connected to the broadening of viewpoint: worldbuilding. This idea is obviously central to Rowling’s achievement, as it has been to franchises since Star Wars. But Keating lifts the idea to a central role in how films engage us. The richly realized world of Potter is only an extreme instance of what every narrative does. Borrowing from critic V. F. Perkins, Keating suggests that any film narrative supplies us with the possibility of many stories that are only hinted at, or merely latent.
Most movies prune those secondary offshoots, the better to force us to concentrate on our protagonist. But Tom Stoppard showed that Rosencrantz and Guildenstern deserved their own play. Similarly, franchise films, with the ever-present prospect of sequels, crossovers, or reboots, make us aware that any character, even any item of furniture, secretes a new story, or a bunch of them. The Potter films are committed to this spinoff aesthetic, packing in as many suggestions of sidestories as the screen will bear. This principle finds tangible expression in the portraits jammed into the Gryffindor common room and dorms guarded by the Fat Lady.
Overwhelming us with characters and situations, many in motion, this gallery is perfectly in keeping with English traditions of floor-to-ceiling decor. It’s also a groaning feast of other stories that could yet, somehow, intersect with Harry’s fate. Keating’s shrewd commentary on worldmaking is one of the book’s highlights.
Keating ties these ideas to phases of production and division of labor, reviewing how the novel’s viewpoint and worldbuilding strategies are transposed and extended by script, camerawork, editing, performances, set and costume design, and music. Throughout he weaves what he takes to be the film’s binding theme, that of time. Is the future preordained, as Ms. Trelawney insists in her frantic, fumbling lectures? Or is it open, as Hermoine and others tell Harry? This makes the film’s tour de force climax with the Time Turner into a synthesis of restricted viewpoint (we’re with Harry as he witnesses an alternative future) and worldbuilding (the future is what you make it).
I might quarrel with Keating’s suggestion that the impulse driving Harry’s action is a struggle with the dementers. I saw his relation to Sirius Black as more than the subplot Keating considers it. Overall, though, Keating has produced not only a subtle, supple analysis of the film but also a model for how to understand cinematic storytelling in the age of the blockbuster.
Wiseguy’s progress
If Keating’s book is a classical sonata, Glenn Kenny’s Made Men: The Story of Goodfellas is bop. Keating offers a tidy analysis through crisply defined categories. Kenny provides a hardcopy approximation to a packed DVD.
 At the center is a 150 page scene-by-scene account of the film: a commentary track in your hands. Alongside that sit chapters that function as bonus materials. They include a brief introduction to the filmmaker just before he started work on the film, chapters on preproduction, the music (Kenny is an expert on pop and rock), the editing, the critical reception, and the ultimate fate of the real-life protagonist Henry Hill. Then, like the narrator of a Criterion video supplement, Kenny surveys Scorsese’s career after Goodfellas. Finally, an epilogue is virtually a monologue: Scorsese talks almost without interruption for twenty-five pages, as if this were the interview rounding off the disc. There’s also a bibliography, a timeline of the production, and the recipe for Henry Hill’s ziti.
At the center is a 150 page scene-by-scene account of the film: a commentary track in your hands. Alongside that sit chapters that function as bonus materials. They include a brief introduction to the filmmaker just before he started work on the film, chapters on preproduction, the music (Kenny is an expert on pop and rock), the editing, the critical reception, and the ultimate fate of the real-life protagonist Henry Hill. Then, like the narrator of a Criterion video supplement, Kenny surveys Scorsese’s career after Goodfellas. Finally, an epilogue is virtually a monologue: Scorsese talks almost without interruption for twenty-five pages, as if this were the interview rounding off the disc. There’s also a bibliography, a timeline of the production, and the recipe for Henry Hill’s ziti.
It’s overwhelming. Kenny has evidently read everything about the real-life sources of the story, and his interviews turn fan service toward crime reporting. It is no small thing to pursue hard cases who were recruited for bit parts. Kenny has also garnered a lot of information from staff like AD Joseph Reidy, who are seldom given much attention. Keating would probably be happy to see Kenny’s narrative splinter into stories leading to other stories, such as the effects of the film on the careers of Barbara De Fina and Ileanna Douglas.
I compared the book’s central chapter to a DVD commentary. Anybody delivering a voice-over play-by-play regrets that you have to keep up with the film and can’t devote as much time to a big scene as you might like. Thanks to the print format, Kenny is able to pause the film and spiral out from it to fill in backstory or behind-the-scenes dynamics.
Early on, he can give us three pages on Tuddy, both his original (who died in prison) and Frank DiLeo, the actor playing the role. Kenny explains that DiLeo was a music executive who oversaw Michael Jackson’s “Bad” video, which included a Wanted poster of Scorsese in a subway scene, which ties to a sneaky reference to the “Smooth Criminal” video featuring a character named Frank Lideo, played by Joe Pesci. . . well, you get the idea. Likewise, in an astonishing cadenza, Kenny identifies every actor and wiseguy in the long POV tracking shot in the Bamboo Lounge.
His account of the cast rummages through filmographies and personal histories, and adds the sort of oversharing we welcome: “Behind the placid mook mug seen in the movie was a remorseless killer.”
All these exfoliating tales don’t conceal a sustained performance of film criticism. Kenny’s governing idea is that Goodfellas cons us through a bait and switch. Lured in by a rapid-fire opening that arouses a bemused attraction to these bad boys, we’re gradually forced to a more sober, even horrified, realization of their moral and emotional brutality. I think that this fairly reflects most viewers’ experience. But how does the trap work?
Kenny plots an “arc of disengagement” between the killings of Tommy and Spider. A rise-and-fall pattern links the parallel scenes of the Bamboo Lounge, the Copacabana, and the shabby tavern where the gang meets to whack Morrie. Kenny draws nuanced comparisons with The Godfather and is very detailed on Scorsese’s visual techniques, particularly the freeze-frames and fadeouts, which usually get less attention than the flashy camera moves. One of the book’s main points is that Scorsese, newly aware of how TV commercials trained viewers in quick pickup, deliberately decided to make his fastest-paced movie. And of course the music is central to managing our mood and commenting on the story.
As a seasoned reviewer, Kenny can write. “Frisky newlyweds still hot for each other; you love to see it.” Henry (“a walking appetite”) eventually pulls Karen into his schemes: “The revitalized marriage will find its sense of twisted teamwork.” And digression is welcome when it humanizes the author. Listening to Sid Vicious’ version of “My Way” is comparable to “say, eating the fried chicken from the Kansas City restaurant Stroud’s for the first time.” (The “say” makes the sentence.) A movie about food begs the critic to sample a little synaesthesia, with music evoking mouth-watering chicken. Come to think of it, that linkage of music and food is in Goodfellas too.
I especially enjoyed Kenny’s rebuke to fans who bust this carefully constructed work into “movie moments.” You probably know that one school of criticism thinks that films are more or less loose assemblages of scenes, out of which certain instants become incandescent. Certainly there are such moments in many movies, and sometimes they stand out from a gray pudding. But often strong moments ravish us because they’ve been prepared for by careful craft. So Kenny’s guided tour of Goodfellas shows its affinities with Keating’s holistic approach:
Serrano and his crew reduce movies to anthologies of “cool” or shocking moments, as opposed to fictions whose circumscribed worlds aspire to create beauty or sorrow or horror or joy in some formally coherent whole.
Mon semblable, mon frère.
Dead end at the ocean’s edge
La La Land (2016).
On the other hand, I ought to be out of sympathy with Mick LaSalle’s Dream State: California in the Movies. It’s unabashedly reflectionist, tracing how films project contradictory images of the Golden State. The screen image of California promises pure self-fulfillment, but that leads to loneliness, danger, conformity, and loss of dignity. If Kenny and Keating see movies as made by an army of artisans, LaSalle treats them as springing full-blown from American mythology. There is barely a mention of a director, let alone a sound mixer, in his account.
 Instead, California-ism makes its way to the screen through a surge of a “collective mentality.” For instance, the blockbusters’ endless images of urban annihilation spring from “a people disseminating and celebrating visions of their own obliteration. . . . Something is seriously wrong with the nation producing such visions.” He suggests that “the fear of extraterrestrials is the disguised fear of illegal aliens. . . . the fear of the apocalypse is the disguised fear of terrorism.” Hollywood takes dictation from mass anxieties.
Instead, California-ism makes its way to the screen through a surge of a “collective mentality.” For instance, the blockbusters’ endless images of urban annihilation spring from “a people disseminating and celebrating visions of their own obliteration. . . . Something is seriously wrong with the nation producing such visions.” He suggests that “the fear of extraterrestrials is the disguised fear of illegal aliens. . . . the fear of the apocalypse is the disguised fear of terrorism.” Hollywood takes dictation from mass anxieties.
I’ve explained elsewhere (here and here) why I find such claims unpersuasive. I think that reflectionism is every smart person’s mistaken idea about cinema. But sometimes, as with Susan Sontag’s essay “The Imagination of Disaster,” a reflectionist account of a film can activate some valuable ideas and information along the way, and it can host some entertaining writing. These benefits, I think, emerge throughout Dream State. In kaleidoscopic bursts, LaSalle provides suggestive takes on movies familiar and obscure, and the way they link to one another.
For example, he tracks recurring plot patterns. There’s California’s version of the One Great Night, when individual transformation takes place in a few hours of turbid activity (Superbad, Modern Girls). American Graffiti is the prototype, and in just two pages LaSalle evokes the way audience knowledge races ahead of the characters, far into the future. (Curt winds up in Canada, which probably has to be explained to young viewers today.)He’s very good on the cost-of-stardom plot, from What Price Hollywood to La La Land, this last the only film that faces the fact “that every great advance requires sacrifice, and that even though there is nothing like the joy of first love , there is nothing more important than the fulfillment of one’s inner self.”
 LaSalle considers our willingness to take stars as surrogates for us, and here I was reminded of another critic who tried to pierce the Hollywood Hallucination, the great Parker Tyler. He had, I think, a more meta attitude toward the movies, since he avoided straight reflectionism by treating every film as a charade, a narcissistic exercise in make-believe. For Tyler, Hollywood movies were always primarily about Hollywood, filled with symbolic surrogates for their makers and their viewers. In this respect, LaSalle’s opening chapter is agreeably Tyleresque, positing The Wizard of Oz as a film enacting the flight to a dream city; the Emerald City as Hollywood. Like Tyler as well, LaSalle searches for what he calls a movie’s complex finish, as with a glass of wine. Wizard ends not on a note of ambiguity exactly, but on something like a chord that sets off contrary overtones. Tyler’s books were built on this chord.
LaSalle considers our willingness to take stars as surrogates for us, and here I was reminded of another critic who tried to pierce the Hollywood Hallucination, the great Parker Tyler. He had, I think, a more meta attitude toward the movies, since he avoided straight reflectionism by treating every film as a charade, a narcissistic exercise in make-believe. For Tyler, Hollywood movies were always primarily about Hollywood, filled with symbolic surrogates for their makers and their viewers. In this respect, LaSalle’s opening chapter is agreeably Tyleresque, positing The Wizard of Oz as a film enacting the flight to a dream city; the Emerald City as Hollywood. Like Tyler as well, LaSalle searches for what he calls a movie’s complex finish, as with a glass of wine. Wizard ends not on a note of ambiguity exactly, but on something like a chord that sets off contrary overtones. Tyler’s books were built on this chord.
Another critical avenue that LaSalle opened up for me was iconographic: the differences between LA movies and San Francisco movies. He deftly contrasts the ambience and topography of the cities. Noir and disaster films are primarily anchored in LA, while San Franciso movies tend to be steeped in nostalgia (e.g., Jobs, Milk). He keeps finding new angles to comment on. Avoiding the obvious effort to discuss California’s boom during and after the war, he skips back to the months around Pearl Harbor to bring to light films, mostly exploitation quickies like Secret Agent of Japan and Little Tokyo, USA, that rushed to treat Japanese Americans as potential spies. Meanwhile, the unoffending citizens were shipped off to internment. On a lighter note, anybody who’s bold enough to praise Gidget as a more mature film than Easy Rider gets my admiration (and agreement).
LaSalle, who came to California from the east, weaves in bits of memoir that highlight his main theme. And like Kenny, he writes with conversational wit.
“Home is horrible. Oz is horrible, too. . . but at least it’s in color.”
On Saturday Night Fever and Grease: “One seems tough, but it’s soft. (Of course, that’s the New York film.) One seems soft, but it’s hard. (Of course, that’s the Los Angeles film.)”
In Hollywood “integrity is so original it might just work as a strategy.”
In Out of the Past, “sex can kill you, but it’s worth it anyway.”
In San Francisco (1936) “if only to get Jeanette MacDonald to stop singing, the Earth had to intervene.”
Contrasting Monterey Pop to Woodstock‘s utopian fantasy, LaSalle nearly had me on the floor.
This is a model? Hundreds of thousands of intoxicated people, unable to wash, all but sitting in their own slop, cheering for a series of aristocrats that swoop down to entertain them and then leave? Meanwhile, the army flies in food and the slave classes clean out the Port-O-Sans? That’s sustainable as a societal model?
In addition to all this, through engaging appreciation, LaSalle has prompted me to seek out a great many films I hadn’t heard of. That’s another duty of the good critic. After seeing so much–pounding the beat every day–the movie reviewer can steer you to new discoveries.
Cinephile into cineaste and back again
He Said, She Said (1991).
All of these critics have participated in filmmaking. Mick LaSalle has written and produced documentaries. Glenn Kenny has been an actor in several films (including Soderbergh’s Girlfriend Experience). Patrick Keating, who has an MFA in cinematography, has been a DP on independent projects. Reciprocally, director Ken Kwapis started out wanting to be a film critic–in third grade, no less.
 In college he devoured classic movies and gorged on film criticism. Kwapis went on to become a director of consequence, overseeing many features (Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants, He’s Just Not That into You) and TV episodes (The Garry Shandling Show, The Office). Yet he didn’t leave his cinephilia behind. But What I Really Want to Do Is Direct: Lessons from a Life behind the Camera has an intellectual heft rare in career memoirs and moviemaking manuals. It’s at once thoughtful and practical, suffused throughout by an ethic of modesty, tenacity, and what I can only call a desire to remain both a good artist and a decent person. It also contains some first-rate film criticism.
In college he devoured classic movies and gorged on film criticism. Kwapis went on to become a director of consequence, overseeing many features (Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants, He’s Just Not That into You) and TV episodes (The Garry Shandling Show, The Office). Yet he didn’t leave his cinephilia behind. But What I Really Want to Do Is Direct: Lessons from a Life behind the Camera has an intellectual heft rare in career memoirs and moviemaking manuals. It’s at once thoughtful and practical, suffused throughout by an ethic of modesty, tenacity, and what I can only call a desire to remain both a good artist and a decent person. It also contains some first-rate film criticism.
Kwapis intercuts three sorts of chapters. There is the chronological account of the filmmaking process, with advice on taking meetings, establishing rapport on the set, giving actors “playable notes,” and coping with postproduction and marketing. Kwapis insists at every turn that you need to be both firm and flexible, open to every suggestion from the production team but still adhering to your conception of the project.
But this is not auteurism on steroids. If you’re not a Spielberg or a Nolan, the director has to learn tact and strategy. Kwapis emphasizes not abstract technique but the interactive, interpersonal demands of filmmaking, He suggests ways of responding to producers’ notes or actors’ complaints that allow everyone to keep their dignity. Just stepping away from the Video Village, that cluster of people around the monitor, and positioning yourself by the lens is a way of proactively steering the scene. He even gives good advice about bad reviews. His creative process? “I want to stand behind the camera and make sure there’s something alive going on in front of it, something recognizably human.”
A second batch of chapters shows this aesthetic/ethos in action through case studies from Kwapis’ career. Starting with Follow That Bird (1985), the Big Bird movie, and running up to A Walk in the Woods (2015), these chapters are about concrete problem-solving. How do you direct puppets? Or orangutans? Or Rip Torn? How do you support an actor who’s just not physically up to the role? There’s a fascinating account of staging options in The Office, where different situations force choices between developing the action in the “bull pen” or in the conference room.
The 1990s were rife with narrative experiments, and He Said, She Said (1991) was one of them. Unfolding over two days, its first part uses flashbacks to present Dan’s memory of his romance with Lorie, while the second part shifts to her version, with replays and gap-filling scenes that show the biases of his account. Kwapis and his wife Marisa Silver (Permanent Record) decided to divide responsibilities, with him directing the man’s scenes and her directing the woman’s. They also built in stylistic differences.
We pre-visualized each version to create as much contrast between Lorie’s and Dan’s personaities as possible. For example, I often show Dan’s literal point of view of Lorie, while Marisa uses camera movement and choreography to underscore how Lorie feels about herself (i.e., insecure).
They created specific ground rules for shooting the scenes. Kwapis’ portion came first, so that Silver could see it and fine-tune the replay. Kwapis is admirably specific about how their strategy shaped performance and plot, with minor characters in one half becoming major in the second.
In other words, a cinephiliac idea. (Kwapis prepared for his task by watching Rashomon, The Killing, and Citizen Kane.) The third type of chapter he offers is pure, sharp film criticism, always informed by the demands of craft. His account of American Graffiti is quite different from LaSalle’s, but no less appealing, emphasizing Curt’s visit to Wolfman Jack as an epiphany that needs no formal underlining (“no ham-fisted push-in”).
Other chapters scrutinize 2001, Lawrence of Arabia, The Graduate, I Vitelloni, and other classics. Without being pretentious Kwapis manages to invoke the “objective correlative” (e.g., shoes in Jojo Rabbit) and reflexivity (no big deal). I especially appreciated his detailed analysis of staging in a scene often overlooked in The Magnificent Ambersons: George’s confrontation with a gossipy neighbor, handled in one deftly choreographed close framing.
Kwapis designed the book to explore these three dimensions, but he isn’t puritanical about keeping them apart. Case studies and problem-solving pop up in the general advice sections, and the critical acumen shines through even brief examples of on-set tips (e.g., decisions about a score for Traveling Pants). It all flows together.
The result ranks with Sidney Lumet’s Making Movies and Alexander MacKendrick’s On Film-Making, the most acute personal reflections on Hollywood directing. But like those, it’s more than a testament to the power of craft. It’s also a vision of how, as the first chapter says, to go “beyond success and failure in Hollywood.” You do it, Kwapis maintains, by knowing your plan, respecting your co-workers, inviting discovery through accidents, and staying humane. I like to think that studying films as a critic helped him get there. Not every director, after all, can quote Jean Renoir.
“Only a hack cares about the goddam script”
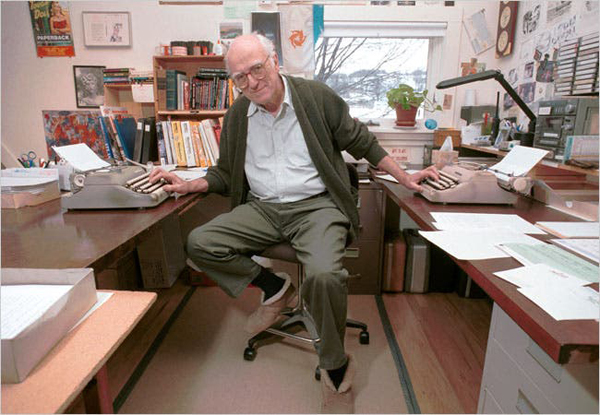
Donald Westlake (David Jennings for the New York Times).
I promised you a murderer, and he arrives in Donald E. Westlake’s Double Feature, a pair of novellas originally published as Enough (1977). The second, Ordo, takes place in Hollywood, when a sailor learns that his first wife has become a movie star and decides to look her up. It’s remarkable in several ways, but the story that grabbed me was A Travesty. On the first page a film critic kills his girlfriend.
 True, it’s an accident, but even then he seems less distressed than he should be. He wipes down the crime scene and slips out. Of course he becomes a suspect. Once he seems to be cleared, the trusting cop lets him mosey along on later investigations. They discover that the critic has a knack for solving crimes, including an old-fashioned locked-room puzzle. He gets caught thanks to a plot twist that owes a good deal to Westlake’s early days writing happily overblown softcore porn.
True, it’s an accident, but even then he seems less distressed than he should be. He wipes down the crime scene and slips out. Of course he becomes a suspect. Once he seems to be cleared, the trusting cop lets him mosey along on later investigations. They discover that the critic has a knack for solving crimes, including an old-fashioned locked-room puzzle. He gets caught thanks to a plot twist that owes a good deal to Westlake’s early days writing happily overblown softcore porn.
The plot lives up to its title, being a travesty of whodunits and man-on-the-run thrillers. Westlake invokes mystery conventions like the dying message and the final twist: “As with all Least Likely Suspects, I was in reality the Murderer.” But this guilty protagonist is writing a profound essay on Top Hat and interviewing an over-the-hill director who undermines his belief in the auteur idea that “it’s up to the director to color and shape the material and so on.”
A: Yeah, that’s fine, but you got to have the material to start with. You got to have the story. You got to have the script.
Q: Well. . . . I thought the director was the dominant influence in film.
A: Well, shit, sure the director’s the dominant influence in film. But you still gotta have a script.
Well, that wasn’t any help. What was I supposed to do, go ask three or four screenwriters for suggestions?
A Travesty reveals that Westlake followed East Coast cinephile taste pretty closely. In the passage after this one, the killer regrets placing Brant so high in the Pantheon–a clear reference to Andrew Sarris’s writings. Better to ask a real director like Hawks or Ford or Hitchcock, or even Fuller.
Hip movie references are de rigueur in most mysteries today. (Grudge-reading The Woman in the Window, I thought: Just kill me now.) But how many thrillers in 1977 invoked Marion Davies or Manny Farber’s Negative Space? Our anti-hero argues with a girlfriend about circumstantial evidence in The Wrong Man and Call Northside 777. And as you’d expect, the big clues that reveal the killer to her come from Gaslight.
Westlake has long been one of my heroes; his Richard Stark novels get a chapter in that manuscript I mentioned at the outset. (Go here and here to gauge my dedication.) Like Elmore Leonard, he had a pragmatic approach to movie versions of his work. As far as I know, he complained only of Godard’s handling of The Jugger, which became Made in USA, not that anybody could tell. He wrote screenplays, notably The Stepfather (1987) and The Grifters (1990), and many of his stories have been adapted to the screen (Point Blank, The Outfit).
Nearly all his work I know has a zesty playfulness, and A Travesty is no different. It suggests that, after shooting down movies and destroying reputations, film critics have earned a chance to kill for real. They just turn out to be fairly bad at it.
My stack of reading has barely dwindled. I’ll try to file some more book reports as summer unfolds and the mosquitos discover our shady lawn.
Thanks to Patrick Keating and Mick LaSalle for sending me copies of their books, though I would have bought them anyway. Thanks especially to Patrick Hogan for telling me of his friend Ken Kwapis’s book.
Philip Pullman, a master of the sort of world-building Keating celebrates, argues against dwelling on the story spinoffs harbored by a richly realized milieu. He borrows the scientific idea of “phase space” to suggest that too great a concentration on the indefinitely large possibilities of a story world can freeze a narrative’s progress and distract the reader from the through-line. A story, he says, is a path through a forest and readers are best gripped by sticking to Red Riding Hood’s journey. (Compare Sondheim’s Into the Woods.) Interestingly, he compares this strategy to the cinematic idea of knowing the right spot for the camera, a spot that’s just as valuable for what it excludes as for what it shows. See Daemon Voices: On Stories and Storytelling (Vintage, 2017), 20-24, 122-123.
For more on Parker Tyler, see the chapter in my The Rhapsodes: How 1940s Critics Changed American Film Culture. Avoiding straight reflectionism, Tyler saw the film world as its own sealed-off realm. If the movies reflect anything, it’s not what America thinks but what Hollywood thinks that America thinks. Or rather, what Hollywood imagines that America dreams.
In this entry I write about some of the anti-Japanese films Mick LaSalle discusses.
This entry analyzes the pseudo-documentary style of The Office. I write about 1990s as an era of narrative experimentation in The Way Hollywood Tells It: Story and Style in Modern Movies.
No admirer of Westlake can ignore the addictive Westlake Review or, of course, the official webpage maintained by his son Paul. Westlake’s motto: “My subject is bewilderment. But I could be wrong.”
American Graffiti (1973).
Brains, bodies, and movies: Ways of thinking about the psychology of cinema
Summer at Grandpa’s (Hou, 1984).
DB here:
This is another phantom entry I posted as Private for the seminar I’ve been teaching this term. I’ve opened it up for a wider audience because some readers have written to ask for access to the ideas. These are comments based on assigned reading for the course. Just as important, this entry serves as an introduction to a guest post coming up next week from Malcolm Turvey.
An earlier phantom entry, which considers how critics interpret a movie’s themes, intersects with this one. This is no less wonkish than that was.
The course has been an examination of the theory and practice of a particular perspective on studying film, the poetics of cinema. A poetics of any medium tries to study the principles undergirding the craft (technê) of artistic work in that medium. These principles may be explicit rules, or guidelines steering the makers’ decisions. But poetics can also reasonably try to trace how those principles and practices are designed to shape effects on perceivers. (For film, let’s call them spectators, but they of course listen as well as watch.) What are some fruitful ways to think about effects?
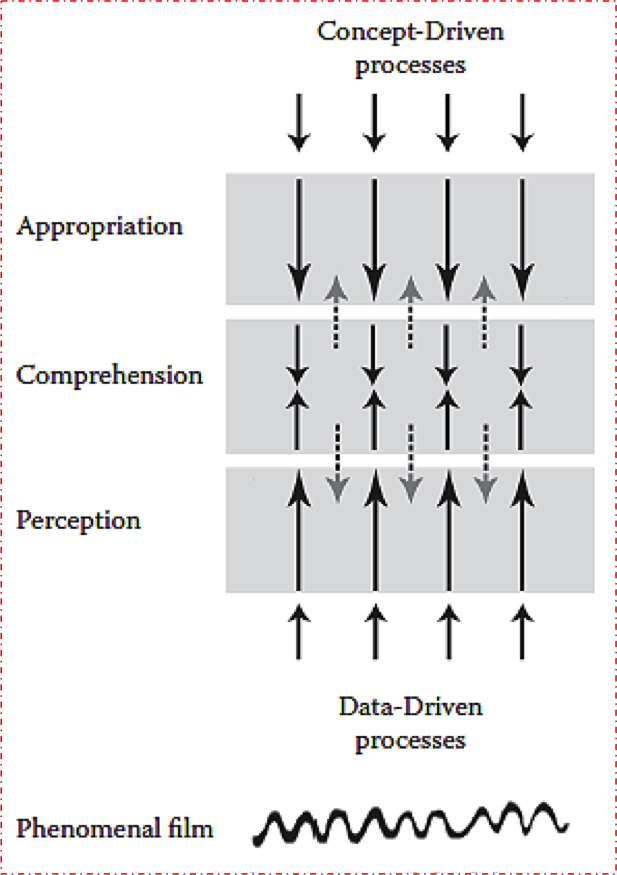
My initial stab at this was the bottom-up/top-down diagram of viewer activity.
To recap: As viewers we have capacities that are data-driven (bottom-up); these yield what we normally call perception. That’s already a huge range of activities, carried out mostly below the level of consciousness. (You can’t watch yourself registering color wavelengths.) In film viewing, perception runs from very fast, encapsulated, specialized, and “dumb” systems, like the phi phenomenon and apparent motion, to somewhat slower (but still fast and involuntary) ones like object recognition, speech recognition, and the like.
The top-down processes, which I called appropriation, are concept-driven, more voluntary, more deliberative, and more extensively funded by experience. A prototypical case would be judging a movie good or bad, or picking a clip to show in class. Interpretation, which I considered in this entry, is a common act of appropriation in the film-viewing community.
In the middle zone are what I called activities of comprehension. A prototypical example is following a story. It’s data-dependent (I can’t make Jackie Chan into James Bond) but it’s also concept-dependent (I can identify the conflicts and combats in a martial-arts film because they make the plot advance in a conventional manner). In non-narrative filmmaking, other comprehension skills come into play, drawing on knowledge bases, heuristics, and the like. You need some experience of art and life to follow the poetic fishing documentary Leviathan.
I wanted to allow feedback too, so the dotted lines in the middle try to suggest how comprehension can fund certain aspects of perception. We recognize Jackie Chan as likely to be the hero, and this concept helps steer our attention to him in his shots. Comprehension of course also funds appropriation, as when after grasping the film’s story we pick it apart in analysis.
One implication, already touched on in the interpretation entry, is this: As we go up from perception to appropriation, the filmmaker’s control wanes and the viewer’s control increases. Spielberg structures Raiders of the Lost Ark the way he wants, but you can appropriate his movie as a piece of imperialist ideology and he can’t do a damn thing about it. In the middle, it’s a negotiation: He steers you to construct the story a certain way, but you can also fill it out with your own inferences, or claim he hasn’t given you enough cues to do so. (Does Marion really love Indy? How much?)
And emotion is involved at all stages of the process, from the jolt of jump scares to the high-level social satisfactions of fandom.
Functions and inferences
 This model was an attempt to be naturalistic—that is, in accord with what the special sciences currently know about how viewers’ minds work—but minimally so. This is an important point. This is a functionalist account. That is, it’s largely indifferent to how the processes are manifested in physical mechanisms.
This model was an attempt to be naturalistic—that is, in accord with what the special sciences currently know about how viewers’ minds work—but minimally so. This is an important point. This is a functionalist account. That is, it’s largely indifferent to how the processes are manifested in physical mechanisms.
Think of all the vending machines you’ve encountered in your life. Each one yielded you those tasty snack treats in a predictable way, but there are different designs and materials. There are those drop-down machines that usually clamp your wrists when you try to reach into their pilfer-proof trenches. There are the little-window ones, which rotate the goodies into place (sometimes). There are even ones that use claws or turntables. And the bits and pieces can be made of plastic or metal, while the gearing and electronics and the machinery for grabbing your money (and denying your change) can be widely varied. But all in all, they have the same basic function and purpose: to take your payment and give you something deliciously unwholesome.
In the same way, my model of the spectator is agnostic about how the processes are instantiated in physical stuff. Doubtless retinas and neurons and inner ears and the nervous system are involved, but I’m not providing the details. I have no idea how to do so. Maybe we should think of the mind as having a core-periphery topography with outward-facing systems (the senses) as discrete modules picking up data while “central systems” supply the top-down treatment. Or maybe the mind is just a tangle of wetware, wires running all over the place, with “higher” functions jammed against, or crisscrossing “lower” ones.
I leave sorting all that out to the experts. But in terms of functions, I think it’s fair to say that most psychologists let the bottom-up/top-down metaphor capture distinct sorts of activities, however they are manifested in our senses, brains, and nervous systems.
More controversial is my argument that these activities are inferential in nature. This signals my commitment to New Look thinking, the early cognitive trend launched by Jerome Bruner, R. L. Gregory, Noam Chomsky et al. Computational models of mind emerged from this research. Nobody doubts that in the comprehension and appropriation phases, inferences are involved. Understanding a story or interpreting a movie as sexist clearly relies on inferences, “going beyond the information given.” The tougher controversy comes with perception.
Following Helmholtz, who believed that perception was “unconscious inference,” the information-processing perspective holds that perception is inference-like. It is defeasible. My eyes can fool me, as with mirages and the bent-looking stick in the pond. This is one reason New Look psychology is interested in illusions.
Moreover, perception operates with assumptions, just as inferences do. Many perceptual assumptions may not be learned but rather “innately specified” to some degree–that is, as presets. It seems, for instance, that we are evolutionarily “wired” to expect light to come from above. It’s also very advantageous for us to be able to separate figure from ground and tell living things from nonliving ones. These basic perceptual acts are funded not only by experience but by presets that steer us in a certain direction. No blank slate here; lots of veins and grooves. And given that we enter a structured ecosystem at birth, rich and flexible innate dispositions can be tuned to information pickup during a critical period. Babies learn fast because they’re primed to set the switches.
This perspective is usually contrasted with the view that holds that perception is “direct.” Most famously, J. J Gibson held that “the information is in the light.” Thanks to evolution and our mobility as creatures, we don’t need any elaborate inferential activity. The input is so redundant that we reliably detect the features of the environment automatically.
I think that the Embodied Cognition theorists are somewhat akin to Gibson in their belief in minimally mediated sensory pickup. Admittedly, though, as Gregory Hickok suggests in The Myth of Mirror Neurons, the Embodied Cognitivists do seem to have a computational side in treating mirror neurons as supplying “representations.” And one strain of Embodied Cognition, identified with George Lakoff and Mark Johnson, denies the inferential and computational model but still adheres to conceptual schemes (like metaphors) as representations of bodily experience. So some categorical, mediating inferences seem to play a role.
The next section discusses how New Look thinking can help us understand visual arts. My comments target two essays in the 1973 collection Illusion and Nature and Art: R. L. Gregeory’s “The Confounded Eye” and E. H. Gombrich’s “Illusion and Art.”
Gregory, Gombrich, and art
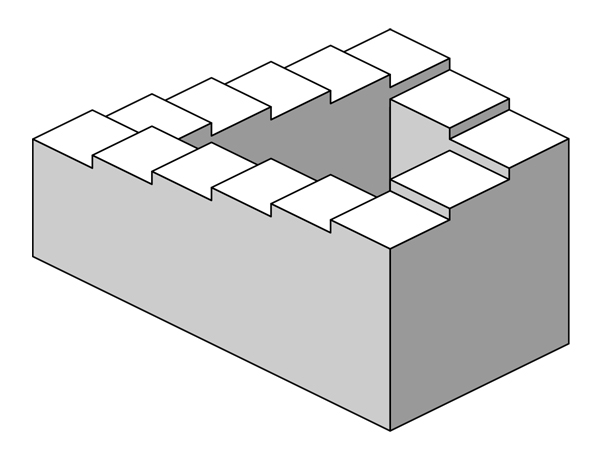
The Penrose steps.
New Look psychologist Sir Richard Gregory (lower right) was a passionate connoisseur of illusions like the Penrose stairsteps. He was famous for pushing the cognitive model of inference-making very far, deep into the basics of perception. He saw perceptions as the usually reliable results of assumptions and hypotheses, in a process significantly similar to what scientists do when they launch hypotheses and check for confirmation. For a career overview, go here.
I take it that he’s trying to answer the question: What perceptual processes generate visual illusions? We evolved to pick up accurate information from the environment, and normally our perception is accurate. The obvious problem with illusions is that they yield false information. What has fooled our eye?
 Gregory’s essay “The Confounded Eye” offers a detailed set of explanations, divided between mechanism failures and misplaced strategies. In cinema, a clear mechanism failure would be apparent motion. Movies trade on a failure of our visual system to detect single frames that are still images. As we didn’t evolve to watch movies, and as we don’t encounter this sort of intermittent illusory motion in a state of nature, inventors found a way to trick our eye and create the impression of movement.
Gregory’s essay “The Confounded Eye” offers a detailed set of explanations, divided between mechanism failures and misplaced strategies. In cinema, a clear mechanism failure would be apparent motion. Movies trade on a failure of our visual system to detect single frames that are still images. As we didn’t evolve to watch movies, and as we don’t encounter this sort of intermittent illusory motion in a state of nature, inventors found a way to trick our eye and create the impression of movement.
As for perceptual strategies, perhaps in film we could cite special effects and green-screen backgrounds, where perspective, lighting, focus and so on are calculated to suggest space that isn’t really in front of the camera. Our visual system assumes regularities of space that aren’t justified; we usually can’t force ourselves to see these backgrounds as flat.
Some controversies dog Gregory’s theory, chiefly in his reliance on prior experience. He thinks that even pretty low-level outputs depend on knowledge of some sort, if only about our world of discrete edges and solid shapes. He doesn’t seem to treat evolution as shaping many of our perceptual proclivities. In this essay “The Confounded Eye,” he appeals to classical conditioning (p. 66) to get the system off the ground.
But crucial are the ideas we also find in the work of E. H. Gombrich. Gregory assumes an active perceiver, one who takes fragmentary stimuli as cues for building up a perceptual conclusion, through a process of hypothesis-testing. Expectation, assumptions, and probabilities all play a role. Perception is inferential because it can be wrong.
In addition, Gregory reminds us of the importance of habituation (sometimes confusingly called “adaptation”). This means simply resetting the threshold of your sensory input. At first the coffee shop seems noisy, but soon enough you’re paying no attention to it and completely sensitive to your partner’s whisper. People can even adjust to wearing eyeglasses that turn the world upside down! Habituation is perhaps the most robust finding in all of psychology—and something that, when it becomes all-powerful, Victor Shklovsky deplores. (“Habitualization devours works, clothes, furniture, one’s wife, and the fear of war.”)
Gregory’s last book, the cleverly titled Seeing through Illusions (2009), published a year before his death, is a detailed expansion of these ideas. He classifies dozens of illusions according to a richer scheme than the one laid out in his 1973 article.
There’s a lot more in Gregory’s essay, not least the homunculus argument which has been broached against a lot of cognitive theorizing (mine included). But now let’s look at Gombrich’s essay “Illusion and Art.” He was a friend of Gregory’s and he borrowed heavily from New Look psychology.
Despite the book’s title, Gombrich’s magnum opus Art and Illusion doesn’t center on illusion as such. In trying to answer the question Why does [European representational] art have a history? he had to confront “illusionistic” styles, but that issue was secondary to the larger issue of continuity and change in representational traditions. So with an essay called “Illusion and Art,” Gombrich offers a more explicit and careful account of illusion.
I take it that his guiding research question is something like How may we explain the artistic and psychological processes that generate illusion in the visual arts? Not surprisingly, he will make use of some of Gregory’s ideas.
What seem to me crucial here are Gombrich’s reflections on animal perception. Far more than in A & I, he posits a continuum of sensory appeals and so a sort of spectrum of degrees of illusion. To a considerable degree, he has turned my vertical diagram into a horizontal one.
There are automatic, involuntary processes he calls “sensory triggers.” Moving along the spectrum, there are more elaborate strategies for conjuring up illusion, but these will rely on more deliberative processes. Throughout, we never lose the sense that we are watching a representation, however realistic it looks.
Moreover, Gombrich attributes the fast and mandatory illusions, the ones Plato called “lower reaches of the soul,” to evolution. He posits that just like other creatures, we have sensory systems that respond to “triggers” automatically, and sometimes we can be deceived–as predators are fooled by the camouflage of their prey.
So what about illusions? At one end is pure delusion, as with say counterfeit money. Trompe l’oeil is a little further along; you really have to get close to detect the difference. Flat objects, like letters tacked to a board, are good for this trickery, as are fictitious postage stamps like those of Donald Evans.
These cues are very realistic, but crucially the trigger need not be a close replica of what it represents. Approximation can work. The duckling can follow a moving brown box if it moseys like its mother; the box doesn’t look like Mom, it just triggers the Mom-response. Stickleback fish will strike a red cloth that doesn’t look much like another fish’s belly–except in being a moving patch of red. Recall as well the Frog Multiplex. These critters are slaves to innate “action programs.”
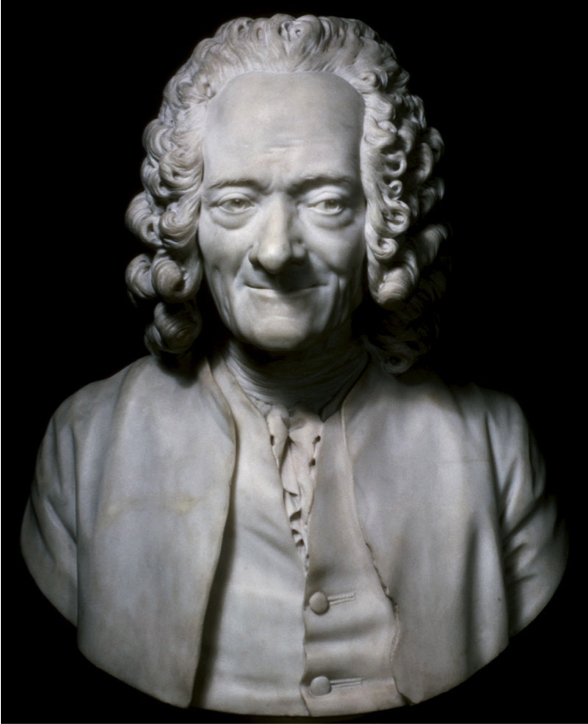
A flat, impoverished display of a wiggling worm is enough to get the right (wrong) reaction. And note a fascinating Gombrich example, Houdon’s bust of Voltaire, where the sparkle in the eye is actually a tiny lump protruding from the surface. You couldn’t get farther from a non-realistic device for depicting a gleam of light.
Hence a typical Gombrich formulation: What matters most is stimulation, not simulation. Images at whatever degree of realism rely on key features that trigger our automatic systems. The big transaction isn’t resemblance. The link is not between image and object but between the activities involved in processing the image and those processing the object. The image has hitched a free ride on perceptual habits, or faults, that we already have and cannot always see beyond.
Further along the spectrum, our response can be more flexible, less data-driven. We can learn to control and use the illusion, appreciating it. We can consciously factor in context, prior experience, interpretative possibilities. We can shift mental sets and adjust our expectations, we can test projections by trial and error. We’re now in my realms of comprehension and appropriation–comparatively self-conscious film experiences. But we couldn’t go so far and wide without anchoring our response in the fast, mandatory “lower reaches of the soul,” whose powers derive from evolution.
 You can see how all this fits Gregory’s hypothesis-testing account of shape perception and object identification. We are already expecting to see something, either because of prior experience or some wayback presets. We don’t need much of a cue to lock in a grasp of what’s there–even if it turns out not to be really there. That’s the case with “phantom percepts,” those imaginary objects that mimes conjure up.
You can see how all this fits Gregory’s hypothesis-testing account of shape perception and object identification. We are already expecting to see something, either because of prior experience or some wayback presets. We don’t need much of a cue to lock in a grasp of what’s there–even if it turns out not to be really there. That’s the case with “phantom percepts,” those imaginary objects that mimes conjure up.
Gombrich’s essay also emphasizes time more than Art and Illusion had. The sequential nature of perceptual activity–scanning an image–doesn’t occupy him much, but I think it’s quite important. I’ll give an example later on. But he’s right to stress the pressure of time in an evolutionary context. Fight-or-flight decisions have to be made fast, and so creatures with oversensitive mechanisms had a better chance of surviving, even if they sometimes wasted effort in avoiding harmless things. This time dimension takes Gombrich to movies, of course, as well as to flight simulators.
The last main point I’d stress is Gombrich’s insistence that we’re always after meaning. In Art and Illusion he proposes that we never see space as such, but rather medium-size objects in an environment. Representing “space” is tough, but people can provide convincing information about the spatial layout of people, places, and things. Mapmakers do it, technical illustrators do it, we make stabs at it, and painters do it with precision, delicacy, and force. Ditto textures, lighting, and other features of the world.
The “effort after meaning” flows from the inferential, seeking nature of perception. In a memorable formulation Gombrich says we don’t see people’s eyes as such: “We see them looking.” We are geared to meaningful objects, actions, and implications, not purely physical metrics. Again, this makes evolutionary sense. Creatures who focus on measuring the distance between a tiger’s eyes aren’t going to leave as many offspring as creatures sensitive to gaze direction and threatening sounds.
Perceptual psychologists will debate whether the New Look/inferential model or the Direct Perception model of Gibson et al. is better for explaining real-life perception. But as my concerns are in studying art, particularly cinema, I think the inferential perspective is better suited to analyze what concerns me. For one thing, it grants that grasping art is active and skilled, something that I think we all acknowledge. Your and my skills of noticing, understanding, and responding complement the skills of the ‘poet’ or maker. We complete the artwork.
Moreover, artworks offer simplified, streamlined displays very different from the blooming, buzzing confusion of the world. Gibson’s perceiver has to hack through a lot of distractions to extract the texture gradients and optical flow that will specify the layout. Art works already do that for us. Art works, films included, are designed with precision to trip our inferential engines at all levels. As a result, an inferential model tracks more closely the critical analysis we want to conduct on films. I’ll try to give two examples at the end.
A personal detour: Monkey see, David do
The Chinese Feast (Tsui Hark, 1995).
In the 1980s, as I was studying narrative and style in Hollywood films, I was struck by the ways in which the films’ designs seemed to aim for particular responses from spectators. I wondered whether the norms in place were coaxing us to perform particular mental acts: assuming, trusting, hypothesizing, anticipating, and so on. A lot of what we see and hear in a film sets up “intrinsic norms” that in effect teach us how to comprehend the story.
This led me to float an approach to spectatorship based on then-current premises of cognitive psychology. I tried to work it out in Narration in the Fiction Film (1985) and later work. Other researchers found this intriguing (to use a Kristin word) and developed well beyond it. Over the years an entire subfield emerged, with its own journal, conferences, and academic network.
The psychological findings I found most useful for my research questions were rather robust, well-confirmed ones involving informal reasoning: the use of schemas, heuristics (quick and dirty inferential routines), prototypes, and other concepts. I call these findings robust because they’re fairly well-replicated phenomena that different theoretical paradigms have tried to explain. They’re especially useful tools for us as students of the arts, for they bear directly on matters of narrative–plot, characterization, causal connections, and the like. They map fairly comfortably onto our analytical categories.
The broad point is that just as visual illusions exploit deficits in our visual system, narrative often plays to biases and shortcuts in more elaborated inferences. We’re good at tracking cause and effect, but the principles we use are “folk psychology,” not the principles of physics. In real life, we may attribute Oscar’s grumpiness to his just having a bad day, but Oscar is a film character and is introduced to us grumpy, we’re inclined to take him as a permanent grouch. (This is called the fundamental attribution error.) This example also trades on the primacy effect, also known as anchoring, which lets the first instance we encounter shape our pickup of information encountered later.
A prime instance of a robust finding was research into eye-tracking.
Film theorists have long considered that attention is central to filmic effects. Once eye-tracking devices became easy to use, researchers could use them to study how people scanned movie images. The pioneering work here was done by Tim Smith. I survey the research program here, and Tim did a powerful guest blog to follow up. His entry, probably the most popular post we ever had, earned him press coverage and a guest visit to film companies to present his research!
For more discussion of these middle-level findings, you can see this reader-friendly version.
Many of these activities are accessible to us, if only in retrospect. In following a narrative, if we pause the movie, we can think about what we’ve noticed and what we expect. As the years went by, though, I began to realize that probably a lot of what engaged us in films wasn’t so easy to tap consciously. Plato’s “lower reaches of the soul” invoked by Gombrich played an important role.
So in the 2000s, when research into mirror neurons was emerging, I drew two lessons. One was that certain primates could respond to film images much as we do–recognize objects, track movements, and so on. I thought, and still think, that this is an exciting piece of information. What was methodology for the researchers is a substantive finding for us. If macaques can recognize what a movie shows, it’s hard to argue that pickup depends on cultural codes.
Second, I thought that the prospect of mirror neurons held promise for carrying inference/computation down into the wiring level. Given all the presets supplied by evolution, isn’t it conceivable that social primates may have evolved to “resonate” to actions, expressions, and even emotions displayed by their conspecifics? It would be another part of a natural endowment that, suitably tuned by the social environment during the critical period of growth, could bootstrap a broader set of skills–such as following stories.
Hence the remarks I made in my 2008 “Poetics of Cinema” essay, where I took the view that “it seems we have a powerful, dedicated system moving swiftly from the perception of action to empathic mind-reading.”
Fairly soon mirror neurons became absorbed into a larger trend toward neuroscientific examination of film viewing. I’m not sufficiently expert to appraise that work, but I do have thoughts about what it can, and can’t, tell us about understanding film.
Mirror, mirror in your head
As I understand it, the Embodied Cognition research program aims to answer this sort of question: What role do automatic, low-level visual processes play in enabling spectators to respond to film? More specifically, do the processes enable us to understand and empathize with action, agents’ intentions, and agents’ emotional states? I think that the general answer proposed is yes.
Mirror neurons play a role in this process. They were first discovered in macaque monkeys, and there is some evidence that they exist in humans. The hypothesis is that when we see a piece of action, in life or in cinema, we spontaneously mimic, in the pattern of cell firings in our brain tissue, the sensory and motor processes that create it. Our brain mimics or “resonates with” the action we perceive. We don’t just “understand” that the man is lifting a glass; in a weakened form we are repeating the experience of his doing so. Of course we may not be holding a glass, but to a degree the sensory and motor cells in our brain tissue rehearse the lifting gesture. Because we’ve executed similar actions, the cell firings are marked out through electrochemical patterns.
This argument takes us into the specialized areas of brain science. A useful account of the general scientific debate is here. The appended articles quickly turn technical, though. An easier read is this piece in Wired. For film, the fullest account of this view is provided by Vittorio Gallese and Michele Guerra in their recent book, The Empathic Screen: Cinema and Neuroscience.
 The reach of Gallese and Guerra’s theory is quite ambitious. They want to explain our understanding of actions (and “from the inside”), our “immersion” in a film, our ascribing intentions to agents, and our “identifying” with or empathizing with those agents.
The reach of Gallese and Guerra’s theory is quite ambitious. They want to explain our understanding of actions (and “from the inside”), our “immersion” in a film, our ascribing intentions to agents, and our “identifying” with or empathizing with those agents.
In our next blog entry, a guest post, Malcolm Turvey will offer an analysis and critique of that book’s arguments. As a pendant to that, I’m just going to signal my reservations about the project and its results. In the last section of this entry I also want to make a point that Malcolm will explore conceptually: How much specificity does a “psychology of cinema” need for us to say useful and unusual things about film?
My first general comment: What the authors mean by understanding, or “involvement,” or the “from the inside” part of experience could do with more specifying. Malcolm will explore this question in detail. In addition, I wonder whether concepts like “identification” and “immersion” fruitfully characterize our engagement with all films, or even those we find exciting.
Camera movement occupies a privileged place in Gallese and Guerra’s scheme. “The involvement of the average spectator is directly proportional to the intensity of camera movements.” Yet what about the first thirty years of cinema, in which camera movement is quite rare? Tableau cinema, as discussed in many entries hereabouts, was presumably quite effective in moving audiences. If camera movement automatically steps up engagement, why didn’t it become more common sooner? And are we talking only about camera movements forward, which are the privileged examples cited from Notorious, The Spiral Staircase, and other 1940s films?
The only effects of the nonmoving camera noted by Gallese and Guerra are expressive ones. “In the absence of movement the editing and arrangement of figures and spaces within a shot can produce a feeling of oppression.” Well, editing and staging within a fixed shot can indeed produce that effect, as we see in Antonioni, but it need not. This makes especially curious the authors’ claim that Dreyer’s La Passion of Jeanne d’Arc, with its close-ups, is a static film evoking through editing “the violent shades of power and persecution.” But of course from start to finish Jeanne d’Arc contains many camera movements.
And are we to assume a “progressivist” conception of history, so that the Steadicam is a step toward “better” (=more engaging) filmmaking? Would all those spectators aroused by crosscut last-minute rescues, from Griffith to Black Panther, have been even more carried away if there had been more camera movements?
Gallese and Guerra don’t assert that every shot would be improved, immersion-wise, by adding camera movement. We also need, they claim, more calm and stable orienting shots so that camera movements can create “peak moments” for maximum impact. Yet, to revert to their favorite director, Hitchcock created quite a peak moment in a certain shower scene wholly through editing. Again, would a flurry of camera movements have made it even more visceral? In fact, the leave-taking camera movement that ends this scene serves as the calm after the perceptual onslaught of cuts.
Of course Gallese and Guerra realize that camera movements aren’t the be-all and end-all of cinematic technique. Yet their discussion of editing seems to me rather unrevealing. Their experiment in varying camera angle through cutting yields the conclusions that “we use the same processes that we employ in our visual perception of the real world” and that our brains register violations of continuity rules to some degree. I am not surprised, though it’s good to have confirmation.
Malcolm will take up several other areas of inquiry in his followup entry. I want to end with a couple of examples to set us thinking about the difference between the neuroscientific arguments and those from a poetics perspective. Here’s a chance to weigh research questions against one another, to see the sort of ideas and information each can yield.
Direction and misdirection: Delicacy via precision
Let’s ask a poetics-weighted question: How can viewers understand the construction of shots designed for perceptual force and narrative comprehension? At the least, we should expect that the pictorial design will solicit attention and emphasis. Deploying these ideas enables us to talk about deflected attention and gradation of emphasis. And we need not assume that the camera is a surrogate for us.
In Summer at Grandpa’s, Hou Hsiao-hsien gives us a somewhat episodic tale of kids sent to live with their grandparents while their mother is hospitalized. In the village they play with the local children and have minor brushups with their stiff grandfather. They’re exposed to aspects of life and death that the modern city has shielded them from. One of those is a madwoman who wanders through the countryside keening.
The boys won’t play with the little girl Ting Ting. So, bearing the toy fan she always carries, she wanders to the railroad tracks and stumbles in the path of a train.
The madwoman’s rescue of Ting Ting is a harrowing, gripping moment. (No need to be energized by camera movement.) The pounding rush of the train, very loud, is an assault on us. The narrowness of her escape is emphasized by glimpses of the two huddling on the other side of the tracks. No need for camera movement to amp up this jolting moment.
But Hou has introduced something else, the fallen fan that tips over and just barely escapes being crushed by the train wheels. Its childishness–pink and orange and green, tipped over by the rush of the wheels–is a kind of stand-in for Ting Ting. It also, by virtue of color and the absence of anything else to look at, rivets our attention.
No less striking is this: When the train has passed, the fan’s blades reverse direction and spin the other way! This tiny bit of movement, visible on a big screen if not here in miniature, provides a kind of coda for the shocking action. This exemplifies, for me, Gombrich’s “visual discovery through art.” We see wind power in miniature, in a natural experiment in the sheer physics of a situation.
All of which proceeds from careful craft decisions. Hou has stretched the norms of framing and staging in fresh ways to achieve a powerful effect. Nothing I see in the mirror-neurons story could address, much less functionally explain, what’s on display here.
Similarly, the Embodied Cognitivist position seems to me too coarse-grained to capture the rather different range of artistic effects in a sequence from River of No Return. Matt Calder and his son Mark help rescue Kay and Harry from their clumsy efforts to raft their way to town. Preminger films the rescue in shots that exploit the CinemaScope ratio. Many critics have noticed how Kay’s wicker trunk of clothes falls into the current and remains visible far into the distance as the dialogue in the foreground develops.
Since the arc of Kay’s character traces the gradual stripping away of her past life as a dance-hall entertainer, this phase of her change is made visible in a soft-pedaled way. Attention and emphasis are played down. Preminger prepares us to watch for secondary and tertiary areas of importance–what Charles Barr has called gradations of emphasis. Alert viewers may notice the drifting basket, others not, but for those who do some inferences will be forthcoming. For one thing, What might be the significance of this basket?
Turns out that this was practice for using our eyes. Having prepped us at the riverside, Preminger again plays with graded emphasis. Before the rescue scene, Matt and Mark share coffee before going out for target practice.
Few of us will notice the rifle in its long holster there on the back wall until Matt takes it down.
Now compare this later scene.
Sparse as it looks, the main shot is busy. The men were decoys but the holster was waiting there to be used at just the right moment. We could have noticed it at any time. Maybe some folks did.
When the rifle pokes into the shot, stressed by Harry’s line, it probably surprises us. But those of us who may have noticed the empty holster earlier may experience suspense rather than surprise: Where did the gun go? We have to wait and see.
This sort of multilayered visual effect seems to lie beyond the sort of responses that G & G attribute to aggressive camera movements. We may not be “immersed,” but we are definitely engaged–albeit coolly. The image is a visual display we search, not a space we imagine ourselves interacting with.
You may say that this sequence is so atypical it’s unfair to use it as a counterexample. But I think it’s just an extreme instance of what filmmakers are doing all the time. Preminger uses classic cues: the holster is isolated, it’s sitting near the center of the picture format, and it’s well-lit. On the big screen in a 1954 movie house, it would be very evident, in principle. And we’ve seen it used before in a very similar camera setup.
But Preminger has steered us away from what’s important by creating competing centers of attention. There are the men’s faces and gestures, the words spoken the dynamically unfolding drama, the woman and the boy executing repetitive actions (what Gombrich in Art and Illusion calls the “etc.,” take-as-read principle). Attention and emphasis are led by lines of least resistance; you’d have to be pretty stubborn to study that holster.
Of course there is a neurological story behind attention and eye tracking. And perhaps Matt’s gesture of reaching and seizing the rifle may “resonate” with our neural circuitry. But for the artistic effect Preminger prompts, it’s surely less salient than our acts of following, scanning, noticing, and registering all that’s going on in this misleadingly muted visual, auditory, and dramatic array. Our neural circuitry isn’t available to us for inspection, but we can bring to awareness the way that directors direct–direct our attention, weight various areas of the shot–usually to supply information, sometimes to suppress it.
In bringing this scene’s constant flow of information and withholding to light, we’re homing in on an uncommon but precise craft decision that has distinct artistic effects on us. This is, I think, an instance of analytical poetics–analyzing a particular film by using the norms and practices we reconstruct on the basis of historical research.
I lay my cards on the table. If our research question asks about the fine-grained principles of cinematic craft, its creation and consequences, its norms and options, we are likely to have little need for generalizations about how all traveling shots may mimic cell firings. Functional explanations can be enlightening when we don’t know about the mechanics. We can attend to precise, often delicate, effects as results of weighted choices from a historically available menu of options. After all, artists are achieving these effects in other media. Even if neuroscientists don’t care about these things, filmmakers do. We should.
So much other bibliography I could suggest! Good introductory overviews are Michael Morgan, The Space between Our Ears: How he Brain Represents Visual Space (2003) and Jennifer M. Groh, Making Space: How the Brain Knows Where Things Are (2014). Both have clear, nontechnical accounts of fascinating experiments. More advanced, but a trailblazing study, is Jerry Fodor’s The Modularity of Mind (1983), a fun read.
I hijack the Frog Multiplex for a discussion of cinematic coding. For more on gradation of emphasis, see this long-ago entry in homage to Charles Barr. I discuss ‘Scope aesthetics from the standpoint of poetics in this online video. I consider Hou’s staging strategies in my book, Figures Traced in Light.
During the current health crisis, Berghahn has made all issues of Projections: The Journal of Movies and Mind freely available. Several articles over the years debate issues around cognitive film theory and brain-based explanations of media effects. My version of cognitivism is discussed in the June 2016 issue. For still more, there’s this web essay and this broad overview.
Inception (2010).