Archive for the 'Film genres' Category
(50) Days of summer (movies), Part 1

Ponyo on a Cliff by the Sea.
DB here:
Travel took me out of Madison for half of June and nearly all of July. While overseas, I saw only one recent US release. So I caught the American Summer Movies in two gulps–over a couple of weeks early on and over the last month or so. In all, exactly 50 days? Well, were there exactly 50 first dates in that movie?
Herewith, comments on a batch of titles. There are spoilers sprinkled throughout, but most of what I say won’t harm your encounter with the film. Because all my remarks amounted to an even longer blog than usual, I’ve broken it into two parts. The next installment, coming up in a few days, talks about The Taking of Pelham 123, Public Enemies, and Inglourious Basterds.

My summer movies were bracketed by two animated pictures. Up is to my mind the most mature Pixar film yet. It has all the virtues we associate with this studio: quick but not frantic pacing, expert handling of resonant motifs, technical brilliance (especially in its depiction of settings), and one-off gags. The poker-playing dogs had me laughing out loud. But as we’ve argued in other blogs (here and here and here), the Pixar team likes to set itself tough challenges. First there is the technical challenge of 3-D, which is easily surmounted. The 3-D effects get more pronounced once the plot lands in South America. More important, I think, is the challenge of representing the emotion of sorrow.
Another movie would have organized its plot around the kid, Russell, and let him meet the elderly Carl in the course of his adventures. That way, Carl would emerge as a merely touching secondary character. But by focusing point of view around Carl’s life, showing his marriage and widowhood, Pete Docter and his team have tackled one of the hardest problems of classic moviemaking. How do you render pure sentiment without becoming sentimental?
The protagonist’s portrait is surprisingly hard-edged. Carl is tightly wound even in his youth, unlike the exuberant and extroverted Ellie. Yet the couple seems to have no friends throughout their marriage, and it becomes easy to see how Carl could will himself into crabby isolation after her death. Thanks to the choice of viewpoint, Carl becomes no mere crank but a truly empathetic figure.
This is fragile stuff, and Docter handles it with tact. Many movies want you to cry at the end, but Up daringly invites you to indulge in its first ten minutes. It then spends the rest of its running time brightening your mood, so that the title could describe the film’s emotional trajectory. It’s one of my two favorite new movies I saw this summer.
Just a few days ago Kristin and I saw Ponyo on a Cliff by the Sea. We’ve been Miyazaki fans since Totoro, and have especially admired Kiki’s Delivery Service and Spirited Away. As with this last and with Howl’s Moving Castle, I have a hard time figuring out the premises of the plot. What rules govern Ponyo’s transformations? Why can’t she become a real girl, exactly? And then why is she permitted to? The well-timed interventions of her mother, like the Witch’s change of heart in Howl, seems a way out of plot difficulties, and as often happens in Miyazaki the plot resolution seems rushed in comparison with the leisurely development of characters’ relationships.
But as usual I was won over by the effortless virtuosity of the imagery and the weird conviction suffusing Miyazaki’s concept of nature. As in Spirited Away, animation becomes animistic. The sea is bursting with hidden forces: goldfish with extraordinary powers of group effort, waves that turn into blue fish, and bubbles as solid and slippery as balloons. Nobody but Miyazaki could imagine the quasi-Wagnerian scale of Ponyo’s race, atop gigantic fish-waves, to catch up with Sosuke and his mother fleeing in their car.

These shots burst with more dynamic shifts of mass and scale than I’ve felt in any official 3-D picture.
Sometimes Nature is scary. Although nothing here is as traumatic as Spirited Away‘s transformation of parents into swine, the tsunami scenes induce genuine awe at nature’s exuberant destructiveness. There follows a reassuring calm. Ponyo and Sosuke glide along the flood waters while ancient creatures zigzag in the depths, and the townspeople quietly accept that their homes have been engulfed. Ponyo is a gentle movie, aimed (as Miyazaki explains here) at a younger audience than was his recent work. It’s suffused with simple human affection, seen in acts of spontaneous generosity. What American movie could include a moment when Ponyo, fish become girl, offers a nursing mother a sandwich to help her make milk for her baby? Again, sentiment without sentimentality. Ponyo offers more evidence that whatever the disappointments we may find in live-action movies, we are living in a golden age of animation.

Am I just being perverse in finding Transformers 2: Revenge of the Fallen not as abysmal as others have? Don’t get me wrong. It is not what you’d call good. It is rushed and overblown. What other movie accompanies its opening company logos with gnashing sound effects? Its plot is even more preposterous than the first one’s. Its performers bear that sheen of meretriciousness that fills nearly every Michael Bay project. It is also lazy in its plotting. Worse, I couldn’t really make out the design of the ‘bots. It’s not that the cutting is abnormally swift (a mere 3.0 seconds ASL, about the same as in Up and slower than that in The Hurt Locker). The problem is that the digital camera is swirling around the damn things so fast as they take shape that you can’t get a fix on what they actually look like. All those spinning wheels and dangling carburetors ought to be worth a glance.
But still….For non-Transformers shots Michael Bay at least puts his camera on a tripod, which these days counts as a plus with me. And a minibot humps the heroine’s leg. And John Turturro is in it. Would he grace a movie that signals the fall of Western Civilization?
 In a similar vein but more satisfying was District 9. Its “racial subtext” is as perfunctory and confused as such weighty hidden meanings usually are, and anyhow whatever political points the movie wants to make drift out of view halfway through. Moreover, its “documentary immediacy” is inconsistent: despite footage marked as coming from surveillance and TV cameras, we have unimpeded access to all plot matters. But here the Bumpicam probably allows for cheaper CGI, and as a run-around-shooting-things movie, it needs to keep things simple.
In a similar vein but more satisfying was District 9. Its “racial subtext” is as perfunctory and confused as such weighty hidden meanings usually are, and anyhow whatever political points the movie wants to make drift out of view halfway through. Moreover, its “documentary immediacy” is inconsistent: despite footage marked as coming from surveillance and TV cameras, we have unimpeded access to all plot matters. But here the Bumpicam probably allows for cheaper CGI, and as a run-around-shooting-things movie, it needs to keep things simple.
I found the smash-and-grab look far more distracting in The Hurt Locker. Kathryn Bigelow has directed several first-rate movies, notably Near Dark (where she used a tripod), Blue Steel (ditto), and Point Break (tripod mostly). On this project, she seemed to me to be doing more conventional work. There are the titles telling us that time is running out (“16 Days Left”). There’s classic redundancy of characterization, as when we’re told that James is a hot dogger–“He’s reckless!” “You’re a wild man!”–as we watch him be all that he can be, and more. There’s the hapless kid who is so near to the end of his tour that you know he’s a marked man. There are even aching slow-mo replays of explosions bowling guys to the camera. What if war films gave up this convention and just showed bombs going off and bodies hurled around as fast as in reality? Might war look a little less picturesque?
The camera is locked down for these iconic slow-mo shots, but most of the scenes are handled in heat-seeking pans, artful misframings, chopped-off zooms, and would-be snapfocusing that can’t find something to fasten on. The editing plucks out bits of local color and sprinkles in some glimpses of onlookers that tend to turn them into props. I’ve tried to show elsewhere that this trend in rough-hewn technique nonetheless adheres to the conventions of classical style: establishing/ reestablishing shots, eyelines, reactions, and close-ups to underscore story points. Even wavering rack-focus can still orient us to the action quite clearly.


The question is what the harsher surface adds, especially when it’s so pervasive. Habituation is one of the best-proven phenomena in psychology, and movies like this seem to prove that it works. After the first few minutes, we’ve adapted to any visceral punch that the Unsteadicam hopes to provide. Maybe it serves to ratchet up suspense? Doubtful. A director would have to be a real duffer to dissipate suspense in a movie about dismantling an explosive device. The trick is to do something different, as in bomb-disposal movies like the Chinese Old Fish and the British Small Back Room.
Still, the plot is decently engaging, and there’s a taut, unpredictable siege in the desert. That long sequence displays a disciplined interplay of optical viewpoints, a sense of constantly revised tactics, a new aspect of James’s leadership style, and nice details about sharing juice boxes. In another era, The Hurt Locker would have been a studio picture in the vein of Anthony Mann’s bleak Men in War. I suppose it shows that yesterday’s genre film, executed with conviction and a certain edginess, can become today’s art movie.
Speaking of suspense: I thought that the setup to A Perfect Getaway was reasonably engrossing. There was some clever self-referential teasing: our hero’s a screenwriter, and there’s talk of a “second-act twist.” And it was mostly shot on a tripod. I hoped that director-writer David Twohy would have the courage to stick with its initial premise and be Deliverance in Hawaii. But sure enough, the things that smelled like red herrings were red herrings, and the reversal that you feared comes to pass in one of those point-of-view switcheroos that movies now indulge in. Come to think of it, that was the second-act twist. But I did like the strategically placed telemarketer call.

We’re evidently allotted one crossover indie movie per summer, a fact acknowledged in the title of this year’s hit. (500) Days of Summer, which really needs its parentheses not just because everybody now overuses them (there’s even a blog confessing it), but because its strategy is to disarm you with its knowing cuteness. It is so self-consciously winning your teeth will ache. It’s a twentysomething romance of the sort usually called “bittersweet.” The guy’s after love and the girl withholds commitment. Guaranteed result: emotional roller coastering, because we’ve seen her flighty sort before in kooky-girl figures like Petulia. There’s a fantasy musical number with a touch of animation, an avuncular narrating voice sliding in and out, a shuffled time scheme sorted out for us with a sort of daily odometer reading, and pop-culture references including retro ones to The Graduate and Ringo Starr. Everybody smiles a lot, and when they’re not smiling they’re crinkling up their faces.
(500) Days plays by the book. Tom and Summer work for a greeting-card company, a satiric target only a little harder to hit than the Pentagon. As in the movies mentioned above, the cutting is intent on making sure we see everybody deliver every syllable. (What ever happened to offscreen dialogue? Did TV kill it?) (Sorry about the parentheses.) The four-part script layout is as neat as embroidery: the first kiss at the photocopiers comes at 24:00, the splitup comes at 47:00, Tom delivers his diatribe against the lies about love at about 72:00, and the epilogue, with its fatal final line, finishes at 90:00. Yet I’m not curmudgeon enough to despise a movie so desperate to be liked, and at last I found a film whose narration clicks along in syncopation with my little tally counter.

The real indie film I admired in my fifty days was Ramin Bahrani’s Goodbye Solo, or Good Bye Solo as the credit title has it. Kristin and I have registered our admiration for Bahrani’s films here and here on this site, and his latest is no less modest, well-crafted, and affecting. A Senegalese emigre cab driver befriends an enigmatic old man who at the start of the film offers him $1000 to pick him up on October 20 and drive him to Blowing Rock Mountain. Solo infers that William is planning a suicide and so starts to intervene in his life. His involvement with William gets intertwined with his family problems and his hopes of becoming an airline attendant.
Goodbye Solo exemplifies the “character-driven” movie. Solo is sunny, quick-witted, and socially adroit; his audition for the airline managers shows him as an ideal employee. William is just the opposite–morose, aggrieved, profoundly unhappy. The treatment is observational, with lengthy shots (an average of over twelve seconds) capturing dialogue and slowly shifting character response.
 The characters change, but Bahrani and his co-screenwriter Bahareh Azimi, wary of quick fixes, don’t push this too far. It would be easy to make William soften more, even eventually make him likeable, and to keep Solo an indefatigable force for optimism. Instead, if William accepts more of Solo’s ministrations, it’s largely due to his passivity, not a fundamental change of heart. Meanwhile, Solo becomes more anxious and pessimistic, shedding some of that casual charm that captivated us in the opening. Neither executes that neat character arc that Hollywood tends to favor and that’s visible in Up and (500) Days of Summer.
The characters change, but Bahrani and his co-screenwriter Bahareh Azimi, wary of quick fixes, don’t push this too far. It would be easy to make William soften more, even eventually make him likeable, and to keep Solo an indefatigable force for optimism. Instead, if William accepts more of Solo’s ministrations, it’s largely due to his passivity, not a fundamental change of heart. Meanwhile, Solo becomes more anxious and pessimistic, shedding some of that casual charm that captivated us in the opening. Neither executes that neat character arc that Hollywood tends to favor and that’s visible in Up and (500) Days of Summer.
Bahrani’s hatred of cliché obliges him to make his story events mundane and equivocal. As in Man Push Cart and Chop Shop, the plot emerges from variations in routine, a lesson well-taught by European festival cinema of the 1950s. But when you have a stubborn, taciturn character like William, and you’re restricted to another character’s range of knowledge, it’s hard to give the film a forward propulsion. You have a deadline, but no momentum. So plot dynamics arise from Solo’s relation to his wife and daughter, his career goals, and above all his investigation of William’s past–his search for what could drive the man to suicide. And this investigation turns on conveniently discovered clues.
Someday I must do a blog entry on tokens in narratives. Any plot of some complexity seems to need physical objects that encapsulate dramatic forces, spread out information, or become emotion-laden motifs. The photograph is probably the most traditional one, but notes, diaries, rings, and so on are useful too. In Goodbye Solo, William’s tokens move the drama of disclosure forward, and it’s possible to object to the film’s reliance on so many of them.
The problem Bahrani faces is that the film has to give us personal information about William while retaining tact and respect for characters’ integrity. For William to open up into a Tarantino-style confession would tear the movie apart; even a quiet moment of sobbing vulnerability is too indiscreet here. The film needs its tokens, however awkward they may seem as narrative devices, to keep faith with its people.
Staying a little outside the characters, allowing them to retain some private motives, is exactly what (500) Days of Summer doesn’t attempt. Bahrani’s discretion extends to the very last scene. The title becomes a line that someone should speak but doesn’t. Up till now, the quietly precise images have been shot by a camera locked down, but atop a mountain the camera leaves its tripod and supplies some mildly shaky imagery. And now it fits. It’s not just that the drama has reached an emotional pitch. The camera is simply buffeted by the wind. Once more Bahrani lets his world do its work.
You can read about our summer film-related travel here and here and here and here and here.
Overwhelmed by all the material on Pixar and Up, I merely point to two encyclopedic experts: the ever independent-minded Mike Barrier and the always-informative Bill Desowitz, who offers information on Pixar’s approach to 3-D here. For Ponyo background and an interview with Miyazaki, turn again to Bill D, here; he provides a transcript of a conversation between Miyazaki and John Lasseter here. A fat book of Miyazaki interviews and essays has just been published, and it includes some incendiary stuff, such as “Everything that Mr. Tezuka [Osamu, the ‘god of animation’] talked about or emphasized was wrong” (197).
The parentheses in (500) Days of Summer are explained by screenwriter Scott Neustadter at Jeff Goldsmith’s Creative Writing podcast.
Roger Ebert has reviewed nearly all these films and as always he has sensitive things to say, particularly on Goodbye Solo. He’s been championing Bahrani’s films for many years and he offers a warm career appreciation here.


Goodbye Solo.
Class of 1960
DB here:
By now most people accept the idea that 1939 was a kind of Golden Year of cinema. You know, Rules of the Game, Stagecoach, Wizard of Oz, that movie about the Civil War, etc. TCM has even made a movie about 1939. On this site Kristin and I have talked about earlier wonder years, like 1913 and 1917. So in planning this year’s Bruges week-long Zomerfilmcollege (aka Cinephile Summer Camp), Stef Franck and I discussed building my lectures around a single year. I proposed 1941, but he countered with 1960.
1960 was a logical choice in providing spread for the whole program. At Bruges we intertwine several threads of lectures and screenings, and this year we had silent films (The Cat and the Canary, The Wind), Hollywood’s cinema of emigration (Florey, Siodmak, Ophuls, etc.), and contemporary Korean film. All in 35mm, of course. So picking 1960 filled in another area.
As so often happens, a contingent choice came to seem a necessary one. By the time I opened my mouth to introduce The Bad Sleep Well, I had convinced myself that 1960 was another watershed year. Consider these releases:
Rocco and His Brothers (Visconti), La Dolce Vita (Fellini), L’Avventura (Antonioni), Le Testament d’Orphée (Cocteau), Plein Soleil (Clement), À bout de souffle (Godard), Les Bonnes femmes (Chabrol), La Verité (Clouzot), The Bridge (Wicki), Wild Strawberries (Bergman), The Devil’s Eye (Bergman), Lady with the Little Dog (Heifetz), The Letter that Wasn’t Sent (Kalatozov), The Steamroller and the Violin (Tarkovsky short), The Teutonic Knights (Alexander Ford), Innocent Sorcerors (Wajda), Saturday Night and Sunday Morning (Reisz), Tunes of Glory (Neame), Sergeant Rutledge (John Ford), Psycho (Hitchcock), Spartacus (Kubrick), Elmer Gantry (Brooks), 101 Dalmatians (Disney/ Reitherman), The Magnificent Seven (Sturges), Exodus (Preminger), Home from the Hill (Minnelli), Comanche Station (Boetticher), Verboten! (Fuller), The Bellboy (Lewis), The Young One (Buñuel), TheYoung Ones (Alcoriza), The Shadow of the Caudillo (Bracho), Devi (Ray), The Cloud-Capped Star (Ghatak), This Country Where the Ganges Flows (Karmakar), Red Detachment of Women (Xie Jin), The Back Door (Li Han-hsiang), Enchanting Shadow (Li Han-hsiang), The Wild, Wild Rose (Wang Tian-lin), Desperado Outpost (Okamoto), Spring Dreams (Kinoshita), When a Woman Ascends the Stairs (Naruse), Daughter, Wives, and Mother (Naruse), Cruel Story of Youth (Oshima), The Sun’s Burial (Oshima), Night and Fog in Japan (Oshima), The Island (Shindo), Pigs and Battleships (Imamura), Sleep of the Beast (Suzuki), and Fighting Delinquents (Suzuki).
We didn’t show any of them.
Several factors constrained our choices, including the availability of good prints with Dutch subtitles, or at least English ones. We also didn’t want to run too many official classics. And we fudged a little for pedagogy’s sake. We had to include a Godard, but instead of À bout de souffle, we picked Le Petit soldat—made in 1960 but not released until 1963. The World of Apu was released in 1959 in India, though it made its world impact in the following year. Lola was finished in 1960 but released in early 1961. A dodge, but I wanted a Nouvelle Vague counterpoint to Godard, and it fit well with the Ophuls thread, and—well, it’s Demy. In any case, we wound up with a list of outstanding movies.
 Running alongside my titles were horror films and thrillers from the same year, including Peeping Tom, Black Sunday, The Leech Woman, and Corman’s House of Usher. William Castle’s 13 Ghosts was shown with reconstructed versions of the original two-color Ghost Viewers. (Look through red if you believe in ghosts, blue if you don’t.) Imagine the shot above through a red filter. The creature, pink on the print, turns satanically crimson—confirmation that ghosts exist, although they look less like Casper and more like those Red Devil candies you ate in theatres as a kid. In a prologue, available here, Mr. Castle explains it all.
Running alongside my titles were horror films and thrillers from the same year, including Peeping Tom, Black Sunday, The Leech Woman, and Corman’s House of Usher. William Castle’s 13 Ghosts was shown with reconstructed versions of the original two-color Ghost Viewers. (Look through red if you believe in ghosts, blue if you don’t.) Imagine the shot above through a red filter. The creature, pink on the print, turns satanically crimson—confirmation that ghosts exist, although they look less like Casper and more like those Red Devil candies you ate in theatres as a kid. In a prologue, available here, Mr. Castle explains it all.
All in all, quite a week. My sessions ran from 9:00 AM to 12:30 or 1:00 PM, with the film embedded. After lunch, there were more talks and screenings, usually winding up at about 1:00 AM. Other speakers included Kevin Brownlow, Tom Paulus, Steven Jacobs, Muriel Andrin, Egbert Barten, and Christophe Verbiest (linking his talks on contemporary Korean film to the absolutely nuts 1960 Kim Ki-yong melodrama The Maid). The locals’ lectures were in Dutch, but these worthies are fluent in English, so sharing meals with them allowed me to catch up with their ideas.
Pegging a batch of movies to a single year can seem gimmicky, so I treated the films as exemplifying different trends, many of which started before 1960 and have continued since. I concentrated on trends within world film culture, though in several cases those were tied to still broader social and political developments. Above all, the 1960 frame allowed me to do the sort of comparative work I enjoy.
Generations
My first grouping was “Twilight of the Masters.” This allowed me to develop the idea that, remarkably, people who had started making films in the 1910s and 1920s were still active in the 1960s—and often making films that recalled their youthful efforts. Renoir revisited La Grande illusion in The Elusive Corporal, and Dreyer returned to his origins in tableau cinema through the staging of Gertrud.
In this connection, Fritz Lang’s 1000 Eyes of Dr. Mabuse, his final movie, revisits his Mabuse cycle in the way his previous films for Artur Brauner revise the “sensation-films” he wrote for Joe May (especially The Indian Tomb). Drawing on some ideas in my online essay, “The Hook,” we studied Lang’s crisp transitions between scenes. From this angle, 1000 Eyes is a sort of encyclopedia of ways you can connect scenes (visual link, auditory link, association of ideas, etc.). The transitions whip up a breathless pace and steer past some plot holes, and sometimes they generate a level of mistrust, implying story possibilities that don’t turn out to be valid.
Testament’s motif of eyes and vision became expanded to television surveillance in 1000 Eyes. There might even be an oblique connection between the Hotel Luxor’s panopticon and the rise of television ownership in Europe at the period. Here, as ever, cinema doesn’t have good things to say about TV.
Twilight of another, not quite so old master: Late Autumn by Ozu. I reviewed some features of Ozu’s style and then analyzed the film as a multiple-character drama. Ozu and his collaborator Noda Kogo split up the plot in order to present different characters’ attitudes to the central situation: the question of a daughter’s marriage. The plot ingeniously withholds information about the attitude of Akiko, the mother, by deleting certain scenes that would clarify it. Here too, the old master recalls earlier films by having characters discuss their college flirtations, which invoke scenes from Days of Youth and Where Now Are the Dreams of Youth?
Both Billy Wilder and Akira Kurosawa furnished me with a second generational cohort. I know, probably nobody in his right mind would see common features between these two directors. But desperation can fuel audacity. Both emerged during the late 1930s, began directing in the 1940s, and enjoyed a string of great successes in the 1950s; but both fell on harder times in the 1960s. Both became accusatory living legends, haunting local industries that had kept them from working.
Leading up to The Apartment, I considered Wilder’s contribution to two trends. First, the industry had hit the doldrums. In Europe television and new leisure lifestyles were not yet the threat they would become, but in America, the industry needed to pull its audience away from the TV set and the barbecue. Wilder proved skilful in using Hollywood’s turn to sex as the basis for his cynical comedies. The Lubitsch touch, a worldly appreciation of the oblique approach to matters of sex, was replaced by something harsher. In Wilder’s world, there are mostly sharks and shnooks, those who take and those who are taken.
Second, I situated Wilder as a leading figure in the emergence of the writer-turned-director in the 1940s (Sturges, Huston, Brooks, Fuller, Mankiewicz, etc.). This encouraged me to probe his dramaturgy, and so we analyzed the taut structure of The Apartment’s plot. It has rightly been recognized as a model screenplay, making us sympathize with a careerist covering up his bosses’ infidelities, all the while whetting our interest by shifting the range of knowledge away from the protagonist at key moments. It also displays a nice interweaving of motifs that function both dramatically and metaphorically (especially Miss Kubelik’s hand mirror). Of course at the end I had to run a clip showing the influence of The Apartment on the opening of Jerry Maguire.
By the mid-1960s, however, Wilder was pushing his luck, especially with Kiss Me Stupid. In The Apartment he wanted to make “a movie about fucking,” and he predicted that some day people would do the deed onscreen. But having glimpsed the promised land of the 1970s, he was unable to enter. Despite some worthy efforts, notably The Private Life of Sherlock Holmes, he haunted Hollywood as a major director who had outlived his moment.
Human, all too human
Kurosawa’s international fame came largely through the growth of the film festival as a prime institution of international movie culture. This situation let me sketch in the importance of festivals in bringing directors like him to world recognition. (By the way, Richard Porton has just brought out an informative collection of thoughts on film festivals.) With The Bad Sleep Well, I was able to talk a bit about something that is often forgotten—Kurosawa’s efforts in social, even political cinema. From Sugata Sanshiro, a tribute to Japanese martial arts, and The Most Beautiful, the loveliest movie you’ll ever see about girls making lenses for gunsights, up through Occupation projects like No Regrets for Our Youth and Scandal, Kurosawa engaged with political subject matter. Ikiru and I Live in Fear made this side of his work even more salient in the 1950s.
The Bad Sleep Well’s attack on corporate corruption sits well with this tendency. It considers the “iron triangle” of Japanese politics, the collusion of bureaucrats, politicians, and private industry—particularly the building industry, whose livelihood depends on bids for government projects. Still, it’s hard to believe that while Kurosawa made the film, and while Ozu made the serene Late Autumn, students were fighting police in the streets over the US-Japan security treaty. That turmoil surfaced in Oshima Nagisa’s demanding and formally daring Night and Fog in Japan.
The movie is shot with Kurosawa’s usual muscularity, including virtuoso compositions in what he called, following Toland, “pan-focus.”
The film’s twists also seemed to me worth examining. The protagonist is a minor presence in the first scenes, and his reticence in the beginning is mirrored in the finale, when he simply vanishes and his pal has to tell us what happened to him. Such a daring structure, reminiscent of the abrupt midway break in Ikiru, gives the film an almost Brechtian discomfiture, as well as highlighting the secondary characters’ rather perverse reaction to the hero’s fate.
Kurosawa was widely called a “humanist” director, and this concept sheds light on what we might call the “international film ideology” pervading festivals in the 1950s. In various areas of social and philosophical thought, a notion of humanism emerged out of disillusionment with the “age of ideology” that had engulfed the world in war. Several thinkers declared that the age of religious dogma and social collectivism, either Nazi or Communist, was over. Now what mattered were the features that drew people of all societies together, and the prospect of enlightened social action based on those commonalities—tolerance, respect, and a belief that people ultimately took individual responsibility for their communities. Catholics, Communists, and people of all stripes scrambled to call themselves humanists. As Dwight Macdonald, former Trotskyite, put it, “The root is man.”
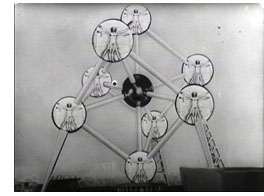 This frame of reference can be seen in Steichen’s 1955 photo exhibition, circulated around the world in a best-selling book, called The Family of Man, as well as in the 1958 Brussels Expo, the first major world’s fair since the war. There films like For a More Human World (frame right) presented technology, science, education, and cooperation as teaming up to improve the lives of people in all nations.
This frame of reference can be seen in Steichen’s 1955 photo exhibition, circulated around the world in a best-selling book, called The Family of Man, as well as in the 1958 Brussels Expo, the first major world’s fair since the war. There films like For a More Human World (frame right) presented technology, science, education, and cooperation as teaming up to improve the lives of people in all nations.
Film festivals embraced this universalism, pointing to the great films of Italy’s Neorealist trend as proof of cross-cultural communication. Although these films often scored specifically Italian political points, they could also be seen as human documents speaking to audiences anywhere. Who could not empathize with Ricci and his son in Bicycle Thieves (named at the 1958 Expo as the third-greatest film ever made)?
The turn to humanism helps answer a puzzling question: Why Satyajit Ray? Virtually no Europeans had ever seen a film from India. What enabled a director from this country to achieve worldwide renown? And why not other Indian directors of his era, such as Raj Kapoor, Guru Dutt, Mrinal Sen, and Ritwik Ghatak? All of these had to wait many years for discovery by European tastemakers.
For one thing, Ray was highly westernized himself. He was a child of the Bengali Renaissance, a virtuoso in many fields (he composed music, drew with facility, wrote detective stories and children’s books), and an admirer of European cinema. A stint assisting Jean Renoir exposed him to one of the greatest of Western filmmakers. A viewing of The Bicycle Thieves determined him to make films. He was skeptical of imitating Hollywood, which had been a prime inspiration for Hindu cinema. He criticized Bollywood’s reliance on schematic romance and musical numbers. If any Indian director was to make the move to the festival circuit, it would be him. (You can argue that other non-European filmmakers who made it into the fold were the most “western”—Kurosawa, Leopoldo Torre Nilsson, etc.).
Just as important, Ray’s stories suited the humanist program. Whereas Ghatak and Sen made politically charged films, Ray concentrated on the individual. In The World of Apu, social conditions are shown, but as a background to the development of personality and psychological tensions. At the film’s start, students are holding a street march demanding political rights, but they are offscreen, a backdrop to Apu’s meeting with his old professor as he gets his letter of recommendation. What follows is a drama of artistic failure, blossoming love, and a young man’s confused growth to maturity and responsibility.

It’s a simple story, rendered lyrical through constantly developing imagery: Apu stretched out prone, the famous grimy window curtain, and a cluster of visual motifs I hadn’t noticed on previous viewing. Ray’s concise direction links the torn curtain in Apu’s room to the famous (Langian?) transition from a movie screen to a carriage window, the cluster unified by associating Apurna with male children. Thanks to Andrew Robinson’s book on Ray, we know that in the carriage scene she is already thinking of the son she will bear.
It’s easy to romanticize this handsome, happy-go-lucky hero. I think the College participants thought I was a little hard on Apu, since I treated him as far from the “conscientious and diligent” young man his professor wrote of. Surely his idealistic-novelist persona is sympathetic. But if he is to grow as the film suggests, he must have failings, and Ray shows them to us—dreamy indolence, self-centeredness, even poutiness. The film is a character study, a sort of Bildungsroman tracing how Apu learns his place in his world. Our discussion after this film was particularly rich, with one participant suggesting that in accepting his son he isn’t abandoning his art entirely, but giving it human significance: He promises to tell Kajal stories.
Ray came to directing in middle age, a somewhat rare option. So too did Gillo Pontecorvo, but the latter made many fewer films. Although Kapò, isn’t as strong a movie as our other entries, it did allow us to talk a bit about coproduction, about European cinema’s relation to World War II, and about what came to be known as the morality of technique.
European coproductions are another fundamental part of the 1960 landscape, and they illustrate how economic considerations penetrate artistic choices. (Why are American and Italian actors in the “German” film 1000 Eyes of Dr. Mabuse? Why do we find Anouk Aimée in 8 ½ and Jeanne Moreau in La Notte? Follow the money.) For the Italian production Kapò, the primary roles are taken by an American (Susan Strasberg, playing the heroine Edith) and two French actors—the concentration camp translator played by Emmanuelle Riva and the heroic Soviet soldier played by Laurent Terzieff. The film was shot in Yugoslavia.
The story centers on a young Jewish girl who, in order to survive Nazi internment, passes herself off as a Gentile and becomes a camp commandant, whipping other prisoners into line. Other Italian films of the period, notably Rossellini’s Generale Della Rovere, were dealing with issues of conscience during the war, but Kapò was apparently the first fictional feature in Western Europe to confront the Holocaust since Alessandrini’s Wandering Jew of 1947. In 1960, Adolf Eichmann had been captured by the Mossod and stood trial the following year, and after Kapò came a few other films addressing the camps, notably Wajda’s Samson (1961) and Lumet’s The Pawnbroker (1965). So the film had a strong contemporary resonance; after its US release, it would be nominated for an Oscar.
One reason Stef and I picked Kapò was the controversy around Jacques Rivette’s accusation in Cahiers du cinéma that for a particular tracking shot Pontecorvo deserved “the most profound contempt.” The film, as Rivette indicates, is dominated by an already compromised conception of realism: grimed faces, make-up that hollows cheeks, somewhat ragged clothes, moderately shabby bunks. The shot shows the body of Theresa hurled against the electrified barbed wire, with the camera coasting slowly toward it. Her silhouette is almost classically composed, with the hands artfully pivoted and standing out against the sky. For Rivette this pictorial conceit is virtually obscene.
It seems to me that Rivette’s essay sought in part to reply to those who thought that Cahiers’ policy amounted to pure formalism. In calling for an ethics of technique, Rivette argues that artistic choices which might seem to be in the service of correct politics can betray a deeper immorality: using a historical cataclysm as an occasion for a safe realism and self-congratulatory flourishes. Similar complaints could be lodged against Kramer’s Judgment at Nuremberg and Stone’s World Trade Center. And because for the Cahiers team artistic cinema was an expression of a creator’s vision, the morally maladroit traveling shot brands the director as a man of bad faith.
Rivette isn’t saying that film artists shouldn’t try to represent historical trauma. He simply argues that other paths could be taken. For instance, Resnais’ Night and Fog and Hiroshima mon amour acknowledge that some events cannot be encompassed by normal understanding, and the form of each film enacts an effort to understand, not a fixed conclusion. What we see in Night and Fog is “a lucid consciousness, somewhat impersonal, that is unable to accept or understand or admit this phenomenon.” For Rivette, Pontecorvo seems convinced that romantic love and self-sacrifice can overcome Nazism, albeit with some help from the Red Army. He tries to explain, even prettify, an event that cannot be understood within the usual humanistic categories.
New Wave, still new
Lola.
Godard’s Le Petit soldat is far more preoccupied with uncertainties, even confusions, than Kapò is. 1960 saw an extraordinary number of former colonies, especially in Africa, gain independence, and during that year the Algerian war of resistance was spreading to Europe. Godard’s central character Bruno is working with the OAS vigilantes dedicated to killing Algerian terrorists, but when he meets the lovely Veronica Dreyer he decides to leave politics behind and flee with her to Brazil. Perhaps “decides” is the wrong word, since his actions are impulsive: he abruptly shies away from committing a political assassination, and he abruptly abandons his colleagues. But he’s captured by FLN terrorists and, in the film’s most famous sequences, tortured. At the end, he commits the assassination, not knowing that Veronica, herself in league with the Algerians, has been captured by his pals and killed. But his final voice-over is almost a shrug, and his act of murder takes on the flavor of an existentialist acte gratuite.
Le Petit soldat doesn’t offer heroic figures, as Kapò does in Theresa and the Soviet soldier. Nor does it allow us to sympathize much with the egotistical, capricious Bruno. The texture is more disjunctive, littered with the usual digressions and citations. Since the film was shot in Geneva, there’s a persistent motif of Swissness, with citations of Paul Klee. A sneaky one I never noticed before: the seduction game Bruno plays is modeled on the three fundamental shapes in the Bauhaus basic course, which Klee taught.
Having experimented with discontinuous imagery in À bout de souffle, Godard in his second feature turns his attention to the soundtrack, creating one of the most minimalist ones I know. If Bresson whittles down his soundtrack to a spare but recognizable realism, Le Petit soldat goes a step further, scrubbing out nearly every noise until we’re almost watching a silent film. Traffic scenes lack traffic noises, with only a car horn or a bit of dialogue breaking in. One passage on a train could almost be a sound loop.
The strategy of suppressed sound is carried to a paroxysm in the torture scenes, with the clink of handcuffs and the soft tapping of typewriter keys highlighted and bits of music played spasmodically…but no sounds of pain. Only during the rushed and almost throwaway climax, is something like a plausible city ambience heard. In a dichotomy that will be familiar throughout Godard’s work, there’s a split between image (Bruno is a photographer, and in the early part of the film he takes snapshots of Veronica in her apartment) and sound (the political factions rely on telephones and tape recorders, and the OAS thugs trick their way into Veronica’s apartment through sound recording).
In all, Le Petit soldat isn’t exactly fun but it’s exhilarating in its bursts and unexpected frictions. Next time somebody tells me that Godard’s technical innovations have all become commonplace, I’ll point to this film of 1960, which would be daring and demanding if released tomorrow.
Fun, albeit grave, is what Lola is all about. It takes formal artifice far beyond realism, creating a sort of non-musical musical. (It has one number, and even that is a sketchy rehearsal.) As geometrical as a minuet, its plot plays out in a hall of mirrors, where characters share names, pasts, and sentiments. The sailor Frankie and the wandering Michel, both in love with Lola, are blonde giants. Lola is actually named Cécile, and the little girl of the same name seems in some ways an early version of her, while Cécile’s mother has a dash of Lola in her past.
Roland starts out as the protagonist, but as he warms and cools and warms to Lola, the story momentum shifts to others. There’s Lola of course, and young Cécile who strikes up a friendship with Frankie, and Cécile’s mother who yearns a bit for Roland, and Michel, who left Nantes years ago and has lived in another movie, specifically, Mark Robson’s Return to Paradise (1952). Here the structure of the plot unfolds the network of relationships among people, linked mostly by casual encounters across a few days. The last section accordingly consists of a series of farewells, as if the story can end only by breaking ties of affection.
In surveying these films, I was struck by how much most of them owed to the growth of postwar institutions of film culture, and how strong those institutions remain. Coproductions and subsidies were feeding a massive buildup of European cinema. Contrary to what you might expect, as attendance cratered from the late 1950s onward, the number of European films produced went up. The EU countries still overproduce, releasing nearly 1200 theatrical features in 2008.
Film festivals were promoting not only universal humanism; they were also packaging films under rubrics of authorship or the New XXX Cinema and the Young ZZZ Cinema. 1940s Neorealism, aka “New Realism in Italian Cinema,” seems to have been, once more, the prototype. Festivals must make discoveries and emphasize novelties. At the same period film schools taught professional standards, and film archives showed classics and gave postwar filmmakers a more secure sense of the medium’s history. Lang, Ozu, and Wilder weren’t dependent on such institutions, but younger filmmakers were. And still are.
1960 is an arbitrary data point, but it stands out as an extraordinary year for quality. In addition, picking it as a benchmark allowed me to think about some important trends of the period. What probably didn’t show through my lumbering PowerPoints, with their charts, diagrams, and frame enlargements, was how much I learned from my Bruges stay. One of the deep satisfactions of teaching is remembering, no matter how confidently you declare your claims, how much more there is to know. Of things cinematic there is no end.
We also asked participants to read Serge Daney’s essay, “The Tracking Shot in Kapò.” Daney’s elaborate exercise in autobiography, irony, and moral reflection could not be plumbed in the time at my disposal, there or here. But it did help me understand Rivette’s argument. In preparing my lectures, I also owed a debt to some excellent books, notably Tom Gunning, The Films of Fritz Lang: Allegories of Vision and Modernity; Andrew Robinson, Satyajit Ray: The Inner Eye; Carlo Celli, Gillo Pontecorvo: From Resistance to Terrorism; and Richard Brody, Everything Is Cinema: The Working Life of Jean-Luc Godard. As ever, the invaluable documentation provided by the print editions of Screen Digest over the years enabled me to compile my tables of attendance, releases, and the like.
Late Autumn.
P.S. 3 Aug: Stef has posted snapshots from our Zomerfilmcollege here.
P.P.S. 3 Aug: This helpful correction from Roland-François Lack on Le Petit Soldat:
One small point: the organisation Bruno works for cannot be the O.A.S., which wasn’t active until the end of 1960.
He is working, rather, for ‘La main rouge’, a government sponsored counter-terrorist agency run by a Colonel Mercier (hence the name of Bruno’s associate).
Nice! Thanks.
Virginia Theatre on our minds
Left to right: Kristin, unidentified ardent moviegoer, Erik Gunneson, and Meg Hamel.
Kristin here–
A year ago, those of us attending Roger Ebert‘s Film Festival were forced to do without the presence of the moving force at the center of this lively annual event. Still in therapy from his health crisis of 2005, Roger fell and broke his hip. Characteristically, he struggled to convince his doctors that he could take an ambulance to Champaign/Urbana, but their caution prevailed.
 Since then, Roger has become ambulatory again, and this year he looked very happy to be back (an impression confirmed by his wrapup blog here). He still can’t talk, but he was a benign presence at the opening reception at the university president’s residence. There his wife Chaz took over the speaking duties, introducing the filmmakers and the critics who are this year’s guests.
Since then, Roger has become ambulatory again, and this year he looked very happy to be back (an impression confirmed by his wrapup blog here). He still can’t talk, but he was a benign presence at the opening reception at the university president’s residence. There his wife Chaz took over the speaking duties, introducing the filmmakers and the critics who are this year’s guests.
Roger went onstage at intervals during the festival, and he made his first appearance to introduce the opening night’s film, the director’s cut of Woodstock: 3 Days of Peace and Music (1970). Thanks to dedicated software, Roger tapped out messages on a laptop and pushed a button. A voice with a British accent conveyed his words of welcome to us and to director Michael Wadleigh. Then Roger retired to the back of the theater, where a comfy chair is reserved throughout the festival for him.
Michael Wadleigh, Jocko Marcellino, and Dale Bell discuss Woodstock.
From the perspective of nearly forty years, Woodstock has become both a record of remarkable musicians in their prime and a valuable document of the youth culture of the late 1960s. I was a junior at the University of Iowa at the time of the concert, only about five months away from taking my first film course and changing the direction of my education from tech theater to cinema studies. Working on props and make-up for productions every night, I was only dimly aware of the concert or the film that followed.
I also admit I don’t know much about pop music. I kept asking David “Who’s that?” Jefferson Airplane, The Who, Joe Cocker, and others were just names to me, not people whose appearance or music I recognized. But I could appreciate the remarkable way in which the filmmakers were able to capture live performances: the fluidity of multiple, 16mm cameras filming onstage only feet from the performers, the maintenance of focus even when events were recorded at night in less than ideal lighting conditions, and the excellent sound recording.
The screening heralds the release of the new version on DVD on June 9. Amazon has it on pre-order in 3-disc Blu-ray and DVD boxes, as well as a 2-disc set. The third disc has some making-of featurettes and about two hours of additional concert footage left out of even this extended version. I can’t imagine anyone who wants a compilation of performances by this remarkable group of musical talent settling for the smaller set.
Von Sternberg and Jannings, round one
The Alloy Orchestra has become a fixture at Ebertfest. This year’s silent film was Josef von Sternberg’s The Last Command. I hadn’t seen it in thirty years or more, and it’s better than I remembered it being. Of course, seeing a gorgeous print on the big Virginia screen with an excellent musical accompaniment does it more justice than an old 16mm copy. Von Sternberg’s images were luminous, and his depiction of silent filmmaking as accurate as anything you’ll see on the screen.
In von Sternberg’s autobiography, Fun in a Chinese Laundry, he spends most of the six pages devoted to The Last Command badmouthing star Emil Jannings, with a brief sidetrack to badmouth William Powell. Presumably he’s talking about their behavior on the set, since their performances are both impressive, with Jannings emoting away and Powell as stone-faced as Buster Keaton. Von Sternberg reports that he and Jannings vowed never to work together again. Maybe winning the first Academy Award as best actor changed Jannings’ mind, for a few years later he invited von Sternberg to direct him and Marlene Dietrich in The Blue Angel. The rest, as they say, is history.
Drawing on their usual range of odd percussive objects, including a bedpan, the Alloy group provided a lively score. With Chicago Tribune critic Michael Phillips as moderator, Guy Maddin and I joined the orchestra members for a discussion afterwards. One of them hinted to me backstage that a score for Docks of New York might be in the offing, which would round off the von Sternberg series perfectly.
Saturday matinee
Last year the festival presented Tarsem Singh’s The Cell, with its delirious production design by Eiko. Tarsem’s 2008 follow-up, The Fall, got less attention in theatres, not having a star like Jennifer Lopez to carry it with audiences. It’s a complex fantasy set in a hospital during the silent-cinema era. There a suicidal, injured stuntman telling the tale of a band of mythical heroes bent on revenge to a seven-year-old girl with an arm cast. Her visions of the narrated events, set in spectacular landscapes and exotic buildings, mutate as she insists on changes in the story. The Fall was distinctly a crowd-pleaser, at least for the indefatigably enthusiastic audience in the Virginia Theater. Its Romanian child star, Catinca Untaru, is now twelve, and she proved an articulate charmer as she answered questions after the screening.
Ramin Bahrani with Catinca Untaru and her family.
The next film was Sita Sings the Blues, a marvelously imaginative animated feature by Nina Paley. I had seen the film two weeks earlier at the Wisconsin Film Festival, and it was a treat to see it on the big screen again. It’s available for download in various formats here. I had the pleasure of moderating the discussion afterward, and I like the film so much that I’ll be blogging on it separately, including a transcript of the Q&A.
Tattling and bullying
DB here:
A Belgian friend, the late Michel Apers, admired American films above all others. One of the reasons, he explained, was that our films analyzed our political system with uncommon clarity. No other national cinema, he claimed, focused so insistently on the mechanisms and purposes of government, on the duties of citizenship, and on the dilemmas of public life. Not wanting to seem too chauvinistic, I said that we often failed to fulfill our nation’s ideals. “Of course,” he said. “But at least you have ideals. And your films show that it is not easy to live up to them.”
Michel’s remarks reminded me that we do have a tradition of politically critical films: 1930s films opposing lynching and hate groups, 1940s films about political corruption, still later movies like Twelve Angry Men and The Best Man and The Manchurian Candidate. Directors who contributed to this tradition include John Ford (Young Mr. Lincoln, The Last Hurrah), Otto Preminger (Advise and Consent especially), and Alan J. Pakula (All the President’s Men, The Parallax View, Rollover, The Pelican Brief).
Rod Lurie’s favorite film is All the President’s Men, which ought to tell you where his heart is. He made The Contender (2000), a subtle drama about a woman nominated for Vice-President. It has the trappings of a political thriller (the conspiracy at its heart echoes Chappaquiddock, as well as Blow-Out), but that’s just the bait for its serious questions. Graced by a warm but steely performance by Joan Allen, The Contender asks whether a woman in politics is held to a higher standard of sexual conduct than a man would be.
I thought of Michel Apers’ remarks when I watched Lurie’s Nothing But the Truth (2008) at this year’s Ebertfest. The plot revolves around a reporter, Rachel Armstrong (Kate Beckinsale), who outs covert CIA agent Eric van Doren (Vera Farmiga, her of the admirably crooked smile). Rachel refuses to divulge her source and goes to jail. Again, there’s a mystery to draw us through the plot: Who is the source? But more important is the problem of whether a reporter should be forced to name sources in a case that breaches national security. It’s the sort of issue that Preminger or Pakula would have loved to tackle.
 Lurie’s film is as close to a Shavian drama of ideas as I’ve seen in recent American movies. Patton Dubois (Matt Dillon), the prosecutor trying to worm the truth out of Rachel, has plenty of reasonable arguments on his side. During the post-film discussion, Dillon suggested that he leaned toward Dubois’ position: No one should have the power to destroy a person’s career in a sensitive job and go unpunished. In the film, Rachel’s lawyer Alan Burnside (Alan Alda) responds to Dubois with principled refutations, as well as a few pragmatic ones. After all, if Rachel is forced to talk, no whistle-blowers will be likely to step forward. See Roger’s recent review for more thoughts on the political implications.
Lurie’s film is as close to a Shavian drama of ideas as I’ve seen in recent American movies. Patton Dubois (Matt Dillon), the prosecutor trying to worm the truth out of Rachel, has plenty of reasonable arguments on his side. During the post-film discussion, Dillon suggested that he leaned toward Dubois’ position: No one should have the power to destroy a person’s career in a sensitive job and go unpunished. In the film, Rachel’s lawyer Alan Burnside (Alan Alda) responds to Dubois with principled refutations, as well as a few pragmatic ones. After all, if Rachel is forced to talk, no whistle-blowers will be likely to step forward. See Roger’s recent review for more thoughts on the political implications.
While the debate plays out, Rachel languishes in jail, her family and career dissolving. The case has some analogies to the Valerie Plame incident, but Lurie stressed that the film takes on a similar situation but not comparable characters. He was inspired as much by Susan McDougal’s tenacious loyalty to Bill Clinton.
The film’s secret about Rachel’s source is no mere Macguffin. It provides a powerful supplementary reason for Rachel’s silence, yet it doesn’t wholly excuse it. The film’s last scene leaves you wondering whether Rachel exploited her source. The film’s last shot suggests that she’s wondering too. That shot also wraps up a visual motif that hangs Rachel’s face on one extreme edge of the 2.40 frame, making her look precarious and vulnerable.
All in all, Nothing But the Truth is a sober, unsensational, gripping film about the press’s rights and obligations. It’s not surprising that Lurie was a professional journalist. During the Q & A, the questions were probing and he responded with rapid-fire, well-shaped sentences. There was good humor as well. After Lurie promised to tell us who slept with whom on the shoot, he paused and said: “All I’ll say is that Alan Alda was a complete slut.”
The opportunity for ordinary moviegoers to talk with such gifted and committed filmmakers makes Ebertfest one of the great film festivals on this continent. Roger’s urge to communicate with as many people as possible naturally inclines him toward creating communities, and the folks who gather annually in the Virginia Theatre form one of the most genial and generous group of movie lovers I’ve ever encountered.
Slumdogged by the past
DB here:
In graduate school a professor of mine claimed that one benefit of studying film history was that “you’re never surprised by anything that comes along.”
This isn’t something to tell young people. They want to be surprised, preferably every few hours. So I rejected the professor’s comment, and I still think it’s not a solid rationale for studying film history. But I can’t deny that doing historical research does give you a twinge of déjà vu.
For instance, the film industry’s current efforts to sell Imax and 3-D irresistibly remind me of what happened in the early 1950s, when Hollywood went over to widescreen (Cinerama, CinemaScope, and the like), stereophonic sound, and for a little while 3-D. Then the need was to yank people away from their TV sets and barbecue pits. Now people need to be wooed from videogames and the Net. But the logic is the same: Offer people something they can’t get at home. It’s 1953 once more.
So historians can’t resist the “Here we go again” reflex. But they shouldn’t turn that into a languid “I’ve seen it all before.” Because we can genuinely be surprised. Occasionally, there are really innovative movies that, no matter how much they owe to tradition, constitute milestones. In my view, Kiarostami’s Through the Olive Trees, Hou’s City of Sadness, Wong’s Chungking Express, Tarr’s Satantango, and Tarantino’s Pulp Fiction are among the 1990s examples of strong and original works.
More often, the films we see draw on film history in milder ways than these milestones. But this doesn’t mean that these movies lack significance or impact. We can be agreeably surprised by the ways in which a filmmaker energizes long-standing cinematic traditions by blending them unexpectedly, tweaking them in fresh ways, setting them loose on new material. And the more you know of those traditions and conventions, the more you can appreciate how they’re modified. Admiring genius shouldn’t keep us from savoring ingenuity.
Which brings me to Slumdog Millionaire. I happen to like the film reasonably well. Part of my enjoyment is based on seeing how forms and formulas drawn from across film history have an enduring appeal. Many people whose judgments I respect hate the movie, and they would probably call what follows an ode to clichés. But I mean this set of notes in the same spirit as my comments on The Dark Knight (which I don’t admire). Even if you disagree with my predilections, you may find something intriguing in Slumdog’s ties to tradition. These ties also suggest why the movie is so ingratiating to so many.
Warning: What follows contains plot spoilers, revelatory images, and atrocious puns.
Slumdog and pony show
Adaptation is still king. Almost as soon as movies started telling stories, they were borrowing from other media. Many of this year’s Oscar candidates are based on plays, novels, and graphic novels. Slumdog is a redo of Vikas Swarup’s 2005 novel Q & A. The book provides the basic situation of a poor youth implausibly triumphing on a version of Who Wants to be a Millionaire? The novel also lays down the film’s overall architecture: in the present, the hero narrates his past, tying each flashback to a round of the game and a relevant question. In the novel, the video replays are described, but of course they’re shown in the film.
There are many disparities between novel and movie, but for now I simply note two. First, Swarup’s book has several minor threads of action, but the film concentrates on Jamal’s love of Latika. (The screenwriter Simon Beaufoy has melded two female characters into one.) Correspondingly, the book introduces a romance plot comparatively late, whereas the film initiates Jamal’s love of Latika in their childhoods. Such choices give the film a simpler through-line. Second, whereas Q & A skips back and forth through Jamal’s life, keying story events to the quiz questions, the film’s flashbacks follow the chronology strictly. This is a good example of how screenwriters are inclined to adjust the plasticity of literary time to the fact that, at least in theatrical screenings, audiences can’t stop and go back to check story order. Clarity of chronology is the default in classical film storytelling.
Then there’s the double plotline. The streamlining of Swarup’s novel points up one convention of Hollywood narrative cinema. The assortment of characters and the twists in the original novel are squeezed down to the two sorts of plotlines we find in most studio films: a line of action involving heterosexual romance and a second line of action, sometimes another romance but just as often involving work. The common work/ family tension of contemporary film plotting is to some extent built into the Hollywood system.
Beaufoy has sharpened the plot by giving Jamal a basic goal: to unite with Latika. The quiz episodes form a means to that end: the boy goes on the show because he knows she watches it. If told in chronological order, the quiz-show stretches would have come late in the film and become a fairly monotonous pendant to the romance plot. One of the many effects of the flashback arrangement is to give the subsidiary goal more prominence, creating a parallel track for the entire film to move along and arousing anomalous suspense. (We know the outcome, but how do we get there?)
Q & A. Swarup’s novel begins: “I have been arrested. For winning a quiz show.”
We have to ask: What could make such a thing happen? Soon the police and the show’s producers are wondering something more specific. How could Ram, an ignorant waiter, have gotten the answers right without cheating?
Noël Carroll proposes that narratives engage us by positing questions, either explicitly or implicitly. Stories in popular media, he suggests, induce the reader to ask rather clear-cut ones, and these will get reframed, deferred, toyed with, and in the short or long run answered.
Slumdog accepts this convention, presenting a cascade of questions to link its scenes and enhance our engagement. Will Jamel and Salim get Bachchan’s autograph? Will they survive the anti-Muslim riot? Will they escape the fate of the other captive beggar children? And so on.
More originally, the film cleverly melds the question-based appeal of narrative with the protocols of the game show, so that we are confronted with a multiple-choicer at the very start. (As in narrative itself, the truth comes at the end.) The principal question will be answered in the denouement, in a comparably impersonal register.
Flashbacks are also a long-standing storytelling device, as I was saying here last week. A canonical situation is the police interrogation that frames the past events, as in Mildred Pierce, The Usual Suspects, and Bertolucci’s The Grim Reaper. This narrating frame is comfortable and easy to assimilate, and it guides us in following the time shifts.
But 1960s cinema gave flashbacks a new force. From Hiroshima mon amour (1958) onward, brief and enigmatic flashbacks, interrupting the ongoing present-tense action, became common ways to engage the audience. Such is the case with the glimpse of Latika at the station that pops up during the questioning of Jamal, rendered as almost an eyeline match.
At this point we don’t know who she is, but the image creates curiosity that the story will eventually satisfy. Flashbacks can also remind us of things we’ve seen before, as when Jamal recalls, obsessively, the night he and Salim left Latika behind to Maman’s band. Boyle and company call on these time-honored devices in the assurance that wewill pick up on them immediately, as audiences have for decades.
Flashforwards are trickier, and rarer. The 1960s also saw some experimentation with images from future events interrupting the story’s present action. Unless you posit a character who can see the future, as in Don’t Look Now, flashforwards are usually felt as externally imposed, the traces of a filmmaker teasing us with images that we can’t really assimilate at this point. (See They Shoot Horses, Don’t They?) Such flashforwards pop up during the initial police torture of Jamal.
Encountering the bathtub shot so early in the film, we might take it as a flashback, but actually it anticipates a striking image at the climax, after Jamal has been released and returned to the show. I’d argue that the shot functions thematically, as a vivid announcement of the motif of dirty money that runs through the movie and is associated with not only the gangster world but also the corrupt game show.
Slumdog days
Empathy. One of the most powerful ways to get the audience emotionally involved is to show your protagonist treated unfairly. This happens in spades at the start of Slumdog. A serious-faced boy is subjected to awful torture, then he’s intimidated by unfeeling men in authority. He’s mocked as a chaiwallah by the unctuous host of the show, and laughed at by the audience. Once Jamal’s backstory starts, we see him as a kid (again running up against the law) and suffering a variety of miseries.
To keep Jamal from seeming a passive victim, he is given pluck and purpose. As a boy he resists the teacher, boldly jumps into human manure, shoves through a crowd to get an autograph, and eventually becomes a brazen freelance guide to the Taj Mahal. This is the sort of tenacious, resourceful kid who could get on TV and find Salim in teeming Mumbai. The slumdog is dogged.
Our sympathies spread and divide. Latika is also introduced being treated unfairly. An orphan after the riot, she squats in the rain until Jamal makes her the “Third Musketeer.” By contrast, Salim is introduced as a hard case—making money off access to a toilet, selling Jamal’s Bachchan autograph, resisting bringing Latika into their shelter, and eventually becoming Maman’s “dog” and Latika’s rapist. The double plotline gives us a hero bent on finding and rescuing his beloved; the under-plot gives us a shadier figure who finds redemption by risking his life a final time to help his friends. Jamal emerges ebullient from a sea of shit, but Salim dies drowned in the money he identified with power.
Our three main characters share a childhood, and what happens to them then prefigures what they will do as grownups. This is a long-standing device of classical cinema, stretching back to the silent era. Public Enemy and Angels with Dirty Faces give us the good brother and the bad brother. Wuthering Heights, Kings Row, and It’s a Wonderful Life present romances budding in childhood. These are plenty of less famous examples. Here, for instance, is a synopsis of Sentimental Tommy (1921), a film that may no longer exist.
The people of Thrums ostracize Grizel, a child of 12, and her mother, known as The Painted Lady, until newcomer Tommy Sandys, a highly imaginative boy, comes to the girl’s rescue and they become inseparable friends. Six years later Tommy returns from London, where he has achieved success as an author, and finds that Grizel still loves him. In a sentimental gesture he proposes, but she, realizing that he does not love her, rejects him. In London, Tommy is lionized by Lady Pippinworth, and he follows her to Switzerland. Having lost her mother and believing that Tommy needs her, Grizel comes to him but is overcome by grief to see his love for Lady Pippinworth. Remorseful, Tommy returns home, and after his careful nursing Grizel regains her sanity.
The device isn’t unknown in Indian cinema either; Parinda (1989) motivates the character relationships through actions set in childhood. Somehow, we are drawn to seeing one’s lifetime commitments etched early and fulfilled in adulthood.
This story pattern carries within it one of the great thematic oppositions of the cinema, the tension between destiny and accident. In Slumdog, The Three Musketeers may be introduced casually, but it will somehow provide a template for later events. Lovers are destined to meet, even if by chance, and when chance separates them, they are destined to reunite . . . if only by chance. A plot showing children together assures us that somehow they will re-meet, and their childhood traits and desires will inform what they do as adults. It is written.
This theme reaffirms the psychological consistency prized by classic film dramaturgy as well. Characters are introduced doing something, as we say, “characteristic,” and this first impression becomes all the more ingrained by the sense that things had to be this way. What you choose—say, to pursue the love of your childhood—manifests your character. But then, your character was already defined with special purity in that childhood.
Just another movie conceit? The existence of Classmates.com seems to suggest otherwise.
Chance needs an alibi, however. Hollywood films are filled with coincidences, and the rules of the game suggest that they need some minimal motivation. Not so much at the beginning, perhaps, because in a sense every plot is launched by a coincidence. But surely, our plausibilists ask, how could it happen that an uneducated slumdog would have just the right experiences to win the quiz? A lucky guy!
As Swarup realized, the flashback structure helps the audience by putting past experience and present quiz question in proximity for easy pickup. Yet as Beaufoy indicates in one of the most informative screenwriting interviews I know, the device also softens the impression of an outlandishly lucky contestant. At the start we already know that Jamal has won, so the question for us is not “How did he cheat?” but rather “What life experience does the question tap?” Each of the links is buried in a welter of other details, any one of which could tie into the correct answer. Moreover, sometimes the question asked precedes the relevant flashback, and sometimes it follows the flashback, further camouflaging the neat meshing of past and present.
It’s a diabolical contrivance. If you question Jamal’s luck, you ally with the overbearing authorities who suspect cheating. (You just think the film cheated.) Who wants to side with them? By the end the inevitability granted by the flashback obliges us to accept the inspector’s conclusion: “It is bizarrely plausible.”
The film has an even more devious out. Jamal can reason on his own, arriving at the Cambridge Circus answer. More important, his street smarts have made him such a good judge of character that he realizes that the MC is misleading him about the right answer to the penultimate question. So his winning isn’t entirely coincidence. Life experience has let him suss out the interpersonal dynamics behind the apparently objective game. As for the final answer—a lucky guess? Fate?—it’s a good example of how things can be written (in this case by Alexandre Dumas).
Slumdoggy style
The whole edifice is built on a cinematic technique about a hundred years old: parallel editing. Up to the climax, we alternate between three time frames. The police interrogation takes place in the present, the game show in the recent past (shifting from the video replay to the scenes themselves), and Jamal’s life in the more distant past. Any one of these time streams may be punctuated, as we’ve seen, by brief flashbacks. So the problem is how to manage the transitions between scenes in any one time frame and the transitions among time frames.
Needless to say, our old friend the hook—in dialogue, in imagery—is pressed into service often. A sound bridge may link two periods, with the quiz question echoing over a scene in the past. “How did you manage to get on the show?” Cut to Jamal serving tea in the call center. In a particularly smooth segue, the boys are thrown off the train as kids and roll to the ground as teenagers. There are negative hooks too. At the end of a quarrel with Salim, Jamal walks off saying, “I will never forgive you.” The next scene opens with the two of them sitting on the edge of an uncompleted high-rise building, having come to an uneasy truce.
In the climax, the three time frames all come into sync, creating a single ongoing present. Jamal will return to the show. The double-barreled questions are reformulated. Now we have genuine suspense: Will he win the top prize? Will Latika find him? To pose these engagingly, directors Danny Boyle and Loveleen Tandan create an old-fashioned chase to the rescue.
Each major character gets a line of action, all unwinding simultaneously: Salim prepares to sacrifice himself to the gangster Khan, she flees through traffic, and Jamal enters the contest’s final round. A fourth line of action is added, that of the public intensely following Jamal’s quest for a million. He has become the emblem of the slumdog who makes good.
The rescue doesn’t come off; Latika misses Jamal’s phone plea for a lifeline, and he is on his own. Fortunately, he trusts in luck because “Maybe it’s written, no?” The lovers reunite instead at the train station, where Jamal had pledged to wait for Latika every day at 5:00. Fitting, then, that in the epilogue a crowd shows up, standing in for all of Mumbai, singing and dancing to “Jai Ho” (“Victory”). All the remaining lines of action—Jamal, Latika, and the multitudes—assemble and then disperse in a classic ending: lovers turning from the camera and walking into their future, leaving us behind.
Then there’s the film’s slick technique. The whole thing is presented in a rapid-fire array, with nearly sixty scenes and about 2700 shots bombarding us in less than two hours. Critics both friendly and hostile have commented on the film’s headlong pacing and flamboyant pictorial design. If some of Slumdog’s storytelling strategies reach back to the earliest cinema, its look and feel seems tied to the 1990s and 2000s. We get harsh cuts, distended wide-angle compositions, hurtling camerawork, canted angles, dazzling montage sequences, faces split by the screen edge, zones of colored light, slow motion, fast motion, stepped motion, reverse motion (though seldom no motion). The pounding style, tinged with a certain cheekiness, is already there in most of Danny Boyle’s previous work. Like Baz Luhrmann, he seems to think that we need to see even the simplest action from every conceivable angle.
Yet the stylistic flamboyance isn’t unique to him. He is recombining items on the menu of contemporary cinema, as seen in films as various as Déjà Vu and City of God. (That menu in turn isn’t absolutely new either, but I’ve launched that case in The Way Hollywood Tells It.) More surprisingly, we find strong congruences between this movie’s style and trends in Indian cinema as well.
Over the last twenty years Indian cinema has cultivated its own fairly flashy action cinema, usually in crime films. Boyle has spoken of being influenced by two Ram Gopal Varma films, Satya (1998) and Company (2002). Company‘s thrusting wide angles, overhead shots, and pugilistic jump cuts would be right at home in Slumdog.
It seems, then, that Slumdog’s glazed, frenetic surface testifies to the globalization of one option for modern popular cinema. The film’s style seems to me a personalized variant of what has for better or worse become an international style.
Slumdogma
Boot Polish.
I’d like to mention many other ways in which the movie engages viewers, such as running (an index of popular cinema; does anybody run in Antonioni?). But I’ve said enough to suggest that the film is anchored in film history in ways that are likely to promote its appeal to a broad audience. The idea of looking for appeals that cross cultures rather than divide them isn’t popular with film academics right now, but a new generation of scholars is daring to say that there are universals of representation and response. It is these that allow movies to arouse similar emotions across times and places.
Patrick Hogan has made such a case in his fine new book Understanding Indian Movies: Culture, Cognition, and Cinematic Imagination. There he shows that much of what seems exotic in Indian cinema constitutes a local specification of factors that have a broad reach—certain plot schemes, themes, and visual and auditory techniques. Hogan, an expert in Indian history and culture, is ideally placed to balance universal appeals with matters of local knowledge that require explication for outsiders.
For my part, I’d just mention that a great deal of what seems striking in Slumdog has already been broached in Indian cinema. Take the matter of police brutality. The torture scene at the start might seem a piece of exhibitionism, with an outsider (Boyle? Beaufoy?) twisting local culture to western ideas of uncivilized behavior. But look again at the gangster films I’ve mentioned: they contain brutal scenes of police torture, like this from Company.
Like Hong Kong cinema and American cinema, Indian filmmaking seems to take a jaundiced view of how faithful peace officers are to due process.
More basically, consider the representation of the Mumbai slums. Doubtless the title slants the case from the first; Beaufoy claims to have invented the word “slumdog,” though Ram is called a dog at one point in the novel. The insult, and the portrayal of Mumbai, has made some critics find the film sensationalistic and patronizing. Most frequently quoted is megastar Amitabh Bachchan’s blog entry.
If SM projects India as [a] Third World dirty underbelly developing nation and causes pain and disgust among nationalists and patriots, let it be known that a murky underbelly exists and thrives even in the most developed nations.
Soon Bachchan explained that he was neutrally summarizing the comments of correspondents, not expressing his own view. In the original, he seems to have been suggesting that the poverty shown in Slumdog is not unique to India, and that a film portraying poverty in another country might not be given so much recognition.
It’s an interesting point, although many films from other nations portray urban poverty. More generally, Indian criticisms of the image of poverty in Slumdog remind me of reactions to Italian Neorealism from authorities concerned about Italy’s image abroad. The government undersecretary Giulio Andreotti claimed that films by Rossellini, De Sica, and others were “washing Italy’s dirty linen in public.” Andreotti wrote that De Sica’s Umberto D had rendered “wretched service to his fatherland, which is also the fatherland of . . . progressive social legislation.” Liberal American films of the Cold War period were sometimes castigated by members of Congress for playing into the hands of Soviet propagandists. It seems that there will always be people who consider films portraying social injustice to be too negative and failing to see the bright side of things, a side that can always be found if you look hard enough.
Moreover, Neorealists made a discovery that has resonated throughout festival cinema: feature kids. Along with sex, a child-centered plot is a central convention of non-Hollywood filmmaking, from Shoeshine and Germany Year Zero through Los Olvidados and The 400 Blows up to Salaam Bombay, numerous Iranian films, and Ramchandi Pakistani. Yes, Slumdog simplifies social problems by portraying the underclass through children’s misadventures, but this narrative device is a well-tried way to secure audience understanding. We have all been children.
There is another way to consider the poverty problem. The representation of slum life, either sentimentally or scathingly, can be found in classic Indian films of the 1950s. One of my favorites of Raj Kapoor’s work, Boot Polish (1954), tells a Dickensian tale of a brother and sister living in the slums before being rescued by a rich couple. (Interestingly, the key issue is whether to beg or do humble work.) Another example is Bimal Roy’s Do Bigha Zamin (Two Acres of Land, 1953). Later, shantytown life was more harshly presented in Chakra (1981), shot on location.
And of course poverty in the countryside has not been overlooked by Indian filmmakers.
Slumdog may have become a flashpoint because more recent Indian cinema has avoided this subject. In an email to me Patrick Hogan (who hasn’t yet seem Slumdog) writes:
There was a strong progressive political orientation in Hindi cinema in the 1940s and 1950s. This declined in the 1960s until it appeared again with some works of parallel cinema. Thus there was a greater concern with the poor in the 1950s–hence the movies by Kapoor and Roy that you mention. There are some powerful works of parallel cinema that treat slum life, but they had relatively limited circulation. On the other hand, that does not mean that urban poverty disappeared entirely from mainstream cinema. At least some sense of social concern seemed to be retained in mainstream Indian culture, thus mainstream cinema, until the late 1980s.
 However, at that time Nehruvian socialism was more or less entirely abandoned and replaced with neo-liberalism. In keeping with this, ideologies changed. Perhaps because the consumers of movies became the new middle classes in India and the Diaspora, there was a striking shift in what classes appeared in Hindi cinema and how classes were depicted. As many people have noted, films of the neoliberal period present images of fabulously wealthy Indians and generally focus on Indians whose standard of living is probably in the top few percentage points. . . . I don’t believe this is simply a celebration of wealth and pandering to the self-image of the nouveau riche–though it is that. I believe it is also a celebration of neoliberal policies. Neoliberal policies have been very good for some people. But they have been very bad for others. . . .
However, at that time Nehruvian socialism was more or less entirely abandoned and replaced with neo-liberalism. In keeping with this, ideologies changed. Perhaps because the consumers of movies became the new middle classes in India and the Diaspora, there was a striking shift in what classes appeared in Hindi cinema and how classes were depicted. As many people have noted, films of the neoliberal period present images of fabulously wealthy Indians and generally focus on Indians whose standard of living is probably in the top few percentage points. . . . I don’t believe this is simply a celebration of wealth and pandering to the self-image of the nouveau riche–though it is that. I believe it is also a celebration of neoliberal policies. Neoliberal policies have been very good for some people. But they have been very bad for others. . . .
In this neoliberal cinema (sometimes misleadingly referred to as “globalized”), even relatively poor Indians are commonly represented as pretty comfortable. The difference in attitude is neatly represented by two films by Mani Ratnam—Nayakan (1987) and Guru (2007). The former is a representation of the difficulties of the poor in Indian society. The film already suffers from a loss of the socialist perspective of the 1950s films. Basically, it celebrates an “up from nothing” gangster for Robin Hood-like behavior. (This is an oversimplification, but gives you the idea.)
Guru, by contrast, celebrates a corrupt industrialist who liberates all of India by, in effect, following neoliberal policies against the laws of the government. Neither film offers a particularly admirable social vision. But the former shows the urban poor struggling against debilitating conditions. The latter simply shows a sea of happy capitalists and indicates that lingering socialistic views are preventing India from becoming the wealthiest nation in the world. Part of the propaganda for neoliberalism is pretending that poor people don’t exist any longer–or, if they do, they are just a few who haven’t yet received the benefits.
Paradoxically, then, perhaps local complaints against Slumdog arise because the film took up a subject that hasn’t recently appeared on screens very prominently. The same point seems to be made by Indian commentators and by Indian filmmakers who deplore the fact that none of their number had the courage to make such a movie. The subject demands more probing, but perhaps the outsider Boyle has helped revive interest in an important strain of the native tradition!
Finally, the issue of glamorizing the exotic. Some critics call the film “poverty porn,” but I don’t understand the label. It implies that pornography of any sort is vulgar and distressing, but which of these critics would say that it is? Most such critics consider themselves worldly enough not to bat an eye at naughty pictures. Some even like Russ Meyer.
So is the issue that the film, like pornography, prettifies and thereby falsifies its subject? Several Indian films, like Boot Polish, have portrayed poverty in a sunnier light than Slumdog, yet I’ve not heard the term applied to them. Perhaps, then, the argument is that pornography exploits eroticism for money, and Slumdog exploits Indian culture. Of course every commercial film could be said to exploit some subject for profit, which would make Hollywood a vast porn shop. (Some people think it is, but not typically the critics who apply the porn term to Slumdog.) In any case, once any commercial cinema falls under the rubric of porn, then the concept loses all specificity, if it had any to begin with.
The Slumdog project is an effort at crossover, and like all crossovers it can be criticized from either side. And it invites accusations of imperialism. A British director and writer use British and American money to make a film about Mumbai life. The film evokes popular Indian cinema in circumscribed ways. It gets a degree of worldwide theatrical circulation that few mainstream Indian films find. This last circumstance is unfair, I agree; I’ve long lamented that significant work from other nations is often ignored in mainstream US culture (and it’s one reason I do the sort of research I do). But I also believe that creators from one culture can do good work in portraying another one. No one protests that that Milos Forman and Roman Polanski, from Communist societies, made One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest and Chinatown. No one sees anything intrinsically objectionable in the Pang brothers or Kitano Takeshi coming to America to make films. Most of us would have been happy had Kurosawa had a chance to make Runaway Train here. Conversely, Clint Eastwood receives praise for Letters from Iwo Jima.
Just as there is no single and correct “Indian” or “American” or “French” point of view on anything, we shouldn’t deny the possibility that outsiders can present a useful perspective on a culture. This doesn’t make Slumdog automatically a good film. It simply suggests that we shouldn’t dismiss it based on easy labels or the passports of its creators.
Moreover, it isn’t as if Boyle and Tandan have somehow contaminated a pristine tradition. Indian popular films have long been hybrids, borrowing from European and American cinema on many levels. Their mixture of local and international elements has helped the films travel overseas and become objects of adoration to many westerners.
I believe we should examine films for their political presuppositions. But those presuppositions require reflection, not quick labels. If I were to sketch an ideological interpretation of Slumdog, I’d return to the issue of how money is represented in an economy that traffics in maimed children, virgins, and robotic employees. Money is filthy, associated with blood, death, and commercial corruption. The beggar barracks, the brothel, the call center, and the quiz show lie along a continuum. So to stay pure and childlike one must act without concern for cash. The slumdog millionaire doesn’t want the treasure, only the princess, and we never see him collect his ten million rupees. (An American movie loves to see the loser write a check.) To invoke Neorealism again, we seem to have something like Miracle in Milan–realism of local color alongside a plot that is frankly magical.
Perhaps this quality supports the creators’ claims that the film is a fairy tale. As with all fairy tales, and nearly all movies I know, dig deep enough and you’ll find an ideological evasion. Still, that evasion can be more or less artful and engrossing.
So it seems to me enlightening and pleasurable to see every film as suspended in a web, with fibers connecting it to different traditions, many levels and patches of film history. Acknowledging this shows that most traditions aren’t easily exhausted, and that fresh filmmaking tactics can make them live again. Thinking historically need not numb us to surprises.
The amount of Web writing on Slumdog is exploding. Go to GreenCine for a good sampling of commentary from late 2008. The film’s technique is discussed in Stephanie Argy, “Rags to Riches,” American Cinematographer 89, 12 (December 2008), 44-61. Boyle shows his camera to Darren Aronofsky at Slantfilm. Kim Voynar of Movie City News reviews, critically, the Slumdog backlash.
For a more detailed rationale for this entry’s suspension of value judgments for the sake of analysis, try my earlier blog entry here. Noël Carroll discusses question-and-answer structures in narrative in several books, notably The Philosophy of Horror; or, Paradoxes of the Heart (New York: Routledge, 1990), 130-136. On recent Indian action movies, see Lalitha Gopalan, Cinema of Interruptions: Action Genres in Contemporary Indian Cinema (London: British Film Institute, 2002). The quotations from Giulio Andreotti come from P. Adams Sitney, Vital Crises in Italian Cinema: Iconography, Stylistics, Politics (Austin: University of Texas Press, 1995), 107; and Millicent Marcus, Italian Film in the Light of Neorealism (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1986), 26.
Thanks to Cathy Root, who is at work on a book on Bollywood, for advice and links. Thanks as well to Patrick Colm Hogan and Lalita Pandit for corrections, information, and ideas.
PS 2 Feb: David Chute, expert on Indian cinema, has written a helpful and balanced entry on Slumdog at his Hungry Ghost site.
PPS 14 Feb: From another expert on Indian film, Corey Creekmur, at the University of Iowa, some further ideas and references on the childhood motif:
I would emphasize that establishing a film’s narrative direction through childhood events is a dominant narrative trope in popular Indian cinema, animating many famous “golden age” examples, including Raj Kapoor’s Awara (1951), Mehboob Khan’s Anmol Ghadi (1946), and Bimal Roy’s Devdas (1955), along with a number of the major 1970s films starring Amitabh Bachchan, which often carry childhood traumas into the adult character’s life. The story of brothers growing up on two sides of the law is also a Hindi film staple, central to Bachchan’s emergence as a superstar in Deewar in 1975. It seems to me curious that Slumdog Millionaire’s Western filmmakers draw on these conventions more fully than the source novel [Q & A] by a non-resident Indian does.
I attempt to explain the decades-long cultural function (and eventual waning) of this narrative trope — often achieved through a specific formal device (a dissolve from boy to man) moving from the lives of children to adults (skipping over adolescence) that I call the “maturation dissolve” — in an article “Bombay Boys: Dissolving the Male Child in Popular Hindi Cinema,” in Where the Boys Are: Cinemas of Boyhood, ed. Murray Pomerance and Frances Gateward. (Detroit: Wayne State UP, 2004). In that essay I suggest that some of the Hollywood examples — as well as Citizen Kane — you mention could have inspired the Indian examples, but also suggest certain Indian sources (the childhood love of the god Krishna and his consort Radha, which informs all versions of Devdas) as well. Since I’m citing myself, I’ll also note a recent essay on the “Devdas” phenomenon in Indian cinema: “Remembering, Repeating, and Working Through Devdas,” which appears in Indian Literature and Popular Cinema: Recasting Classics, ed. Heidi R. M. Pauwels (Routledge, 2008). By the way, you might also enjoy a website devoted to popular Hindi cinema by my colleague Philip Lutgendorf (with whom I regularly teach Indian cinema classes). Most of the entries on his site are his, but as you will note, sometimes he lets me put my two cents in there as well: http://www.uiowa.edu/~incinema/
PPPS 21 February: Several scholars comment on the film’s representation of the Dahravi neighborhood and the multilayered significance of Indian protests against Slumdog. See today’s New York Times here and here.