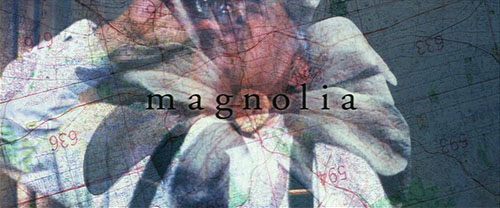Archive for the 'Film industry' Category
Filling the New Line gap
The Loews Santa Monica Beach Hotel, one of the AFM venues
Kristin here-
The 2008 American Film Market started yesterday. Like the film festivals at Cannes, Toronto, and, increasingly, Berlin, the AFM is one of the major places where independent and foreign-language films get sold. Distributors from all over the world come to sell their products and to buy the films that they will release at home. It seems a good occasion to look at what effect the folding-in of New Line Cinema into a unit within Warner Bros. early this year has had on the international independent film market.
The good old days
In my book The Frodo Franchise, Chapter 9 dealt with the impact of The Lord of the Rings on the film industry. There I discuss what effects the trilogy had on New Line and its parent company Time Warner. I also analyze the rise of the fantasy genre, the technological advances, and the boost given to the depressed indie market internationally. The 26 international independent distributors that financed a substantial portion of the film’s production through presales—with commitments to all three parts, sight unseen, at very steep prices—grew dramatically as a result of its success.
In 2001, an international slump in independent and foreign-language cinema started. The causes were complex, and I detail them in the book; they included a sag in advertising, the dot-com bust, the September 11 attacks, and the American dollar’s high exchange rate. With perfect timing, The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring came out in December of 2001. Its theatrical and DVD earnings in 2002 poured money into the market through the 26 companies’ ability to buy new product when other distributors were still strapped for cash. By early 2004, the market had substantially recovered. Rings wasn’t the only factor aiding that recovery, but it was a major one.
That section of Chapter 9 is one of the parts of the book I’m proudest of. Most people interested in film knew something about most of the topics I covered. They were probably at least vaguely aware of the video games and other tie-in products, the highest successful internet campaign, the growth in filmmaking and tourism in New Zealand, and so on. But the fact that this massive blockbuster was an independently financed film, sold on the independent market, and highly beneficial to that market was something completely unknown except to specialists within the industry. I cottoned onto it only because there were a few references to these distributors’ unusual buying power during the coverage of the 2003 Cannes Film Festival and AFM in Variety and The Hollywood Reporter.
Beyond those brief discussions, there was really no way I could research the topic without talking to people involved. That meant interviewing some of the executives of those 26 companies and someone very expert in the international indie market. A very helpful source was Mads Nedergaard, then of SF-Film, Copenhagen, who provided marvelous information for my major case study in that chapter. For the expert, I decided upon Jonathan Wolf, then and now the Managing Director of the AFM. Luckily he agreed to be interviewed. During our conversation Jonathan remarked that he had been very struck that I understood that Rings was an independent film and that it had had a positive impact on international markets. I gather that’s why he agreed to the interview, during which he furnished me with valuable insights. Those two interviews really made that part of the chapter possible.
Despite the huge success of the trilogy, New Line continued to function as an independent, financing its films through presales of distribution rights and of licensing fees for ancillary products. It continued to sell them at events like the AFM, as well as having regular output deals with some of the same overseas companies that it had been dealing with for nearly a decade. New Line was one of the main U.S. firms supplying such distributors. Its growing success ultimately became part of what got the studio into trouble.
What had worked so well for Rings continued to work until the blockbuster fantasy trilogy that had been touted as the successor to Rings. The Golden Compass was financed in the same way, with special rights pre-sold to foreign distributors, many of them the same ones that had handled Rings. The problem was that Compass did tepid business in the U.S. but was a distinct success abroad. That money stayed with the foreign distributors.
Absorbed into Warner Bros.
The Compass problem coincided with the promotion of Jeff Bewkes as CEO of Time Warner at a time when the conglomerate’s stock price was low. The real problem was the encumbrance of AOL, but that was a problem that would take time to solve. New Line’s lack of success with its big Christmas release made it a target. Bewkes could slash the company as a signal to stockholders that he would streamline Time Warner. On February 25, he announced that New Line would be folded into Time Warner, to become a production unit specializing in the sort of genre fare that had sustained New Line for so long, such as the Nightmare on Elm Street series. It would also continue to produce the occasional major film, such as The Hobbit.
The point of absorbing New Line into Warner Bros. was largely to downsize the former by eliminating its distribution and other departments that could be handled by Warners. With Warners distributing New Line films abroad, the income would return to the studio rather than remaining with foreign distributors. Receiving financing from Warners, New Line would no longer need to finance films through presales.
For Time Warner, this made sense, but it was a blow to the overseas distributors with regular output deals with New Line. New Line and Miramax had provided steady product to these companies, which otherwise would have to compete in the open market on a film-by-film basis. With the departure of the Weinstein brothers from Miramax, that firm had dried up as a source, leaving the burden on New Line. Now New Line was disappearing as well.
What now?
In the 7 March 2008 issue of Screen International (the online version is subscription only), Mike Goodridge discussed where these distributors might be able to turn after the expiration of their New Line contracts. He pointed out, “The distribution partners had good years and bad with New Line. None were thrilled with The Long Kiss Goodnight or The Island Of Dr. Moreau but for every flop, there was a Seven or Austin Powers, a Mask or Rush Hour.” He also confirms my claims about the Rings trilogy’s impact on its international distributors: “The success of the three films for the international partners cannot be overestimated. Nor can the fact that they, more than anybody involved, took a huge risk on the trilogy. The risk paid off. The Greens at Entertainment [the U.K. distributor], the Hadidas at Metropolitan [the French distributor] and others genuinely shared in the profits of one of the box-office phenomenons of the last 20 years. It was the international buyers’ dream. Instead of losing money on studio cast-offs, they had a hefty piece of a trilogy which grossed nearly $2bn outside North America.” New Line’s disappearance as a source of hit films “brings a dramatic sea change to the complexion of the global business,” according to Goodridge. These independent firms “will be competing for an increasingly small number of tentpole pictures available to them.”
Where have these distributors turned for films? In some cases their contracts with New Line, which predate the studio’s absorption into Warner Bros., are good through 2009. That means, however, that those distributors are already looking ahead for releases after the contracts end. At Cannes this year, New Line had a much-reduced presence. Camela Galano, one of the executives who had been in the studio’s international sales wing for years, was promoted to being its president in May. She brought only Journey to the Center of the Earth. Galano told Variety, “We just won’t be selling movies … but we’ll be doing what we normally do with our outputs, which is go through the lineup, releases and materials.”
A number of firms at Cannes stepped up to fill in the void left by New Line’s withdrawal from distribution. One up-and-coming firm, QED, was selling Oliver Stone’s W, the sci-fi film District 9 (produced by Peter Jackson and due out in the U.S. next August 14), and the Milla Jovovich thriller A Perfect Getaway. Gary Michael Walters, co-president of Bold Films, commented that he saw an opportunity presented by Warners’ takeover of New Line’s foreign distribution. “We see a sweet spot in that niche of $10 million-$30 million smart but commercial pictures.” Similar rising firms include IM Global, formed by the former head of Miramax International, Stuart Ford. (See Variety‘s summary here.)
John Hazleton analyzed the impact of New Line’s withdrawal from the international market for Screen International just before Cannes (May 9, 2008 issue). Hazleton harks back to the impact of Rings and other New Line franchises:
Many sales executives, in fact, go further and suggest that by boosting the fortunes of the distributor partners with which it had ongoing output or package deals—companies including the UK’s Entertainment, France’s Metropolitan, Australia’s Villege Roadshow and Spain’s Tri Pictures—New Line effectively elevated the independent international industry as a whole. Other sellers benefited, for example, when the New Line distributors reinvested profits from The Lord of the Rings and Rush Hour movies—or from last Christmas’ The Golden Compass—in the acquisition of non-New Line films.
No wonder, then, [that] the decision by parent Warner Bros to turn New Line into a stripped-down genre label whose films will (once current deals expire) be distributed worldwide by the studio is having such an impact in the independent arena. Filling the New Line void has suddenly become a pressing need, or an enticing opportunity, for all sorts of independent players.
One such player is Hyde Park International, whose president Lisa Wilson told Hazleton, “We’re certainly seeing an uptick in interest from distributors who previously didn’t need as much product because they were secure in having the New Line output. They’ve been making more of an effort than usual to meet us before Cannes.” Another is The Film Department, selling two films under production, Law Abiding Citizen, a thriller starring Gerard Butler, and The Rebound, a Catherine Zeta-Jones vehicle.
Hazleton identifies two major independent films suppliers that are stepping into the supply gap left by New Line’s departure:
Leading the field of remaining big picture suppliers are Summit Entertainment and the combination of Lionsgate and Mandate formed when the former acquired the latter last September. Crucially, like New Line, each group now has its own North American theatrical distribution operation, giving international buyers assurance that films will get a domestic theatrical launch and allowing the co-ordination of domestic and international release dates.
Summit is new to the domestic distribution business. But it is a company with vast international experience that plans to handle 10-12 films in the $15m-$45m budget range a year. Its Cannes slate includes Terrence Malick’s drama Tree of Life, starring Brad Pitt, and it already has output deals for its own productions in France, Germany, UK and Scandinavia.
In Lionsgate, Mandate has a well-proven domestic distribution outlet that last year scored three $50m-plus box-office hits and this year has a bigger market share than any independent or studio specialty division.
As the combination’s international arm, Mandate—which will be in Cannes with titles including Whip It! featuring rising star Ellen Page, and family animation Alpha And Omega—handles around half of Lionsgate’s domestic slate plus titles from third-party producers.
New Line’s withdrawal, says Helen Lee Kim, president of Mandate International, “just puts us in a better situation, because you can count on one hand the independent companies able to bring studio-level product to the marketplace.”
Hazleton also points out that “Studio-owned sales operations Paramount Vantage and Focus Films International [a Universal subsidiary] will be another alternative source for buyers.” In general, though, the Hollywood studios’ recent retreat from art-house divisions means that they will have less to contribute to foreign distributors.
Summit and Mandate are both participating in the AFM as well. Another major firm is Relativity Media, a rapidly expanding production-distribution independent responsible for such recent films as 3:10 to Yuma, Atonement, Baby Mama, and Pineapple Express. Relativity had expanded into international sales this year at Cannes. In October it offered $150 million for Universal’s Rogue Pictures and will gain the 40-50 projects that genre division has in the works. As the AFM began, it had just signed long-term output contracts with nine foreign distributors. Finally, Relativity has, according to Variety, “partnered with sales company Mandate Intl. to oversee sales in non-output territories as well as provide worldwide servicing of the slate.”
Other sales firms at Cannes included Odd Lot and Essential, and new companies debuting at the AFM this year were FilmNation, Exclusive Film Distribution, Icon Entertainment, and WestEnd Films. Some of these companies will grow, others won’t. But gradually they will absorb the market position formerly held by New Line.
So does all this mean that the impact of New Line’s glory days is over? Not entirely. I believe that although the distribution of The Lord of the Rings has receded five years into the past and New Line has now disappeared as an independent entity, the trilogy’s impact still lingers in the international industry. Steve Bickel, president of The Film Department, commented to Screen International shortly before Cannes, “The loss of any independent or independent-spirited company is a loss to the industry. New Line provided a great service to all of us because they helped make strong companies that we’re now able to sell to.”
Women and children first
Ten AM on a Tuesday, and I’m at my local megaplex, Star Cinema. I’m here to not to see a movie, exactly, but to catch a phenomenon I’ve been curious about for some years.
To back up: Kristin and I have fallen a bit behind in our blogging. For one thing, the presidential election has been so exciting that we spend more time staring at cable news than ever before. (But the time hasn’t been wasted: the campaigns have given me an idea for a blog entry, which I hope to post next week.) Secondly, we’ve been going over the copy-edited version of the third edition of our textbook, Film History: An Introduction. It’s due out this spring, and we’ll have more to say about it later. If you want a preview now, check the new essay I posted elsewhere on this site. It’s called “Doing Film History,” and it’s an updated version of the introduction that appeared in earlier editions of FH.
Kristin has been laboring over an epic blog on character subjectivity. As for me, to take a break from both politics and the textbook, I headed to Star.
The youngest demographic
The phenomenon I was interested in goes by different names, but here in Madison it’s called Baby Box Office.
Every Tuesday morning Star runs screenings for parents and their pre-schoolers. It’s billed as a chance to bring your child to see a film in a welcoming setting. The theatre is a little more illuminated than normal, the sound a little softer. Nobody will ask the kid to shush; you can even nurse your baby. Incidentally I hope that this gets babies to associate movies with oral gratification. The future needs passionate filmgoers, not to mention film students.
You can get more details from the Kerasotes chain’s website, and they’re pretty interesting. (Some theatres offer a Stroller Valet Service.) So I got curious and headed to the ‘plex.
I was surprised that five films were lined up to be screened—not Saw V and Max Payne, naturally, but a fairly wide range, including W. and a couple of animated titles. If none of the customers chooses a film, it’s not run. I asked which movie was today’s top pick, and Susan the cashier suggested The Secret Life of Bees. Buying my ticket, I met Meg and her son Connor. I asked whether she came often. With a smile, she said: “It’s been a life-saver.” She regularly meets a friend, who also has an infant, at the show.
Outside the auditorium there was a changing cot, with baby powder at the ready. Somehow, knowing it was there comforted me.
I counted twelve non-kids at the show, including a guy more or less like me (graying, maybe retired) and three young women who might have been playing hooky from high school. The show was an ordinary screening. There were local ads and video commercials. There were trailers for upcoming releases The Boy in the Striped Pajamas (Nazis with, natch, British accents), Marley and Me (a dog running in surf), The Soloist (Oscar bait), and Australia (part African Queen, part Out of Africa; I gather that She Will Fall in Love with a Man. . . and a Country).
I wish I could report that a dramatic incident, or at least an epiphany, took place during my visit. But the kids were mostly quiet. Occasionally I heard a wail or gurgle, and at one point a mother took a fretful baby out. The screening went fine. Glancing at the kids, I saw many of them staring at the screen transfixed and uncomprehending. On the basis of this experience, I’ve decided it’s better to have a squad of babies in a theatre than a few teenage boys.
As for The Secret Life of Bees: Cynics will say it’s ready for the Hallmark Channel, but I liked it. It’s what the Japanese call a “wet” film, affording many occasions for tears, in which I freely indulged. Not of much pictorial interest, it is saved, at least for me, by a robust script (tailored to Kristin’s four-part template), solid performances, and sentimental situations centering on racism, child abuse, female bonding, and raging male inadequacy. Needless to say, thanks to intensified continuity a lot of reaction shots drive home each moment. Appropriately, the mommy audience was seeing a movie about mommies; the idealistic but forlorn little heroine winds up with three, at least.
Afterwards, I talked to a pair of ladies who had brought a toddler. While he wrestled with the steering wheel on an arcade driving game, they explained that they frequently come to the shows and are glad that Star Cinema offers them the option. I then talked at length with Star’s savvy general manager, Craig Hussin, who has been part of the Madison movie scene for many years. Craig sees Baby Box Office as part of what every theatre should do—offer the patrons many options, and do it with the sort of flair that used to be called showmanship.
Mom, dad, and dollars
Susan Hansen, Meg Teter, and Connor.
There’s a broader point of interest to us as students of cinema. I think that the phenomenon is a good example of market segmentation, which David Waterman has talked informatively about in Hollywood’s Road to Riches. (1)
Obviously, people’s preferences about movies, as about anything else, differ. Some people want to see a movie the day it’s released; others are willing to wait a while. So it’s better business to charge the eager consumer more than the more cautious one. This is a form of price discrimination.
What makes the film business unusual, Waterman points out, is that it has a very wide range of price demands. Some people will pay a lot to see a film on opening night, others will pay a smidgeon to see it years later on basic cable TV, and there is a wide range of pricing options in between. Just on DVD, you can rent it new, or rent it later for less. You can buy it new, buy it discounted a few months later, or buy a used copy for still less.
In the classic studio days, the principles of market segmentation and price discrimination gave birth to a systematic strategy of distribution, discussed by historians Tino Balio and Doug Gomery (2): The run/ zone/ clearance system. A run was the period during which a film was screened in theatres. The first-run showing, usually at a well-appointed downtown cinema, gave city viewers the first chance to see the movie. The second-run shows, in neighborhood theatres and small towns, took place later, at lower ticket prices. Zones established the territory in which any title could play exclusively. Clearances were the intervals of time separating the runs, typically a matter of weeks or months.
What’s interesting is that the system is still with us. Your average Hollywood movie has its first run at a multiplex. It may get a second theatrical run at a budget theatre or campus venue. Then begins its most profitable string of runs, in the nontheatrical sector. The movie is released on various video platforms sequentially–pay per view, premium cable, airline and hotel systems, DVD, Internets, and eventually free cable. As in the old days, there are clearances between these runs; today they’re called “release windows.” You’ve probably noticed that films come to the ancillary platforms faster than they did only a few years ago. This trend toward shrinking windows is, as you’d expect, a bone of contention with distributors.
The point of the system is to extract the most money from the film. If films were only shown first-run, some people wouldn’t go at all. The price would be set too high for their level of interest. So the prices shrink over time, with broadcast or basic cable airings becoming the last link in the chain. Spreading out the opportunities to see the film allows people with different preferences and budgets to buy in at different points.
So I’m thinking that the Baby Box Office is a nice example of market segmentation. Parents with young children tend not to go to movie theatres. A night out is expensive, especially reckoning in babysitter costs, and many couples I know are just too tired to enjoy a movie at the theatre. If the parents take an infant to a show, it might squall and disturb others. So many parents just stay home. Baby Box Office goes after a niche market.
It’s shrewd policy to screen a recent release for Baby Box Office. If the film were in second-run, the screenings might seem a step down from what else the ‘plex is showing. But if parents see a first-run title, they can then gain the sense of participating in a current pop-culture event—an important motivator for first-run patrons—and they, like other first-run patrons, can spread word of mouth.
Do the costs make sense? At first glance, no. Babies get in free. Mom or Mr. Mom pays $5. If the child is three years old or more, that ticket costs $3. Not a huge amount of money in all: the 12 adults at my screening yielded only $60. But it’s a mistake to compare the takings with Friday-night box office, fattened by hordes of teens.
First, some of the theatre staff are working in the morning anyhow, preparing for the day’s shows, checking prints and projection equipment, talking with bookers on the phone, supervising cleaning, priming the concession stand. So running a few prints at that time of day isn’t a big extra expense. Tuesdays are theatres’ slowest days, so since you’re open you might as well get some people through the turnstiles. Then there’s the intangible factor of good will. Parents are likely to think well of a business that takes pains to cater to them, and they may be likely to return to that theatre when they get other chances.
As for price, five bucks is a little more than a DVD rental these days, so the off-hours screening is a bargain compared to standard ticket prices, but it preserves the integrity of the runs/ windows system. And the concession stand is open. There, where the real money is made, a parent can indulge a guilty impulse for Raisinets.
You can argue that the phenomenon is really a reaction to thinning theatre attendance, and that may indeed be part of the story. But more positively, Baby Box Office sessions seem to lie on a continuum with making a movie available on video, on iPods or phones, and on the Internets. Media moguls have long said that today’s consumers want their objects of desire, no matter how obscure, with maximum convenience. Media distribution has had to adapt itself to audiences’ schedules. Granted, theatres can’t do that as flexibly as video can. Still, Baby Box Office seems a logical effort by exhibitors to adjust to a world in which people expect entertainment to adjust itself to their lifestyles, kids and all. Kids especially.
(1) David Waterman, Hollywood’s Road to Riches (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2005), 9-10.
(2) Gomery explains the origins of the strategy in The Hollywood Studio System: A History (London: British Film Institute, 2005), 19-20.
Title wave
The very first drafts of the outline always had Cloverfield on them. . . . Cloverfield was what I always wanted to call the movie. . . . It’s a terrible title . . . if you’re trying to sell something, who the hell’s gonna go see that?. . . But it’s cool. There’s a reason. I could state the reason, but it’s very clear it is meant to be obtuse. I believe that the film answers why it is called Cloverfield, I believe that it’s in the film, I believe that you can make that argument. It says exactly what I want it to say. But it’s very clear that we don’t want to explain it.
Screenwriter Drew Goddard, at Creative Screenwriting podcast
DB here:
Don’t think about a movie title too long. Even a familiar one can turn strange before your eyes.
This was brought home to me long ago when I showed Lubitsch’s Lady Windermere’s Fan in a course. Before the film started, a student asked me, “Who is it?” I didn’t understand. “I mean, who is her fan?” It never occurred to me to take the title this way, but actually in the movie Lady W does attract a big fan.
Titles can be explicit, but they’re often metaphorical, associative, and oblique. Sometimes they’re downright obscure. But as Drew Goddard says, they can be cool.
Don’t Worry, We’ll Think of a Title (1966)
The least provocative titles are based on the protagonist’s name: Brubaker, Anthony Adverse, Erin Brockovich, Norma Rae, Speed Racer. One step removed is the title that describes the protagonist’s job or role: Gladiator, Hitman, The Cable Guy, Bob le flambeur, perhaps also The Godfather. Then there are the titles, like The Last Action Hero or Prince of Players or Little Caesar, that characterize the protagonist more figuratively.
If the movie has a pair of protagonists, the title can reflect that, as in David and Bathsheba, Pete’n’Tilly, and Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid. When the title elevates a secondary figure, as in Melvin and Howard or Harry and Tonto, it has the effect of making us consider the relationship between the two as central to the action. When there are several main characters, we can get a title characterizing the group, not just Bob & Carol & Ted & Alice but The Professionals and The Breakfast Club.
Things get a little more curious when the title focuses on a character other than the protagonist(s). Rebecca identifies a dead character, but her aura haunts the (unnamed) heroine. Both versions of The Man Who Knew Too Much refer, at least literally, to a minor figure. Why is The Wizard of Oz not called Dorothy Goes to Oz? Why does Mizoguchi’s great Sansho the Bailiff take its title from the name of the villain? It’s not as if Mizoguchi was trying to do an Ian Fleming (Dr. No, Goldfinger).
Perhaps Wizard and Sansho bear their titles because they’re adapted from literary sources that had those titles. But that just pushes the problem back a step: Why do the originals have these titles? And in asking why, I’m not asking for information about what went on in an author’s mind or a story conference. The why question here is about purpose and function. What does the title do in relation to the film’s plot or theme?
For instance, you can argue that the title of The Wizard of Oz works to highlight the seductive world of Oz, so different from Kansas, with the Wizard himself being a figure with one foot in fantasy and one in reality (since the Wizard is actually a prairie mountebank). Similarly, I’m inclined to say that Sansho the Bailiff’s title reminds us of the socially sanctioned cruelty at its center. Zushio and Anju, the fugitive brother and sister, may each escape in a different way, but Sansho’s world remains; it is our world.
Some titles are simply place names, like Casablanca, Macao, Philadelphia, or New York, New York. Others specify dates: 1860, 1900, 1941, 1984. In both strategies, the title often evokes symbolic associations or parallels with the here and now.
The title can refer to the core situation, as with Back to School or Being John Malkovich, or to a key scene, as in Sophie’s Choice and Gunfight at the OK Corral. This can get abstract and metaphorical. Housekeeping features a very offbeat approach to housekeeping. The Birth of a Nation characterizes America reborn after the Civil War. Being There describes more or less all that the cipher-like hero does. The title can even predict the action, as in The Great Escape, A Man Escaped, and Killing of a Chinese Bookie. In these instances we have anomalous suspense: Why and how will an announced action be carried out?
Reaching for the Moon (1917/ 1930/ 1933)
More rarely, the title can refer to the film’s central formal device. Through Different Eyes and Vantage Point announce that they will play with subjective point of view. The Blair Witch Project justifies its title by posing as a dossier of found student footage. The Prestige warns us that a magic trick’s surprise payoff might well be matched by one at the end of this movie. Kristin and I have long assumed that the title of Tati’s Play Time refers not only to the anarchic relaxation unleashed in the Royal Garden restaurant but also to the movie’s own perceptual strategy of making us see amusement in banal incidents.
Hitchcock, the tireless formalist, provided titles that give away his game. Rear Window announces a stationary viewpoint and a limited field of action. More fancifully, you could take Rope as announcing the film’s sinuous long takes. Family Plot is nicely equivocal, referring at once to a communal grave, a conspiracy among kin, and of course the movie’s own mysterious plot of knotty kin relations.
Then there are the generic characterizing titles, usually single-word titles like Notorious or Spellbound or Pushover or Identity or Slacker or Speed or even, probably most generic of all, Conflict (borne by at least five films, from 1916 to 1955). Here again, though, we can find puzzles.
We know why Homicidal is called Homicidal, but what purpose is served by calling a movie Psycho? Again, the source book provides the title, but Robert Bloch’s novel is narrated in the first person and the title gives us a big clue about the sort of mind we’re in. Hitchcock’s film presents the story more objectively, and it begins with Marion Crane’s theft. Those critics who see the film as blurring the boundaries between sanity and insanity would say that Marion, who impulsively commits a crime, and Norman are points on a continuum. People we take to be normal have irrational impulses, a point reinforced by Norman’s line, “We all go a little mad sometimes. Haven’t you?” After their conversation about private traps, Marion seems to recognize herself in his question.
Same old song (1997)
Many titles are citations or quotations, and they usually highlight a thematic element. Both Yankee Doodle Dandy and Born on the Fourth of July are drawn from the same song: both offer portraits of patriotism, but in very different keys. Pennies from Heaven is highly, perhaps heavily, ironic, something you can’t say about Meet Me in St. Louis.
Not all citations are as transparent as these. The Little Foxes explains its title in a prologue, seen above. The Bible verse is then linked to the story we’ll see.
We’re ready to understand the family as creating a milieu that could easily corrupt the tender vine, Xan.
A catch phrase can work too, such as The Sweet Hereafter or It Takes a Thief or It’s a Wonderful Life. You Can’t Take It With You emphasizes pursuing fun rather than riches. Phffft suggests that a couple has split, but how would you explain that outside the U. S.? (The French title is, perhaps surprisingly, Phffft.)
Some catchphrase titles suggest the sort of multiple meanings we saw in Family Plot and Play Time. All That Jazz packs a lot into three words: most basically, a flurry of trivial stuff (pushing our hero into overdrive), but also music and the heights of emotion (being jazzed). You Only Live Once at first suggests seizing the moment, but by the end of the film you begin to think it implies: “Who could bear to live twice?” I especially like The Best Years of Our Lives, which also changes its significance across the film. The bulk of the movie asks: The returning servicemen have given their prime years for us, but how do we reward them? By the end of the movie, the title seems to be suggesting that their best years, of healing and self-understanding and integration into families, lie ahead of them.
I’ve known students, especially from outside the U. S., to have trouble with His Girl Friday. It’s a two-tiered reference. First is Robinson Crusoe’s “man Friday,” his aboriginal servant. But in American slang, a girl Friday is the boss’s closest female assistant, an all-around tough worker and troubleshooter. That’s what Hildy is to Walter Burns, until she decides to marry Bruce and move to Albany. She reverts to her girl Friday role in the course of the film, as the title has predicted she would.
We don’t always know when a quotation is at work. I have always found Some Came Running obscure. The phrase isn’t used in the film, or in the text of the James Jones source novel. But the novel’s epigraph takes a passage from Mark 10: 17:
And when he was gone forth into the way, there came one running, and kneeled to him, and asked him, Good Master, what shall I do that I may inherit eternal life?
This is the passage where Jesus asks the rich man to give all that he has to the poor, apparently as unlikely an event then as now. The problem is that in the Biblical passage, only one came running. The reader has to imagine several characters in the novel as “running” to ask how they will get into heaven. But the citation seems to me a mismatch, since the characters of novel and film aren’t all rich. In any case, without the epigraph tacked to the movie, its significance gets lost. This doesn’t stop me from liking the title, though.
One of my favorite instances of the obscure catchphrase-title is Ozu’s I Was Born, But . . . To decipher it you have to know that during the Depression, Japanese college graduates often couldn’t find work, and the sentence “I graduated, but . . . ,” trailing off, suggesting “. . . I’m unemployed,” was a topical one at the time. Ozu in fact made a film with that title. But then he decided to have fun with it, making a college comedy called I Flunked, But . . . Then came an even sillier extension: When he makes a film about boys, it becomes I Was Born, But . . . [I still have problems…]. Our parallel, I suppose, is the move from Honey, I Shrunk the Kids to Honey, I Blew Up the Kid.
Which reminds me: Titles have a strange habit of speaking for the character. We have I Was a Teenage Werewolf, I Dood It, I Love Melvin, Me and the Colonel, My Favorite Brunette, My Cousin Vinny, Blackmail Is My Life, and so on. This convention points up the difference between literature and film. A book with one of these titles would lead us to expect first-person narration, and it would be strange if it didn’t. A movie with such a title might provide voice-over commentary from the protagonist, as How Green Was My Valley and I Walked with a Zombie do, but more likely it won’t.
For Your Eyes Only (1981)
Many titles seem enigmatic when you first hear them. They create curiosity and build up an urge to check out the film. In most cases, the mystery gets cleared up in the course of the movie. Erik Gunneson’s Milk Punch does this through a bit of action, but more commonly the title is clarified in a line of dialogue or a motif. You have to wait for the very end of They Shoot Horses, Don’t They? or Rio Bravo to get a reference to the title. A good embedded title shifts its meanings, as Best Years does. One scene of Silence of the Lambs explains the title’s relevance to Clarice’s character and shows what drives her to pursue Buffalo Bill. By the end of the film it points toward a moment when her inner pain will start to fade. And the title may reverberate beyond that moment, pointing to larger themes of injured innocence in a world of slaughter.
Sometimes the title is more oblique. Take North by Northwest. Many critics believe that it refers to Hamlet’s confession that “I am but mad North-northwest: When the wind is southerly, I know a hawk from a handsaw.” Roger Thornhill, caught off balance by the espionage game he’s plunged into, could be said to have lost his bearings. But I’ve always thought that the compass-point title logo and the cross-hatched latitude/ longitude array that launch the movie prepare us for travel, in a roughly westerly, then northwesterly direction (New York-Chicago-South Dakota). And when Roger is sent from Chicago to Rapid City, he travels by airliner: He flies north, by Northwest. A Hitchcock joke?
We occasionally encounter a title that isn’t explained in the course of the action, so we are invited to ponder its implications. 8 ½ is a famous example; insiders know Fellini treated it as an opus number (seven features + two shorts + this new feature = 8 ½). American Graffiti can refer to the transitory events of the single night the film shows—the kids have scrawled their dramas on the town in one long summer blast. But I think you can also read the title as referring to the pop tunes that engulf and comment on the action. Americans write their graffiti on the airwaves.
In recent times Hong Kong films have tried to make their English-language titles more comprehensible, but in the golden years there were some delirious ones. We had Banana Cop, Wheels on Meals, Why Wild Girls, Gun Is Law, Tiger on Beat, Devil Fetus, Burning Sensation, Boys?, Kung-Fu vs. Acrobatic, Evil Black Magic, Ghost Punting, Takes Two to Mingle, Vampire’s Breakfast. . . Even Chungking Express and Ashes of Time aren’t straightforward. A real problem in studying Hong Kong films seriously is to explain to people that a movie called Police Story or Naked Killer can be pretty interesting. And if the titles don’t perturb them, the subtitles will.
But most of the Hong Kong titles are inadvertently puzzling, sort of accidental surrealism. Of course Surrealist filmmakers have given us many willfully meaningless titles, such as Emak Bakia and The Andalusian Dog. Arguably Brazil and even A Hard Day’s Night are in this vein (although I think that both of these can be explained in roundabout ways).
Today’s American films seem drawn to recherché titles. I heard Jonathan Caouette remark that he chose the title Tarnation for reasons he couldn’t specify; it just seemed to fit. One catchphrase, “the elephant in the room,” has founded two movies, but in such an abbreviated form—Elephant—that you might not recognize the link. I never thought I’d find synecdoche on a movie credit, since few Americans know how to pronounce it, let alone know what it means. But trust Charlie Kaufman to give it a try. (He also inadvertently stole a pun I’ve been using in film theory courses since the seventies.) But at least I think I get the title’s point, given the protagonist’s obsession to build a miniature city. Other titles are flat-out baffling.
Take Reservoir Dogs. Tarantino says “it’s more of a mood title, it just sums up the movie, don’t ask me why.” (1) I like the title. I just don’t understand why it works so well. Do certain dogs guard reservoirs, as some guard junkyards? Are these guys as vicious as dogs, as dirty as dogs, or doggy in the sense of losers, or what? In other words, why does it seem more fitting than, say, Sump-Pump Ferrets?
Despite the logo showing faces spilling out of a blossom, Magnolia doesn’t explain its title unless you dig around outside the film. During the rain of frogs, the traffic collisions take place on Magnolia Boulevard in the San Fernando Valley. So in a way, Magnolia is one point of convergence for several of the story lines that crisscross the plot. But that’s pretty thin motivation.
What about Syriana? Before I went to the film, I had heard that the title referred to an imaginary, prototypical Middle Eastern territory used in Pentagon war games and computer simulations. But Stephen Gaghan, in another Creative Screenwriting podcast, supplies details:
It was a real term. I heard it for real in a very conservative think-tank, where they said, “We’re going to redraw the map in the Middle East, we’re going to make a new country out of Syria, Iraq, and Iran—the borders of ancient Persia, less Pakistan. We’re going to call it Syriana.” I’m like, “Excuse me? Would you repeat that?” So I shot it, I had William Hurt explaining it. But I didn’t think it helped at the end of the day. We’re not going to make a new country in the Middle East right now.
As he saw the collapse of America’s invasion of Iraq, Gaghan came to believe that explaining the title would date the movie.
I wanted to go for a title that couldn’t be pegged to right now. You notice there’s no reference to Iraq in the movie, there’s just the most passing reference to 9/11, which was an improv thing we did, and there’s no Israel. I wanted the more permanent sense of what it is inside of men, particularly men in the west, that makes them believe that they can remake any region to suit their own purposes. . . . I wanted it to be specific to the film, not to the time. So that if you think about the tone of the film, when you think about what happened in the movie, it would only be Syriana, and Syriana could not skid into some other reference point.
Then there’s Cloverfield, which I’ve discussed earlier this year. Part of the movie’s mystique is that nobody can agree on what the title refers to. The creature? Central Park, where the video camera is found? An exit on California Interstate 10, near where producer J. J. Abrams has his office? On this last option, screenwriter Drew Goddard says no way:
If we would do that, we would be dicks. We would be assholes.
I don’t want to get into the labyrinthine question of the relations of Cloverfield to Lost and to the film’s viral marketing campaign online. What interests me is the fact that part of the fun around, if not exactly in, the film is playing with all these possibilities . . . and waiting to see if a sequel will explain further. Perhaps a teasing title can help get people into theatres for a followup movie.
Finally, Primer. Not only do I not understand the significance of the title; I don’t know how to pronounce it.
I Love a Mystery (1945)
Why have we seen such a rise in cryptic titles in recent years? Several factors seem important. A puzzling title lifts your film above the clutter and creates buzz as people wonder what this movie could be about. This buzz factor is multiplied by the Internet. The title can be researched through Google and discussed endlessly in chatrooms. Filmmakers know that we can revisit a film on video whenever we want, so the movie can be rescanned by eager eyes searching for clues to the title’s meaning. Mystery titles summon up the geek in us.
Which means that the current wave of peculiar titles probably owes a lot to Tarantino. In the interview I already cited, Tarantino stressed that that title of Reservoir Dogs let the audience play with the possibilities.
The main reason that I don’t go on record is because I really believe in what the audience brings. . . . People come up to me and tell me what they think it means and I am constantly astounded by their creativity and ingenuity. As far as I’m concerned, what they come up with is right, they’re 100 percent right. (2)
But then, as Jonathan Walley pointed out to me, cool opacity isn’t confined to movie titles.
Band names have always been evocative: The Rolling Stones weren’t literally rolling stones, The Pixies not literally pixies. But what many of them evoke now strikes me as much more obscure and, to quote Grandpa Simpson, “weird and scary”: System of a Down, Teeth of Lions Rule the Divine, One Day as a Lion, My Morning Jacket, etc. Many of these are alternative bands, and many of the films with these obscure titles are alt/indie films, or at least films with those pretensions, so there’s a parallel there, I’d say. The willful obscurity of title, of band or film, evokes an ironic, think-outside-the-box, you’re-not-meant-to-get-it indie attitude that appeals to the intended audience.
That is, obtuse titles for an acute public.
For comments, suggestions, and memory-jogging, thanks to the Badger Filmies: Susan Antani, Colin Burnett, Andrea Comiskey, Sydney Duncan, Stew Fyfe, Jason Gendler, Doug Gomery, Jonah Horwitz, Tristan Mentz, Jason Mittell, Tim Palmer, John Powers, Brad Schauer, Chris Sieving, and Jonathan Walley.
(1) Quoted in “Reservoir Dogs Press Conference,” in Quentin Tarantino Interviews, ed. Gerald Peary (Oxford: University of Mississippi Press, 1998), 38.
(2) Some writers have hazarded that the title derives from Tarantino’s awkward pronunciation of Au revoir les enfants, coupled with Straw Dogs, but as far as I can tell, this relies on a second-hand source–ie, a former girlfriend–and Tarantino hasn’t confirmed it.
Superheroes for sale
DB here:
After a day at the movies, maybe I am living in a parallel universe. I go to see two films praised by people whose tastes I respect. I find myself bored and depressed. I’m also asking questions.
Over the twenty years since Batman (1989), and especially in the last decade or so, some tentpole pictures, and many movies at lower budget levels, have featured superheroes from the Golden and Silver age of comic books. By my count, since 2002, there have been between three and seven comic-book superhero movies released every year. (I’m not counting other movies derived from comic books or characters, like Richie Rich or Ghost World.)
Until quite recently, superheroes haven’t been the biggest money-spinners. Only eleven of the top 100 films on Box Office Mojo’s current worldwide-grosser list are derived from comics, and none ranks in the top ten titles. But things are changing. For nearly every year since 2000, at least one title has made it into the list of top twenty worldwide grossers. For most years two titles have cracked this list, and in 2007 there were three. This year three films have already arrived in the global top twenty: The Dark Knight, Iron Man, and The Incredible Hulk (four, if you count Wanted as a superhero movie).
This 2008 successes have vindicated Marvel’s long-term strategy to invest directly in movies and have spurred Warners to slate more comic-book titles. David S. Cohen analyses this new market here. So we are clearly in the midst of a Trend. My trip to the multiplex got me asking: What has enabled superhero comic-book movies to blast into a central spot in today’s blockbuster economy?
Enter the comic-book guys
It’s clearly not due to a boom in comic-book reading. Superhero books have not commanded a wide audience for a long time. Statistics on comic-book readership are closely guarded, but the expert commentator John Jackson Miller reports that back in 1959, at least 26 million comic books were sold every month. In the highest month of 2006, comic shops ordered, by Miller’s estimate, about 8 million books (and this total includes not only periodical comics but graphic novels, independent comics, and non-superhero titles). There have been upticks and downturns over the decades, but the overall pattern is a steep slump.
Try to buy an old-fashioned comic book, with staples and floppy covers, and you’ll have to look hard. You can get albums and graphic novels at the chain stores like Borders, but not the monthly periodicals. For those you have to go to a comics shop, and Hank Luttrell, one of my local purveyors of comics, estimates there aren’t more than 1000 of them in the U. S.
Moreover, there’s still a stigma attached to reading superhero comics. Even kitsch novels have long had a slightly higher cultural standing than comic books. Admitting you had read The Devil Wears Prada would be less embarrassing than admitting you read Daredevil.
For such reasons and others, the audience for superhero comics is far smaller than the audience for superhero movies. The movies seem to float pretty free of their origins; you can imagine a young Spider-Man fan who loved the series but never knew the books. What’s going on?
Men in tights, and iron pants
The films that disappointed me on that moviegoing day were Iron Man and The Dark Knight. The first seemed to me an ordinary comic-book movie endowed with verve by Robert Downey Jr.’s performance. While he’s thought of as a versatile actor, Downey also has a star persona—the guy who’s wound a few turns too tight, putting up a good front with rapid-fire patter (see Home for the Holidays, Wonder Boys, Kiss Kiss Bang Bang, Zodiac). Downey’s cynical chatterbox makes Iron Man watchable. When he’s not onscreen we get excelsior.
Christopher Nolan showed himself a clever director in Memento and a promising one in The Prestige. So how did he manage to make The Dark Knight such a portentously hollow movie? Apart from enjoying seeing Hong Kong in Imax, I was struck by the repetition of gimmicky situations–disguises, hostage-taking, ticking bombs, characters dangling over a skyscraper abyss, who’s dead really once and for all? The fights and chases were as unintelligible as most such sequences are nowadays, and the usual roaming-camera formulas were applied without much variety. Shoot lots of singles, track slowly in on everybody who’s speaking, spin a circle around characters now and then, and transition to a new scene with a quick airborne shot of a cityscape. Like Jim Emerson, I thought that everything hurtled along at the same aggressive pace. If I want an arch-criminal caper aiming for shock, emotional distress, and political comment, I’ll take Benny Chan’s New Police Story.
Then there are the mouths. This is a movie about mouths. I couldn’t stop staring at them. Given Batman’s cowl and his husky whisper, you practically have to lip-read his lines. Harvey Dent’s vagrant facial parts are especially engaging around the jaws, and of course the Joker’s double rictus dominates his face. Gradually I found Maggie Gyllenhaal’s spoonbill lips starting to look peculiar.
The expository scenes were played with a somber knowingness I found stifling. Quoting lame dialogue is one of the handiest weapons in a critic’s arsenal and I usually don’t resort to it; many very good movies are weak on this front. Still, I can’t resist feeling that some weighty lines were doing duty for extended dramatic development, trying to convince me that enormous issues were churning underneath all the heists, fights, and chases. Know your limits, Master Wayne. Or: Some men just want to watch the world burn. Or: In their last moments people show you who they really are. Or: The night is darkest before the dawn.
I want to ask: Why so serious?
Odds are you think better of Iron Man and The Dark Knight than I do. That debate will go on for years. My purpose here is to explore a historical question: Why comic-book superhero movies now?
Z as in Zeitgeist
More superhero movies after 2002, you say? Obviously 9/11 so traumatized us that we feel a yearning for superheroes to protect us. Our old friend the zeitgeist furnishes an explanation. Every popular movie can be read as taking the pulse of the public mood or the national unconscious.
I’ve argued against zeitgeist readings in Poetics of Cinema, so I’ll just mention some problems with them:
*A zeitgeist is hard to pin down. There’s no reason to think that the millions of people who go to the movies share the same values, attitudes, moods, or opinions. In fact, all the measures we have of these things show that people differ greatly along all these dimensions. I suspect that the main reason we think there’s a zeitgeist is that we can find it in popular culture. But we would need to find it independently, in our everyday lives, to show that popular culture reflects it.
*So many different movies are popular at any moment that we’d have to posit a pretty fragmented national psyche. Right now, it seems, we affirm heroic achievement (Indiana Jones and the Kingdom of the Crystal Skull, Kung Fu Panda, Prince Caspian) except when we don’t (Get Smart, The Dark Knight). So maybe the zeitgeist is somehow split? That leads to vacuity, since that answer can accommodate an indefinitely large number of movies. (We’d have to add fractions of our psyche that are solicited by Sex and the City and Horton Hears a Who!)
*The movie audience isn’t a good cross-section of the general public. The demographic profile tilts very young and moderately affluent. Movies are largely a middle-class teenage and twentysomething form. When a producer says her movie is trying to catch the zeitgeist, she’s not tracking retired guys in Arizona wearing white belts; she’s thinking mostly of the tastes of kids in baseball caps and draggy jeans.
* Just because a movie is popular doesn’t mean that people have found the same meanings in it that critics do. Interpretation is a matter of constructing meaning out of what a movie puts before us, not finding the buried treasure, and there’s no guarantee that the critic’s construal conforms to any audience member’s.
*Critics tend to think that if a movie is popular, it reflects the populace. But a ticket is not a vote for the movie’s values. I may like or dislike it, and I may do either for reasons that have nothing to do with its projection of my hidden anxieties.
*Many Hollywood films are popular abroad, in nations presumably possessing a different zeitgeist or national unconscious. How can that work? Or do audiences on different continents share the same zeitgeist?
Wait, somebody will reply, The Dark Knight is a special case! Nolan and his collaborators have strewn the film with references to post-9/11 policies about torture and surveillance. What, though, is the film saying about those policies? The blogosphere is already ablaze with discussions of whether the film supports or criticizes Bush’s White House. And the Editorial Board of the good, gray Times has noticed:
It does not take a lot of imagination to see the new Batman movie that is setting box office records, The Dark Knight, as something of a commentary on the war on terror.
You said it! Takes no imagination at all. But what is the commentary? The Board decides that the water is murky, that some elements of the movie line up on one side, some on the other. The result: “Societies get the heroes they deserve,” which is virtually a line from the movie.
I remember walking out of Patton (1970) with a hippie friend who loved it. He claimed that it showed how vicious the military was, by portraying a hero as an egotistical nutcase. That wasn’t the reading offered by a veteran I once talked to, who considered the film a tribute to a great warrior.
It was then I began to suspect that Hollywood movies are usually strategically ambiguous about politics. You can read them in a lot of different ways, and that ambivalence is more or less deliberate.
A Hollywood film tends to pose sharp moral polarities and then fuzz or fudge or rush past settling them. For instance, take The Bourne Ultimatum: Yes, the espionage system is corrupt, but there is one honorable agent who will leak the information, and the press will expose it all, and the malefactors will be jailed. This tactic hasn’t had a great track record in real life.
The constitutive ambiguity of Hollywood movies helpfully disarms criticisms from interest groups (“Look at the positive points we put in”). It also gives the film an air of moral seriousness (“See, things aren’t simple; there are gray areas”). That’s the bait the Times writers took.
I’m not saying that films can’t carry an intentional message. Bryan Singer and Ian McKellen claim the X-Men series criticizes prejudice against gays and minorities. Nor am I saying that an ambivalent film comes from its makers delicately implanting counterbalancing clues. Sometimes they probably do. More often, I think, filmmakers pluck out bits of cultural flotsam opportunistically, stirring it all together and offering it up to see if we like the taste. It’s in filmmakers’ interests to push a lot of our buttons without worrying whether what comes out is a coherent intellectual position. Patton grabbed people and got them talking, and that was enough to create a cultural event. Ditto The Dark Knight.
Back to basics
If the zeitgeist doesn’t explain the flourishing of the superhero movie in the last few years, what does? I offer some suggestions. They’re based on my hunch that the genre has brought together several trends in contemporary Hollywood film. These trends, which can commingle, were around before 2000, but they seem to be developing in a way that has created a niche for the superhero film.
The changing hierarchy of genres. Not all genres are created equal, and they rise or fall in status. As the Western and the musical fell in the 1970s, the urban crime film, horror, and science-fiction rose. For a long time, it would be unthinkable for an A-list director to do a horror or science-fiction movie, but that changed after Polanski, Kubrick, Ridley Scott, et al. gave those genres a fresh luster just by their participation. More recently, I argue in The Way Hollywood Tells It, the fantasy film arrived as a respectable genre, as measured by box-office receipts, critical respect, and awards. It seems that the sword-and-sorcery movie reached its full rehabilitation when The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King scored its eleven Academy Awards.
The comic-book movie has had a longer slog from the B- and sub-B-regions. Superman, Flash Gordon, and Dick Tracy were all fodder for serials and low-budget fare. Prince Valiant (1954) was the only comics-derived movie of any standing in the 1950s, as I recall, and you can argue that it fitted into a cycle of widescreen costume pictures. (Though it looks like a pretty camp undertaking today.) Much later came revivals of the two most popular superheroes, Superman (1978) and Batman (1989).
The success of the Batman film, which was carefully orchestrated by Warners and its DC comics subsidiary, can be seen as preparing the grounds for today’s superhero franchises. The idea was to avoid simply reiterating a series, as the Superman movie did, or mocking it, as the Batman TV show did. The purpose was to “reimagine” the series, to “reboot” it as we now say, the way Frank Miller’s The Dark Knight Returns re-launched the Batman comic. Rebooting modernizes the mythos by reinterpreting it in a thematically serious and graphically daring way.
During the 1990s, less famous superheroes filled in as the Batman franchise tailed off. Examples were The Rocketeer (1991), Timecop (1994), The Crow (1994) and The Crow: City of Angels (1996), Judge Dredd (1995), Men in Black (1997), Spawn (1997), Blade (1998), and Mystery Men (1999). Most of these managed to fuse their appeals with those of another parvenu genre, the kinetic action-adventure movie.
Significantly, these were typically medium-budget films from semi-independent companies. Although some failed, a few were huge and many earned well, especially once home video was reckoned in. Moreover, the growing number of titles, sometimes featuring name actors, fueled a sense that this genre was becoming important. As often happens, marginal companies developed the market more nimbly than the big ones, who tend to move in once the market has matured.
I’d also suggest that The Matrix (1999) helped legitimize the cycle. (Neo isn’t a superhero? In the final scene he can fly.) The pseudophilosophical aura this movie radiated, as well as its easy familiarity with comics, videogames, and the Web, made it irrevocably cool. Now ambitious young directors like Nolan, Singer, and Brett Ratner could sign such projects with no sense they were going downmarket.
The importance of special effects. Arguably there were no fundamental breakthroughs in special-effects technology from the 1940s to the 1960s. But with motion-control cinematography, showcased in the first Star Wars installment (1977) filmmakers could create a new level of realism in the use of miniatures. Later developments in matte work, blue- and green-screen techniques, and digital imagery were suited to, and driven by, the other genres that were on the rise—horror, science-fiction, and fantasy—but comic-book movies benefited as well. The tagline for Superman was “You’ll believe a man can fly.”
Special effects thereby became one of a film’s attractions. Instead of hiding the technique, films flaunted it as a mark of big budgets and technological sophistication. The fantastic powers of superheroes cried out for CGI, and it may be that convincing movies in the genre weren’t really ready until the software matured.
The rise of franchises. Studios have always sought predictability, and the classic studio system relied on stars and genres to encourage the audience to return for more of what it liked. But as film attendance waned, producers looked for other models. One that was successful was the branded series, epitomized in the James Bond films. With the rise of the summer blockbuster, producers searched for properties that could be exploited in a string of movies. A memorable character could tie the installments together, and so filmmakers turned to pop literature (e.g., the Harry Potter books) and comic books. Today, Marvel Enterprises is less concerned with publishing comics than with creating film vehicles for its 5000 characters. Indeed, to get bank financing it put up ten of its characters as collateral!
Yet a single character might not sustain a robust franchise. Henry Jenkins has written about how popular culture is gravitating to multi-character “worlds” that allow different media texts to be carved out of them. Now that periodical sales of comics have flagged, the tail is wagging the dog. The 5000 characters in the Marvel Universe furnish endless franchise opportunities. If you stayed for the credit cookie at the end of Iron Man, you saw the setup for a sequel that will pair the hero with at least one more Marvel protagonist.
Merchandising and corporate synergy. It’s too obvious to dwell on, but superhero movies fit neatly into the demand that franchises should spawn books, TV shows, soundtracks, toys, apparel, and so on. Time Warner’s acquisition of DC Comics was crucial to the cross-platform marketing of the first Batman. Moreover, most comics readers are relatively affluent (a big change from my boyhood), so they have the income to buy action figures and other pricy collectibles, like a Batbed.
The shift from an auteur cinema to a genre cinema. The classic studio system maintained a fruitful, sometimes tense, balance between directorial expression and genre demands. Somewhere in recent decades that balance has split into polarities. We now have big-budget genre films that made by directors of no discernible individuality, and small “personal” films that showcase the director’s sensibility. There have always been impersonal craftsmen in Hollywood, but the most distinctive directors could often bring their own sensibilities to projects big or small.
David Lynch could make Dune (1984) part of his own oeuvre, but since then we have many big-budget genre pictures that bear no signs of directorial individuality. In particular, science-fiction, fantasy, and superhero movies demand so much high-tech input, so much preparation, so many logistical tasks in shooting, and such intensive postproduction, that economy of effort favors a standardized look and feel. Hence perhaps the recourse to well-established techniques of shooting and cutting; intensified continuity provides a line of least resistance. A comic-book movie can succeed if it doesn’t stray from the fanbase’s expectations and swiftly initiates the newbies. Not much directorial finesse is needed, as 300 (2007) shows.
The development of the megapicture may have led the more talented directors to the “one for them, one for me” motto. Think of the difference between Burton’s Planet of the Apes or even Sweeney Todd and, say, Ed Wood or Big Fish. Or think of the moments of elegance in Memento and The Prestige, as opposed to the blunt handling of Batman Begins and The Dark Knight.
 Shock and awe in presentation. The rise of the multiplex meant not only an upgrade in comfort (my back appreciates the tilting seats) but also a demand for big pictures and big sound. Smaller, more intimate movies look woeful on your megascreen, and what’s the point of Dolby surround channels if you’re watching a Woody Allen picture? Like science-fiction and fantasy, the adventures of a superhero in yawning landscapes fill the demand for immersion in a punchy, visceral entertainment. Scaling the film for Imax, as Superman Returns and The Dark Knight have, is the next step in this escalation.
Shock and awe in presentation. The rise of the multiplex meant not only an upgrade in comfort (my back appreciates the tilting seats) but also a demand for big pictures and big sound. Smaller, more intimate movies look woeful on your megascreen, and what’s the point of Dolby surround channels if you’re watching a Woody Allen picture? Like science-fiction and fantasy, the adventures of a superhero in yawning landscapes fill the demand for immersion in a punchy, visceral entertainment. Scaling the film for Imax, as Superman Returns and The Dark Knight have, is the next step in this escalation.
Too much is never enough. Since the 1980s, mass-audience pictures have gravitated toward ever more exaggerated presentation of momentary effects. In a comedy, if a car is about to crash, everyone inside must stare at the camera and shriek in concert. Extreme wide-angle shooting makes faces funny in themselves (or so Barry Sonnenfeld thinks). Action movies shift from slo-mo to fast-mo to reverse-mo, all stitched together by ramping, because somebody thinks these devices make for eye candy. Steep high and low angles, familiar in 1940s noir films, were picked up in comics, which in turn re-influenced movies.
Movies now love to make everything airborne, even the penny in Ghost. Things fly out at us, and thanks to surround channels we can hear them after they pass. It’s not enough simply to fire an arrow or bullet; the camera has to ride the projectile to its destination—or, in Wanted, from its target back to its source. In 21 of earlier this year, blackjack is given a monumentality more appropriate to buildings slated for demolition: giant playing cards whoosh like Stealth fighters or topple like brick walls.
I’m not against such one-off bursts of imagery. There’s an undoubted wow factor in seeing spent bullet casings shower into our face in The Matrix.
I just ask: What do such images remind us of? My answer: Comic book panels, those graphically dynamic compositions that keep us turning the pages. In fact, we call such effects “cartoonish.” Here’s an example from Watchmen, where the slow-motion effect of the Smiley pin floating down toward us is sustained by a series of lines of dialogue from the funeral service.
With comic-book imagery showing up in non-comic-book movies, one source may be greater reliance on storyboards and animatics. Spfx demand intensive planning, so detailed storyboarding was a necessity. Once you’re planning shot by shot, why not create very fancy compositions in previsualization? Spielberg seems to me the live-action master of “storyboard cinema.” And of course storyboards look like comic-book pages.
The hambone factor. In the studio era, star acting ruled. A star carried her or his persona (literally, mask) from project to project. Parker Tyler once compared Hollywood star acting to a charade; we always recognized the person underneath the mime.
This is not to say that the stars were mannequins or dead meat. Rather, like a sculptor who reshapes a piece of wood, a star remolded the persona to the project. Cary Grant was always Cary Grant, with that implausible accent, but the Cary Grant of Only Angels Have Wings is not that of His Girl Friday or Suspicion or Notorious or Arsenic and Old Lace. Or compare Barbara Stanwyck in The Lady Eve, Double Indemnity, and Meet John Doe. Young Mr. Lincoln is not the same character as Mr. Roberts, but both are recognizably Henry Fonda.
Dress them up as you like, but their bearing and especially their voices would always betray them. As Mr. Kralik in The Shop around the Corner, James Stewart talks like Mr. Smith on his way to Washington. In The Little Foxes, Herbert Marshall and Bette Davis sound about as southern as I do.
Star acting persisted into the 1960s, with Fonda, Stewart, Wayne, Crawford, and other granitic survivors of the studio era finishing out their careers. Star acting continues in what scholar Steve Seidman has called “comedian comedy,” from Jerry Lewis to Adam Sandler and Jack Black. Their characters are usually the same guy, again. Arguably some women, like Sandra Bullock and Ashlee Judd, also continued the tradition.
 On the whole, though, the most highly regarded acting has moved closer to impersonation. Today your serious actors shape-shift for every project—acquiring accents, burying their faces in makeup, gaining or losing weight. We might be inclined to blame the Method, but classical actors went through the same discipline. Olivier, with his false noses and endless vocal range, might be the impersonators’ patron saint. His followers include Streep, Our Lady of Accents, and the self-flagellating young De Niro. Ironically, although today’s performance-as-impersonation aims at greater naturalness, it projects a flamboyance that advertises its mechanics. It can even look hammy. Thus, as so often, does realism breed artifice.
On the whole, though, the most highly regarded acting has moved closer to impersonation. Today your serious actors shape-shift for every project—acquiring accents, burying their faces in makeup, gaining or losing weight. We might be inclined to blame the Method, but classical actors went through the same discipline. Olivier, with his false noses and endless vocal range, might be the impersonators’ patron saint. His followers include Streep, Our Lady of Accents, and the self-flagellating young De Niro. Ironically, although today’s performance-as-impersonation aims at greater naturalness, it projects a flamboyance that advertises its mechanics. It can even look hammy. Thus, as so often, does realism breed artifice.
Horror and comic-book movies offer ripe opportunities for this sort of masquerade. In a straight drama, confined by realism, you usually can’t go over the top, but given the role of Hannibal Lector, there is no top. The awesome villain is a playground for the virtuoso, or the virtuoso in training. You can overplay, underplay, or over-underplay. You can also shift registers with no warning, as when hambone supreme Orson Welles would switch from a whisper to a bellow. More often now we get the flip from menace to gargoylish humor. Jack Nicholson’s “Heeere’s Johnny” in The Shining is iconic in this respect. In classic Hollywood, humor was used to strengthen sentiment, but now it’s used to dilute violence.
Such is the range we find in The Dark Knight. True, some players turn in fairly low-key work. Morgan Freeman plays Morgan Freeman, Michael Caine does his usual punctilious job, and Gary Oldman seems to have stumbled in from an ordinary crime film. Maggie Gylenhaal and Aaron Eckhart provide a degree of normality by only slightly overplaying; even after Harvey Dent’s fiery makeover Eckhart treats the role as no occasion for theatrics.
All else is Guignol. The Joker’s darting eyes, waggling brows, chortles, and restless licking of his lips send every bit of dialogue Special Delivery. Ledger’s performance has been much praised, but what would count as a bad line reading here? The part seems designed for scenery-chewing. By contrast, poor Bale has little to work with. As Bruce Wayne, he must be stiff as a plank, kissing Rachel while keeping one hand suavely tucked in his pocket, GQ style. In his Bat-cowl, he’s missing as much acreage of his face as Dent is, so all Bale has is the voice, over-underplayed as a hoarse bark.
In sum, our principals are sweating through their scenes. You get no strokes for making it look easy, but if you work really hard you might get an Oscar.
 A taste for the grotesque. Horror films have always played on bodily distortions and decay, but The Exorcist (1973) raised the bar for what sorts of enticing deformities could be shown to mainstream audiences. Thanks to new special effects, movies like Total Recall (1990) were giving us cartoonish exaggerations of heads and appendages.
A taste for the grotesque. Horror films have always played on bodily distortions and decay, but The Exorcist (1973) raised the bar for what sorts of enticing deformities could be shown to mainstream audiences. Thanks to new special effects, movies like Total Recall (1990) were giving us cartoonish exaggerations of heads and appendages.
But of course the caricaturists got here first, from Hogarth and Daumier onward. Most memorably, Chester Gould’s Dick Tracy strip offered a parade of mutilated villains like Flattop, the Brow, the Mole, and the Blank, a gentleman who was literally defaced. The Batman comics followed Gould in giving the protagonist an array of adversaries who would even raise an eyebrow in a Manhattan subway car.
Eisenstein once argued that horrific grotesquerie was unstable and hard to sustain. He thought that it teetered between the comic-grotesque and the pathetic-grotesque. That’s the difference, I suppose, between Beetlejuice and Edward Scissorhands, or between the Joker and Harvey Dent. In any case, in all its guises the grotesque is available to our comic-book pictures, and it plays nicely into the oversize acting style that’s coming into favor.
You’re thinking that I’ve gone on way too long, and you’re right. Yet I can’t withhold two more quickies:
The global recognition of anime and Hong Kong swordplay films. During the climactic battle between Iron Man 2.0 and 3.0, so reminiscent of Transformers, I thought: “The mecha look has won.”
Learning to love the dark. That is, filmmakers’ current belief that “dark” themes, carried by monochrome cinematography, somehow carry more prestige than light ones in a wide palette. This parallels comics’ urge for legitimacy by treating serious subjects in somber hues, especially in graphic novels.
Time to stop! This is, after all, just a list of causes and conditions that occurred to me after my day in the multiplex. I’m sure we can find others. Still, factors like these seem to me more precise and proximate causes for the surge in comic-book films than a vague sense that we need these heroes now. These heroes have been around for fifty years, so in some sense they’ve always been needed, and somebody may still need them. The major media companies, for sure. Gazillions of fans, apparently. Me, not so much. But after Hellboy II: The Golden Army I live in hope.
Thanks to Hank Luttrell for information about the history of the comics market.
The superhero rankings I mentioned are: Spider-Man 3 (no. 12), Spider-Man (no. 17), Spider-Man 2 (no. 23), The Dark Knight (currently at no. 29, but that will change), Men in Black (no. 42), Iron Man (no. 45), X-Men: The Last Stand (no. 75), 300 (no. 80), Men in Black II (no. 85), Batman (no. 95), and X2: X-Men United (no. 98). The usual caveat applies: This list is based on unadjusted grosses and so favors recent titles, because of inflation and the increased ticket prices. If you adjust for these factors, the list of 100 all-time top grossers includes seven comics titles, with the highest-ranking one being Spider-Man, at no. 33.
For a thoughtful essay written just as the trend was starting, see Ken Tucker’s 2000 Entertainment Weekly piece, “Caped Fears.” It’s incompletely available here.
Comics aficionados may object that I am obviously against comics as a whole. True, I have little interest in superhero comic books. As a boy I read the DC titles, but I preferred Mad, Archie, Uncle Scrooge, and Little Lulu. In high school and college I missed the whole Marvel revolution and never caught up. Like everybody else in the 1980s I read The Dark Knight Returns, but I preferred Watchmen (and I look forward to the movie). I like the Hellboy movies too. But I’m not gripped by many of the newest trends in comics. Sin City strikes me as a fastidious piece of draftsmanship exercised on formulaic material, as if Mickey Spillane were rewritten by Nicholson Baker. Since the 80s my tastes have run to Ware, Clowes, a few manga, and especially Eurocomics derived from the clear-line tradition (Chaland, Floc’h, Swarte, etc.). I believe that McCay and Herriman are major twentieth-century artists, with Chester Gould and Cliff Sterrett worth considering for the honor too.
You can argue that Oliver Stone’s films create ambivalence inadvertently. JFK seems to have a clear-cut message, but the plotting is diverted by so many conspiracy scenarios that the viewer might get confused about what exactly Stone is claiming really happened.
On the ways that worldmaking replaces character-centered media storytelling, the crucial discussion is in Henry Jenkins, Convergence Culture: Where Old and New Media Collide (New York University Press, 2007), 113-122.
On franchise-building, see the detailed account in detail in Eileen R. Meehan, “‘Holy Commodity Fetish, Batman!’: The Political Economy of a Commercial Intertext,” in The Many Lives of the Batman, ed. Roberta E. Pearson and William Uricchio (Routledge, 1991), 47-65. Other essays in this collection offer information on the strategies of franchise-building.
Just as Star Wars helped legitimate itself by including Alec Guinness in its cast (surely he wouldn’t be in a potboiler), several superhero movies have a proclivity for including a touch of British class: McKellan and Stewart in X-Men, Caine in the Batman series. These old reliables like to keep busy and earn a spot of cash.
PS: 21 August 2008: This post has gotten some intriguing responses, both on the Internets and in correspondence with me, so I’m adding a few here.
Jim Emerson elaborated on the zeitgeist motif in an entry at Scanners. At Crooked Timber, John Holbo examines how much the film’s dark cast owes to the 1990s reincarnation of Batman. Peter Coogan writes to tell me that he makes a narrower version of the zeitgeist argument in relation to superheroes in Chapter 10 of his book, Superhero: The Secret Origin of a Genre, to be reprinted next year. Even the more moderate form he proposes doesn’t convince me, I’m afraid, but the book ought to be of value to readers interested in the genre.
From Stew Fyfe comes a letter offering some corrections and qualifications.
*Stew points out that chain stores like Borders do sell some periodical comics titles, though not always regularly.
*Comics publishing, while not at the circulation levels seen in the golden era, is undergoing something of a resurgence now, possibly because of the success of the franchise movies. Watchmen sales alone will be a big bump in anticipation of the movie.
*As for my claim that film is driving the publishing side, Stew suggests that the relations between the media are more complicated. The idea that the tail wags the dog might apply to DC, but Marvel has made efforts to diversify the relations between the books and the films.
They’ve done things like replacing the Hulk with a red, articulate version of the character just before the movie came out (which is odd because if there’s one thing that the general public knows about the character is that he’s green and he grunts). They’ve also handed the Hulk’s main title over to a minor character, Hercules. They’ve spent a year turning Iron Man, in the main continuity, into something of a techno-fascist (if lately a repentant one) who locks up other superheroes.
Stew speculates that Marvel is trying to multiply its audiences. It relies on its main “continuity books” to serve the fanbase who patronizes the shops, and the films sustain each title’s proprietary look and feel. In addition, some of the books offer fresh material for anyone who might want to buy the comic after seeing the film; this tactic includes reprinted material and rebooted continuity lines in the Ultimate series. Marvel has also brought in film and TV creators as writers (Joss Whedon, Kevin Smith), while occasionally comics artists work in TV shows like Heroes, Lost, and Battlestar Galactica. So the connections are more complex than I was indicating.
Thanks to all these readers for their comments.