Archive for the 'Global film industry' Category
It takes all kinds
Kristin here—
How many directors are there whose bad reviews just make you more eager to see their new films? I’m not at Cannes and haven’t seen Jean-Luc Godard’s Film socialisme. But I’ve read some negative reviews, mainly those by Roger Ebert and Todd McCarthy. Now I’m really hoping that Film socialisme shows up at the Vancouver International Film Festival this year. (Please, Mr. Franey? I promise to blog about it.)
As you can tell from my writings, I’m no pointy-headed intellectual who won’t watch anything without subtitles. I love much of Godard’s work and have analyzed two films from early in what a lot of people see as his late, obscurantist period (Tout va bien and Sauve qui peut (la vie) in Breaking the Glass Armor). But I also love popular cinema. If I made a top-ten-films list for 1982, both Mad Max II (aka The Road Warrior) and Passion (left and below) would be on it.
Of course, those are old films by most people’s standards. Godard’s films have gotten much more opaque since I wrote those essays. I wouldn’t dare to write about King Lear or Hélas pour moi. That’s partly because I don’t speak French, though a French friend of ours has assured us that that doesn’t help much. Here Godard thwarts the non-French-speaker further by not translating the dialogue. Variety‘s Jordan Mintzer describes the subtitles that appear in the film: “To add fuel to the fire, the English subtitles of “Film Socialism” do not perform their normal duties: Rather than translating the dialogue, they’re works of art in themselves, truncating or abstracting what’s spoken onscreen into the helmer’s infamous word assemblies (for example, “Do you want my opinion?” becomes “Aids Tools,” while a discussion about history and race is transformed into “German Jew Black”).” Mintzer’s review provides a long description of the film; he mentions how baffling it is but doesn’t offer any real value judgments on it. Like other reviews, though, it piques my interest in the film.
Since Godard has increasingly moved into video essays, I’ve not kept as close track of him. But I always look forward to seeing his occasional new features on the big screen. The man has a mysterious knack for making beautiful images out of the mundane. How could a shot of a distant airplane leaving a jet-trail across a blue sky be dramatic? Godard manages it in the first shot of Passion. (I won’t show a frame from that shot, since it depends on the passage of time for its effect.) His soundtracks are dense and playful. Every few years the man cobbles together an incomprehensible plot based on rather tired political ideas and turns out something so visually striking that it might as well be an experimental film. I’m willing to watch and listen hard without assuming that I’m obliged to strain to find a message. McCarthy comments, “More personally, I have become increasingly convinced that this is not a man whose views on anything do I want to take seriously. […]” Did we take his views all that seriously back when he was a Maoist? I didn’t, but La Chinoise is a terrific film.
That’s not my point, though. As Ebert’s and McCarthy’s reviews both mention there are devotees of Godard who will most likely enjoy and defend Film socialisme. Ebert: “I have not the slightest doubt it will all be explained by some of his defenders, or should I say disciples.” McCarthy says that Godard is one of an “ivory tower group whose work regularly turns up at festivals, is received with enthusiasm by the usual suspects and then is promptly ignored by everyone other than an easily identifiable inner circle of European and American acolytes.” (McCarthy’s review is entitled “Band of Insiders.”)
I’m not sure what’s wrong with being devoted to Godard, even to the point of defending films that may be obscure or even maddening. I personally haven’t enjoyed his more recent theatrical releases like Forever Mozart and Éloge pour l’amour as much as his earlier work, but they’re still better than most Hollywood, independent, and foreign art-house films. The man is pushing 80 and not likely to change, so live and let us acolytes live.
Not coming to a theater remotely near you
I’m not here to defend Godard—not yet, anyway. But on May 19, Roger posted an essay calling for more “Real Movies” to be made, essentially narratives based on psychologically intriguing characters in situations with which we can empathize. He doesn’t say so, but I suspect this idea was inspired in part by his reaction to Film socialisme. His examples of real movies are some of the films he’s enjoyed this year at Cannes. I haven’t seen those, either, but I’ve read enough of Roger’s writings and been to Ebertfest often enough to know he loves U. S. indie films like Frozen River and Goodbye Solo. Excellent films with fascinating characters, but they and most of the foreign-language films that get released in the U.S. play mostly at festivals and in art-houses, both of which tend to be confined to cities and college towns. I’m sure that such character-driven films would be more likely than Film socialisme to get booked into art-houses, but they wouldn’t wean Hollywood from its tentpole ways.
Even the films that play festivals and arouse great emotion and admiration in the audiences will seldom break through into the mainstream. There simply aren’t enough of those art-houses.
As with many of Roger’s posts, “A Campaign for Real Movies” has aroused comments from people complaining about the lack of an art-house within driving distance of where they live. Jeremy Chapman remarked:
But Roger, if they did that (“Real Movies”), then I’d return to the cinema. And those in charge of the movie industry have proven again and again that they don’t wish to see me there. They’d rather show regurgitated nonsense to people so desperate for some distraction from their lives that they’ll go even though they know that they’re watching rubbish.
If any of these films you mention play nearby, then I shall see them. But they won’t. Instead I’ll have the option of Avatar II or some remake of a movie that was quite good enough (or not) the first time it was made. I love the movies, but I’m so over the movie industry (at least in the US).
Talking to regulars at Ebertfest, one hears time and again that some of them journey across several states to have a quick, intense immersion in films that haven’t played near their homes. Similarly, many who post comments on Roger’s essays refer to having been limited to seeing indie and foreign films on DVDs or downloads from Netflix.
 I completely sympathize with that problem. Even with Sundance’s six-screen multiplex and the University of Wisconsin’s Cinematheque series and Wisconsin Film Festival, most of the movies David and I see at events like Vancouver or Hong Kong don’t play here. Sundance has to book pop films on some of its screens to allow them to bring art films to the others. Right now Iron Man 2 and Sex in the City 2 are playing there, alongside The Secret in Their Eyes and Letters to Juliet. If that’s what it takes to keep the place going, then so be it.
I completely sympathize with that problem. Even with Sundance’s six-screen multiplex and the University of Wisconsin’s Cinematheque series and Wisconsin Film Festival, most of the movies David and I see at events like Vancouver or Hong Kong don’t play here. Sundance has to book pop films on some of its screens to allow them to bring art films to the others. Right now Iron Man 2 and Sex in the City 2 are playing there, alongside The Secret in Their Eyes and Letters to Juliet. If that’s what it takes to keep the place going, then so be it.
However much people decry the crassness of Hollywood—and there’s plenty of it to go around—or denounce audiences who only go to the latest CGI spectacle, the simple fact is that the market rules. Indeed, if there were a truly free market, we probably would see far fewer indie and foreign-language films. Film festivals are supported largely by sponsors, and the films they show are often wholly or partially subsidized by national governments. The festival circuit has long since become the primary market for a range of films that otherwise never reach audiences.
That may sound terrible to some, but consider the other arts. Some presses only publish books they hope will be best-sellers, while poetry and other specialist literature is relegated to small presses whose output doesn’t show up in Barnes & Noble. That’s very unlikely to change. Amazon and other online sales have been a shot in the arm for small presses, just as Netflix has made it far easier for people to see films they probably would not otherwise have access to. (Our plumber told me the other day that he had been watching a bunch of recent German films downloaded from Netflix. Well, that’s Madison, as we say; high educational level per capita. But most people have the same option, if they wish.)
Art-houses are scarce in small cities and towns, but such places are not likely to have opera houses either, or galleries with shows of major modern artists, or bookstores which offer 125,000 titles. (As I recall, that’s what Borders claimed to have when it first opened in Madison. Now they seem to be working on that many varieties of coffee.) Opera or ballet lovers are used to traveling to cities where they can see productions, and serious Wagner buffs aim to make the pilgrimage to Bayreuth at least once in their lives.
David and I are lucky. It’s vital to our work to keep up on world cinema, so now and then we travel to festivals and wallow in movies for a week or two. Quite a few civilians plan their vacations around such events, too. We’ve run into people in Vancouver who say they save up days off and take them during the festival. Naturally not everyone can do that, but not everybody can see the current Matisse exhibition in Chicago (closes June 20) or the recent lauded production of Shostakovich’s eccentric opera The Nose at the Metropolitan. I really wish I had seen The Nose, but I don’t really expect the production to play the Overture Center here.
To some people, film festivals might sound like rare events that inevitably take place far away, like the south of France. Those are the festivals that lure in the stars and get widespread coverage. But there are thousands of lesser-known festivals around the world, dedicated to every genre and length and nationality of cinema. For those who like to see old movies on the big screen, Italy offers two such festivals, Le Giornate del Cinema Muto (silent cinema) and Il Cinema Ritrovato (restored prints and retrospectives from nearly the entire span of cinema history; this year’s schedule should be posted soon). Last month in Los Angeles, Turner Classic Movies successfully launched its own festival of, yes, the classics. Ebertfest itself began with the laudable goal of bringing undeservedly overlooked films to small-city audiences, specifically Urbana-Champaign, Illinois. It was and is a great idea, and it would be wonderful if more towns in “fly-over country” had such festivals.
The films we don’t see
Usually when someone calls for more support of independent or foreign films, there seems to be an implicit assumption that all those films are deserving of support, invariably more so than Hollywood crowd-pleasers. If a filmmaker wants to make a film, he or she should be able to, right? But proportionately, there must be as many bad indie films as bad Hollywood films. Maybe more, because there are always lots of first-time filmmakers willing to max out their credit cards or put pressure on friends and relatives to “invest” in their project. There’s also far less of a barrier to entry, especially in the age of DYI technology.
True, the indie films we see seem better. By the time most of us see an indie film in an art cinema, it has been through a pitiless winnowing process. Sundance and other festivals reject all but a relatively small number of submitted films. A small number of those get picked up by a significant distributor. A small number of those are successful enough in the New York and LA markets to get booked into the art-house circuit and reach places like Madison. Yes, some worthy films get far less exposure than they deserve. But many more films that would give indies a bad name mercifully get relegated to direct-to-DVD, late-night cable, or worse. On the other hand, most mainstream films, no matter how dire their quality, get released to theaters. Their budgets are just too big to allow their producers to quietly slip them into the vault and forget about them.
The winnowing process for art-house fare happens on an international level as well. A prestige festival like Cannes dictates that a film they show cannot have had a festival screening or theatrical release outside its country of origin. Programmers for other festivals come to Cannes and cherry-pick the films they like for their own festivals. Toronto has come to serve a similar purpose, especially for North American festivals. Some films fall by the wayside, but the good ones attract a lot of programmers. These films show up at just about every festival. By the way, that kind of saturation booking of the year’s art-cinema favorites at many festivals means that the distributors are more and more often supplying digital copies of films to the second-tier events. Going to festivals is no longer a guarantee that you’ll be seeing a 35mm print projected in optimal conditions. At the 2009 Vancouver festival, I watched Elia Suleiman’s The Time that Remains twice, because it was a good 35mm print and I suspected that I’d never have another chance to see it that way.
To each film its proper venue
There’s no way that every deserving film will reach everyone who might admire it. Condemning the crowds who frequent the blockbusters won’t help open new screens to offbeat fare. If someone loves Avatar, as long as they keep their cell phones off, refrain from talking, and don’t rustle their candy-wrappers too loudly, as far I’m concerned they can go on believing that this is the best the cinema has to offer. Simply showing these audiences a film like A Serious Man, say, or Precious isn’t going to change their minds about what sort of cinema they prefer. To break through decades of viewing habits, such people would need to learn new ones, which takes time and effort. People’s tastes can be educated, but the odds are usually against it actually happening.
Finally, in defending art cinema against mainstream multiplex fare, commentators often cite Avatar or Transformers or the latest example of Hollywood’s venality and audience’s herd-like movie-going patterns. Yet every year major studio films come out that get four stars or thumbs up or green tomatoes. Last year, we had Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs, Up, Inglourious Basterds, Coraline, and a few others that were well worth the price of a ticket. All of them did fairly well at the box-office while playing in multiplexes. Some readers might substitute other titles for the ones I’ve mentioned, but to deny that Hollywood is bringing us anything worth watching seems blinkered. As I said in 1999 at the end of Storytelling in the New Hollywood, where I criticized some aspects of recent filmmaking practices, “In recent years, more than ever, we need good cinema wherever we find it, and Hollywood continues to be one of its main sources.”
Ultimately my point is that in this stage in cinema history, international filmmaking has settled into a defined group of levels or modes. Hollywood gives us multiplex blockbusters and more modest genre items like horror films and comedies. They bring us the animated features that are among the gems of any year’s releases. Then there are the independent films and the foreign-language ones which together form festival/art-house fare. There are also the experimental films, which play in festivals and museums. The institutions that show all these sorts of films have similarly gelled into specialized kinds of venues suited to each type. A broad range of films is still being made. There are some few really good films in each category made each year. The question is not how many worthy films are getting made but how much trouble it takes to see them.
None of the current types of institutions is likely to change on its own. What will make a difference is the growing possibilities of distribution via the internet. Filmmakers who get turned down by film festivals can produce, promote, and sell their movies via DVD or downloads. True, recouping expenses that way is so far a dubious proposition; it’s probably easier to get into Sundance than to do that. As I mentioned, digital projection may make some festivals less attractive to die-hard film-on-film cinephiles. On the other hand, in some towns opera-lovers who can’t get to the big city now can see a digital broadcast of a major production each week at their local multiplex. Not as exciting as a trip to the city to see it live, but a lot cheaper and hence within the reach of a lot more people’s means. All sorts of other digital developments will change movie viewing in ways we can’t yet imagine.
_______________
Jim Emerson has been covering the Film socialisme battle of the reviews on Scanners, with quotes and links to the ones I mentioned and more. He also demonstrates that people have been baffled by Godard since Breathless, with reviews that “are, incredibly, the same ones he’s been getting his entire career — based in part on assumptions that Godard means to communicate something but is either too damned perverse or inept to do so. Instead, the guy keeps making making these crazy, confounded, chopped-up, mixed-up, indecipherable movies! Possibly just to torture us.” He offers as evidence quotes from New York Times reviews over the decades.
Eric Kohn gauges the controversy and offers a tentative defense of the film on indieWIRE.
For our reports on various festivals, see the categories on the right. We discuss Godard’s compositions, late and early, here and his cutting here.
Festival as repertory
DB here:
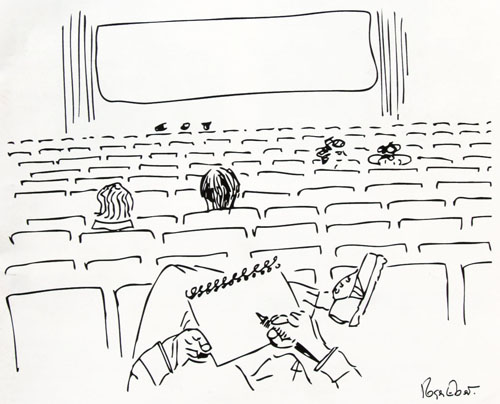
This picture points backward and forward. It looks back to the days when movies were shown on a big screen to hundreds of people in real time. No pausing or fast forwarding; you take what you get. Some viewers are settled in pretty close to the screen, and a few dare to sit in the front row. (Save me the center seat, fortunately still vacant.) The critic sits slumped far back, implying coolly distant appraisal. The pen is poised to note down moments of power, beauty, or stupidity.
But the big auditorium is nearly empty, and this makes the drawing foreshadow the approaching end of moviegoing. The warning signs are emerging: Visit any movie, even an Imax spectacular, in the off-hours (Monday through Wednesday, especially matinees) and you’re likely to find the house as empty as it is here. As for the critic, ready to jot down notes for a review: An anachronism these days, as many will tell you.
But wait. Isn’t the theatrical business booming? We’re told that 2009 was a banner year, and 2010 will be even better. True, worldwide admissions for 2009 totaled $29.9 billion, a new high. But the increase, according to the MPAA, is mostly due to 3D. In the US, the format accounted for 11 % of the country’s $10.6 billion box-office income, a sum about equal to the gain over last year’s take. Moreover, the number of domestic tickets sold increased only a little from recent years, to 1.4 billion. Overall, the years 2005-2009 have fallen off from the high points of 2002-2004, when attendance was 1.5 billion or more.
Nor is the international film industry expanding its audience. For the last five years or so, worldwide attendance has been remarkably flat, with only the Asia-Pacific region seeing signs of growth. Overall, it seems, 3D serves to let Hollywood hang on to its audience, and charge more.
The spurt in theatrical income helps offset the decline of packaged media. The DVD sell-through boom lasted from 1998 to about 2008, when subscription rental companies (Netflix, Lovefilm) and kiosks (Redbox et al) pushed down retail sales. The slump was accelerated by a glut of DVD releases, big-box stores offering discs at rock-bottom prices, the rise of downloading and video on demand, and, not least, a massive recession that made consumers cost-conscious. Today, many industry observers think that young people are more inclined to graze in the luxuriance of YouTube than visit the multiplex. At best, the Millennials might watch a current hit streaming on their cellphones or laptops or TV monitor. An admittedly small-scale inquiry in the recent Screen Digest (April, p. 100; here, but proprietary) suggests that most young entertainment fans don’t feel a need to rent a disc, let alone buy one. Moreover, all those sampled saw far more movies on monitors, often through shady downloads, than on theatre screens.
It’s not hard to imagine a near future when a movie opens simultaneously on the global market to satisfy its most devoted public before moving in a very few weeks to DVD, VOD, iTunes, and other digital platforms. It then snuggles into hundreds of thousands of hard drives around the world, ready to be awakened when somebody feels the urge to watch. These seem to be the two poles we’re moving toward: the brief big-screen shotgun blast, and the limbo of everlasting virtual access. You can argue that the very success of home video, cable, and the internet have cheapened our sense of a movie’s identity.
Which is one reason why film festivals are very, very important.
Apocalypse then and now
I’ve spent most of the last several weeks at festivals. The Hong Kong International Film Festival is a 2 1/2 week showcase of global cinema, attached to a major regional market assembly and spiced with local attractions and international retrospectives. The Wisconsin Film Festival is a 4 1/2 day local event highlighting US independent cinema but with a leavening of recent arthouse titles and restored classics. Ebertfest, formerly Roger Ebert’s Festival of Overlooked Films, is a topical festival held in a single venue, featuring a wide array of guests, and reflecting its founder’s eclectic tastes.
Each offers unique pleasures, and each reaffirms the value of the theatrical motion-picture experience. I’ve already written a bit about Hong Kong here and here and here, and I hope to write more about the Wisconsin event soon. For now I’ll concentrate on a few high points of Ebertfest, which took Roger’s cartoon above as its emblem. Kristin and I have been guests for many years (our posts are in the Festivals: Ebertfest category on the right), but this time she was in Egypt scouring the sands for pieces of statues. So I’ve had to blog solo.
Fortunately, we now have a vast archive of what happened in Urbana. With the generosity typical of Roger’s event, all the Q & A sessions and panel discussions were recorded and streamed. They’re available here. And for an appreciative account of what it all means, see Jim Emerson’s piece on Roger’s site.
Start with the obvious. Apocalypse Now Redux was shown in a Technicolor restoration in the Virginia Theatre, a picture palace built in 1926. The image loomed, the sound engulfed you. Several people, most of them young, told me that they felt privileged to have seen the film, for once in their lives, as it must be seen. As soon as you get a home theatre that matches this presentation in sheer primal impact, call me. I’m coming over.
Editor and sound designer Walter Murch, one of my heroes, was prevented from coming by the European volcano ash. So I tried in my introduction to pay homage to what is surely one of the most complex soundtracks of any film of the period—a mixture of synthesizer, rock and roll, and layer upon layer of subtly enhanced noises. During the screening I was able to appreciate some of the daring soundfields Murch created. When Willard gets up to look out the blinds of his Saigon hotel, the sound in the left and right and surround channels narrows abruptly to the central speaker, bringing him back to mundane R & R reality. Later, most ordinary dialogue comes from the central speaker, but when Willard voices his commentary, we hear him from all three front speakers; the soft tone creates an intimacy, while the auditory spread gives it weight and authority.
A panel of commentators including Ali Arikan, Michael Phillips, and Janet Pierson did a fine job of probing various aspects of the film. Ali considers it Coppola’s crowning achievement and one of the great American films. Michael, by contrast, thought that what he aptly called the “terror and grandeur” of its opening half gives way to off-kilter and pretentious scenes in Kurtz’s compound. Janet, who had seen the film on the big screen more often than any of us, found it an enduringly impressive accomplishment in both sound and image. With the audience we had a lively exchange about the role of women in the film and the inclusion of the notorious French plantation sequence. Matt Zoller Seitz made a shrewd point about how the film shows Americans bringing along homegrown entertainments (Playmate performances, rock music, surfing) to redefine the war in familiar terms.
Despite all the shock and awe, I like the film only moderately. It’s a stunning logistical accomplishment, and it has some brilliant moments; but I think it has problems almost as soon as Willard moves upriver. I might be the only person who finds the Kilgore scenes overdrawn, almost Dr. Strangeloveish. When Kurtz bends down to give water to the wounded Vietnamese, he’s interrupted by news of surfing, and he yanks his canteen away as the VC scrabbles for it.
Heavy, heavy—as is the repeated motif of Americans strafing civilians and then tending to their wounds. Willard spells it out: “We cut them in half and then give them a Band-Aid.” Yet I still admire the utterly disorienting opening, which mixes thrumming choppers with ceiling fans and justifies what Michael Herr called it: the rock-and-roll war. Later we’ll see battles wreathed in psychedelic haze, and a hallucinatory assault on the bridge, with Willard stumbling through the dark and watching battle-fried infantrymen hurl ordnance into a void. It’s like a light show at the climax of a rock concert.
One of my favorite comments about the movie came during Dick Cavett’s television show circa 1980. Dick asked Jean-Luc Godard what he thought of Apocalypse Now. This was a period in which most of the press coverage obsessed about the film’s soaring budget. Godard remarked that Coppola had not spent enough. Cavett asked for an explanation. Godard: “Well, he spent only fifty million dollars and the war cost fifty billion. You cannot film this war on such a small budget.” That’s the way I remember it, anyhow.
From Rwanda to LA
Quick notes on two other E’fest titles. (I’ve already discussed Departures here.)
“I wanted to make a film for a Rwandan audience.” Not what you might expect to hear from an American director of Korean descent. Accordingly, Lee Isaac Chung gave Munyurangabo a leisurely pace and structure. The plot centers on two young men, Sangwa and Munyurangabo (aka Ngabo), taking what seems to be an enigmatic journey. One is Hutu, the other Tutsi. Longish takes and fairly distant framings follow them hitchhiking and stopping over at Sangwa’s home. Gradually, hints such as Ngabo’s carefully wrapped machete suggest that they are heading toward a confrontation. When the revelation comes, our attachment shifts from Sangwa and his family conflicts to Ngabo’s mission of vengeance. Chung explained that the soundtrack develops accordingly, moving from objectivity to subjectivity as we start to hear what his two protagonists hear.
The production background, explained by Chung and his colleagues Sam Anderson (co-writer and producer) and Jenny Lund (co-producer and sound recordist), was fascinating. The script consisted largely of a scene outline, and the dialogue was developed with the actors. The Americans worked with translators in guiding the performances. In some cases they drew on their own experiences. Perhaps partly because of its respect for everyday life, the film has been shown on local television and in the Parliament. It has become a Rwandan film.
My colleague J. J. Murphy has written an acute analysis of Munyurangabo. He rightly praises the sudden entrance of a bardic young man who recites a six-minute poem celebrating liberation and reconciliation. The performance wasn’t planned, Chung said, but it has become a high point of the film. J. J. also links to other enlightening interviews given by Chung, Anderson, and Lund.
If Munyurangabo’s loose structure evokes the Dardennes brothers, Michael Tolkin’s The New Age has the coiled-serpent dramaturgy of a classic psychodrama-comedy. It’s 1994, and a prosperous LA couple is suddenly without income. Facing bankruptcy, Katherine and Peter auction off their paintings, try to borrow from Peter’s father, and eventually open a boutique catering to the tastes of their friends. At the same time they slide into casual affairs and ceremonies of New Age spirituality. Ebert’s review captures the movie’s range of reference:
Tolkin gives us one richly detailed set piece after another, involving luncheons, openings, massages, telephone tag, psychic consultations, sex, heartfelt conversation, and pagan rituals led by a bald-headed woman who sees what others cannot see. Meanwhile, the material universe remains the one thing Peter and Katherine can really count on.
Few American films examine money and class, but this one is actually about needing a paycheck. By the end, when each of our protagonists becomes a seller rather than a buyer, we have seen a remarkably sharp dissection of a lifestyle.
In the Q & A afterward, Tolkin said that the genesis of the film came from watching a Melrose shop sink into failure. When I saw the film on its initial release, lines like “It’s not an insult, it’s an intervention” and “We need space” (psychological, but also retail) leaned me toward taking the film as satire. I still do. But Tolkin insists that it’s not. The plot dares to have two truly repellant protagonists, but Tolkin doesn’t find them nasty. “I like them.” He majored in religion in college and he takes his characters’ beliefs, no matter how shallow, seriously—not a big surprise from the creator of The Rapture.
He elaborated on some differences between novels and films. When he rereads one of his novels, he thinks, “How was I ever that smart?” but when he rewatches a film it’s the imperfections that jump out. A movie has to be more compressed and rhythmically varied than a novel—something The New Age demonstrates in its brisk montages alternating with slowly unfolding scenes. In the discussion Jim Emerson praised the film’s density of detail, Tolkin elaborated by invoking William Carlos Williams’ belief in compact expression.
The next two paragraphs include plot details you may prefer to pass over.
Tolkin’s script is indeed firmly contoured. The couple’s crucial quarrel takes place at the thirty-minute mark and launches the two major plot lines. They decide to try a separation (while sharing the house), and they launch their boutique. The development section begins about halfway through, as they conduct their love affairs and watch the shop founder. The last act presents their options: bankruptcy, suicide, low-end work.
Arguably the climax is Peter’s desperate effort to make his first telemarketing sale. Here, I think, Tolkin’s ambivalent sympathies come out. Early in the film Peter had asked a cold-caller whether he ever thought he’d be doing this as a career; it’s less a moral condemnation than glib snobbery. But when Peter has to close the sale, his self-loathing is mixed with a certain pride. The cashiered ad exec finds that he can do this. He’s on the road back.
The gorgeously designed movie, with hard blacks and saturated primaries, has a developing palette (“swatches for each act,” Tolkin says). Unhappily, I can’t study the design arc here because The New Age seems never to have had a DVD release. So much for the Celestial Multiplex. Good old 35mm pulled us through, in a radiant print.
Scholars seem now to agree that film festivals serve as an alternative international distribution system. Like Hollywood’s more formal and routinized machine, festivals bring movies to audiences. Usually the movies are current ones, and a festival is offering local viewers their only chance to see such pictures before video release.
Ebertfest shows that there’s an essential place for what we might call the repertory festival. That’s one that revives and reappraises films from earlier periods—and “earlier” may mean only a few years ago. Jumping from 1929 (Man with a Movie Camera, accompanied by the Alloy Orchestra) to the 1980s (Apocalypse Now, Barfly) and the 1990s (The New Age) and then right up to 2008 (Vincent, Trucker, Departures, Synecdoche, New York, Song Sung Blue), this year’s edition reminds us that every film, old or new, is a part of history.
To come fully into history, I’m convinced, a film needs scale. Even intimate dramas attain their true gravity when spread out like a gigantic picnic on a pale blanket. It’s not the only way to enjoy cinema, certainly; but it’s one that we must never abandon. Like the note-taker in the back row and the geeks up front, everyone needs a full view.
Apocalypse Now Redux.
PS 28 April: I just discovered this piece by Steven Zeitchik, who argues that reviving classics in a big-screen event format could also be good business.
Paris-Berlin-Brussels express
Doktor Satansohn.
Our trip to Europe has come to an end, and so we finish with a post scanning some highlights.
The magic lantern learns new tricks
DB here:
What am I seeing? Many avant-garde films pose this question. Mainstream fiction film and documentary cinema have mostly relied on the idea that the image should be recognizable as “what it is.” But one strain of experimental film has worked to delay or even prevent us from making out what’s in front of the camera.
Sometimes we lose our bearings only briefly, as when we eventually identify pot lids in Ballet Mécanique or bits of sunlit linoleum in Brakhage films. Sometimes language points out what’s really there. The titles of Joris Ivens’ Rain and the Eames’ Blacktop: The Washing of a School Play Yard allow us to enjoy the ways that ordinary sights can yield unexpected abstraction. Sometimes we toggle back and forth, as when in Ken Jacobs’ Tom, Tom, the Piper’s Son recognizable human figures, however grainy, jump into sheer blotchiness and then back into something like legibility. But other times we can’t ever tell what we’re seeing. Brakhage’s Fire of Waters offers one of the best examples I know, with its jagged bursts of light in a smoky void.
What am I seeing? The uncertainty was doubled during my visit to Ken Jacobs’ Nervous Magic Lantern performance at the Cinémathèque Française. I say “doubled” because at least with Fire of Waters and Tom, Tom I knew I was watching a film. With this display, What am I seeing? started as a question about the format itself. Was it a film, a video, or something else?
Then the question became the customary one. Off-white textures—pebbly, dribbly, stalagmite-like—swim in and out of focus. Some are viscous and globular, some are like tangled foliage. They seem to spiral, but actually (I put up a finger to measure) they barely move. The effect of movement is given by pulsations of pure black, breaking the lyrical effect of the surfaces with a harshness that becomes aggressive. Aggressive as well is the soundtrack, blocks of sound from subway platforms and traffic and kitsch Latin percussion, all played at high volume. The surfaces just keep shifting and not shifting, sort of rotating while jabbing out at us, lovely and anxiety-inducing at the same time.
At the end of the performance, people crowded around the cardboard booth in the middle of the theatre. As Ken and Flo Jacobs packed up, they showed how they had generated the effects. What had I been seeing? Neither a film nor a video but a true magic-lantern display, assembled on the spot. But what had I been seeing? Something created with home-made equipment of a startling simplicity. (Strapping tape was involved.) Our magicians explained their tricks, like magic-lantern operators of earlier centuries explaining the science behind their shows. But I think it’s best that you not know until after you have a chance to see what they create.
In earlier entries (here and here) Kristin and I have praised Jacobs’ films for showing how very slight adjustments in technique or technology can create disturbing cinematic illusions. In this vein, the first item on the Cinémathèque program, a video called Gift of Fire, turned Louis Le Prince’s brief 1888 street scene into a 3D movie. (The homage was appropriate because Le Prince experimented with multiple-lens cameras.) The Nervous Magic Lantern performance generated a different sort of illusion, one conjuring up micro-landscapes and otherworldly vortices. In all, Jacobs makes us realize how many evocative effects are still to be discovered by tinkering with images thrown on a screen.
Detour to Berlin
KT here:
As David mentioned in last week’s entry, I took a week in the middle of our visit to Europe for research at the Ägyptisches Museum in Berlin. The staff there welcomed me into their storerooms, and I spent the days looking at fragments and the records of their discovery and the nights downloading and backing up my photos. No time for filmgoing. The most I managed was a trip to the well-stocked arts bookshop Bücherbogen, which has one of the best selections of film books to be found in Germany. Our old friend, experimental filmmaker Carlos Bustamente, met me there, and we had a quick cup of tea–most welcome on a cold morning when the results of the biggest snowfall in decades were still blanketing many sidewalks and roads.
I did note one film-related phenomenon, however. Every day I took the S-Bahn from Savignyplatz to Friedrichstrasse. The tracks pass directly across the street from the Theater des Westens (that is, the western part of Berlin). It was playing Der Schuh des Manitu, a musical version of the  highly successful 2001 German film of the same name. (I hope the publicity photo at the left was taken in warmer weather than I experienced.) I mentioned the film here, in reference to the fact that every major producing country, and some minor ones as well, turn out their own local comedies, films that don’t travel well but are very popular locally.
highly successful 2001 German film of the same name. (I hope the publicity photo at the left was taken in warmer weather than I experienced.) I mentioned the film here, in reference to the fact that every major producing country, and some minor ones as well, turn out their own local comedies, films that don’t travel well but are very popular locally.
By now it’s a familiar phenomenon in the U.S. for successful Hollywood films to be turned into stage musicals. It wasn’t always so. Back in the 1950s and 1960s, films were made of popular musicals, sometimes successfully, as with My Fair Lady, and sometimes not, as with Mame. But now the trend is the other way, with everything from Shrek to Hairspray getting the Broadway treatment.
It’s interesting to know that the same thing goes on abroad, though I’m not sure how prevalent such adaptations are. Der Schuh des Manitu, directed by Michael “Bully” Herbig, remains the highest grossing German film. Herbig doesn’t act in the stage play, as he did in the film, but he served as a creative advisor. The musical is a hit, having premiered on December 7, 2008 and it is expected to continue until at least the autumn of this year. There are several clips from both the film and the musical on YouTube. This one, at 8 minutes, gives a generous dose of the show. There are no subtitles.
I had only a couple of days back in Paris before we headed for Brussels for the final week of our trip. The German theme continued, since a few of the 1910s films David needed to see at the Cinematek here were German. The one I most wanted to see was Edmund Edel’s 1916 feature, Doktor Satansohn. Its main claim to fame is probably the fact that Ernst Lubitsch plays the title role. My book with Lubitsch started with his 1918 move to features, when he began to concentrate more on directing and less on acting. By 1920, with Sumurun, he appeared onscreen for the last time; being discontented with his performance as the tragic clown, he decided it was time to move behind the camera for good.
In the short films he starred in before 1918, Lubitsch often played a brash, ambitious Jewish youth, as in Der Stoltz der Firma (“The Pride of the Firm,” 1914). In Doktor Satansohn he’s a physician with a magical machine that transforms older women into beautiful young ones. We’re first introduced to a couple and the wife’s mother. When the latter makes a pass at her son-in-law and is rejected, she seeks the doctor’s help. His machine works by capturing the wife’s essence in a statuette and making the mother look like her daughter. Problem is, every time she’s about to kiss the husband, the doctor pops up with his devilish leer, visible only to the “wife.” David and I decided that the film is a comedy, though perhaps one only Germans of the day would find truly amusing. For one thing, the title character is clearly a Jewish caricature, one played to the hilt by Lubitsch. He decorates his machine with the Star of David and a Hebrew inscription (not to mention vipers and an image of Saturn).
Stylistically it’s a fairly conventional film for its day, though the black background of the doctor’s office, with its stylized youth machine and satyr-like bust, gives a hint of Expressionism to come. (See our topmost image.) Inevitably near the end there comes the moment beloved of historians of pre-World War II German cinema. The real daughter, released from her imprisonment in the statuette, confronts her double in the doctor’s waiting room. The Doppelgänger motif strikes again.
I wonder if German films actually have more Doppelgängers in them than appear in other national cinemas. Do they really reflect the disturbed soul of the nation? Or did the possibilities of filmic special effects draw moviemakers to try and multiply single figures? Georges Méliès and Buster Keaton used in-camera techniques to multiple their own figures in virtuoso displays. I recall being impressed by The Parent Trap‘s duplication of Hayley Mills when I saw it as a kid, and the whole notion of a single actor playing twins and other lookalike relations is a common enough convention. In Doktor Satanssohn, the doubled figure appears only in this one shot, and it’s the leering Lubitsch, delighted with his own nastiness, who walks off with the picture.
The 1910s, again, and still
DB again:
We saw Doktor Satansohn while I was studying staging and cutting strategies of the 1910s, thanks to the remarkable holdings of the Royal Film Archive of Belgium, also known as the Cinematek. My comments on last summer’s visit are here.
Another German film, in a choppy Russian print, vouchsafed a new glimpse of Asta Nielsen. In Totentanz (Urban Gad, 1912), she plays a guitarist-dancer who must take to the stage to support her infirm husband. She attracts the devotion of a composer, and soon she feels attracted to him. Torn between desire and duty, she snaps during a rehearsal of his latest piece, “Totentanz.” In a chilling gesture, she uses his dagger to slice her lute strings.
Soon the two are locked in a violent erotic struggle, and a stabbing ensues. In all, melodrama as ripe as one could want.
As ever, I was happy to have my hypotheses about tableau staging confirmed by several of the titles I saw. A minor French bedroom farce, Le Paradis (M. G. Leprieur, 1914 or 1915), had a brief passage of the sort of blocking and revealing we find in many films of the period. The painter Raphael Delacroix (no kidding) is pretending to be the lover of Claire Taupin to deflect the advances of randy M. Pontbichot. But Claire is actually the mistress of M. Grésillon. . . .
First, very frontal staging strings out Pontbichot, Raphael, and Claire. The older man relents in his pursuit of her.
In the vivid depth characteristic of the tableau tradition, Pontbichot withdraws. But his position accentuates that central door, which starts to open.
Most remarkably, Pontbichot ducks almost entirely behind the couple, giving pride of place to M. Grésillon’s arrival in the center of the shot.
Pontbichot slides out in time to register Grésillon’s outraged reaction to finding his mistress in another man’s arms.
Grésillon rushes to the frontal plane, furious. As ever, a thrust to the foreground creates a major spatial/ dramatic event.
Although the Le Paradis passage is ABC compared to the emotionally powerful patterns of staging we find in Ingeborg Holm (1913), it illustrates how even average films could resort to the blocking/ revealing tactic within the deep-space geometry of the tableau.
More flamboyant was Il Jockey della Morte (1915), an Italian circus film made by the Dane Alfred Lind. Its bold lighting and varied angles on the Big Top recalled the Danish films of a few years before. Halfway through, Lind launches a dazzling chase that features leaps from a tall bridge and bicycling stunts on a cable stretched across a river.
Another Italian film, this time a diva vehicle, suggests that by 1917 1923 (see below) the tableau style was already giving way had given way to scenes organized around close shots. (See below.) L’Ombra (Mario Almirante) starred Italia Almirante Manzini as a lively, trusting wife who becomes paralyzed. While her husband betrays her with her younger protégée, she gradually recovers bodily movement. Yes, a paralyzed diva seems a contradiction in terms, but one small-scale scene shows a remarkable range of emotions. Berta’s hands start twitching, one lifts up, and she stares wildly, as if it were an alien being.
In an earlier scene, Berta had asked that a mirror facing her be tipped upward so that she would never see herself sitting immobile. This shot pays off now, when the hand ascends almost magically into the bit of reflection she can see.
When the hand descends, her astonishment turns into joy. She experimentally shoves the hands together, as if asserting her control.
In the end, she kisses her hands as if they were pampered children.
Manzini runs through many more micro-emotions than I’ve indicated here, but this sample is typical of the ways in which L’Ombra avoides the long-shot choreography of only a few years before and builds a performance out of face, body, and arms in a close framing. The mirror-shot motif shows that fairly careful filmic construction was emerging at this point too.
During my stay, I learned more about tinting and toning from the ever-helpful Noël Desmet. On the seldom-seen World War I drama L’Empreinte de la patrie (M. Dumeny, 1915), some images had curious oscillating patches of rusty brown. Noël explained that when Prussian Blue toning was combined with rose tinting, the chemicals eventually reacted to alter the pink cast. An example is shown at the top of this section, though the blue is more saturated in the original.
Once we get back to Madison, I’ll have to sort out all that I’ve learned from these movies. Onward and upward with the 1910s!
For more on Jacobs’ Nervous Magic Lantern, see Scott Foundas’ interview here. The Youtube clip doesn’t do the spectacle justice. If you must know something of Jacobs’ tools, the Dailymotion video from the performance I saw offers some clues. My notions about 1910s staging are laid out in On the History of Film Style and Figures Traced in Light. You can also find several discussions in earlier entries on this site. Just execute a search on tableau.
Now is a good time to thank Noël Desmet and Marianne Winderickx, both of whom are retiring from the archive in March. The research that Kristin and I have done over the years owes an enormous lot to them, and of course to the Director of the Cinematek Gabrielle Claes.
P.S. 15 November 2013: Ivo Blom has pointed out that the version of L’Ombra I saw wasn’t from 1917 but rather from 1923. Hence the corrections above. Thanks very much to Ivo! Go here for his blog and information about his newest publication on silent Italian cinema.
A tinting and toning sample card from the early 1920s. Courtesy Noël Desmet.
Don’t knock the blockbusters

Promoting Pirates of the Caribbean in Japan (By tralala.online)
Kristin here:
When was the last time you heard someone complaining about the high cost of the latest Toyota prototype? Probably not recently, since car manufacturers don’t tend to boast about how much it costs them to design a new model. In fact, I couldn’t find any information on how much the development of automobile prototypes costs. Some new models catch on, some don’t. Presumably some don’t make a profit for their makers. The same tends to be true for other big-ticket items.
In a way, a film’s negative is like a prototype. It costs a lot for a mainstream commercial film to be made, tens or hundreds of millions of dollars in many cases, before the first distribution print is struck and the first ticket sold. Yet once that prototype exists, any number of distribution prints can be struck, and a film may make back many times its negative cost.
[Added October 28: A friend of mine privy to information about car manufacturing informs me that an ordinary prototype runs $50 to 250 million. A radically new product like an electric car could run over a billion. And car companies do keep those figures secret, so it’s no wonder I couldn’t find them.
Coincidentally, $50 to 250 million is pretty much the range of budgets for mainstream commercial Hollywood features these days.
My friend told me other things about car manufacturing that make it sound as though the comparison between the two industries is a pretty reasonable one. For example, car companies can save money by releasing new, slightly modified versions of a popular model, such as the Honda Civic, rather than designing a new model from the ground up. Sort of like sequels in the film industry. More surprisingly, when car manufacturers (and some companies in other industries) make their products by outsourcing some of the components, they call it the “Hollywood model.”]
For some reason, the cost of making that negative is often public knowledge. To some extent, at least, since we all know that the budget as acknowledged by a studio may be considerably less than the actual costs. The notion that a movie set its company back by $200 million is to some extent a selling point. I’m sure that back in 1922 Universal wasn’t happy that Erich von Stroheim’s Foolish Wives ended up costing more than a million dollars. Still, they turned it to their advantage by advertising it as the first million-dollar movie, and studios have been using the same tactic ever since.
The producers and makers of other kinds of artworks don’t tend to make such information public. How much does it cost to put on a symphonic concert or publish a book? We may hear about big advances paid to an author, but that’s basically a lump-sum against future royalties, and the author doesn’t get any more until–if ever–the advance is paid off. But how much do editorial supervision, printing, and binding set a publisher back? What kind of money goes into the creation of a large stone sculpture?
Journalists looking for a hook for an article about movies find a sturdy one in the idea that today’s film budgets are bloated. They point to classic movies of decades past that cost only a few million to make and then compare these to the loud, overblown summer tentpoles of today, with their multi-hundred-million-dollar costs. Of course this overlooks the inflation of the dollar over the years. In the 1950s the average family income was about $5000 and an average house cost under $20,000. A penny bought a gumball and could be used in parking meters. Just about everything costs a lot more now.
To be sure, other factors have raised the budgets of films well beyond what they would be through inflation alone. The key factors have been star salaries and computer-generated special effects. The latter can account for half the cost of an effects-heavy film. Beyond the negative cost, typical budgets for prints and advertising have skyrocketed.
Some people seem to see an innate immorality in today’s biggest budgets, as well as an almost inevitable lack of quality in the films that result. Here’s one of the first results of a search on “big budget movies,” from Dmitry Sheynin on suite101.com. He even makes the car comparison:
The film industry has had a good summer this year – action sequences were bigger than ever, and expensive displays of pyrotechnics and CGI showcased new and exciting ways to destroy cinematic credibility.
With the economic crisis forcing many companies to scale down or even discontinue some of their more opulent product lines (think GM), it’s comforting to know Hollywood studios are still spending inordinate sums of money producing bad movies.
I think that’s fairly typical of the grousing you find on the internet and in print. No doubt Hollywood produces many bad movies. But actually, it is comforting to know that Hollywood is still spending great sums of money, ordinate or in-, if you think of the welfare of the country as a whole.
Every now and then I’ve pondered the possibility that American movies must be one of the products, if not the product, that has the most favorable balance of trade. While the US doesn’t have quite the stranglehold on world film markets that it used to, most significant Hollywood films get exported to numerous countries. Conversely, very few films from abroad are imported, and those that come in, especially the foreign-language ones, play in far fewer theaters and sell far fewer tickets than do domestic films. In 2006, according to US census figures, foreign films took in $216 million in the U.S., while domestic films sold $7.1 billion worth of tickets. So that’s 3% of the U.S. market for imported films, which is the figure I’ve heard pretty consistently for decades.
(In passing, I note from the same report that theaters made 66% of their income on tickets, meaning that we moviegoers spend about a third of our cash on all that stuff in the lobby.)
Turns out my ponderings have been correct. On the Motion Picture Association of America’s “Research & Statistics” page, there appears the claim, “We are the only American industry to run a positive balance of trade in every country in which we do business.” (“The industry” includes both film and television.) In April the MPAA put out its latest annual report, “The Economic Impact of the Motion Picture & Television Industry on the United States.” The combined trade surplus in the moving-picture industry for 2007 was $13.6 billion, or 10% of the US trade surplus in private sector services. According to the report, “The motion picture and television surplus was larger than the combined surplus of the telecommunications, management and consulting, legal, and medical services sectors, and larger than sectors like computer and information services and insurance services.”
Lest anyone think these figures are mere industry propaganda, the MPAA’s information, though made public, is gathered for the benefit of the film studios, which collectively own the association. Screen Digest, a highly respected trade publication, summarized some of the report’s material in its September issue (“Film and TV Are Key to US Economy,” p. 265).
For better or worse, most films that are really successful abroad are big-budget items, with lots of expensive special effects and (usually) top stars. Back in 1997 people were aghast at the first $200 million movie, Titanic—until it brought in nearly $2 billion around the world. Here, in unadjusted dollars, are the top foreign earners for the past nine years (not including domestic box-office):
2008 Indiana Jones and the Kingdom of the Crystal Skull $469,534,914
2007 Pirates of the Caribbean: At World’s End $651,576,067
2006 Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man’s Chest $642,863,913
2005 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire $605,908,000
2004 Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban $546,093,000
2003 The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King $742,083,616
2002 Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets $616,655,000
2001 Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone $657,158,000
2000 Mission: Impossible II $330,978,216
Add in the DVDs and ancillary products, and the balance of trade gets even more favorable.
Yes, it may sound absurd that it requires $200 million to make a movie, especially one that gets mediocre reviews from critics and fans. Still, from a business point of view, it makes sense and it’s good for the country. It’s especially important in a period of financial crisis, when the movie industry’s income seems considerably less affected than many others. Our overall trade deficit is falling, since Americans are saving more and buying less from abroad. This year the film and television industry’s share of the surplus will presumably grow.
Apart from the balance of trade, according to the MPAA report, in 2007 the moving-image industry also employed 2.5 million people, paid $41.1 billion in wages, spent $38.2 billion at vendors and suppliers, and handed over $13 billion in federal and local taxes.
If you think the trade deficit doesn’t affect you, think again the next time you travel abroad and curse the exchange rate with the euro or the yen.
No doubt there’s a great deal of waste and slippery dealing involved in those huge budgets, but there are definite advantages that don’t get considered often enough.
I do see a lot of foreign cars on the roads.
[October 23: Coincidentally, two days ago Steven Saito posted a story on how foreign-language films that have achieved blockbuster status in the rest of the world don’t stand much of a chance of getting into the American market. He mentions the “Christmas Vacation” series that I referred to in an earlier post.]