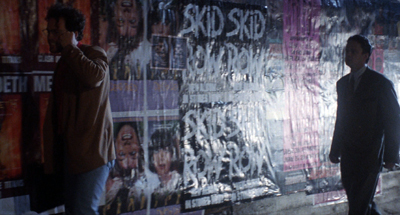Archive for the 'Hollywood: Artistic traditions' Category
The quietest talkie: THE DONOVAN AFFAIR (1929)
DB here:
The Donovan Affair was Columbia’s first all-talking picture, and Frank Capra’s as well. We discussed it a little in an entry devoted to a Cinema Ritrovato retrospective of Capra’s films. The film lacked, and still lacks, a soundtrack, which may be lost.
The Donovan Affair is an unusually fluid early talkie, and that led me to speculate we might be seeing the silent release version. Wrong! It really does survive only as a sound film without a soundtrack; the Library of Congress print I studied last month has a leader labeled “synchronized version.”
The clunky plot didn’t improve on repeated viewing, but the film did teach me some things about those transitional years 1928-1932, when filmmakers were figuring out how to make a sound feature. I thought I’d share some of those findings with you today.
But I must warn you that there’s one big spoiler coming up. I tell you whodunit. It’s necessary to make a point, but I will warn you just before the offending paragraph, so you can skip if you wish.
Blood-spattered footlights
Murder ran wild on the Anglo-American stage of the 1920s. While melodramas of love and betrayal waned, mysteries rose in popularity. There were plays about gangsters, trials, and domestic homicide. There were comedies of lethal intrigue in spooky settings, like The Bat (1920), The Last Warning (1922), and The Cat and the Canary (1922). A little more seriously, in response the rise of the genteel British detective novel (Christie, Sayers, Allingham et al.), there emerged plays that dumped murder into society drawing rooms.
You know the format. The setting is typically a mansion, with portraits, plush salons, and an impressive library. The victim, usually a bounder, deserves killing. The suspects are both high and low: businessmen, doctors, lawyers, dowagers, flappers, playboys, ne’er-do-wells, gangsters, and servants. Into this ménage steps a police inspector, often with a bumbling assistant, who will more or less skillfully reveal the culprit. In the process, though, someone else is likely to die.
The prototype is Bayard Veiller’s play The Thirteenth Chair (1916), but by the 1920s Britain and the US produced a host of popular and well-reviewed drawing-room mysteries: The Nightcap (1920), In the Next Room (1923), The Creaking Chair (1924), Interference (1927), The Man at Six (1928), The Clutching Claw (1928), and The Canary Murder Case (1928). The most famous entry in this cycle is probably Patrick Hamilton’s Rope (1929), which stands out because it presents the crime from the killers’ viewpoint. The question isn’t “Who did it?” but “Will they get away with it?” Rope’s “inverted” structure (no pun intended; it’s a trade term) was anticipated by A. A. Milne’s The Fourth Wall (1928).
Owen Davis’s play The Donovan Affair (1926) fits snugly into this cycle. The action starts with Inspector Killian and his assistant Carney ushering the suspects into the Rankin family library. The rakish Jack Donovan has been murdered at a birthday dinner. The circumstances are odd: To demonstrate a glowing ring Donovan wears, the lights were turned out. In the darkness, he was stabbed with a carving knife.
Most of those at the table have good reason to kill Donovan. He was having affairs with married women and had an eye on Rankin’s daughter Jean, whom David hoped to marry. The first act is centered on exposition that emerges from Killian’s questioning of the guests. One, Horace Carter, comes forward to declare he knows who the killer is, because the victim’s missing ring was slipped into his pocket. Killian doubts that the ring could have been visible, and so the lights are switched off a second time as a test. Bad idea: When the lights come back on, Horace has been stabbed with the same knife. Score one for law and order. Later one character will shoot another as Killian looks on.
The next two acts expose more motives, lay false trails (David has brought a gun to dinner and has blood on his cuff), and string out physical clues, including a fake ring and some threatening letters to Donovan. In frustration, Killian leaves the suspects to pool their information, in hopes that they’ll discover the killer. Once more the lights are put out to allow the culprit to replace the ring and a missing letter. The killer is revealed, and there’s a struggle in semidarkness. Killian and his men burst in to seize the guilty party.
Among all this claptrap, the blackout gimmick is worked very hard. Bayard Veiller’s Thirteenth Chair had staged a stabbing in a dimly-lit séance, and Davis himself had let the electricity fail in The Haunted House (1924). The blackout-covering-a-killing would be reused in The Spider (1927). The Donovan Affair justifies the device through the luminous ring. In plot terms, it’s another red herring, but it plausibly motivates darkening the stage during the murders. The effect seems to have come off.
The audience found itself frequently strung almost to the endurance limit, and now and then a voice from the crowd would beg a relentless actor not to turn out those lights again. For it was generally in the darkness that stabbings, shootings and assorted mayhem would stalk through the play.
It must have been riveting to see the ring (a green-tinted flashlight) floating around the darkness. Capra’s film is at pains to reproduce this signature effect, but with some differences.
The screenplay subtracts some of the characters and adds a sinister caretaker and Porter, a gambler to whom Donovan owes money. The plot begins well before the crime, with an opening that establishes Porter among his cronies. A second scene shows Donovan brushing off Mary, the Rankin family maid; in the play their liaison is revealed very late. Then guests gather for the birthday dinner, and after some salon byplay they sit down to eat, with Donovan demonstrating the power of the cat’s-eye ring. In the darkness he’s murdered.
A title, “One hour later,” introduces the main stretch of the film, which corresponds more closely with the play’s action. Inspector Killian arrives and sizes up the suspects. Most of the play’s clues emerge, with suspicion scattered around freely.
Like the play, the film is built around blackouts showing off the wandering ring, but now these are motivated as reenactments of the crime. Killian puts Porter in Donovan’s seat, and in the darkness he becomes the second victim. After more intrigue, Killian demands another go-round, and this time the killer is exposed.
The film’s blackout scenes run 36 seconds, 42 seconds, and about 100 seconds for the climax. This last scene varies the treatment by showing some silhouettes.
These scenes feel surprisingly protracted: 30 seconds is a long time on the screen. Likely there would have been dialogue and sound effects, as there are in the play’s blackout intervals.
Here’s the paragraph with the spoiler. In both play and film, the butler Nelson is revealed as the murderer. (At this point in history, having hired help commit the crime wasn’t yet out of bounds.) Nelson is in love with Mary, whom Donovan has seduced. The film hints at this in a way that the play doesn’t. Mary is introduced early as Donovan’s mistress, Nelson seems to have eyes for her, and during a test to see if any woman’s handwriting matches that on a telltale letter, he lingers solicitously over Mary.
Variety praised Capra’s film as well-constructed and surprisingly funny, chiefly because of a whimsical old couple added to the ensemble. Capra claims that The Donovan Affair taught him to add doses of comedy as much as possible: “Comedy in all things.” Actually, though, Owen Davis claimed that he was teasing the genre in his original. “The Donovan Affair was, naturally, a success, although I am, I think, the only one who knows that it was as deliberate a burlesque as The Haunted House had been.”
Opening up the proscenium
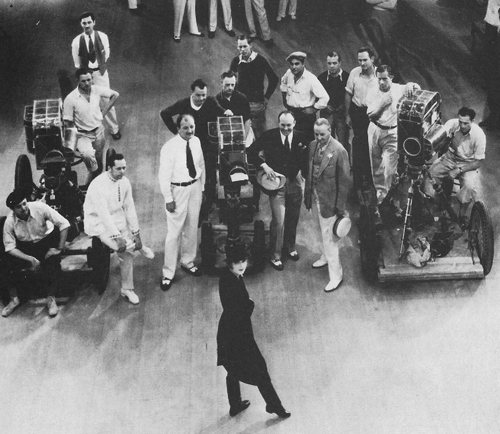
A posed shot of the multiple-camera teams for Sunny (1930).
In his autobiography Capra regarded The Donovan Affair as a turning point in his career. While complaining about the constraints on sound cameras, he regarded the film as “the beginning of a true understanding of the skills of my craft: how to make the mechanics—lighting, microphone, camera—serve and be subject to the actors.” To my way of thinking, what he did within the confines of early talkies was inject some of the pictorial fluidity and impact on display in the silent cinema. The Donovan Affair is a lot less pictorially stilted than most of the 1929 American films I’ve seen.
Like many early talkies, the film relies heavily on multiple-camera shooting of the sort still used in TV comedies and soap operas. For this film, according to Joseph McBride, five cameras were used. The range of coverage allowed for continuous sound recording while preserving the option of analytical editing. While one camera recorded a wide framing, a long lens could scoop out a closer view without moving that camera into the space.
So when Mary calls on Donovan in the second scene, we can see her arrive in a long-lens mid-shot, then we can see Donovan’s reaction in a long shot. Mary comes forward and a third camera picks them up in a two-shot.
The technique permits smooth matches on action, as when Mary turns her head in a medium shot and leaves in the background of the master shot.
But it’s also clear that multiple-camera shooting allowed for alternative takes. The mismatches we can detect across some cuts suggest this. During continuous dialogue, Lydia’s arm is up in one shot and down in the next.
Capra claims that Columbia allowed him to print only one take, but he got around this by not slating his shots. He simply let the camera run and replayed the action, sometimes several times. This allowed actors to improve their performances in a fluid process. CApra wound up with only one take number, out of which he could pick the take he wanted. This tactic might explain disparities of figure position.
Multiple-camera shooting could yield some awkwardness, especially when shot scale wasn’t adjusted. Here’s an interesting example showing Jean’s quarrel with her stepmother Lydia. As Lydia crosses in front of Jean, the match cut on my second frame below creates a little bump by not sufficiently changing the angle and figure size. The slight pan following the women accentuates the disparity.
A jerky cut like this would be very rare later in the 1930s, as it is today. As recording technology improved, Hollywood would move back to single-camera shooting for most scenes, and shot scales were more exactly planned and executed.
If multiple-camera shooting feels a bit theatrical, it’s because it surrenders a degree of freedom in camera placement. We always seem to be watching things from outside a proscenium, even when items are enlarged. I think that the early talkies’ habit of starting with a flamboyant camera movement, as in Sunny Side Up (1929) and The Broadway Melody (1929), was a way of saying, “Don’t worry, this is still cinema.” Capra follows this habit by beginning on a close view of a pile of Donovan’s IOUs and then tracking back very far to set his first scene among the gamblers.
The film’s second “act” starts with a comparable flourish. A long shot of the library shows Carney bustling toward the offscreen front door in the background. The camera tracks in and waits for him to return.
Presumably we would be hearing him greeting Inspector Killian offscreen, but the frame is empty for about fifteen seconds. Then Carney and Killian stride in, and the camera pulls back to something like the initial master framing.
Another way to add fluidity was to insert shots that don’t require lip synchronization. Cutaways to objects or reaction shots could be inserted into the dialogue-laden stretches. For example, Nelson and Mary peer into the library to watch the guests, and Ted Tetzlaff’s cameras give us two shots from positions different than we’ve seen so far.
More boldly, after Donovan is killed, Capra gives us not only a shot of Mrs. Lindsey wailing but brief close-ups of Jean’s and Lydia’s reactions.
These two shots are only 32 and 36 frames respectively, harking back to the punchy montage of silent cinema, and they stand out by contrast with the extreme long-shots around them.
Similarly, you have to think of all those subjective POV shots in 1920s silent films when we watch Killian survey the suspects. As he talks with Rankin, he scans them right to left in a series of POV shots, including one longish, zigzag pan. Here are some extracts.
The end of the pan shot shows Lydia shifting her gaze from Killian to her husband, off left. We then cut to her husband and Killian, who’s just finishing his scanning of the suspects. Her gesture cast suspicion on her; after all, she’s hiding her affair with the dead man.
Most ambitious of all is Capra’s handling of the dinner table situation. Smoothly integrating singles and two shots of characters around a table was one of the triumphs of classical Hollywood style in the late 1910s. Matching character positions and eyelines from shot to shot became part of every director’s craft. Capra adapts talking pictures to these constraints in a flow of shots that include dialogue and keep all characters’ relationships clear and consistent while picking out important details and reactions.
For example, when Donovan talks with Mrs. Lindsey, we get her husband’s glare as he watches from across the table.
Here the proscenium is broken. Instead of covering the action from outside, now the camera penetrates space and can take up a variety of angles among the characters.
This camera ubiquity can be exploited to dramatize the murder weapon. A master shot shows the dinner party, with Rankin at the head of the table and his wife Lydia at the foot, turned from us.
Mary brings the roast and the carving knife to the table. Cut in to Mary lifting the knife, which glints.
Donovan flinches as the reflection dazzles him. Cut to Lydia, from the foot of the table, saying, “Mary,” and looking down the table to where Mary would be.
We’re in a sort of triangular space—Mary-Donovan-Lydia—and the relationships are reaffirmed when a return to the earlier setup shows Mary responding to Lydia’s look.
The dialogue continues within these shots. Capra’s changing setups must have required quite a bit of effort in 1929, what with cameras in booths and the pressures to stick with continuous multi-camera takes. But, reviving silent-film table coverage, he gives us what would be one conventional way to handle such an action in the 1930s.
There are other felicities in the film, but I think I’ve said enough to indicate how it’s an enlightening transitional work. Tied to the multi-camera technique for most of its running time, Capra breaks away for significant stretches. He found a way to give camerawork and cutting some moments of the sort of fluidity that would pervade Hollywood in the 1930s.
Capra wasn’t the only major director to cut his talkie teeth on adaptations of stage thrillers. Hawks made The Criminal Code (1931) from a 1929 prison drama, while Hitchcock based Blackmail (1929) and Number Seventeen (1932) on popular plays from 1928 and 1925. Film mysteries would change in the 1930s, with sophisticated detective comedies like The Thin Man and adaptations of the adventures of Charlie Chan and Perry Mason.
Creaky though it might seem in later decades, the manor-house murder would remain a reference point. On stage its premises were given a new twist in Christie’s The Mousetrap (1952), enhanced with social criticism in J.B. Priestley’s An Inspector Calls (1945), and parodied in Tom Stoppard’s The Real Inspector Hound (1962). You can argue that the provincial procedurals with a British accent (Wexford, Midsomer Murders, Inspector Morse, and so on) grow out of the spillikins-in-the-parlor tradition, but shifting the viewpoint to that of the detectives.
Thanks to Lynanne Schweighofer, Zoran Sinobad, and Mike Mashon of the Library of Congress and Jim Healy, Mike King, and Roch Gersbach of our Cinematheque for arranging my viewing of The Donovan Affair. Thanks also to Ben Brewster for discussions of the film and 1920s theatrical practice.
A fleshed-out synopsis of the film was published at the time.
Bruce Goldstein had the excellent idea of adding live performers to screenings of The Donovan Affair. He details his efforts to find the original dialogue in this TCM article.
Ray Collins fans may be interested to know that in the stage version he played the butler–described in the script as “really the only acting part in the play.”
My quotation about rapt audiences for the stage version comes from the review, “’The Donovan Affair’ Thrills in Mystery,” The New York Times (31 August 1926), 15. Quotations from Capra are from the first edition of his autobiography, The Name above the Title (New York: Macmillan, 1971), 105. Joseph McBride has written the most comprehensive and probing biography, Frank Capra: The Catastrophe of Success (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1992).
In his autobiography Owen Davis remarks that the failure of The Haunted House, a “burlesque mystery melodrama” impelled him to write The Donovan Affair. That was a play that “could hardly be accused of not being mysterious enough, and one that actually dripped with blood and missed no trick at all of the tried and true tricks of mystery story writing from Gaboriau through Poe and Doyle and Anna Katherine Green and Mrs. Rinehart, even taking in the tricks of the present, and very skillful, crop of hard-boiled detective story writers who were at that time printing their first compositions on a slate in some primary school.” See My First Fifty Years in the Theatre (Boston: Baker, 1950), 94-95.
My exploration of theatrical thrillers has been aided by Amnon Kabatchnik’s two excellent reference books: Blood on the Stage: Milestone Plays of Crime, Mystery, and Detection: An Annotated Repertoire, 1900-1925 (Scarecrow, 2008) and Blood on the Stage, 1925-1950: Milestone Plays of Crime, Mystery, and Detection: An Annotated Repertoire (Scarecrow, 2010).
As ever in such matters, Mike Grost’s encyclopedic website offers background information and critical discussion of authors, periods, and conventions.
On multiple-camera shooting in early sound film, see Chapter 23 of The Classical Hollywood Cinema: Film Style and Mode of Production to 1960. A good primary source is Karl Struss’s article “Photographing with Multiple Cameras,” TSMPE XIII, 38 (1929), 477-478.
The Donovan Affair (1929).
Who got played? A guest post by Jeff Smith on THE PLAYER
The Player (1992).
Jeff Smith, our collaborator on Film Art: An Introduction just recorded an installment of our Observations on Film Art series for the Criterion Channel on FilmStruck. Here’s a supplement to that. –DB
In my installment, focusing on genre play in The Player, I discuss Robert Altman’s film in relation to two important traditions in Hollywood cinema: crime thrillers and films about filmmaking. As anyone who knows Altman’s other films would expect, The Player toys with the conventions of both genres in a number of different ways.
As I note in the video, The Player was received as something of a comeback film for Altman. It augured a resurgence in the director’s career that ultimately produced such late masterpieces as Short Cuts and Gosford Park.
Today, I sketch out some additional ideas about The Player’s use of genre conventions. I hope to shed light on some other connections to the crime thriller that I didn’t discuss in the video. I also hope to show just how unusual the film is in this context. Spoilers ahead, not only for The Player but for the novel and film of The Ax.
Will the real Griffin Mill please stand up?
In Reinventing Hollywood, David notes that there are usually four sorts of characters involved in a crime thriller plot: victims, lawbreakers, forces of justice, and more or less innocent bystanders. Filmmakers customarily organize the film’s narration around one or more of these character roles. Typically, a cascade of further choices flows from this initial decision about whose perspective forms the focal point of the story.
In The Player, much of the narration is restricted to the knowledge of the protagonist, Griffin Mill. The film includes a few scenes where Griffin is not present, like the one where the studio’s management awaits his arrival at a meeting. That, in itself, is not unusual. Many thrillers, like Chinatown or The Ghost Writer, employ similar tactics. What is slightly unusual is the fact Griffin takes on two of the typical character roles in the crime thriller as both victim and lawbreaker.
Griffin is a suit, and as a studio functionary he doesn’t immediately engender audience sympathy. Our first glimpse of Griffin shows him listening to pitch sessions. His questions to the people proposing new film projects are glib and capricious, representing the worst aspects of Hollywood commercialism.
Yet The Player does marshall some sympathy for Griffin as the victim of a stalker. Every time Griffin finds a postcard in his mail or on his car, it reminds us that he might be in mortal danger. After the stalker plants a venomous rattlesnake in Griffin’s passenger seat, we can’t believe the threats are empty.
Any sympathy that Griffin garners as a result of this psychological warfare is mollified, though, when the victim becomes victimizer. As Griffin later explains to June, his job is to tell people “no” more than a thousand times each year. Griffin believes that one of these rejections is the reason for the threatening postcards he receives. But he tragically miscalculates in targeting aspiring screenwriter David Kahane as the likely suspect.
Griffin contrives a meeting with Kahane at a Pasadena movie theater, and having bumped into him, tries to make amends. Yet Kahane recognizes that he is being pimped. This leads to a shouting match in a parking lot with Kahane threatening to ruin Griffin’s reputation. And when Kahane accidentally knocks Griffin over with his car door, Griffin reacts with rage, grabbing the screenwriter’s head and banging it repeatedly against the lot’s concrete surface. Although it seems clear that Griffin was acting on impulse, he’s nonetheless crossed a line that separates victims from perpetrators.
More importantly, Griffin’s violent action complicates the viewer’s allegiance to him. Altman establishes a dramatic context in which the motivations for Griffin’s crime seem completely understandable. Yet whatever sympathies viewers might have for Griffin are muddled by his creepy romantic interest in Kahane’s girlfriend; his cruel treatment of Bonnie, his current partner; and the general smarminess he exudes as a successful but shallow executive. Crime thrillers often ask audiences to sympathize with heels. There’s nothing that Griffin does that is inherently evil, but there’s nothing to really like. It’s less about his crime and more about his slime.
Griffin’s passage from victim to lawbreaker also alters the typical thriller plot. At the start of the film, Griffin himself functions as the investigative agent, trying desperately to figure out who is threatening him. Once Griffin becomes a suspect himself, though, that line of action halts, and the Pasadena police’s investigation of Kahane’s death springs up in its place.
This shift in the direction of the plot doesn’t really change the film’s pattern of narration. We remain as ignorant of the police’s activities as Griffin is. What does change are the stakes of the narrative. Instead of eliciting curiosity and suspense about Griffin’s stalker, we now wonder whether he’ll ever be brought to justice for Kahane’s death. Despite its strong connections and frequent allusions to crime fiction, The Player is not so much a whodunit as it is a will-he-get-away-with-it.
They smile in your face, all the time they want to take your place….
Besides blurring the boundaries between Griffin’s role as both victim and lawbreaker, The Player falls into a specific subgenre of crime fiction: the corporate thriller. Since, the corporate thriller is mostly defined by its setting, it blends pretty easily with the typical thriller plots and characters.
Like the spy thriller, the corporate thriller can focus on protagonists engaged in industrial espionage, as we see in Duplicity, Demon Lover, or Paycheck. Christopher Nolan’s Inception blends the plot mechanics of these corporate espionage thrillers with science fiction tropes to provide a narrative frame, but then embeds elements of the heist film within it.
Like the political thriller, the corporate thriller might also focus on the backroom deals and machinations that enable the protagonist to move up the company ladder. A film like Disclosure is a paradigm case. But even romantic comedies or prestige dramas can borrow elements from it. (Think Working Girl and Glengarry Glen Ross.)
More commonly, though, corporate thrillers feature elements drawn from the crime thriller. The roots of this approach to the genre stretch back a long way and can be found in both literary and cinematic antecedents. Some plots, for example, follow investigations that expose corporate malfeasance. Others focus on murders committed within a corporate environment, as in Dorothy Sayers’s novel Murder Must Advertise and Kenneth Fearing’s novel (and film) The Big Clock and in more modern instances like Michael Crichton’s Rising Sun and John Grisham’s The Firm. Other corporate crime thrillers, like Bret Easton Ellis’s American Psycho (below) and Cindy Sherman’s Office Killer, involve serial murders in white-collar environments.
The corporate crime thriller enables writers and filmmakers to explore thematic parallels between the acts of brutality and violence committed by individuals and the cutthroat tactics employed by business institutions. The plots of many gangster films center on rival mobs battling for competitive dominance in black market trades. Such conflicts often seem like a logical extension of the laissez-faire principles that undergird capitalism. Corporate crime thrillers tread similar thematic territory. They sometimes suggest that the personality traits that make for good business executives and titans of industry are the same ones that produce sociopaths and serial killers.
The Player presents the familiar corporate-thriller rivalry, as Griffin works behind the scenes to outmaneuver Larry Levy. For example, Griffin momentarily ponders using Larry’s admission that he attends Alcoholics Anonymous meetings as a way of embarrassing him within the company. Larry quickly undercuts this strategy, though, when he states that he just goes to the meetings because they are a great place to network.
Even more telling is Griffin’s efforts to saddle Larry with a loser project, Habeas Corpus. Midway through The Player, Griffin makes a deal with Andy Civella and Tom Oakley at a Los Angeles restaurant. The next day, he convinces his boss to greenlight the project with Larry as producer, knowing that Tom will likely prove difficult to work with and that his plan to use unknown actors has disaster written all over it. Larry, though, has the last laugh when we get a sneak peek of Habeas Corpus at film’s end. Not only does it have big stars in Julia Roberts and Bruce Willis. It also has the kind of happy ending that the pretentious Tom claimed was too Hollywood when he pitched the project. It turns out Tom cares more about the results of preview screenings than he does the purity of his artistic vision.
Not surprisingly, Altman doesn’t give us a wholly straightforward version of the corporate thriller. In a reflexive and ironic touch, Griffin’s successful ascent to studio boss seems to be secured by the same mysterious stalker who’d been taunting him at the start of the film. In a phone call, the stalker pitches Griffin the plot of the film we’ve just been watching, using his knowledge of Griffin’s crime to leverage his project into development. Here we see Altman slightly reframing the genre’s thesis about the relationship between crime and business. Griffin’s pact with his blackmailing stalker is simply a mildly illicit version of the sorts of quid pro quo arrangements upon which thousands of business deals are made.
If Griffin’s efforts to forestall a rival evoke the political thriller, then his killing of screenwriter David Kahane connects The Player to the corporate crime thriller. Once again, Altman deviates from some of the conventions. The crime doesn’t take place inside a corporate setting, as in Rising Sun and Murder Must Advertise. Griffin kills Kahane in the very public space of a Pasadena parking lot, with film noir overtones.
Similarly, Griffin’s victim is not a colleague, co-worker, subordinate, or client. Rather, Kahane is someone with whom Griffin has had minimal contact, a name plucked almost randomly from a directory of screenwriters in order to jog Griffin’s memory. Consequently, Griffin’s motives for confronting Kahane seem quite different from the culprits in other corporate crime thrillers. More often than not, the murderers in these other stories fear job loss or try to silence others in an effort to cover up some smaller crime or bungled action. Griffin’s actions with Kahane spring from fear about threats to his physical well-being, not from threats to his continued employment. (The latter is Larry’s role.)
 Some of The Player’s deviations from more conventional corporate crime thrillers come into relief if we compare it to Donald Westlake’s novel The Ax, a purer example of the genre. The Ax tells the story of Burke Devore, a production line manager recently downsized out of his job at a paper company. Still unemployed after eighteen months, Burke creates a phony job advertisement, and then begins to kill off the seven applicants he believes have the same qualifications he does. His plan is to eliminate all of the other unemployed middle managers in the paper business so that his resumé will land at the top of the pile when a new factory opens in his area.
Some of The Player’s deviations from more conventional corporate crime thrillers come into relief if we compare it to Donald Westlake’s novel The Ax, a purer example of the genre. The Ax tells the story of Burke Devore, a production line manager recently downsized out of his job at a paper company. Still unemployed after eighteen months, Burke creates a phony job advertisement, and then begins to kill off the seven applicants he believes have the same qualifications he does. His plan is to eliminate all of the other unemployed middle managers in the paper business so that his resumé will land at the top of the pile when a new factory opens in his area.
Like Altman, Westlake has some fun with his central conceit. Just as The Player includes faux film clips and rushes as a means of satirizing Hollywood production practices, The Ax incorporates fictional resumes that tweak jobseekers’ business-speak. What makes Westlake’s social criticism in The Ax so resonant, though, is the utter banality of Burke’s ambitions. He doesn’t aspire to the garish lifestyle we see displayed by Tony Montana or Jordan Belfort in Scarface and The Wolf of Wall Street respectively. Instead Burke just wants to return to his modest middle-class lifestyle and to the dignity that a decent job afforded him. Serial murder just seems like the simplest way to achieve that.
As this comparison suggests, one of the things that makes The Player somewhat unusual as a corporate crime thriller is its play with character motivation and point of view. Facing threats and intimidation, Griffin looks more like the target of a crime than a perpetrator. In corporate thrillers, the lawbreaker is more likely to be somewhere in the middle of the corporate ladder, like Burke, than at the top of it. Moreover, although his actions are motivated by a strange combination of both vanity and insecurity, Griffin more or less stumbles into the crime he commits rather than coolly plotting it the way Burke does.
Despite these differences, The Player and The Ax share an important feature that markedly deviates from the crime thriller as a whole. Both Griffin and Burke get away with it. The plots of most crime thrillers resolve in ways that balance the scales of justice. The bad guys are usually either arrested or killed after climactic confrontations with law enforcement. But this doesn’t always happen. Burke, Patrick Bateman in American Psycho, and Dorine in Office Killer escape punishment. Even though Jordan Belfort is arrested in The Wolf of Wall Street, he gets a slap on the wrist for his crimes.
Perhaps this aspect of the corporate crime thriller reflects the cynicism and amorality that pervades the genre. After all, if your belief is that most corporations get away with murder in a figurative sense, then it’s not hard to accept this idea when it occurs in fictional contexts in a literal sense.
Still, in the case of The Player, the Pasadena police’s failure to prove their case against Griffin Mill may reflect a meshing of both authorial and generic tendencies. When Griffin embraces June in the stylized happy ending of The Player, it quite deliberately parallels the tacked on happy ending of Habeas Corpus we’ve seen just moments earlier. The dialogue Griffin exchanges with June amplifies the similarity between these scenes. When June asks, “What took you so long?”, Griffin responds, “Traffic was a bitch.” These are the exact same lines exchanged by Julia Roberts and Bruce Willis in Habeas Corpus. By allowing Griffin to get away with it, The Player’s “up” ending sharpens Altman’s critique of Hollywood convention, and allows him to subvert the kinds of mainstream genre filmmaking he’s long detested.
Both allusive and elusive: Comparing The Player to Hollywood Story
One of the other topics I discuss in my video essay on The Player is the way the film pays homage to various aspects of Hollywood tradition. Much of this is bound up with its satire of commercial filmmaking. But it also strengthens the film’s relation to the crime thriller. Throughout The Player, Altman makes reference to Hollywood’s past in multiple ways. Celebrity cameos, film posters, and production stills populate the mise-en-scene. The characters also frequently mention older film titles in dialogue.
Perhaps the most interesting allusion in The Player involves a poster of Hollywood Story that hangs in Griffin’s office. The latter is a 1951 film noir directed by William Castle, who later became famous for his use of outrageous gimmicks in the production and promotion of horror films. For The Tingler, Castle supervised the installation of devices that would vibrate theater seats, anticipating today’s 4DX Theater Experience in places like Los Angeles, New York, Seattle, and Orlando.
Hollywood Story dramatizes the efforts of film producer Larry O’Brien to develop a project around the unsolved murder of silent film director Franklin Ferrara. O’Brien hires one of Ferrara’s old scenarists to write the script. He also develops a close relationship with Sally Rousseau, the daughter of one of Ferrara’s biggest stars. Once the project is announced, O’Brien finds himself the target of an assassin’s bullet. He surmises that his assailant is trying to prevent the case from being reopened. And as Sally reminds O’Brien, he doesn’t have an ending to his movie is he can’t determine the killer’s identity. O’Brien, thus, sets out to solve the crime, bringing closure to one of the biggest scandals in Hollywood’s history. Hollywood Story offers an even better synthesis of The Player’s mixture of industry exposé and crime film story beats. O’Brien’s lone wolf investigation is treated as being a necessary stage of project development.
If the Franklin Ferrara story sounds vaguely familiar to you, well….it should. Hollywood Story offers a fictionalized account of the unsolved murder of William Desmond Taylor, who was shot to death in his bungalow in the wee hours of a February night in 1922. (David blogged about the crime here.) The subsequent investigation of Taylor’s death ensnared some of the industry’s biggest stars of the period. Mabel Normand’s reputation was tainted by her association with Taylor and by reports of drug use. She took a brief hiatus from filmmaking because of the scandal, but never completely recovered from it. Normand later died of tuberculosis in 1930 at the tender age of 37.
As a fictionalized account of a notorious unsolved crime, Hollywood Story anticipates more modern thrillers that provide speculative solutions to real-life murders. Zodiac and The Black Dahlia are prime examples, as are any number of Jack the Ripper films. Hollywood Story’s approach was not unprecedented. James M. Cain based Double Indemnity on the Ruth Snyder case that was fodder for New York tabloids in the late 1920s. That said, Taylor’s death lingered for decades in popular memory in a way that the Snyder case did not.
What are we to make of The Player’s citation of Hollywood Story? On the one hand, viewers might well notice the almost immediate parallel of our “film execs in jeopardy” storylines. Just as Griffin is stalked by an unknown assailant, so, too, is Larry the target of a shadowy aggressor. Moreover, Hollywood Story, along with Sunset Boulevard, might well be an inspiration of one of The Player’s most interesting features: its intermingling of real life stars with fictional characters. Hollywood Story includes cameos by Joel McCrea and several noted performers of the silent era, such as William Farnum, Francis X. Bushman, and Betty Blythe (below). The Player pushes this aspect of Hollywood Story to extremes, containing plentiful cameos by Cher, Jack Lemmon, Burt Reynolds, Lily Tomlin, Susan Sarandon, and other A-listers.
In several other respects, though, The Player seems like an inversion of Hollywood Story with Griffin emerging as a more venal counterpart to the latter’s crusading producer, Larry. In Hollywood Story, Larry’s investigation actually produces results. This strongly contrasts with Griffin’s guesswork, which, as the result of a tragic mistake, leads to David Kahane’s death in a Pasadena parking lot. In Hollywood Story, Larry’s blossoming romance with Sally furnishes the standard double plotline commonly found in classical cinema. In The Player, though, Griffin’s interest in June seems genuinely sleazy. It also exacerbates the Pasadena police’s doubts about Griffin’s alibi, making him their prime suspect. Finally, the revelation of screenwriter Vincent St. Clair as Franklin Ferrara’s killer provides closure both to Larry’s script and to Hollywood Story itself. In contrast, none of the crimes presented in The Player are really solved. Griffin is blackmailed into greenlighting a project during the film’s epilogue, but the audience never learns the identity of the mysterious stalker. Similarly, although the Pasadena police believe that Griffin is guilty of murder, the botched lineup ensures that he will go free and that David Kahane’s death will remain an unsolved crime. In an odd way, The Player returns to the narrative roots of Hollywood Story. The fate of Kahane, our aspiring screenwriter, seems destined to mirror that of poor William Desmond Taylor, our successful silent film director.
A thriller with no thrills
I’ve sketched out a number of different ways in which The Player relates to the basic conventions of the crime thriller, but all of this is ultimately, in the parlance of the genre, a red herring. This is because The Player is that rare bird: a crime film that engenders relatively little curiosity about its solution and even less suspense about the fate of its protagonist.
This is largely because Robert Altman mostly uses crime film conventions as scaffolding for the things that really interest him: quirky characters, digressive dialogue, and a loose, improvisatory feel to the film’s performances. At its heart, The Player is a comedy that draws upon crime film conventions in much the way Altman’s adaptation of Raymond Chandler’s The Long Goodbye does.
Compare, for example, each film’s tweaking of the genre’s standard interrogation scenes. In The Long Goodbye, Detective Farmer’s tough questioning of Philip Marlowe is punctured by the latter’s goofy responses. At one point, Marlowe uses the ink from his fingerprinting procedure like it was the “eye black” used by an athlete. Later, he smears the ink all over his face and sings “Swanee” in a mocking homage to Al Jolson in blackface. Similarly, in The Player, the Pasadena police’s interrogation of Griffin is disrupted by Detective Avery’s disarming exchange with her partner about tampons, her mangled pronunciation of “Gudmundstottir,” and her dialogue with Paul about Todd Browning’s Freaks.
The Player has many ingredients characteristic of crime films: a dead body, an investigation, a shady suspect, and a campaign of stalking and extortion. Yet, by the time Altman’s film reaches its ironic and deeply reflexive conclusion, viewers might well conclude that they are the ones who just got played.
Thanks as usual to Peter Becker, Kim Hendrickson, Grant Delin, and all their Criterion colleagues. A list of our Observations on Film Art series is here.
For more on Robert Altman’s career, see Patrick McGilligan’s excellent biography, Robert Altman: Jumping Off the Cliff. There are also several books featuring interviews with the iconoclastic director. These include David Sterritt’s Robert Altman: Interviews, Mitchell Zuckoff’s Robert Altman: The Oral Biography, and David Thompson’s Altman on Altman.
Those interested in learning more about crime fiction should consult Martin Rubin’s Thrillers, Charles Derry’s The Suspense Thriller: Films in the Shadow of Alfred Hitchcock, John Scaggs’s Crime Fiction, Richard Bradford’s Crime Fiction: A Very Short Introduction, and Martin Priestman’s The Cambridge Companion to Crime Fiction.
Hollywood Story (1951).
HIS GIRL FRIDAY never goes away (good thing, too)
DB here:
FilmStruck and The Criterion Channel are running His Girl Friday this month, in the fine restoration that Criterion released on Blu-ray last year. Accompanying this rerun is a bevy of bonus materials, including the restored Front Page and a video essay I worked on. There’s a larger thematic bundle on the streaming service as well: “Howard Hawks and the Art of Screwball Comedy,” featuring three other films as well as an 11-minute extra on “The Hawksian Approach to Screwball Comedy” by Taylor Ramos and Tony Zhou.
For more on His Girl Friday, you can check two of our blog entries, one on how His Girl Friday got into the canon, and a second with analysis and historical background based on the initial Criterion release.
Now, if you’ll excuse me, I’ll go watch it again.
Thanks, as usual, to the Criterion folks–Kim Hendrickson, Grant Delin, and Peter Becker–along with Erik Gunneson and his able staff, all of whom worked on the video essay.
His Girl Friday (1940).
Everything new is old again: Stories from 2017
Silence.
DB here:
This is a sequel to an entry posted a year ago. Like many sequels, it replays the ending of the original.
I don’t want to leave the impression that as I’m watching new release a little homunculus historian in my skull is busily plotting schema and revision, norm and variation. I get as soaked up in a movie as anybody, I think. But at moments during the screening, I do try to notice the film’s narrative strategies. Later, when I’m thinking about the movie and going over my notes (yes, I take notes), affinities strike me. By studying film history, most recently Hollywood in the 40s, I try to see continuities and changes in storytelling strategies. These make me appreciate how our filmmakers creatively rework conventions that have rich, surprising histories.
Parts of those histories are traced in the book that came out in the fall, Reinventing Hollywood. Some of my blog entries have already served to back up one point I tried to make there: that contemporary filmmakers are still relying on the storytelling techniques that crystallized in American studio films of the 1940s.
Relying on here means not only utilizing but also, sometimes, recasting. In keeping with earlier entries (including one from the year before last), I want to explore some films from 2017. These show that the process of schema and revision creates a tradition. Hollywood is constantly recycling, and sometimes revitalizing, Hollywood.
Of course here be spoilers.
Back to basics
The Big Sick.
The US films I’ll be considering all adhere to canons of classical Hollywood construction. Some of these are laid out in the third chapter of Reinventing.
Classically constructed films have goal-oriented protagonists who encounter obstacles, usually in the form of other characters. The goals are often double, involving both romantic fulfillment and achievement in some other sphere. (Somewhere Godard says that love and work are the only things that matter. Hollywood often thinks so too.) Alternatively, the goal might be prodding someone else to action (Three Billboards outside Ebbing, Missouri). Often there’s a clash between the goals, as when work tugs the protagonist away from love (La La Land).
The plot is typically laid out in large-scale parts. A setup is followed by a complicating action that redefines character goals. In Downsizing, once Paul has gotten small, he has to reconceive his goals in the face of his wife’s last-minute defection from their plan. There follows a development section that delays goal achievement through characterization episodes, backstory, subplots, parallels, setbacks, digressions, twists, and new obstacles. That marvelous slab of show-biz schmaltz, The Greatest Showman, relies for its development on a potential love triangle and a secondary couple’s romantic intrigue.
There follows a deadline-driven climax that resolves the action and an epilogue (sometimes called the tag) that celebrates the stable state achieved and perhaps wraps up a motif or two. The Greatest Showman presents Barnum’s success in creating a genuine circus and reconciling with his family. The tag shows a big production number, with the subplot resolved (Carlyle embracing Anne) and the motif of swirling points of light—initiated in Barnum’s spinning Dreams gadget—washing over the final spectacle and his daughter’s ballet performance.
Classical narration—what’s usually called point of view—typically attaches us to the main characters. But not absolutely: we’re usually given access to things they don’t know, mostly for the sake of arousing curiosity and suspense. And throughout, the film is bound together through recurring motifs that reveal character (and character change) or significant plot information. Think of the roles Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 2 assigns to “Brandy, You’re a Fine Girl,” Pac-Man, David Hasselhoff, and that “unspoken thing.”
Or take The Big Sick, a semi-serious romantic comedy. Kumail’s initial goal is success in standup comedy, but he also falls in love with Emily. His Pakistani-American family constitutes the main antagonist, as his mother and father want him to go to law school and submit to an arranged marriage. He hasn’t told his family about Emily, which precipitates the couple’s big quarrel: “I can’t lose my family.” Kumail’s goal shifts when Emily is stricken by a mysterious disease. In the development section , as she lies in a coma, he gets to know her parents, and a tense sympathy develops between them. The crisis comes when Kumail confesses his true goals to his parents, they disown him, and Emily’s disease hits a life-threatening phase.
In the climax portion, Emily revives and breaks off with him, his parents grudgingly accept his move to New York, and he mounts a somewhat successful one-man show there. The film is tightly tied to Kumail’s range of knowledge, so we’re surprised when he is—as when Emily’s parents decide to move her to another hospital, and when Emily pops up in his New York audience, ready to reconcile with him.
The Big Sick exploits many comic motifs: the parade of would-be fiancées Kumail’s mother invites to dinner, the photos he keeps of them (which ignite Emily’s jealousy), the repeated sit-downs he has with his family, the dumb catchphrases deployed by other comics, and especially Emily’s “Woo-hoo!” heckling, which eventually attests to the rekindling of their love.
The power of classical plotting is shown in its ability to spotlight a Pakistani-American protagonist, an Islamic family demanding that a son adhere to tradition, and the pathos of parents facing the death of a daughter. But that ability to flexibly absorb new subjects and themes and emotional registers has kept the classical template going for about a century.
Time travel
Wonder Woman.
One of the hallmarks of Forties cinema, I argue in Reinventing’s second chapter, is a eagerness to explore what flashbacks can do. Flashbacks were already well-established, but a more pervasive acceptance of nonlinear storytelling, so familiar to us now, became firmly part of Hollywood sound cinema in this period.
One-off flashbacks are so common now we don’t particularly notice them. In The Big Sick, when Kumail visits Emily’s apartment with her parents, he peeks into her closet, and we get glimpses of her wearing the outfits earlier in the film. In this case, flashbacks function as memories. At the climax of Guardians 2, Quill flashes back to moments of listening to music with his mother. Similarly, in Get Out, Chris recalls his childhood TV viewing and, at the climax, he remembers earlier moments at the Armitage garden party when he asks, “Why black people?”
Flashbacks usually aren’t pure representations of memory, though. They often include information that the character doesn’t or couldn’t know. In fact many flashbacks are addressed simply to us, coming “from the film” rather than from a character’s mind. These may remind us of things already seen, or fill in gaps, or plant hints about things that will develop.
So, for instance, in Logan Lucky, when Logan says, “I know how to move the money,” we get a flashback to him studying the pneumatic pipes that feature in the heist plan.
He’s not necessarily recalling the moment; the filmic narration seems merely to be tipping us the wink. At the climax, other “external” flashbacks plug gaps we didn’t notice earlier. These reveal some aspects of the heist we weren’t aware of, such as the extra bags of money carried off.
1940s filmmakers also explored how flashbacks could be “architectonic,” how they could inform the overall shape of the movie. Here the flashback rearranges story order to build up curiosity and suspense, and it may come from purely from the narration or be motivated as character memory.
One large-scale pattern is the extensive embedded flashback, as in How Green Was My Valley, I Remember Mama, and innumerable biopics. Wonder Woman gives us a framed inset of this sort, when a modern-day Diana opens the chest harboring the World War I photo. That scene segues to the past. The origin story and war episodes are ultimately closed off by a return to the present, and a reminder of a motif—Steve’s watch (which, in one of the film’s jokes, stands in for something more private). The purpose of this is to provide what I call in the book “hindsight bias.” While building curiosity about the past, the opening primes us to expect certain things to have been inevitable (such as chance meetings).
Another common framing strategy begins at the climax and then a long flashback lays out the conditions that led up to it. A reliable source tells me that Pitch Perfect 3 does this, starting with an explosion followed by a title announcing that the action began three weeks earlier. In films like this, there may be no closing frame; the internal action of the flashback catches up, perhaps via a replay, with what we saw at the outset, and the film proceeds to the resolution and epilogue. The somewhat phantasmic opening number of The Greatest Showman comes to fruition during the finale.
To and fro
Loving Vincent.
Sustained blocks like this are fairly rare nowadays, I think. More common, as in the Forties, is an alternation of past and present. The main examples in Reinventing Hollywood include Passage to Marseille, The Locket, Lydia, Kitty Foyle, and Sorry, Wrong Number. Again, though, these are motivated as memories, while current examples tend to be more “objective.”
A simple instance is Film Stars Don’t Die in Liverpool. Here clusters of events in 1981 alternate with incidents in 1979: Gloria Grahame returns to her young lover, and we flash back to their earlier affair. Neither protagonist is firmly established as recalling the 1919 events. Another feature of 1940s flashbacks, the replay from different viewpoints, comes in here as well. The couple’s crucial quarrel in New York is shown first from Peter’s perspective, and later from Gloria’s. He suspects her of infidelity, but we learn that her secret involves her cancer. As often happens, our restriction to the protagonist is modified by knowledge he doesn’t gain at the moment.
The alternation of past and present is given a more geometrical neatness in Wonderstruck. In maniacally precise parallels, Rose in 1927 runs away to Manhattan to find her mother, while in 1977 Ben runs there to find his father.
The parallels are reinforced by a host of motifs: wolves, movie references, the asteroid in the Museum of Natural History, a bookmark, and so on. The linear chronology gets straightened out, and the gaps filled, by an integrative flashback played out among miniatures and cutouts adapted to the scale model of Manhattan. The dovetailing flashbacks create a sense of cosmic design; in many films, convergences like these can suggest destiny.
For modern audiences, Citizen Kane is the prototypical flashback film of the 1940s, and its investigation structure, while not completely original, was hugely influential. I was surprised to see Kane’s schema revived this year in Loving Vincent. Once the postman has given Armand his mission, to take Vincent’s last letter to brother Theo, we embark on an inquiry into Vincent’s life and death. It’s refracted through the testimony of many who knew him during his sojourn in Arles. Armand’s goal gets recast when he learns of Theo’s death, but in the course of his travels he comes to understand how Vincent’s kindness and art touched many lives.
As in several Forties films, Loving Vincent’s past scenes jumbled out of chronological order, so we must piece together the story Armand gradually discloses. And there’s the driving force of mystery, a distinctive thrust in many Forties genres, for reasons I talk about in one chapter of Reinventing. Very modern, and not so much like the 1940s, is the brief, fragmentary quality of the flashbacks; I counted thirty-six of them.
The boldest experiment in nonlinear time I saw this year was Dunkirk. The film juxtaposes timelines consuming a week or so, a day, and an hour, and then aligns them in unexpected ways. In this staggered array, the distinction between flashbacks and flashforwards loses its force. Any cut may constitute a jump ahead of the moment just shown, or a jump back to an earlier incident. Christopher Nolan has acknowledged the influence of 1940s cinema on his thinking about time schemes, and here he explores yet again how crosscutting different lines of action can stretch or condense story duration.
Their eyes and ears
Get Out.
Like flashbacks, subjectively tinted storytelling has a long cinematic lineage. Silent films displayed dreams, visions, anticipations, and deformations of mind and eye. Those devices mostly dropped out of 1930s American cinema, which was to some extent more “objective” and “theatrical” in its mode of presentation. Subjectivity came roaring back in the Forties, which is why Reinventing Hollywood devotes two chapters and several other passages to various techniques that go beneath the surface.
Memory-based flashbacks are common options today, but the inward plunge can take other forms. For most of its length, Get Out restricts us to Chris’s range of knowledge, and it relies on optical POV in many stretches. Through his eyes we see Mrs. Armitage staring at him while stirring the tea.
More complex is his view of Georgina at the upper window. That’s followed by a shot going beyond his range of knowledge: she’s looking not at him but herself.
We take a deeper dive into Chris’s mind under hypnosis. The boy Chris sinks into a stellar cavity and becomes Chris staring at Mrs. Armitage as if she were appearing on the TV screen. The shift dramatizes his guilt at his mother’s death and his susceptibility to this Bad Mom figure.
Once Chris becomes a prisoner, the narrational range widens again to show Rod’s efforts to rescue him, along with the family’s plans for him. But the film tightly realigns us with Chris at the climax, so that the attacks from Rose, Jeremy, and others come as surprises.
Chris, a photographer, channels his experience through vision, though the hypnotism scene blends sounds from the present with the rain drizzling in the past. Subjectivity goes more fully sonic in Baby Driver, about a whey-faced lad who lives in the auditory ether.
Edgar Wright, now exercising straight the percussive dashboard details he parodied in Hot Fuzz, punches up the visual exhilaration of Baby’s rubber-shredding takeoffs and getaway 180s. He locks us into Baby’s auditory world as well. We’re almost completely attached to Baby, learning what he learns when he learns it. Notably, the robberies are rendered from his perspective, including optical POV shots as he waits in the getaway car.
Again, fragmentary flashbacks replay his mother’s death and the childhood damage to his hearing. We even get a fantasy, with Baby imagining his escape with Debora in black and white.
What’s just as subjective, though, is the music Baby incessantly cues up on his iPod. Blocking out the shriek of his tinnitus, it provides a soundtrack to his life—danceable tunes as he bops down the street, ballads when he flirts and falls in love with Debora, and pulsing rock during robberies (what the psycho Bats calls, “a score for a score”). Through volume and texture, Wright suggests that we hear the music as Baby does; only the loudest environmental sounds poke through. Sometimes, when he pulls out one earbud, the volume drops. His growing attachment to Debora is signaled by his dialing up a song using her name and sharing his precious buds.
Some scenes are handled objectively, as we witness the gang’s conversations in front of Baby. He can read lips, though, and he can keep the iPod cranked up. So a little bit of Baby’s custom soundtrack leaks in for us underneath others’ dialogue. At other times, the score takes over to become nondiegetic accompaniment, as when gunshots in a firefight land on the off-beats of “Tequila.”
As you’d expect, the music comments on the action throughout (“Never ever gonna give you up” when Baby defends Debora from Buddy) and supplies motifs. Queen’s “Brighton Rock,” Baby’s favorite heist accompaniment, briefly enables him to bond with Buddy.
A song about a couple’s devotion reminds us that both thieves are loyal to their women.
Momentary sound changes are rendered through our protagonist’s viewpoint. Wright lets us hear the whine of Baby’s tinnitus as Bats taps his ear. When Buddy blasts his pistols alongside Baby’s head, we suffer his hearing loss and the distorted voices that wobble through it.
Such streams of auditory perception occasionally emerged in early talkies (e.g., Gance’s Beethoven). Those experiments got normalized in 1940s manipulations of sound perspective in different environments. More fancily, in A Double Life (1947), party chatter subsides when the hero covers his ears, and in Pickup (1951), the gradually deafening protagonist hears high-pitched noises. Wright extends these one-off devices to the texture of an entire film.
Confidants
The Keys of the Kingdom (1945).
Large-scale and small-scale, the heritage of the 1940s seems to be everywhere. Many of the flashbacks and fantasies I mentioned already are primed by a track-in to a character’s face, just as in classic studio pictures. There’s also block construction, either unsignaled as in the Wonder Woman and Greatest Showman cases, or signaled, as in the date-stamping in the early alternations of Film Stars Don’t Die in Liverpool. We also get explicit chaptering, as in The Meyerowitz Stories (New and Selected) and Norman: The Moderate Rise and Tragic Fall of a New York Fixer.
Voice-overs come along with flashbacks, as a way of guiding the audience to understand the time shifts. In the Forties, as I discuss in the book’s sixth chapter, voice-overs became more flexible and fluid. Sometimes they were external, issued from an all-knowing commentator (Naked City and other police procedurals). Sometimes they were sonic equivalents for letters and diaries, letting us in on what characters were writing. Deeper intimacy could come from voice-overs serving as inner monologues, the voice of a character’s mind. These, like flashbacks, are associated with film noir, but also like flashbacks they actually emerge in many genres–as they do today.
The voice-over can be perfunctory, as in All the Money in the World. Young Paul Getty, kidnapped in the opening reel, has a couple passages confiding in us, but he’s not heard from again. Moreover, his explanation of his grandfather’s rise to power (during the inevitable flashbacks) could have been supplied in other ways. Paul baldly tells us that we need to know all this to understand what follows (who’s he talking to?). He admits that he’s an expository shortcut. This is why voice-over is sometimes considered lazy storytelling.
It doesn’t have to be. Take Martin Scorsese’s Silence. In subject and strategy it reminded me of The Keys of the Kingdom (1945), which dramatizes the diary of a young missionary to China. Via this novelistic device, we get flashbacks to his youth and his years of service. We get as well the reaction of the skeptical priest whose voice reads the journal. This fairly straightforward schema is in effect revised by Scorsese and co-screenwriter Jay Cocks, who create a floating dialogue among voice-overs.
After initial exposition via an old letter from Father Ferreira, which is recited in his voice, two young priests set out for Japan. They hope to maintain the clandestine Christian community there, and they want as well to discover if Ferreira has truly renounced his faith . The bulk of their grim adventures is commented on through the voice-over of one of them, Father Sebastião Rodrigues. At first he’s vocalizing a letter, which he calls a report, summing up the struggles of the Jesuit mission and their encounters with Christian villagers. In the course of his report, we also get an embedded flashback narrated by Kichijiro, their guide and a sporadically lapsed believer himself.
But at a crucial moment, Father Sebastião’s report ceases to be such and turns into an inner monologue. Seeing a Christian village devastated by the shogun’s forces, he asks, “What have I done for Christ?”
Soon his voice presents a kind of stream of consciousness–praying for the villagers as they walk off in captivity, thanking God when he has a vision of Jesus on his prison wall. His inner voice urges his colleague Father Garupe, severely tortured, to apostatize.
In last stretch of the film, new voices are heard. There’s Jesus, perhaps filtered through Sebastião’s mind (subjectivity again), and then, more objectively, there’s an account from the Dutch trader Albrecht. He drily reports that Sebastião apostatized and followed Ferreira in leading a Japanese life. Albrecht’s narration is interrupted by a dialogue between Sebastião and Jesus, capped by the priest’s blurting out: “It was in the silence that I heard your voice.” Albrecht’s voice-over concludes the film, with his final claim that the priest was “lost to God” belied by the closing image.
From the 1940s onward, voice-over has been a rich resource–describing settings and external behavior, judging other characters’ motives, giving us access to the deepest thoughts of the speaker. I try to show these capacities at work in a fairly ordinary film, The Miniver Story, but for our time, the soundtrack of Silence is another vivid demo. In the juxtaposition of different voices, it achieves some of the density of a novel, and by the end we better understand the initial words and emotions of Father Ferreira, the priest whose apostasy launches the plot.
Passed-along voice-over gets a bigger workout in Dee Rees’s Mudbound. The original novel is somewhat like As I Lay Dying; its sections set various characters’ voices side by side, shifting viewpoint as each takes up a portion of the tale. Constant commentary and perfect alignment with a character’s range of knowledge are hard to sustain in cinema, so what we have onscreen are objectively presented scenes accompanied by an occasional voice-over. Still, it’s a rare option. If Silence gradually opens its voice-over horizons near the film’s end, Mudbound introduces polyphony from the start. Six characters share their thoughts and feelings in alternation, providing backstory and deepening our access to their reactions.
As in Silence, there’s a pattern to the voice-overs. The bulk of the film is an embedded flashback, triggered by the McAllen brothers setting out to bury their father and encountering the Jackson family riding by.
The intersection of two families sets up not only the flashback episodes but the floating voice-overs. As the visuals anchor us initially to the white family, the first voice-overs issue from Laura, the wife of Henry McAllen, and from Henry’s brother Jamie. In the flashback stretch, as America enters World War II, the voice-overs shift to the Jacksons, the father Hap and the mother Florence. The plot proceeds to add the voices of Henry and the Jacksons’ oldest son Ronsel. All the characters narrate the action in the past tense, as if recalling it from a distance in time, but no listener is ever specified–a common feature of voice-overs in the 1940s and afterward.
During the film’s second half, the development and climax sections, the voice-overs nearly vanish. For over an hour, we hear only Laura and Florence, and only once apiece. Jamie and Ronsel, both disaffected returning vets, don’t confide in us during their growing friendship or during the persecution of Ronsel by the local white men. The women are left to provide a sporadic chorus.
At the end, however, a spurt of brief commentaries give the men their inner voices back. We return to the present and see Hap Jackson help the McAllen men bury their father (the inciter of KKK violence against Ronsel). The epilogue features brief comments from Ronsel, Jamie, and Hap, and not the women. Ronsel gets the last word. Ironically, because of the KKK savagery, this narrator has become mute.
Again, I felt a current film’s kinship to those I studied for the book. Mudbound traces the rural home front, the military experiences of a white man and a black one, and the veterans’ problems of adjustment upon returning home. These elements hark back to some of the powerful films of the 1940s, including Home of the Brave and The Best Years of Our Lives. The sympathetic portrait of African-American families isn’t unprecedented either, as seen in Intruder in the Dust and Lost Boundaries. Mudbound‘s passed-along narration, like the ones we find in other modern films, constitute contemporary revisions of the shifting voice-overs we get in Citizen Kane and All About Eve.
Career women careening
Molly’s Game.
Molly’s Game and I, Tonya offer good wrapup examples of many of these strategies, with some unreliability thrown in.
As you’d expect in a film by Aaron Sorkin, the flashback organization of Molly’s Game is fairly complicated. Just as The Social Network intercut two arrays of flashbacks triggered by two legal inquiries, the new film scrambles together crucial moments in Molly’s childhood , scenes of her current legal troubles, and sequences showing her rise to become the Poker Princess, the arranger of high-stakes games. The film gains a bit of the structural symmetry of Wonder Woman by beginning and ending with a childhood defeat that Molly rises above.
The flashbacks are stitched together by Molly’s voice-over. A filmmaker who recruits a narrating voice has to choose. Do you show the narrating situation? Or do you leave it unspecified? In this last instance, the narration might be wholly internal, a mental summing up of events, or it might feel like a confidence shared with an intimate, even though we’re shown no listeners. In Molly’s Game, her bare-it-all confession might seem to be simply her unspoken thoughts, but at one point it’s suggested that what we’re getting is her book’s version of her life.
Molly’s attorney Charlie is reading her memoir while he researches her case, and he asks her about a passage we saw in a flashback: her boss chews her out for bringing him “poor people’s bagels.” The attorney suggests that nobody uses that phrase, and that probably the boss used a racial slur that she suppressed in the book. This throws a little bit into question the reliability of Molly’s flashback, while also hinting at something we learn later: she sanitized the book to spare the reputations of the high rollers she serviced.
I, Tonya takes another option. Again there are disordered flashbacks and bursts of subjectivity tied together by the voice track. Whereas Molly is the sole speaker in her film, though, Tonya shares the soundtrack with other characters, in the manner of Mudbound. But these commentaries aren’t private musings. They’re the self-justifying testimony of people talking to a documentary camera. (Even though these sequences are said to be occurring forty years after the earliest events, the format is an anachronistic 4:3–presumably to help us keep the time frames distinct.
Once you get characters in conflict recounting past events, you have the possibility of disparate stories. Forties filmmakers exploited this in Thru Different Eyes and a certain Hitchcock film too famous to mention. Tonya says explicitly that there are different versions of the truth. A brief scene shows her battering Nancy Kerrigan, and a more complicated one occurs in a tale recounted by her husband Jeff. She fires a shotgun at him and turns to the camera saying, “I never did this”–before briskly ejecting a shell.
The comic possibilities of to-camera address on display here were exploited in My Life with Caroline, Mr. Blandings Builds His Dream House, and other 1940s films. Then the momentary breaking of the fourth wall was reserved for the frame story and kept separate from the embedded flashbacks. But I, Tonya‘s revision is easy to understand as a zany equivalent for her verbalized denial. Given the defiant way she brandishes the gun, we’re permitted to doubt her denial–which means that the film is refusing to settle the matter. The possibility that the overall filmic narration could be unreliable was rehearsed occasionally in the Forties, perhaps most vividly in Mildred Pierce (analyzed here, sampled here).
Other paths
Foxtrot.
The 1940s were important for other national cinemas too. The book’s last chapter suggests that filmmakers in Britain, France, Mexico, and other countries engaged in similar narrative explorations–sometimes in imitation of America, sometimes on their own. I go on to suggest that eventually non-Hollywood narrative models came to international attention, and still later those affected American cinema.
Italian Neorealism was a prime source of alternatives. A good example of its long-term impact, I think, is The Florida Project, which embraces a slice-of-life pattern. Once you’re committed to episodic plotting, you need to organize the incidents coherently. Sean Baker follows European and US indie precedent in tracing a rhythm of daily routines that change in sync with the characters’ relationships. So Halley’s quarrel with her friend Ashley means that Moonee can no longer claim leftover food from the diner, which helps push Halley toward prostitution, which leads to the intervention of child welfare authorities.
The drama arises less from crisply defined goals than from circumstances that alter life routines. In addition, like many Neorealist films and others in this vein afterward, the poignancy gets sharpened by the presence of children caught up in adults’ bad choices.
The Florida Project presents many actions elliptically, leaving us to infer what has happened offscreen. (I think, for instance, that it’s motel manager Bobby Hicks who contacts the authorities, but I don’t think it’s made explicit.) Moving to films made outside the US, Michael Haneke’s Happy End takes ellipsis even further.
Haneke uses the strategy of delayed and distributed exposition. He presents some apparently casual events at the outset, then gradually reveals what’s actually going on, all the while tracing out ultimate consequences. Instead of presenting a clear-cut chain of causes and effects, he asks us to fill in unspoken plans, offscreen actions, and hidden motives. Haneke has specialized in suggesting how vague forces can disturb rich, smug families and their shady schemes. His mystery-driven narrational tactics suit Happy End as well as Code inconnu and Caché.
I speculate in Reinventing Hollywood that the European art cinema’s story-based mysteries and narrational uncertainties owe something to 1940s American films. So too perhaps does the use of block construction, which emerged in overseas portmanteau films of the postwar era (e.g., Dead of Night, Le Plaisir, The Gold of Naples). Samuel Maoz’s Foxtrot is a striking example of block construction.
His Lebanon (2009) took POV restriction to a limit by confining its action to a military tank in the heat of battle. (This tactic has Forties precedents as well, as Lifeboat and Rope remind us.) Foxtrot operates differently. Broken into three parts, it looks at a single situation–a young soldier’s duties at a checkpoint–through shifts in time and viewpoint. The opening shot, at first enigmatic, gets specified in an epilogue that recasts all that went before. Maoz also incorporates monotonous routines into his plot, the better to throw a single shocking incident into relief.
So classical construction isn’t the only option available. But other choices have histories as well. As viewers we learn these alternative stoytelling traditions, and we use that knowledge to make sense of new examples. No less than the Hollywood model, these other formal strategies engage us through familiar pattern and unexpected novelty, schema and revision.
I don’t mean to obsess over this 1940s thing. Our current films owe debts to silent cinema and to other eras too. It’s just that I continue to be fascinated by finding repetitions and variants of storytelling strategies that got consolidated in the period I was studying. Denounce them as formulaic if you want, but I prefer to think that these and other recent films illustrate, in fine grain, the continuity and sometimes the vitality of a major cinematic tradition.
Maybe this is my hook to an entry for the start of 2019?
Many thanks to Michael Barker of Sony Pictures Classics for help on this entry.
On the four-part structure of classical films see Kristin’s 2008 entry and my essay “Anatomy of the Action Picture.” Today’s entry deploys the analytical categories trotted out at length in this essay and more briefly in this discussion of The Wolf of Wall Street.
Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 2.