Archive for the 'Hollywood: Artistic traditions' Category
Creating a classic, with a little help from your pirate friends

DB here:
In early April of 1940, His Girl Friday came to Madison, Wisconsin. It ran opposite Juarez, The Light that Failed, Of Mice and Men, and a re-release of Mamoulian’s Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. Pinocchio was about to open. Most screenings cost fifteen cents, or $2.21 in today’s currency.
Before television and home video, film was a disposable art. Except in big cities, a movie typically played a town for a few days. Programs changed two or three times a week, and double bills assured the public a spate of movies—nearly 700 in 1940 alone. People responded, going to the theatres on average 32 times per year. Given the competition, it’s no surprise that His Girl Friday didn’t stand out in the field; it was nominated for no Academy Awards and honored by no prizes. On just a single day in Madison, the cast of His Girl Friday was up against icons like Muni, Colman, March, and Bette Davis.
Nowadays, of course, nearly everyone regards HGF as one of the great accomplishments of the studio system. Most would consider it a better movie than any of the others it played opposite in my home town. A typical example of critical exuberance is Jim Emerson’s comment here. Or read James Harvey’s 1987 encomium:
It would be hard to overstate, I think, the boldness and brilliance of what Hawks has done here: not only an astonishingly funny comedy, but a fulfillment of a whole tradition of comedy—the ur-text of the tough comedy appropriated fully and seamlessly to the spirit and style of screwball romance. His Girl Friday is not only a triumph, but a revelation.
Oddly, this extraordinary film lay largely unnoticed for three decades. How did it become a classic? The answer has partly to do with the rising status of Howard Hawks, the director, among critics. It also owes something to changes in how academics thought about film history. And a little movie piracy didn’t hurt.
An unseen power watches over the Morning Post
Hawks the Artist is a creation of the 1960s. Before that, American film historians almost completely ignored him. Andrew Sarris often reminds us that he’s absent from Lewis Jacobs’ Rise of the American Film (1939), but he’s also missing from Arthur Knight’s The Liveliest Art (1957), the most popular survey history of its day. Apart from press releases and reviews of individual films, there were few discussions of Hawks in American newspapers and magazines. The most famous piece is probably Manny Farber’s “Underground Movies” of 1957, which treats Hawks along with other hard-boiled directors like Wellman and Mann.
From the start, Hawks was more appreciated in France. There film historians acknowledged A Girl in Every Port (1928), in part because of the presence of Louise Brooks, and they usually flagged Scarface (1932) as well, which they could see and Americans couldn’t. (Howard Hughes kept it out of circulation for decades.) But Hawks is barely mentioned in Georges Sadoul’s one-volume Histoire du cinéma mondiale (orig. 1949) and he’s ignored in the 1939-1945 volume of René Jeanne and Charles Ford’s monumentally monotonous Histoire encyclopédique du cinéma (1958).
The essay that marked the first phase of reevaulation was evidently Jacques Rivette’s “The Genius of Howard Hawks” in Cahiers du cinéma in 1953. Inspired by Monkey Business, Rivette’s philosophical flights and you-see-it-or-you-don’t tone helped define the auteur tactics identified with Cahiers’s young Turks. Rivette and his colleagues became known as “Hitchcocko-Hawksians.” The essay, however, doesn’t seem to have been immediately influential. Antoine de Baecque claims that within Cahiers, an admiration for Hawks was controversial in a way that liking Hitchcock was not. (1) It took some years for Hawks to ascend to the Pantheon.
 The story of that ascent has been well-told by Peter Wollen in his essay, “Who the Hell Is Howard Hawks?” In France, the Young Turks’ tastes had been nurtured by Henri Langlois, who showed many Hawks films at the Cinémathèque Française. In New York, Andrew Sarris and Eugene Archer had become intrigued by Cahiers but were ashamed that as Americans they didn’t know Hawks’ work. They persuaded Daniel Talbot to show a dozen Hawks films at his New Yorker Theatre during the first eight months of 1961. The screenings’ success allowed Peter Bogdanovich to convince people at the Museum of Modern Art to arrange a 27-film retrospective for the spring of 1962. The package went on to London and Paris, sowing publications in its wake.
The story of that ascent has been well-told by Peter Wollen in his essay, “Who the Hell Is Howard Hawks?” In France, the Young Turks’ tastes had been nurtured by Henri Langlois, who showed many Hawks films at the Cinémathèque Française. In New York, Andrew Sarris and Eugene Archer had become intrigued by Cahiers but were ashamed that as Americans they didn’t know Hawks’ work. They persuaded Daniel Talbot to show a dozen Hawks films at his New Yorker Theatre during the first eight months of 1961. The screenings’ success allowed Peter Bogdanovich to convince people at the Museum of Modern Art to arrange a 27-film retrospective for the spring of 1962. The package went on to London and Paris, sowing publications in its wake.
For the MoMA retrospective, Hawks granted Bogdanovich a monograph-length interview, which was to be endlessly reprinted and quoted in the years to come. (2) Sarris, now knowing who the hell Hawks was, wrote a career overview for the little magazine, The New York Film Bulletin, and this piece became a two-part essay in the British journal Films and Filming. Both Bogdanovich and Sarris made brief reference to His Girl Friday, as did Peter John Dyer in another 1962 essay, this one for Sight and Sound. At the end of 1962, another British magazine, Movie, published an issue on Hawks. At the start of 1963, Cahiers devoted an issue to him, including an homage by Langlois himself. Thanks to the work of Archer, Bogdanovich, Sarris, and MoMA, Hawks was rediscovered.
Sarris provided a condensed case for Hawks in his far-reaching catalogue of American directors, published as an entire issue of Film Culture in spring of 1963. There followed an interview with Hawks’s female performers in the California journal Cinema (late 1963), an appreciation by Lee Russell (aka Peter Wollen) in New Left Review (1964), another Cahiers issue (November 1964), J. C. Missiaen’s slim French volume Howard Hawks (1966), Robin Wood’s Howard Hawks (1968), and Manny Farber’s Artforum essay (1969). There were doubtless other publications and events that I never learned about or have forgotten. In any case, by the time I started grad school in 1970, if you were a film lover, you were clued in to Hawks, and you argued with the benighted souls who preferred Huston. . . even if you hadn’t seen His Girl Friday.
Light up with Hildy Johnson

One of my obsessions in graduate school was the close analysis of films. But I was also interested in whether one could build generalizations out of those analyses. My initial thinking ran along art-historical lines. My Ph. D. thesis on French Impressionist cinema sought to put the idea of a cinematic group style on a firmer footing, through close description and the tagging of characteristic techniques. But that approach came to seem superficial. I wasn’t satisfied with my dissertation; although it probably captured the filmmakers’ shared conceptions and stylistic choices, I couldn’t offer a very dynamic or principled account of formal continuity or change.
Watch a bunch of movies. Can you disengage not only recurring themes and techniques, but principles of construction that filmmakers seem to be following, if only by intuition? As I was finishing my dissertation, reading Russian Formalist literary theory pushed me toward the idea that artists accept, revise, or reject traditional systems of expression. These become tacit norms for what works on audiences. My reading of E. H. Gombrich pushed me further along this path. We should, I thought, be able to make explicit some of those norms. Eventually I would call this perspective a poetics of cinema.
I was assembling my own version of some ideas that were circulating at the time. In the early 1970s, several theorists floated the idea that different traditions fostered different approaches to filmic storytelling. People were seeing more experimental and “underground” work, as well as films from Asia and what was then called the Third World. Being exposed to such alternative traditions helped wake us up to the norms we took for granted. The mainstream movie, typified by what Godard called “Hollywood-Mosfilm,” seemed more and more an arbitrary construction.
People began examining films not as masterworks or as expressions of an auteur, but as instances of a representational regime. Films became “tutor-texts,” specimens of formal strategies that were at play across genres, studios, periods, and directors. Again, the French pointed the way, particularly Raymond Bellour, Thierry Kuntzel, and Marie-Claire Ropars. At the same moment, Barthes’ S/z was published in English, and it seemed to provide a model for how one might unpick the various strands of a text, either literary or cinematic. Screen magazine was a conduit for many of these ideas in the English-speaking world.
Some of my contemporaries disdained the mainstream cinema and moved toward experimental or engaged cinema. Others read the dominant cinema symptomatically, for the ways it revealed the contradictions of ideology. I learned from both approaches, but I believed that the current analysis of how Hollywood worked, even considered as a malevolent machine, was incomplete. Could we come up with a more comprehensive and nuanced account of the mainstream movie? This line of thinking was already apparent in non-evaluative studies of form and style, such as essays by Thomas Elsaesser, Marshall Deutelbaum, and Alan Williams. (3)
At some point in graduate school at the University of Iowa, between fall 1970 and spring 1973, I saw a screening of His Girl Friday. I fell in love with its heedless energy. It seemed to me a perfect example of what Hollywood could do.
In my admiration I was channeling the cultists. Rivette, in a review of Land of the Pharoahs: “Hawks incarnates the classical American cinema.” (4) Bogdanovich: He is “probably the most typical American director of all.” Richard Griffith, then film curator of MoMA, had slighted Hawks in his addendum to Paul Rotha’s The Film Till Now, but in his foreword to the Bogdanovich interview he caved to the younger generation: “Hawks works cleanly and simply in the classical American cinematic tradition, without appliquéd aesthetic curlicues.” As for HGF, in the 1963 Cahiers tribute Louis Marcorelles called it “the American film par excellence.”
Praising Hawks, and HGF specifically, was part of a larger Cahiers strategy to validate the sound cinema as fulfilling the mission of film as an art. What traditional critics would have considered theatrical and uncinematic in HGF—confinement to a few rooms, constant talk, an unassertive camera style—exactly fit the style that Bazin and his younger colleagues championed. (For more on that argument, see Chapter 3 of my On the History of Film Style.)
These niceties didn’t inform my reaction at the time. I was already primed to like Hawks, though, having caught what films I could after reading Wood et al. (During my initial summer in Iowa City, I went to a kiddie matinee of El Dorado and got Nehi Orange spilled down my neck.) On my first viewing His Girl Friday delighted me with the sheer gusto of the pace and playing. Clearly the cast was having fun. A press release sent out before the film claimed that during one scene, with Cary Grant dictating frantically to Rosalind Russell, she cracked him up by handing over what she had typed.
Cary Grant is a ham. Cary Grant is a ham. Now is the time for all good men to quit mugging. You don’t think you can steal this scene, do you—you overgrown Mickey Rooney? The quick brown fox jumps over the studio. Cary Grant is a ham.
Even discounting this tale as PR flackery, we know from Todd McCarthy’s excellent biography that Hawks encouraged competitive scene stealing and wily improvisation. Russell hired an advertising copywriter to compose quips she could “spontaneously” conjure up in her duels with Grant.
If there was a “classical Hollywood cinema”—a phrase that was in the early ’70s coming into circulation via Screen—the buoyant forcefulness of His Girl Friday embodied it. Here was a film pleasure-machine that hummed with almost frightening precision. What else do you expect from a director who studied engineering and whose middle name is Winchester?
Production for use
When I saw His Girl Friday, little had been written about it. Despite Langlois’ screenings, before the 1962 touring program, the Cahiers critics seemed to have had limited access to Hawks’ prewar work. His Girl Friday wasn’t released theatrically in France until January of 1945 (not perhaps the most propitious moment), and it apparently made no long-lasting impression on the intelligentsia. I can’t find any critical commentary on it in French writing before the 1963 issue of Cahiers.
In the United States, HGF earned Hawks a courteous write-up in the New York Times by, of all people, Bosley Crowther, (5) but it wasn’t acknowledged as an instant classic like Mr. Smith Goes to Washington or The Philadelphia Story. After the initial flurry of mostly favorable reviews, the movie seems to have been forgotten until Manny Farber’s 1957 essay, and even there it’s only mentioned in a list. Interestingly, it wasn’t screened during the 1961 New Yorker series. Robin Wood’s sympathetic but not uncritical discussion in his Hawks book of 1968 seems to have been the most comprehensive account available since the movie’s release.
At about the time Wood’s book was published, something big happened. Columbia Pictures failed to renew its copyright, and His Girl Friday fell into the public domain.
Entrepreneurs made dupe copies, in quality ranging from okay to terrible. You could rent one for peanuts and buy one for only a little more. Some of these bleary prints have been telecined and turned into the DVD versions of the film that fill bargain bins today. After I got to the University of Wisconsin, where Hawks films stoked the two dozen campus film societies, I bought a public domain print. The copy was better than average, although it lacked the fairy-tale warning title at the start. From 1974 on, I showed the poor thing constantly.
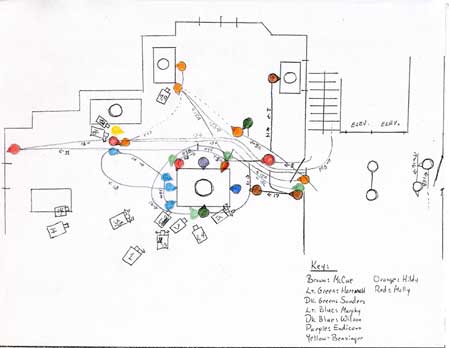
In Introduction to Film, taught to hundreds of students each semester, HGF illustrated some basic principles of classical studio construction. It had the characteristic double plotline (work/ romance), a careful layout of space, an alternation of long takes and quick cutting, manipulation of point-of-view, judicious depth framing (see frame below), and cascading deadlines. In Critical Film Analysis, I asked students to map out scenes shot by shot (see diagram above) and to show how different approaches (genre-based, feminist, Marxist) would interpret the film. In a seminar on “the classical film and modernist alternatives” HGF grounded comparisons with Bresson, Dreyer, Ozu, Godard, and Straub/Huillet. By steeping ourselves in such alternative traditions, could we resist the naturalness of Hollywood artifice?
The movie became a UW staple. It went into the first edition of Film Art (1979) as an instance of classical construction; even the telephones were scrutinized. Marilyn Campbell’s paper from our seminar was published in 1976. (6) Over the years, many of our grad students, exposed to the film in our courses, have gone on to use it in their teaching.
Doesn’t have to rhyme

I can’t let HGF go. I still use moments to illustrate points in my writing and lectures. Madison colleagues and I swap banter from it; Kristin and I talk in Hawks-code, as she explains here. I’ve been told that grad students in another PhD program compared our program to the Morning Post pressroom (favorably or not, I don’t know). Thanks to Lea Jacobs, the invitation to my retirement party was surmounted by a picture of Walter Burns whinnying into his phone.
But seriously, His Girl Friday, isn’t a bad guide to a lot of social life. You can learn a lot from its Jonsonian glee in selfishness and petty incompetence, as well as its sense that virtue resides with the person who has the fastest comeback. Think as well how often you can use this line in a university setting:
If he wasn’t crazy before, he would be after ten of those babies got through psychoanalyzing him.
I’m not claiming special credit for the HGF revival, of course. Plenty of other baby-boomer film professors were teaching it. It became a reference point for feminist film criticism, particularly Molly Haskell’s From Reverence to Rape (1974), and it has never lost its auteurist cachet. Richard Corliss’s 1973 book on American screenwriters flatly declared that “His Girl Friday is Hawks’s best comedy, and quite possibly his best film.”
Most important of all, TV stations were screening their bootleg prints. HGF didn’t become a perennial like that other public domain classic It’s a Wonderful Life, but its reputation rose. Its availability pushed the official Cahiers/ Movie masterpieces Monkey Business and Man’s Favorite Sport? into a lower rank, where in my view they belong.
Once HGF became famous, the proliferation of shoddy prints became an embarrassment. In 1993 it was inducted into the National Film Registry, which gave it priority for Library of Congress preservation. Columbia managed to copyright a new version of the film. A handsomely restored version was released on DVD, and a few years back I saw a 35mm copy whose sparkling beauty takes your breath away.
The lesson that sticks with me is this. If Columbia had renewed its copyright on schedule, would this film be so widely admired today? Scholars and the public discovered a masterpiece because they had virtually untrammeled access to it, and perhaps its gray-market status supplied an extra thrill. Thanks mainly to piracy, His Girl Friday was propelled into the canon.
Epilogue
In May of 1940, His Girl Friday hung around Madison, shifting from its first venue, the Strand downtown, to an east side screen, the Madison. The film came back in late September to yet a third screen, the Eastwood (now a music venue).
HGF was revived in March of 1941, as the second half of a double bill at the Madison (bottom left below). Check out the competition: some killer re-releases from Ford, Lubitsch, Astaire-Rogers, and Hope-Crosby. A Midwestern city of 60,000 could become its own cinémathèque without knowing it.

(1) Antoine de Baecque, Cahiers du cinéma: Histoire d’une revue, vol. 1: À l’assaut du cinéma, 1951-1959 (Paris: Cahiers du cinéma, 1991), 202-204.
(2) Bogdanovich has published a much fuller version in Who the Devil Made It? (New York: Knopf, 1997) , 244-378.
(3) Thomas Elsaesser, “Why Hollywood?” Monogram no. 1 (April 1971), 2-10; “Tales of Sound and Fury,” Monogram no. 4 (1972), 2-15; Marshall Deutelbaum, “The Structure of the Studio Picture,” Monogram no. 4 (1972), 33-37; Alan Williams, “Narrative Patterns in Only Angels Have Wings,” Quarterly Review of Film Studies 1, 4 (November 1976), 357-372.
(4) Jacques Rivette, “Après Agesilas,” Cahiers du cinéma no. 53 (December 1955), 41.
(5) Bosley Crowther, “Treatise on Hawks,” New York Times (17 December 1939), 126. “He brings to his work as a director the ingenious and calculating brain of a mechanical expert. . . . He pitches into the job just as though he were building a racing airplane.”
(6) Marilyn Campbell, “His Girl Friday: Production for Use,” Wide Angle 1, 2 (Summer 1976), 22-27.
For a helpful collection of conversations with the master, see Howard Hawks Interviews, ed. Scott Breivold (Jackson: University of Mississippi Press, 2006). Go here for a 1970s piece by James Monaco on then-current controversies.
PS 24 Feb: Jason Mittell responds to my post with some nice nuancing and draws out the implication for copyright issues: contrary to current media policy, the wider availability of a work can actually enhance its value.
Coming attraction: Kristin is preparing a blog entry commenting on fair use in the digital age.
What happens between shots happens between your ears
DB here:
In Number, Please? (1920) Harold Lloyd plays a lovesick boy who’s been jilted by his girl. Moping at an amusement park, he sees her arrive with a new beau.


He shifts to another spot to watch them. When she notices him, she scorns him, and he reacts.


She and the escort stroll past, then she turns and cuddles up to him, making sure Harold notices.


Her flirting precipitates the rest of the action in this very funny short.
In this scene from Number, Please? Harold and the couple aren’t shown in the same frame. The action is built entirely out of singles of Harold and two-shots of the couple, with an especially emphasized close-up of the girl’s snooty reaction. The sequence is rapidly paced and carefully matched in angle; note the shift in eyelines as the girl and her beau walk a little way and then she looks back at Harold.
This approach to building a scene was consolidated in American studio cinema in the late 1910s, as we noted recently, and it soon spread around the world. One of the places it caught on most fervently was Soviet Russia.
Kuleshov glories in the gaps
The great director and theorist Lev Kuleshov always claimed that he and his associates learned the power of editing from American cinema. Russian films were slowly paced, consisting of long tableaus occasionally broken by an inserted closer view of an actor. (For examples, see my Bauer blog entry from the summer.) Kuleshov noted that the Hollywood films brought into Russia grabbed audiences’ interest more intently, and Kuleshov attributed this effect to the fact that the Americans exploited editing more fully, creating the scene out of many shots.
Kuleshov’s example was the formulaic scene of a man sitting at his desk and deciding to commit suicide. The Russians, Kuleshov claimed, would handle this all in one distant framing, with the result that the key actions were just part of the overall view. By contrast, Americans would shoot the scene in a series of close-ups: the man’s face, his hand taking a pistol out of a desk drawer, his finger tightening on the trigger, and so on. This gave the scene a powerful concreteness, and was cheaper to film besides (no need to have a full set).
But most American filmmakers didn’t create the scene wholly out of close-ups. Typically there would be an establishing shot before the action was broken down into detail shots. The process has come to be called analytical editing. (We discuss it in Chapter 6 of Film Art.) As the label implies, the cutting analyzes an orienting view into its important details.
Less commonly, as in our Number, Please? example, American directors could create a scene entirely out of separate areas of space, without ever showing a master framing. This technique, usually called constructive editing, remains common today as well, especially in action scenes.
While praising analytical editing, Kuleshov was particularly taken with constructive editing, because that shows that cinema can call on the spectator’s tacit understanding to assemble the separate shots. Kuleshov realized that we will build a sense of the scene’s space and action out of separate shots without need for the comprehensive view supplied by an establishing shot.
What the Americans developed, the Soviets thought seriously about. Around 1921, Kuleshov and his students mounted some experiments, several of which he discusses in his books and essays. He probably didn’t need to experiment; the American films were full of examples. Indeed, the Number Please? passage is more intricate than any experiment Kuleshov seems to have mounted. But he had a bit of the engineer about him, and he sought to break the technique into its simplest components.
For one thing, constructive editing offered production efficiencies. You could film two actors separately, at different times, and then cut them together. Further, Kuleshov saw that editing could abolish real-world constraints. It created events that existed only on the screen, with an assist from the viewer’s mind.
This is perhaps best seen in his experiment involving an “artificial person.” Evidently it wasn’t a case of constructive editing, because it seems to have begun with an establishing shot. The first shot shows a girl sitting at her vanity table putting on makeup and slippers. A series of close-ups of lips, hands, legs, and the like were derived from different women, and they were edited together to create the impression of a single woman. (Something of this effect survives in the idea of a body double in contemporary films and TV commercials.) But the point is that the woman on screen, made out of different parts, doesn’t exist in the real world.
The same possibility could apply to geography, if we delete the establishing shot. As Kuleshov describes his experiment, we initially get a shot of a woman walking along a Moscow street. She stops and waves, looking offscreen. Cut to a man on a street that is in actuality two miles away. He smiles at her and they meet in yet a third location, shaking hands. Then together they look offscreen; cut to the Capitol in Washington DC. Kuleshov saw the potential for imaginary geography as both a useful production procedure and a demonstration that editing could create a purely cinematic space, one not beholden to reality.
Kuleshov’s most famous experiment, the one he identified with the “Kuleshov effect” proper, involves a stock shot of the actor Ivan Mosjoukin, taken from an existing film. In his writing he’s rather vague and laconic about the results.
I alternated the same shot of Mosjoukin with various other shots (a plate of soup, a girl, a child’s coffin), and these shots acquired a different meaning. The discovery stunned me—so convinced was I of the enormous power of montage. (1)
Kuleshov’s pupil the great director V. I. Pudovkin offers a different description of the shots: a plate of soup, a dead woman in a coffin, a little girl playing with a teddy bear. He also goes farther in reporting how the audience responded. People read emotions into the neutral expression on Mosjoukin’s face.
The audience raved about the actor’s refined acting. They pointed out his weighted pensiveness over the forgotten soup. They were touched by the profound sorrow in his eyes as he looked upon the dead woman, and admired the light, happy smile with which he feasted his eyes upon the girl at play. But we knew that in all three cases the face was exactly the same. (2)
Now it isn’t only geography or a human body that has been created by editing; it’s an emotion.
These experiments have been poorly documented, and only a couple have survived. One consists of fragments of the imaginary geography exercise. Here is Alexandra Khokhlova waving, but we don’t have the answering shot of the male actor responding. The two meet at the foot of a statue.


After the two shake hands, they look up and out of the frame, but unfortunately we lack the shot of the Capitol.


Kristin and other scholars have written more about these surviving fragments, and their essays are published along with Kuleshov’s proposal for funding the experiments and his wife Khokhlova’s memoir of filming them. (3)
It’s worth taking these prototypes of constructive editing apart a little bit. Clearly, there are several cues that prompt us to see the shots as continuous.
One cue is a common background, or at least a consistent one. Kuleshov thought that sometimes a neutral black background worked best, especially for close shots, as you can see with the handshake shot. Another cue is roughly consistent lighting from shot to shot. Yet another is the presumption of temporal continuity; no moments seem to be omitted in the cut from shot A to shot B. It never occurs to us to consider that Kuleshov’s man is looking at something hours or days before the soup is laid on the table in the second shot.
One of the most important cues goes unmentioned by Kuleshov: the very act of looking. Like most commentators, he seems to take it for granted. Yet it’s crucial in prompting us to imagine an overall space in which the actions take place. Knowing the real world as we do, we can infer that if you’re close enough to watch someone, both people are probably in a shared space, such as the arcade strip in the amusement park in Number, Please?
Another cue is facial expression. In his soup/girl/coffin sequence, Kuleshov supposedly picked a shot of Mosjoukin that doesn’t have a clearly identifiable expression. If Mosjoukin was smiling in his interpolated shot, he would presumably seem not grieving but wicked. Normally, though, performers seen in the single shot are expected to express the appropriate emotion more fully, in order to specify what we take the characters’ mental states to be. Our sequence from Number, Please? makes sure we understand the drama by giving the actors unambiguous expressions.
Finally, in the Kuleshov prototypes each shot should be simple. Its action can be stated in a brief sentence. A woman waves. A man responds. A man looks. A plate of soup sits on a table. Even in Number, Please? we can summarize each shot: Harold looks off. His former girlfriend disdains him. That’s to say that the shots are composed to present only one, quickly grasped point of interest.
Filmmakers don’t need to tease apart all these cues; they use them intuitively. Soon after Number, Please?, Hollywood filmmakers were creating amazing passages of eyeline-match editing—the most virtuoso being probably the racetrack sequence in Lubitsch’s Lady Windermere’s Fan (1926). Within a few years of Kuleshov’s experiments, Soviet filmmakers were creating their own masterworks, like Battleship Potemkin (1925) and Kuleshov’s By the Law (1926). Benefiting from a very compressed learning curve, filmmakers took constructive editing to new heights.
Constructive editing, dissolved relationships
Sometimes constructive editing is used to save a scene when production goes astray. When Doug Liman reshot the climax of The Bourne Identity, Julia Stiles couldn’t be on set, so singles of her taken from the first version were wedged in among the retakes, to create the impression that she was watching Jason confront his controller. More positively, a carefully calibrated constructive editing is central to a sequence I analyzed a while back in In the City of Sylvia. For over 100 shots, the spatial relations are built up without an overall establishing shot. (4)
Constructive editing can be used systematically throughout a film. A good example is Alan J. Pakula’s thriller Presumed Innocent (1990). Spoilers coming up!
Harrison Ford plays Rusty Sabitch, a prosecutor in the District Attorney’s office who becomes infatuated with a new woman on the staff. He has a brief affair with her, but after she’s broken it off she’s found brutally murdered. He has to investigate the crime without involving himself, but eventually he becomes the prime suspect.
At the start of the film before Rusty learns of the murder, Rusty and his wife Barbara are shown at breakfast, and establishing shots bring them together.

At the office Rusty learns of Carolyn’s death, and after he comes home, the conversation between Rusty and Barbara is treated without an establishing shot. Barbara knows about the past affair, and Rusty is wracked by guilt and shame. The cutting seems to reflect the fact that Carolyn’s death has revived the pain in their marriage.


In a series of flashbacks, Rusty relives his affair with Carolyn. Pakula treats their early encounters by means of constructive editing. The common-background cue is especially helpful in this scene in a kindergarten.


Only after Carolyn and Rusty cooperate and win a child-abuse case does the cutting’s rationale become clear. Pakula has saved the traditional two-shot framing for their moment of passion, as they make furious love in the office.

But soon their affair wanes and Rusty is reduced to watching Carolyn from across the street in point-of-view shots.


After the flashbacks end, Rusty is investigated and eventually charged with Carolyn’s murder. In these scenes Pakula often situates Rusty and Barbara in the same frame, as if the threat to him has healed the breach between them.


Yet in the film’s climax—and here is the big spoiler—they are pulled apart again. The last scene is a sustained monologue by Barbara. As Rusty listens, across twenty-six shots the two are never shown in an establishing shot.


Contrary to the standard Hollywood ending, in which the loving couple embrace in reunion, here they are left divided.
Pakula’s use of constructive editing has effectively traced two arcs: the growth and dissolution of Rusty’s affair, and the reuniting and dissolution of his marriage. In such ways, what might seem a purely local effect, confined to a handful of shots, can create stylistic patterning across a film. The judicious use of constructive editing matches the dramatic development.
Godard of the gaps
Robert Bresson has made more varied and complex uses of constructive editing across a film, as I tried to show in Narration in the Fiction Film and in an Artforum essay. (5) A more radical approach, somewhat in the purely Kuleshovian spirit, can be seen in Godard’s films since the late 1970s. In presenting a scene, Godard often omits an establishing shot, so constructive editing takes over. But he makes the technique quite abrasive and ambivalent.
In watching films like Number, Please? and Presumed Innocent, we fill in the gaps between shots with ease. Godard, however, makes his images and sounds more fragmentary by equivocating about the Kuleshovian cues. The background elements and lighting don’t match entirely; time seems to be skipped over; glances and facial expressions are ambivalent. Adding to these factors, lines of dialogue slip in from offscreen. Godard does present a dramatic scene taking place, but he also creates a sense that images and sounds have been pried loose from their place in an ongoing action, floating somewhat free and functioning as objects of contemplation for their own sake. The cues that Lloyd insists on and that Kuleshov plays with are ones that Godard suppresses or makes ambiguous.
I’ve mentioned this tendency in a recent entry, but to elaborate a little, consider the science lecture in Hail Mary (Je vous salue Marie, 1985). A professor who has emigrated from an Eastern bloc country is explaining his theory that life on earth began and evolved because it was directed by extraterrestrials. No establishing shot of the classroom shows us where he, Eva, and two male students are located, so we have to construct a rough sense of their positions on the basis of a few cues. As Eva, perched on a windowsill, toys with a Rubik’s cube, we hear the professor’s lecture begin to speculate on whether life could have evolved spontaneously. His remarks about sunlight coincide with a burst of sun on her face.
After the Biblical title, “In those days,” we get a series of shots that allow us to apply our mental schema of a classroom lecture: attentive students looking off, a professor at the blackboard.
Lacking an establishing shot, we can’t specify how many people are in the class, nor indeed where Eva and her classmate are sitting—since the professor looks off in several directions during his talk.
At the end of his talk he remarks, still scanning the room, that we can presume that life exists in space. “We come from there.” At that point Godard cuts to the head of another student, seen from behind. The sproingy haircut is a little explosion of yellow, and it’s accompanied by a burst of choral music. And as the shot goes on, we start to notice that the professor is pacing in the background, out of focus.
The student, whom we’ll learn is named Pascal, asks a question (at least the slight head movement suggests that it comes from him), and the professor replies. Pascal scratches his head as the professor continues, still out of focus. If I had to choose one shot that condenses Godard’s strategy of suppression in this sequence, this shot would be my candidate.
At the end of the shot, the professor asks Eva to stand behind Pascal. Cut 180 degrees and somewhat farther back to Pascal, now seen from the front. The professor’s hand brings the Rubik’s cube into the shot and Eva comes up behind Pascal as the professor passes.
Later she and the prof will become lovers, but Godard lets them meet first as simply two torsos intersecting behind Pascal. The purpose is a demonstration that a “blind” agent can be steered toward a goal through simple yes/no commands. This models the professor’s theory that an alien intelligence could have guided evolution.
Pascal will twist the facets of the cube under Eva’s hints. Godard makes this a tactile, even erotic exchange, with the close-up of her by his ear and Eva saying, “Yes,” more urgently as Pascal’s hands arrive at a solution, in the close-up surmounting this blog entry.


The next two shots of the sequence center on the prof, who has exited frame right from the “three-shot.” Now he’s at the window, recalling the initial shot of Eva; but unlike her he’s little more than a silhouette. As crashing organ music is heard, he seems to be watching the experiment from afar. The second shot, an axial cut-in, coincides with the offscreen voice of a male student: “Were you exiled for these ideas?”
“These ideas, and others,” the prof replies. He says he’ll see the class on Monday, evoking the idea that he’s dismissing the offscreen students, and he turns his head slightly, though we can’t be sure they’re on his right. This shot will be held for some time as students quiz him more about his theory, and Eva asks him if he’d like to come over for a drink some evening. But we don’t see her say it. Godard cuts to a shot of Eva at the window, bathed in sunlight, opening and shutting her eyes as she slightly lifts and lowers her head.
As we see her, we hear the rustling of people leaving (so the class was evidently larger than three). And we hear him reply to her invitation, “That’s another story [scénario].” Are Eva and the prof looking at each other? We’re inclined to say yes, but her closed eyes and tilting head suggests someone lost in contemplation rather than engaged in conversation. Here the classic facial-expression cue is made indeterminate. We have no way of knowing if the prof’s line comes from offscreen, or is displaced from another point in time; maybe he has left the room. Such displaced diegetic sound occurs elsewhere in the film.
We don’t have to decide; our indecision is the point. By pruning away the most reliable cues, Godard wins both ways. We’re kept somewhat oriented to an intelligible action: a prof sets forth his far-fetched theory of human origins and a woman in his class invites him for coffee. This side of the balance allows us to feel that a story, however sketchy, is moving forward.
But the moment-by-moment texture of the scene allows the individual shots, gestures, and sounds to drift somewhat free. Each image takes on a more intrinsic weight, and the juxtaposition of picture and sound acquires a resonance that we usually call poetic. A shot of Eva in the sun playing with the Rubik’s cube, unanchored in time (during class? before class started?), invites us to apply metaphors, especially once we learn her name. Pascal’s thorny hair suggests not only extraterrestrials but the explosion of a nova. The silhouetted prof, detached from the mechanism he has set in motion, hints at an unknown deity watching the game play out according to his rules. Why do Godard films spawn long essays built out of erudite associations? Because the narrative progression relaxes and we can weave our own connotations out of what we see and hear.
If you don’t want to go down the expanding-association route, there’s another one open. When individual moments no longer accumulate ordinary dramatic pressure, we can savor the fugitive pleasures of the separate shots (light on face, lips by ear) and the patterns they form: flipover cuts, yellow hair and yellow facets, bookended shots of Eva at the window.
Those patterns, it should be clear, depend on our sensing a bump at every shot change, looking for a way to skip across the gap that Godard creates. The same belief that meaning and effect are born of gaps impelled Kuleshov too, and perhaps even Lloyd. If we pay attention to those gaps we can feel minds—both the filmmaker’s and ours—at work in them.
(1) Lev Kuleshov, “’50’: In Maloi Gznezdinokovsky Lane,” Kuleshov on Film, trans. and ed, Ronald Levaco (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1974), 200.
(2) V. I. Pudovkin, “The Naturschchik instead of the Actor,” Selected Essays, ed. and trans. Richard Taylor (Oxford: Seagull, 2006), 160.
(3) See Kristin Thompson, Yuri Tsivian, and Ekaterina Khokhlova, “The Rediscovery of a Kuleshov Experiment: A Dossier,” Film History 8, 3 (1996), 357-367.
(4) The sequence does begin with a long shot of the café, but it is so distant, crowded, and brief that it can’t really be said to establish the spatial relationships among the several characters we see.
(5) “Sounds of Silence,” Artforum International (April 2000): 123.
A behemoth from the Dead Zone

DB here:
The first quarter of the year is the biggest slump time for movie theatres. (1) Holiday fatigue, thin budgets, bad weather, the Super Bowl, and the distractions of the awards season depress admissions. If people go to the movies, they tend to catch up on Oscar nominees, and studios don’t want to release high-end films that might suffer from the competition. But screens need fresh product every week, so most of what gets released at this time of the year might charitably be called second-tier.
Ambitious filmmakers fight to keep out of this zone of death. You could argue that the January release slot of Idiocracy told Mike Judge exactly what Fox thought of that ripe exercise in misanthropy. Zodiac, one of the best films of 2007, opened on 1 March, and even ecstatic reviews couldn’t push it toward Oscar nominations. You can imagine what chances for success Columbia has assigned to Vantage Point (a 22 February bow). [But see my 4 Feb. PPPS below.]
Yet this is a flush period for those of us who like to explore low-budget genre pieces. I have to admit I enjoy checking on those quickie action fests and romantic comedies that float up early in the year. They’re today’s equivalent of the old studios’ program pictures, those routine releases that allowed theatres to change bills often. In their budgets, relative to blockbusters, today’s program pix are often the modern equivalent of the studios’ B films.
More important, these winter orphans are often more experimental, imaginative, and peculiar than the summer blockbusters. On low budgets, people take chances. Some examples, not all good but still intriguing, would be Wild Things (1998), Dark City (1998), Romeo Must Die (2000), Reindeer Games (2000), Monkeybone (2001), Equilibrium (2002), Spun (2003), Torque (2004), Butterfly Effect (2004), Constantine (2005), Running Scared (2006), Crank (2006), and Smokin’ Aces (2007). The mutant B can be found in other seasons too—one of my favorites in this vein, Cellular (2004), was released in September—but they’re abundant in the year’s early months.
By all odds, Cloverfield ought to have been another low-end release. A monster movie with unknown players, running a spare 72 minutes sans credits, budgeted at a reputed $25 million, it’s a paradigm of the winter throwaway. Except that it pulled in $46 million over a four-day weekend and became the highest-grossing film (in unadjusted dollars) ever to be released in January. Here the B in “B-movie” stands for Blockbuster.
I enjoyed Cloverfield. It starts with a sharp premise, but as ever, execution is everything. I see it as a nifty digital update of some classic Hollywood conventions. Needless to say, many spoilers loom ahead.
If you find this tape, you probably know more about this than I do

Everybody knows by now that Cloverfield is essentially Godzilla Meets Handicam. A covey of twentysomethings are partying when a monster attacks Manhattan, and they try to escape. One, Rob, gets a phone call from his off-again lover Beth, who’s trapped in a high-rise. He vows to rescue her. He brings along some friends, one of whom documents their search with a video camera. It’s a shooting-gallery plot. One by one, the characters are eliminated until we’re down to two, and then. . . .
Cloverfield exemplifies what narrative theorists call restricted narration. (Kristin and I discuss this in Chapter 3 of Film Art.) In the narrowest case of restricted narration, the film confines the audience’s range of knowledge to what one character knows. Alternatively, as when the characters are clustered in the same space, we’re restricted to what they collectively know. In other words, you deny the viewer a wider-ranging body of story information. By contrast, the usual Godzilla installment is presented from an omniscient perspective, skipping among scenes of scientists, journalists, government officials, Godzilla’s free-range ramblings, and other lines of action. Instead, Cloverfield imagines what Godzilla’s attack would look and feel like on the ground, as observed by one group of victims.
Horror and science fiction films have used both unrestricted and restricted narration. A film like Cat People (1942) crosscuts what happens to Irena (the putative monster) with scenes involving other characters. Jurassic Park and The Host likewise trace out several plot strands among a variety of characters. The advantage of giving the audience so much information is that it can feel apprehension and suspense about what the characters don’t know is happening. Our superior knowledge can make us worry about those poor victims oblivious to their fate.
But these genres have relied on restricted narration as well. Invasion of the Body Snatchers (1956) is a good example; we are at Miles’s side in almost every scene, learning of the gradual takeover of his town as he does. Night of the Living Dead (1968), Signs (2002), and War of the Worlds (2005) do much the same with a confined group, attaching us to one or the other momentarily but never straying from their situation.
The advantages of restricted narration are pretty apparent. You can build up uncertainty and suspense if we know no more than the character(s) being attacked by a monster. You can also delay full revelation of the creature, a big deal in these genres, by giving us only the glimpses of it that our characters get. Arguably as well, by focusing on the characters’ responses to their peril, you have a chance to build audience involvement. We can feel empathy and loss if we’ve come to know the people more intimately than we know the anonymous hordes stomped by Godzilla. Finally, if you need to give more wide-ranging information about what’s happening outside the characters’ immediate situation, you can always have them encounter newspaper reports, radio bulletins, and TV coverage of action occurring elsewhere.
People sometimes think that theoretical distinctions like this overintellectualize things. Do filmmakers really think along these lines? Yes. Matt Reeves, the director of Cloverfield, remarks:
The point of view was so restricted, it felt really fresh. It was one of the things that attracted me [to this project]. You are with this group of people and then this event happens and they do their best to understand it and survive it, and that’s all they know.
For your eyes only

Restricted narration doesn’t demand optical point-of-view shots. There aren’t that many in Invasion of the Body Snatchers or the other examples I’ve indicated. Still, for quite a while and across a range of genres, filmmakers have imagined entire films recording a character’s optical/ auditory experience directly, in “first-person,” so to speak.
Again, it’s useful to recognize two variants of this narrational strategy. One we can call immediate—experiencing the action as if we stood in the character’s shoes. In the late 1920s, the great documentary filmmaker Joris Ivens tried to make what he called his I-film, which would record exactly what a character saw when riding a bike, drinking a glass of beer, and the like. He was dismayed to find that bouncing and swiveling the camera as if it were a human eye ignored the fact that in real life, our perceptual systems correct for the instabilities of sensation. Ivens abandoned the project, but evidently he couldn’t get the notion out of his head; he called his autobiography The Camera and I. (2)
Hollywood’s most strict and most notorious example of directly subjective narration is Robert Montgomery’s Lady in the Lake (1947). Its strangeness reminds us of some inherent challenges in this approach. How do you show the viewer what your protagonist looks like? (Have him pass in front of mirrors.) How do you skip over the boring bits? (Have your hero knocked unconscious from time to time.) How do you hide the inevitable cuts? (Try your best.) Even Montgomery had to treat the subjective sequences as long flashbacks, sandwiched within scenes of the hero in his office in the present telling us what he did next.
Because of these problems, a sustained first-person immediate narration is pretty rare. The best compromise, exploited by Hitchcock in many pictures and especially in Rear Window (1954), is to confine us to a single character’s experience by alternating “objective” shots of the character’s action with optical point-of-view shots of what s/he sees.
What I’m calling immediate optical point of view is just that: sight (and sounds) picked up directly, without a recording mechanism between the story action and the character’s experience. But we can also have mediated first-person point of view. The character uses a recording technology to give us the story events.
In a brilliant essay on the documentary Kon-Tiki (1950), André Bazin shows that our knowledge of how Thor Heyerdahl filmed his raft voyage lends an unparalleled authenticity to the action. Heyerdahl and his crew weren’t experienced photographers and seem to have taken along the 16mm camera as an afterthought, but the very amateurishness of the enterprise guaranteed its realism. Its imperfections, often the result of hazardous conditions, were themselves testimony to the adventure. When the men had to fight storms, they had no time to film; so Bazin is able to argue, with his inimitable sense of paradox, that the absence of footage during the storm is further proof of the event. If we were given such footage, we might wonder if it was staged afterward.
How much more moving is this flotsam, snatched from the tempest, than would have been the faultless and complete report offered by an organized film. . . . The missing documents are the negative imprints of the expedition. (3)
What about fictional events? In the 1960s we started to see fiction films that presented themselves as recordings of the events as the camera operator experienced them. One early example is Stanton Kaye’s Georg (1964). The first shot follows some infantrymen into battle, but then the framing wobbles and the camera falls to earth. We see a tipped angle on a fallen solider and another infantryman approaches.

He bends toward us; the frame starts to wobble and we are lifted up. On the soundtrack we hear, “I found my camera then.”
The emergence of portable equipment and cinema-verite documentary seems to have pushed filmmakers to pursue this narrational mode in fiction. One result was the pseudo-documentary, which usually doesn’t present the story as a single person’s experience but rather as a compilation of first-person observations. Peter Watkins’ The War Game (1967) presents itself as a documentary shot during a nuclear war, and it contains many of the visual devices that would come to be associated with the mediated format—not only the flailing camera but the face-on interview and the chaotic presentation of violent action. There’s also the pseudo-memoir film, pioneered in David Holzman’s Diary (1967). Later examples of the pseudo-documentary are Norman Mailer’s Maidstone (1971) and the combat movie 84 Charlie MoPic (1989). (4)
As lightweight 16mm cameras made filming easier, directors adapted that look and feel to fictional storytelling. The arrival of ultra-portable digital cameras and cellphones has launched a similar cycle. Brian DePalma’s Redacted (2007), yet another war film, has exploited the technology for docudrama. A digital equivalent of David Holzman’s Diary, apart from Webcam and YouTube material, is Christoffer Boe’s Offscreen (2006), which I discussed here.
Interestingly, Orson Welles pioneered both the immediate and the mediated subjective formats. One of his earliest projects for RKO was an adaptation of Heart of Darkness, in which the camera was to represent the narrator Marlowe’s optical perspective throughout. (5) Welles had more success with the mediated alternative, though in audio form. His “War of the Worlds” radio broadcast mimicked the flow of programming and interrupted it with reports of the aliens’ attack. The device was updated for television in the 1983 drama Special Bulletin.
Sticking to the rules

Cloverfield, then, draws on a tradition of using technologically mediated point-of-view to restrict our knowledge. Like The Blair Witch Project (1999), it does this with a horror tale. But it’s also a Hollywood movie, and it follows the norms of that moviemaking mode. So the task of Reeves, producer J. J. Abrams, and the other creators is to fit the premise of video recording to the demands of classical narrative structure and narration. How is this done?
First, exposition. The film is framed as a government SD video card (watermarked DO NOT DUPLICATE), the remains of a tape recovered from an area “formerly known as Central Park.” This is a modern version of the discovered-manuscript convention familiar from the nineteenth-century novel. When the tape starts, showing Rob with Beth in happy times, its read-out date of April plays the role of an omniscient opening title. In the course of the film, the read-outs (which come and go at strategic moments) will tell us when we’re in the earlier phase of their love affair and when we’re seeing the traumatic events of May.
Likewise, the need for exposition about characters and relationships at the start of the film is given through a basic premise. Jason wants to record Rob’s going-away-party and he presses Rob’s friend Hud into service as the cameraman. Off the bat, Hud picks out our main characters in video portraits addressed to Rob. What follows indicates that Hud will be amazingly prescient: His camera dwells on the characters who will be important in the ensuing action.
Next, overall structure. The Cloverfield tape conforms to the overarching principles that Kristin outlines in Storytelling in the New Hollywood and that I restated in The Way Hollywood Tells It. (Another example can be found here.) A 72-minute film won’t have four large-scale parts, most likely two or three. As a first approximation, I think that Cloverfield breaks into:
*A setup lasting about 30 minutes. We are introduced to all the characters before the monster attacks. Our protagonists flee to the bridge, where Jason dies. Near the end of this portion, Rob gets a call from Beth, and he formulates the dual goals of the film: to escape from the creature, and to rescue Beth. Along the way, Hud declares he’s going to record it all: “People are gonna know how it all went down. . . . It’s gonna be important.”
*A development section lasting about 22 minutes. This is principally a series of delays. Rob, Hud, Lily, and Marlena encounter obstacles. Marlena falls by the wayside. They are given a deadline: At 0600 they must meet the last helicopters leaving Manhattan.
*A climax lasting about 20 minutes. The group rescues Beth and meets the choppers, but the one carrying Rob, Hud, and Beth falls afoul of the beast. They crash in Central Park, and Hud is killed, his camera recording his death at the jaws of the monster. Huddled under a bridge, Rob and Beth record a final video testimonial before an explosion cuts them off.
*An epilogue of one shot lasting less than a minute: Rob and Beth in happier times on the Ferris wheel at Coney Island—a shot left over from the earlier use of the tape in April.
Next, local structure and texture. It takes a lot of artifice to make something look this artless. The imagery is rich and vivid, the sharpest home video you ever saw. The sound is pure shock-and-awe, bone-rattling, with a full surround ambience one never finds on a handicam. (6) Moreover, Hud is remarkably lucky in catching the turning points of the action. All the characters’ intimate dramas are captured, and Hud happens to be on hand when the head of Miss Liberty hurtles down the street.
Bazin points out that in fictional films the ellipses are cunning gaps, carefully designed to fulfill narrative ends—not portions left out because of the physical conditions of the shoot. Here the cunning gaps are justified as constrained by the physical circumstances of filming. When Hud doesn’t show something, it’s usually because it’s what the genre considers too gross, so the worst stretches take place in darkness, or offscreen, or strategically shielded by a prop when the camera is set down.
Mostly, though, Hud just shows us the interesting stuff. He turns on the camera just before something big happens, or he captures a disquieting image like that of the empty Central Park carriage.

At least once, the semi-documentary premise does yield something evocative of the Kon-Tiki film. Hud has to leap from one building to another, many stories above the street. He turns the camera on himself: “If this is the last thing you see, then I died.” He hops across, still running the camera, but when a rocket goes off nearby, a sudden cut registers his flinch. For an instant out of sheer reflex, he turned off the camera.
Overall, Hud’s tape respects the flow of classical film style. Unlike the Lady in the Lake approach, the mediated POV format doesn’t have a problem with cuts; any jump or gap is explained as a moment when the operator switched off the camera. Most of Hud’s “in-camera” cuts are conventional ones, skipping over a few inconsequential stretches of time. There are as well plenty of hooks between scenes. (For more on hooks, go here.) Hud says: “I’ll walk in the tunnels.” Cut to characters walking in the tunnels. More interestingly, visible cuts are rare, which again respects the purported conditions of filming. Cloverfield has much longer takes than any recent Hollywood film I know. I counted only about 180 shots, yielding an average of 24 seconds per shot (in a genre in which today’s films average 2-5 seconds per shot).
The digital palimpsest

We could find plenty of other ways in which Cloverfield adapts the handicam premise to the Hollywood storytelling idiom. There are the product placements that just happen to be part of these dim yuppies’ milieu. There are the character types, notably the sultry Marlena and the hero’s weak friend who’s comically a little slow. There’s the developing motif of the to-camera addresses, with Rob and Beth’s final monologues to the camera counterbalancing the party testimonials in the opening. There’s the final romantice exchange: “I love you.” “I love you.” The very last shot even includes a detail that invites us to re-view the entire movie, at the theatre or on DVD. But let me close by noting how some specific features of digital video hardware get used imaginatively.
I’ve already mentioned how the viewfinder date readout allows us to keep the time structure clear. There’s also the use of a night-vision camera feature to light up those spidery parasites shucked off by the big guy. Which scares you more—to glimpse the pinpoint eyes of critters skittering around you in the dark, or to see them up close in a sickly green light?
More teasing is the fact, set up in the first part, that this video is being recorded over an old tape of Rob’s. That’s what turns the opening sequence of Rob and Beth in May into a prologue: the tape wasn’t rewound completely for recording the party. Later, at intervals, fragments of that April footage reappear, apparently through Hud’s inadvertently advancing the tape. The snippets functions as flashbacks, showing Rob and Beth going to Coney Island and juxtaposing their enjoyable day with this horrendous night.
Cleverly, on the tape that’s recording the May disaster something always prepares the audience for the shift. For instance, when Jason hands the camera over, we hear Hud say, “I don’t even know how to work this thing.” Cut to an April shot of Beth on the subway, suggesting that he’s advanced fast forward without shooting. Likewise, when Rob says, “I had a tape in there,” we cut to another April shot of Beth. As a final fillip, the footage taken in May halts before the tape ends, so we get the epilogue showing Rob and Beth on the Ferris wheel in April, emerging like figures in a palimpsest.
No less clever, but also a little poignant, is the use of the fallen-camera convention. It appears once when Beth has to be extricated from her bed. Hud sets the camera down by a concrete block in her bedroom, which conceals her agony. More striking is the shot when the camera, dropped from Hud’s hand, lies in the grass, and the autofocus device oscillates endlessly, straining to hold on his lifeless face.
In sum, the filmmakers have found imaginative ways of fulfilling traditional purposes. They show that the look and feel of digital video can refresh genre conventions and storytelling norms. So why not for the sequel show the behemoth’s attack from still other characters’ perspectives? This would mobilize the current conventions of the narrative replay and the companion film (e.g., Eastwood’s Iwo Jima diptych). Reeves says:
The fun of this movie was that it might not have been the only movie being made that night, there might be another movie! In today’s day and age of people filming their lives on their iPhones and Handycams, uploading it to YouTube. . . .
So the Dead Zone of January through March yields another hopeful monster. What about next month’s Vantage Point? The tagline is: 8 Strangers. 8 Points of View. 1 Truth. Hmmm. . . . Combining the network narrative with Rashomon and a presidential assassination. . . . Bet you video recording is involved . . . . See you there?
PS: At my local multiplex, you’re greeted by a sign: WARNING: CLOVERFIELD MAY INDUCE MOTION SICKNESS. I thought this was just the theatre covering itself, but I’ve learned that no recent movie, not even The Bourne Ultimatum, has had more viewers going giddy and losing their lunch. You can read about the phenomenon here, and Dr. Gupta weighs in here. My gorge can rise when a train jolts, but I had no problems with two viewings of Cloverfield, both from third row center.
Anyhow, it will be perfectly easy to watch on your cellphone. But we should expect to see at least one pirate version shot in a theatre by someone who’s fighting back the Technicolor yawn, giving us more Queasicam than we bargained for.
(1) The only period that rivals this slow winter stretch is mid-August to October, when genre fare gets pushed out to pick up on late summer business. [Added 26 January:] There are, I should add, two desirable weekends in the first quarter, those around Martin Luther King’s birthday and Presidents’ Day. Studios typically aim their highest-profile winter releases (e.g., Black Hawk Down, 2001) for those weekends.
(2) Joris Ivens, The Camera and I (New York: International Publishers, 1969), 42.
(3) André Bazin, “Cinema and Exploration,” What Is Cinema? Vol. 1, trans. and ed. Hugh Gray (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1967), 162.
(4) Not all pseudodocumentaries present themselves as records of a person’s observation. Milton Moses Ginsberg’s Coming Apart (1969) presents itself as an objective record, by a hidden camera, of a psychiatrist’s dealings with his patients. Like a surveillance camera, it doesn’t purport to embody anybody’s point of view.
(5) Jonathan Rosenbaum, Discovering Orson Welles (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2007), 28-48.
(6) For Kevin Martin’s informative account of the film’s polished lighting and high-definition video capture, go here (and scroll down a bit). For discussions of contemporary sound practices in this genre, see William Whittington’s Sound Design in Science Fiction (Austin: University of Texas Press, 2007).

PS: Thanks to Corey Creekmur for correcting two slips in my initial post!
PPS 28 January: Lots of Internet buzz about the film since I wrote this. Thanks to everyone who linked to this post, and special thanks for feedback from John Damer and James Fiumara.
Some people have asked me to comment on the social and cultural implications of Cloverfield’s references to 9/11. At this point I think that genre cinema has dealt more honestly and vividly with the traumas and questioning around this horrendous event than the more portentous serious dramas like United 93, World Trade Center, and the TV show The Road to 9/11.
The two most intriguing post-9/11 films I know are by Spielberg. The War of the Worlds gives a really concrete sense of what a hysterical America under attack might be like, warts and all. (It reminded me of a TV show I saw as a kid, Alas, Babylon (1960), a surprisingly brutal account of nuclear-war panic in suburbia.) Spielberg’s underrated The Terminal reminds us, despite its Frank Capra optimism, that the new Security State is run by bureaucrats with fixed agendas and staffed by overworked people of color, some themselves exiles and immigrants.
I think that Cloverfield adds its own dynamic sense of how easily the entitlement culture of upwardly mobile twentysomethings can be shattered. Genre films carry well-established patterns and triggers for feelings, and a shrewd filmmaker can channel them for comment on current events—as we see in the changing face of Westerns and war films in earlier phases of Hollywood history.
On this point, Cinebeats offers some shrewd responses to criticisms of Cloverfield here.
 Finally: In the new Creative Screenwriting an informative piece (not available online) indicates that the initial logline for Vantage Point on imdb is misleading. Screenwriter Barry Levy planned to present the assassination from seven points of view, but reduced that to six. As for my speculation that video recording/replay would be involved, a production still seems to offer some evidence. Shall we call it the Cloverfield effect? The same issue of CS has a brief piece on the script for Cloverfield.
Finally: In the new Creative Screenwriting an informative piece (not available online) indicates that the initial logline for Vantage Point on imdb is misleading. Screenwriter Barry Levy planned to present the assassination from seven points of view, but reduced that to six. As for my speculation that video recording/replay would be involved, a production still seems to offer some evidence. Shall we call it the Cloverfield effect? The same issue of CS has a brief piece on the script for Cloverfield.
PPS 30 January: Shan Ding brings me another story about the making of Cloverfield, and Reeves is already in talks for a sequel, says Variety.
PPPS 4 February: A recent story in The Hollywood Reporter offers a nuanced account of how Hollywood is rethinking its first-quarter strategies. Across the last 4-5 years, a few big releases have done fairly well between January and April; a high-end film looks bigger when there is less competition. The author, Steven Zeitchik, suggests that the heavy packing of the May-August period and the need for a strong first weekend are among the factors that will encourage executives to spread releases through the less-trafficked months. I hope, though, that tonier fare won’t crowd out the more edgy, low-end genre pieces that bring me in.
PPPPS 8 February: How often has a wounded Statue of Liberty featured in the apocalyptic scenarios of comics and the movies? Lots, it turns out. Gerry Canavan explains here.
Your trash, my TREASURE

DB here:
More informative about American history than Fahrenheit 9/11. More brain-teasing, and far more enjoyable, than I’m Not There. Less graphically violent than almost any other movie you’re likely to see. What else could I be talking about but National Treasure: Book of Secrets?
Jerry Bruckheimer is, in my view, the most astute producer now working in Hollywood. I could cite many proofs, but let’s stick just to the first National Treasure. Here’s a movie with no pop music, no cusswords, no naked ladies, no drugs, no screwing, and scarcely any violence. (One bad guy accidentally falls to his death down a deep black hole.) When it came out—you can verify this by asking Kristin—I said that it was the ideal movie for grandparents to take the grandkids to. The man who gave us Bad Boys and CSI has realized that there’s a market niche for the PG-rated action film. So we get an amiable romp that mixes together Freemasons, the Knights Templar, the Rosicrucians, Ben Franklin, and for all I know Judge Crater, Atlantis, and the Lindbergh baby.
My colleagues, students, and wife think I’m nuts to like National Treasure. In defense I could point to evocative images like the one surmounting today’s entry, the superimposition of Grandpa Gates’ eye on a pyramid as a condensation of the Masonic/ monetary/ paternity motifs swarming through the movie. But I needn’t strain so far. The pleasures are more elemental.
Secret codes, knights, lost treasure, rich sinister Brits, really deep holes filled with cobwebs, and a cipher on the back of the Declaration of Independence—what’s not to like? All of this is pulled together by a hero who is actually intelligent and knowledgeable. He’s a nerdy patriot (another Bruckheimer touch, reminiscent of The Rock) who can turn a priceless hoard over to the US government without a quiver. How often do you find a story whose protagonists are people who know and care about the past? In the DVD supplement, an alternative ending shows schoolboys eyeing the recovered Declaration. One wonders if there’s really a treasure map on the back. The other mutters, “It’s a plot to make us learn history.” What if he is right?
Of course some will say Spielberg/ Lucas/ Kasdan did it already with Raiders. But that was a knowing effort to relive somebody’s phantom vision of B serials. Besides, does anybody believe that Indy knows as much about archaeology as Ben Gates does about nearly everything? If it recycles anything, National Treasure amounts to a revival of the wholesome 1950s Disney adventure movie. What Treasure Island (1950), Davy Crockett (1955), and The Great Locomotive Chase (1956) were for an earlier generation, National Treasure is for today’s twelve-year-olds. It compares favorably with those entries in verve, wit, and speed. (How it gets that speed is a topic I take up in “The Hook,” a new online essay. That piece tries to show that even if you don’t like the movie, its narration provides a nifty tutorial in some strategies of Hollywood storytelling.) My only regret is that in the epilogue NT 1 actually uses, Ben and Abigail are given a mansion and Riley gets a cherry-colored Ferrari. That’s a bit crass. Knowledge, selflessness, and pluck should be their own rewards.
Your correspondent regrets to report that Book of Secrets is not up to its predecessor. It’s still quite entertaining, and it has some transitions as clever as those I talk about in the aforementioned essay. The premise, involving the Lincoln assassination and the besmirched reputation of Ben’s ancestor, is workable and even moving, grounded as it is in parallel father-son reconciliations. The clue-sequences are more ingenious than, say, the simple linear connectives in Bourne Ultimatum. There are a few nifty compositions (e.g., a reflection of Ben in a windshield) and some nicely-timed reaction shots of Riley and Ben’s dad. (Someday, I swear, I will blog about reaction shots, a key to Hollywood storytelling.) I liked the way that the slapped-together family of the first installment—Dad Ben, Mom Abigail, Riley the kid—is expanded to include the old folks. Of course I regard the rekindled affection between Ben’s father and mother as backup for my Grandparents-Grandkids Hypothesis.
Still, the sequel lacks the throwaway byplay between Ben and Riley and the clever misdirection of certain scenes, principally the extended heist at the National Archives reception. The plot is somewhat too stuffed with incident, jerking us abruptly from continent to continent. (Will American filmmakers please give up the informative title card “Paris, France”?) It seemed to me as well that Ben’s reasoning involved not so much high-context inferences as inspired guesswork. The contrived quarrel in Buckingham Palace between Ben and Abigail is nothing like as enjoyable as Ben’s snippy requests for silence after they’ve lifted the Declaration in NT 1. Sequels don’t have to be a step down from the original, as this entry has argued at length, but alas NT 2 is.
Don’t, however, tell me that the thing is preposterous. Friend, the genre is built upon the preposterous. Preposterosity is its middle name. Jules Verne, H. G. Wells, and Edgar Rice Burroughs all spun their yarns out of hopelessly far-fetched premises. There is nothing as nutty in this franchise as the idea that Tarzan could teach himself to read. The task is always to make a crazy logic out of a farrago, and this the new installment does, skipping from pre-Columbian inscriptions to the idea that, as Riley phrases it, “Mount Rushmore was a coverup.” I buy that, and I completely buy the idea that our Chief Executives pass along a book recording all the Big Secrets in US history. The only item I couldn’t swallow was the prospect that America might elect a President who majored in architectural history.
Compensating for the feature’s drawbacks were the hors d’oeuvres at my screening. Now when we go to the multiplex we get Bonus Supplements, just like in the old days of trailers, shorts, and educational featurettes. My extras were a trailer for the upcoming Pixar release Wall*e, a trailer for the new Narnia installment (produced by our old compadre Mark Johnson), and even a Goofy cartoon, How to Hook Up Your Home Theater. Brainwashed by TV ads, the Goof races to the chain store Shiny $tuf to get his gigantoscreen and peripherals, under signs reading: “Obey—Buy!” At home, he has to sweep a faded pic of Uncle Walt off his sideboard to clear space for the new gear, which arrives in a blizzard of styrofoam peanuts. As fast as a Clampett and as silly as a classic Goofy, the cartoon includes his memorable “Wah-yoo-yah!” holler as he is launched into space.
How to Hook Up Your Home Theater even looked hand-drawn. If it’s on the Book of Secrets DVD, I’ll buy that disc. Hell, I probably will anyhow.
PS 7 January Thanks to Greg Thow for calling my attention to a nice background interview on the making of the Goofy short.
PPS 8 January Thumbing through folders–real ones, made of manila–I find that agents use National Treasure as the model of a “four-quadrants” movie.

























