Archive for the 'National cinemas: Denmark' Category
12 hours, Ritrovato time
DB here:
Reporting on the magnificent Cinema Ritrovato festival at Bologna has become a tradition with us, but it’s become harder to find time during the event to write an entry. The program has swollen to 600 titles over eight days, and attendance has shot up as well; the figure we heard was over 2000 souls. The organizers–Peter von Bagh, Gian Luca Farinelli, and Guy Borlée–have responded to requests for more repetition of titles by slotting shows in the evening, some starting as late as 9:45. (You can scan the daily program here.) There are as well panel discussions, meetings with authors, and some unique events, such as carbon-arc outdoor shows, the traditional screenings on the Piazza Maggiore, and Peter Kubelka’s massive and mysterious Monument Film. Add in time to browse the vast book and DVD sales tables, and the need to socialize with old friends.
In all, Ritrovato is becoming the Cannes of classic cinema: diverse, turbulent, and overwhelming. How best to give you a sense of the tidal-wave energy of the event? I’ve decided to take off one morning and write up just one day, Monday 29 June. I don’t know when Kristin and I will find time to write another entry, for reasons you will discover.
9:00 AM: Ned Med Vaabnene! (Lay Down Your Arms!, 1914) was a big Danish production, based on a popular anti-war novel by the German Bertha von Suttner. It’s a remnant of the days when the rich went to war along with the common folk. (Sounds quaint in today’s America, where the elite have other priorities.) The Nordisk studio specialized in “nobility films,” melodramas that show the upper class brought low by circumstances; Dreyer’s The President (1919) is another example. The film, directed by Holger-Madsen, shows a family devastated by war and its aftermath. It’s shot in tableau style, with the restrained acting and sumptuous, light-filled sets characteristic of Nordisk. The combat scenes are remarkably forceful, but the most harrowing scene, for me, is the shot showing a battlefront hospital, with exhausted nuns and wounded men strewn around the shot–a tangle of limbs and heads.
Premiered soon after the Great War broke out, Lay Down Your Arms! anticipates Nordisk’s wartime policy. Denmark was a neutral country, and the Danish industry depended on both the German and the American markets. As a result, most of the films studiously avoided taking sides. After the war, with the revival of the German industry and the circulation of American films in Europe, Nordisk lost its powerful position in the international market.
The entire film is available for viewing online at the Danish Film Institute site.
Programmer Mariann Lewinsky, in charge of the “100 Years Ago” thread, wisely included other pacifist films from the mid-teens. One of the high points was the evening screening, on the Piazza Maggiore, of the fine Belgian film Maudite soit la guerre (1914), in the hand-colored version I discussed some years back. Not by accident, I suspect, Lay Down Your Arms! featured several Lewinsky dogs.
10:30 AM: Werner Hochbaum was an unknown name to me, but after seeing Morgen beginnt das Leben (Life Begins Tomorrow, 1933), I realized that was my loss. This story of a cafe violinist released from prison is a sort of anthology of 1920s International Style devices: canted angles, rapid montages, City Symphony passages, flamboyant camera movements, multiple-image superimpositions, and huge close-ups of faces, hands, and objects. The work on sound is no less ambitious, with voice-overs, sound motifs (a carousel, a canary’s call-and-response to a chiming doorbell), offscreen dialogue, and harsh auditory montages of traffic and city life. Everything from Impressionist subjective-focus point-of-view to Expressionist shadow work comes into play.
The plot is gripping throughout. At first we don’t know why the violinist was imprisoned, and we learn about the case first from his gossiping neighbors (excellent run of whispers during fast-cut close-ups of housewives), then from his own flashbacks, which build up to a revelation of the murder he committed. Threaded with all this is another uncertainty: Has his wife begun a love affair while he was in jail? Giving us only glimpses of her life as a cafe waitress, Hochbaum leads us to suspect that he will come home to more misery–and perhaps another temptation to murder.
Along with all this were arresting side scenes of cafe life, like a fat woman ordering up a gigolo to dance with her, reminiscent of Georg Grosz and the New Objectivity’s cynical portrait of daily desperation. It’s a lot to pack into 73 minutes, but Morgen beginnt das Leben succeeds smoothly and made me want more. Alex Horwath‘s introduction confirmed that this is a director we should know better. We can hope that a DVD edition is coming soon.
Noon: A packed house for the panel of three American studio archivists: Schawn Belston of Twentieth Century Fox, Grover Crisp of Sony, and Ned Price of Warners. Too many ideas to summarize here, but one that emerged: Digital tools are great for restoration, not so reliable for preservation.
Ned (left) emphasized that now scanners are very sensitive to the oldest negatives, with their shrinkage and warpage. But Ned pointed out that today’s monitors don’t often render the full color scale needed to respect film’s tonal range, so that weak monitors mean that we are “working blind” and may “bake in” flaws that will be evident when display devices improve. Likewise, low bit-depths (often only 10-bit) in outputting to film for preservation can cause problems later. Grain reduction is another big problem. Grover (center) added: “When you do anything to grain, you’re denaturing the film.”
On the restoration front, Schawn showed clips from the 1959 Journey to the Center of the Earth, first from a beautiful photochemical restoration of twelve years ago, then from a recent digital one. To my eye, the warm skin tones of the 35mm image were more attractive than the almost porcelain surfaces of the digital version, but the latter was sharper and contained a healthy amount of grain. Grover screened A/B comparisons of the main titles of Only Angels Have Wings and Vaghe stelle dell’Orsa (Sandra ), both of which showed how handily digital restoration creates a rock-stable image, without the jitter and weave unavoidable with a strip of film.
All the panelists agreed that digital restorations are rapidly improving; ones finished only a few years ago could now be done better. A major problem coming up is that younger restoration workers know the digital tools better than the look and feel of photochemical, particularly the surface of older films. Grover recalled that one eager techie added flicker to a Capra silent because he thought that was how old movies looked.
1:15 PM: Hurried lunch with Schawn. Main topic: The Grand Budapest Hotel, but also the vagaries of the DVD and Blu-Ray market.
 2:30 PM: Ritrovato has mounted an ambitious William Wellman series, and though I’d seen most of the films on the program, I had to catch two 1920s titles.
2:30 PM: Ritrovato has mounted an ambitious William Wellman series, and though I’d seen most of the films on the program, I had to catch two 1920s titles.
You Never Know Women (1926) is an exercise in good old classical storytelling. The plot presents Vera (Florence Vidor), star of a troupe of Russian entertainers, momentarily entranced by a no-good millionaire who wants to seduce her. The magician of the troupe, Norodin (Clive Brook) loves her, but she’s unaware of her feelings for him until the Lothario’s true nature is exposed. El Brendel adds spice as a clown devoted to his pet duck.
Variety‘s review was ecstatic, claiming that “Wellman at the megaphone lifts himself into the ranks of select directors with by his handling of this story, for his direction is never obvious or old-fashioned.” I’ll say. Filled with running gags, seesawing conflicts, and motifs (Ivan’s skill at knife-throwing, the expletive, “Ridiculous!”), You Never Know Women has a headlong pace. With nearly a thousand shots in 70 minutes, it relies on glances, gestures, and reactions to channel the dramatic flow. It needs only three expository titles, letting its 100 or so dialogue titles pinpoint key emotional transitions. In anticipating the sound cinema that was just around the corner, You Never Know Women resembles the more famous Beggars of Life (1928, given pride of place at Ritrovato), which as I recall uses dialogue titles exclusively.
The Man I Love (1929) tells the familiar story of a prizefighter who, as he rises in the game, leaves his loyal woman behind. As an early sound film, it relies on multiple-camera shooting for extended dialogue scenes, but Wellman enlivens the staging with unusual angles, including a view of a quarrel seen through a window in a dressing-room door. The Man I Love boasts the sort of ambitious, somewhat bumpy tracking shots we sometimes find in early talkies. One swaggering camera movement takes us from the locker room into an arena, down the aisle, past the ring, and to Dum Dum’s anxious wife in the crowd, a sketchy prefiguration of the celebrated Steadicam movement in Raging Bull. The fight scenes, not requiring sync sound, are shot with brio, while the dialogue scenes are extremely well-miked, allowing for fairly fast line readings and varied volume and emphasis in the voices.
Gina Teraroli and David Phelps, along with other colleagues, have assembled a wide-ranging dossier on Wellman’s work that serves as a fine complement to the Ritrovato thread.
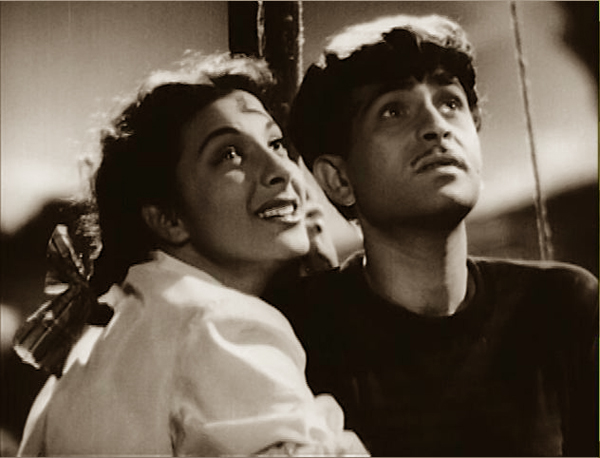
5-something PM: One of the things in the first edition of our Film History: An Introduction that made me proud was the inclusion of sections on Indian cinema, a subject usually ignored in textbook surveys. I remember in the late 1980s and early 1990s watching the 1950s-1960s classics of Hindi filmmaking with a sense of discovery: How could we not have known this invigorating tradition? It was therefore with a sense of homecoming that I visited Raj Kapoor’s Awara (“The Vagabond,” 1951), in a pretty sepia-tinted print.
The young ne’er-do-well Raj (no last name, and this is important) is on trial for attacking a judge in his home. A female lawyer, Rita, takes up his defense and urges the judge, on the witness stand, to tell why he expelled his wife from his home many years ago. The wife had been kidnapped by the gangster Jagga, and the judge assumed that the child she was now expecting was Jagga’s. Before the courtroom, Rita recounts up the story of how young Raj, actually the judge’s legitimate son, took up a life of crime. To add spice, Rita is the judge’s ward and Raj’s lover.
No coincidence, no story, they say, and Awara offers plenty of timely misunderstandings and improbably neat encounters. No matter. We’re told that TV narrative, by stretching its tale over several hours, can introduce novelistic breadth, but so can Indian classics of the 1950s. This one takes us across twenty-four years and as many ups and downs as a mini-series might offer. Not to mention Kapoor’s vigorous visual style, with huge sets, vivacious fantasy sequences, and traces of 1940s Hollywood hysteria (chiaroscuro, fluid track-ins to overwrought faces, even thunder and lightning in the distance). Here Raj, about to stab the judge, shatters the childhood picture of Rita; her simple gaze checks his moment of revenge.
Then there are the songs, lusciously sung by Lata Mangeshkar and Mukesh. Of course the sprightly “Awara Hoon” is the official classic and Kapoor’s signature tune, but this time around my favorite was the duet, “I wish the moon…,” with Rita asking the moon to look away and Raj asking it to turn to him. With its glamorized social realism, its tale of a good boy gone wrong, unjustly punished, and eventually redeemed, and its primal themes of mothers, fathers, and sons, Awara is a milestone in the world’s popular cinema…. and just one of several Indian classics in this year’s Ritrovato.
That was one day. Now I’m off to…what? Polish films in widescreen? The Riccardo Freda retrospective? The rare Ojo Okichi? Or maybe the restored Oklahoma!? In any case, this afternoon an incontro on Nicola Mazzanti‘s book 75000 films, and tonight Guru Dutt’s glorious Pyaasa.
I tell you, it’s hard to keep up, running on Ritrovato time.
Nargis and Raj Kapoor sing to the moon in Awara.
Silent films, old and new
Blancanieves
Kristin here:
February and March have been good to silent cinema. Time for a round-up of some highlights as we impatiently anticipate Il Cinema Ritrovato, coming up in a little over two months.
Publications on Albert Capellani
In reporting on the 2010 and 2011 programs of Il Cinema Ritrovato, I highlighted one of the festival’s major revelations, that of the silent films of Albert Capellani. These generous doses of Capellani’s splendid films were put together by Mariann Lewinsky, who realized his importance after she included some of his shorts in her annual “Cento Anni Fa” programs. In my entries I argued that Capellani was revealed as one of the early cinema’s great masters. (The 2010 entry is here, and the 2011 one here.)
Not surprisingly, during the intervening years, scholars have been busy researching Capellani’s films and career. March 6 to 24 saw a major retrospective at the Cinémathèque Française. (Information on the program is still available online, as is a detailed press release.) Shortly before it began, the first biography appeared: Christine Leteux’s Albert Capellani: Cineaste du Romanesque, with a foreword by Kevin Brownlow.
Leteux discovered Capellani in May of 2012, thanks to seeing Notre-Dame de Paris and Les Misérables at the Forum des Images in Paris. Setting out to learn more about the filmmaker, she realized how thoroughly his memory had nearly vanished from film history. She sought out and received the cooperation of his grandson, Bernard Basset-Capellani, whom she describes as “intarissable” (inexhaustible) on the subject.
The result is a solid, traditional biography, with chapters mostly organized around the companies for which Capellani worked (Pathe, SCAGL, World, Mutual, and so on) and some of his key films (Les Misérables, The Red Lantern). The prose style is easily readable French, at least to someone like me with an average knowledge of the language. For an interview with Leteux concerning the book, see here.
The book is on sale at the Cinémathèque’s shop, which unfortunately does not sell online. It was supposed to be available on Amazon.fr, but so far is not. The easiest way for those outside France to order it is through three third-party book-sellers on amazon.fr, all offering it at the cover price of 14.90 €. Leteux’s book is a vital source for anyone interested in early cinema.
I was pleased to see that the last chapter ends with some quotations from my second entry on Capellani, ending with “With the end of the main retrospective, however, it is safe to say that from now on anyone who claims to know early film history will need to be familiar with Capellani’s work.”
The book includes a filmography and list of films available on DVD. These include a new one, a restoration of The Red Lantern by our friends at the Cinematek in Brussels, available on Amazon.fr or directly from the Cinematek’s shop.
The French-language historical journal on cinema, 1895, timed its March, 2013 issue to coincide with the Cinémathèque’s retrospective. It is entirely devoted to Capellani. I have not had a chance to see it yet, but the table of contents is available here. The only online purchasing source for individual issues I have found is here; the page gives a lengthy summary of the contents.
Mariann continues to search for more surviving prints for restoration and eventual inclusion in future editions of Il Cinema Ritrovato. She has sent me some tantalizing news about recent discoveries and restorations. There will be a third Capellani season in 2014. This will probably include some of the director’s American films: Social Hypocrites (now restored), Flash of the Emerald (the one surviving reel), Inside of the Cup (surviving but so far with no projection print), Eye for Eye (two surviving reals), Sisters, and the French film Le Nabab. Other possible restorations include House of Mirth, La belle limonadiere, and Oh Boy!
A description of the 2013 Ritrovato festival is available here.
Nanook and friends
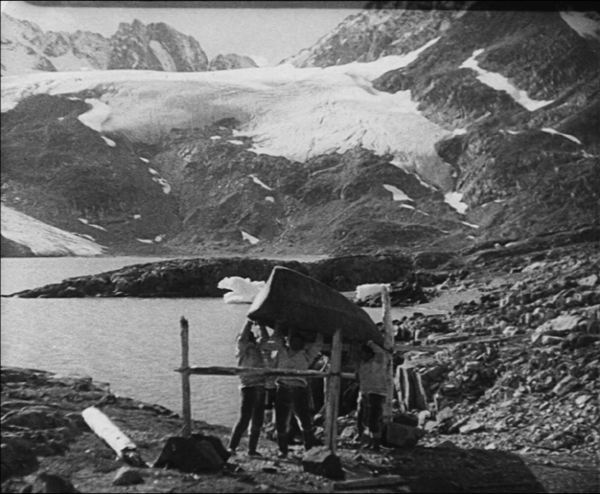
Early this year we posted our annual list of the ten best films of ninety years ago. It featured the classic early documentary, Robert Flaherty’s Nanook of the North. In March our friends at Flicker Alley released a two-disc Blu-ray edition of Nanook paired with the 1934 Danish feature, The Wedding of Palo (Palos Brudefærd). The latter is one of those titles that one occasionally encounters on the fringes of older historical surveys, but it has been difficult indeed to see. This new print is a 2012 restoration from a George Eastman House original 35mm nitrate copy.
 Nanook is familiar enough, but The Wedding of Palo is not. It was made by the Danish explorer and anthropologist Knud Rasmussen, who appears in a brief introductory passage. Clearly he was influenced by Flaherty’s work. He combines a simple fictional narrative with documentary scenes of traditional Inuit life in eastern Greenland. The basic story involves the heroine Navarona, whose brothers are reluctant to lose their housekeeper by allowing her to marry. Two men of the tribe court her and come into violent jealous conflict. Interjected are sequences of a salmon hunt, a festival, a traditional song duel between the two rivals, and a polar-bear hunt. The staged dialogue scenes involve sound recording, with no subtitles but the occasional brief intertitle to translate.
Nanook is familiar enough, but The Wedding of Palo is not. It was made by the Danish explorer and anthropologist Knud Rasmussen, who appears in a brief introductory passage. Clearly he was influenced by Flaherty’s work. He combines a simple fictional narrative with documentary scenes of traditional Inuit life in eastern Greenland. The basic story involves the heroine Navarona, whose brothers are reluctant to lose their housekeeper by allowing her to marry. Two men of the tribe court her and come into violent jealous conflict. Interjected are sequences of a salmon hunt, a festival, a traditional song duel between the two rivals, and a polar-bear hunt. The staged dialogue scenes involve sound recording, with no subtitles but the occasional brief intertitle to translate.
As in Nanook, the non-professional actors are remarkably natural, especially the “actress” portraying the heroine. There is a cute young boy brought in at intervals for comic appeal, and the members of the village seem always to be laughing and enjoying a suspiciously carefree life. The film has the advantage of more spectacular scenery than that in Flaherty’s film, with huge mountains and glaciers in place of the vast ice-covered vistas (see bottom image).
As usual, the Flicker Alley team has gone beyond the call of duty with this release. It includes not only the two features, but six bonus films, as described in the press release:
Nanook Revisited (Saumialuk) by Claude Massot was made in the same locations used by Flaherty. It shows how Inuit life changed in the intervening decades, how Flaherty consciously depicted a culture which was then already vanishing, and how Nanook is used today to teach the Inuit their heritage. Nanook Revisited was produced in 1988 on standard definition video for French television. Dwellings of the Far North (1928) is the igloo-building sequence of Nanook re-edited and re-titled as an educational film; Arctic Hunt (1913) and extended excerpts from Primitive Love (1927) are by Arctic explorer Frank E. Kleinschmidt; Eskimo Hunters of Northwest Alaska (1949) by Louis deRochemont shows many activities seen in Nanook thirty years after, and Face of the High Arctic (1959) depicts the ecology of the region, produced by the National Film Board of Canada.
Altogether, the films run an impressive 281 minutes. There’s also a booklet with excerpts from Flaherty’s book, My Eskimo Friends, an essay by Lawrence Millman, “Knud Rasmussen and The Wedding of Palo,” and notes on the films.
Snow White and the Seven (?) Bullfighting Dwarves
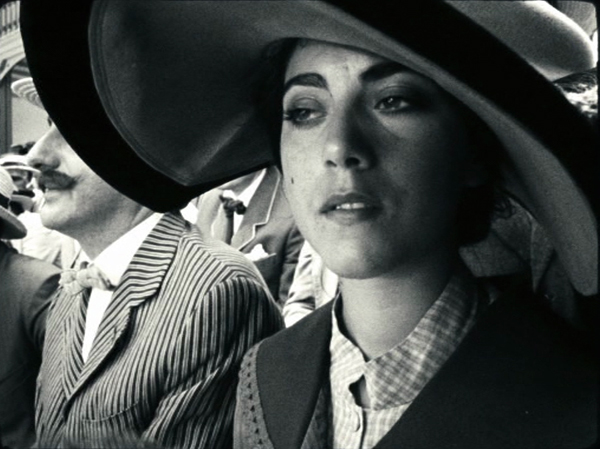
In 2011, a French film, The Artist, gained huge attention in the infotainment media as a modern version of silent cinema, winning yet another Best Picture Oscar for the Weinstein brothers. It was a reasonably successful imitation of mid- to late 1920s cinema during the transition to sound. Now a much better modern silent film has arrived, Pablo Berger’s Blancanieves, a loose version of the Snow White story transposed to 1920s Spain. A famous bullfighter is paralyzed after being gored in the ring. His wife dies in childbirth and his scheming nurse marries him. She keeps his daughter, Carmen, away from her father by setting her to work as a downtrodden servant in his country estate. Upon her father’s death, the evil wife schemes to have her killed, and she escapes to the protection of a troupe of six bullfighting dwarves who, possessing uncertain arithmetic skills, bill themselves as seven bullfighting dwarves.
While The Artist was a fairly good imitation of 1920s Hollywood filmmaking, Blancanieves is a pastiche of the 1928-29 era of European silent cinema. It draws on what I have termed the International Style of filmmaking, a late 1920s blend of influences from the French Impressionism, German Expressionism, and Soviet Montage movements. One could almost pass it off as a genuine film of the era.
At times there are subjective effects à la Impressionism. A superimposition conveys Carmen’s memories of her father’s crucial instructions to her, and superimposed images of hands waving handkerchiefs present the enthusiam of the crowd’s plea for the bull to be pardoned.
This was also the period in which the power of the wide angle lens, particularly in close-ups and in low-angle shots, was exploited, initially in Soviet cinema and then all over Europe. Blancanieves is full of such shots, as in the frame at the top of this entry and in these two shots from the opening scene:
There are also montage sequences, building up to flurries of very short shots. This accelerated-editing technique is typical of both Soviet and French filmmaking of the era.
The too-frequent use of handheld camera in Blancanieves detracts somewhat from the feeling of authenticity. In the late 1920s, cameras were too heavy to be handheld. They could be strapped to the body of the cinematographer with harnesses, but that creates a subtly different look. And during the late 1920s, shots with the camera holding on a character while the background spins around behind him or her would have been achieved by placing both camera and actor on a large turntable. (This effect apparently was pioneered in Germany in the mid-1920s). But the occasional dramatic lighting effects, particularly in the climactic scene, are distinctly reminiscent of German cinema.
In general, the narrative is charming and amusing. The heroine’s pet rooster provides exactly the sort of comic relief that is common in films of the 1920s, and the story has an effective fairy-tale quality. I found the ending a bit disappointing and certainly not typical of the films of the 1920s. Still, Berger has clearly watched an enormous number of 1920s European films and absorbed their styles. He can imitate the International Style remarkably well, telling a tale that is appropriate to the 1920s and yet has a touch of humor that doesn’t belittle the silent era.
Blancanieves was released in the US on March 29 and is currently making the rounds of art-houses and festivals.
Other entries discussing the International Style and wide-angle filming at the end of the silent era can be found here and here.
The Wedding of Palo
Sometimes two shots . . .
The Mormon’s Victim (1911).
DB here:
. . . just knock you out.
Last summer during a trip to the Royal Film Archive of Belgium I came across a single camera setup that bloomed like a flower in an almost casual way. This entry is in the same spirit, but there’s nothing casual about this cut. I spotted it during my current visit to the Danish Film Archive in Copenhagen.
Nina Gram is engaged to Sven Berg, best friend of Nina’s brother Olaf. But Andrew Larsson, a Mormon, fascinates Nina with his courtliness and his gripping sermons. One night, during a visit to her family’s home, Larsson gets Nina alone while Sven, Olaf, and others are playing cards in another room. She’s starting to succumb to Larsson’s charm offensive (though we think he has offensive charm).
As The Mormon’s Victim (Mormonens Offer, 1911; Nordisk Films, directed by August Blom) develops, Larsson will induce Nina to flee to Utah with him, where he’ll keep her prisoner. Sven and Olaf will track them down by train, ship, and auto, the entire flight and pursuit joined through crosscutting reminiscent of Griffith. The Mormon’s Victim has several memorable shots, including some striking ones taken from a car. But in particular there’s this cut. The two shots surmount today’s entry.
A full shot shows Larsson and Nina in the parlor. Earlier in the scene Sven has left the card game in the distant room to check on what his fiancée is up to. He comes forward hesitantly; this is partly to express his vague worries about Larsson, but it’s also Blom’s way of making sure we know it’s Sven in the rear of the tableau. When Sven returns to the game, he settles in directly behind Nina and Larsson, so that he becomes the most visible figure at the card game.
When Larsson entices Nina away from the piano, they place themselves on the settee in the foreground. And in my first image up top, we can see solid, oblivious Sven right behind them. A blow-up of that area of the shot is on the right.
Then Blom cuts directly in. The axial cut was the most frequent sort of editing found within scenes at this period, and Blom’s cut is more or less along the camera axis, though displaced a bit to the right. The result is a medium two-shot of Larsson staring almost hypnotically at Nina and her responding with rising passion.
 You see where I’m going with this. There’s actually a third person in the shot. Sven is still sitting behind them, but now even more tightly sandwiched between the faces–a tiny figure but fully discernible in the 35mm print. On the right I enlarge that portion of the image for you. Dead center, Sven’s tiny head floats between their profiles like a bubble from Nina’s lips or a rose between her teeth.
You see where I’m going with this. There’s actually a third person in the shot. Sven is still sitting behind them, but now even more tightly sandwiched between the faces–a tiny figure but fully discernible in the 35mm print. On the right I enlarge that portion of the image for you. Dead center, Sven’s tiny head floats between their profiles like a bubble from Nina’s lips or a rose between her teeth.
This is a remarkable shot. Since Nina eventually turns away and refuses Larsson’s kiss, we’re tempted to say that the shot creates a visual metaphor, suggesting that Sven “comes between” them. Fair enough, especially since the Danes have the same figure of speech (at komme i mellem). But I’d also want to signal how this possibility of thinly-sliced depth fits smoothly into the tableau style I’ve discussed many times on this blog and in my recently posted video lecture. It relies on hyper-precise staging in depth, accentuated by the axial cut (always a cut that accentuates depth).
It’s all the more remarkable because in those days, the camera viewfinder was mounted alongside the lens. We’re so used to reflex viewing–that is, seeing exactly what the lens of our camera or phone is framing–that we tend to forget that until the 1960s, in most cases a cinematographer had to compose the shot allowing for the parallax difference between the viewfinder and the lens. True, in most tableau shots the camera is far enough back to give some leeway for background planes, and some cameras could swivel (“toe in”) the viewfinder inward as the framing got closer. But this scene remains an extraordinary piece of filmmaking. The cinematographer Axel Graatkjaer, only twenty-six when he shot this film, deserves credit for pulling off a rare stunt.
The Mormon’s Victim is yet another example of the great variety and boldness of the cinema of the 1910s. Had I known it, I would probably have squeezed it into my video lecture, “How Motion Pictures Became the Movies.” Maybe I can work it into the followups I plan to post later this year. In the meantime, take this as another instance of why we should thank film archives for preserving fairly obscure films that have a lot to teach us about what talented creators have done with our favorite medium.
Ron Mottram surveys the local films of this period in his indispensable The Danish Cinema before Dreyer. For more on the tableau style, see the lecture I just mentioned, along with the blog entries in the category. I have more on Danish films and the tableau tradition here, and I discuss that tradition as a background to Dreyer in an essay on the Danish Film Institute’s Dreyer site.
Thanks to Thomas Christensen and Mikael Braae of the archive for all their help. I have devoted other entries to their archive and Danish film culture, but this might be the most relevant today.
Mikael Braae surveys a recently received collection of over 400 35mm film prints. He’s in the process of sorting and examining them. There are still big 35mm collections out there!
More of the world in a multiplex: another dispatch from Vancouver
Kristin here:
Latin America
In my first report, I mentioned that the Iranian film A Respectable Family was an unexpected gem. I’ve come across another, the Brazilian film, Neighboring Sounds (2012). It has a remarkable formal device that unfortunately I can’t disclose without ruining the film for those who haven’t seen it. It’s a technique that takes a while to figure out, since it’s cumulative. (Fortunately, unlike with A Respectable Family, I have yet to find a review or program note that mentions it.)
The film is set in Recife, the fifth largest city in Brazil. It centers around members of two families living in a complex of smaller, older houses surrounded by new condo high-rises that will eventually swallow the entire area. (The image above vividly shows the juxtaposition.) The divide between rich and poor is extreme, however, and the residents live in fear of crime, with elaborate gates and with grilles over their windows. Suspense is generated when a small group of men offer their services to provide security for the block, and once they are hired, we are left for a long time to wonder whether this is a cover for some other devious purpose.
The film is beautifully shot, taking advantage of the abstract compositions created by the modern apartment blocks and their glass windows and doors. As director Kleber Mendonça Filho says in the online press kit, “Architecture gone wrong is a nuisance, but extremely photogenic.”
The film’s title is taken literally, with many layers of offscreen sounds from nearby houses and streets forming much of the soundtrack. The complex use of Dolby Surround makes it especially desirable to view and listen to this film in a theater.
Neighboring Sounds has been picked up for US distribution by the Cinema Guild, which has handled other films we’ve enjoyed here in Vancouver , most notably Once upon a Time in Anatolia and The Strange Case of Angelica (and written about here and here, both available on DVD and Blu-ray.)
The Chilean film No (2012), starring Gael Garcia Bernal, has already gained a high reputation on the festival scene. (Like A Respectable Family, it was shown in the Directors’ Fortnight at Cannes.) David and I both thought it lived up to its buzz.
The plot deals with the 1988 referendum as to whether dictator Augusto Pinochet would remain in power. The side campaigning for the “no” vote was allowed a single 15-minute TV commercial each evening. Bernal plays a successful director of TV ads, Rene, who is lured into devising this commerical; he’s introduced showing off his latest spot for “Free” cola. He conceives of a campaign based on breezy optimism, with musical numbers (below right) and shots of cheerful workers acting as if Pinochet is already out of office. His tactics disgust several of the left-wing party leaders, as well as Rene’s estranged wife.
Technically the film is cleverly done. It was shot on old-fashioned U-matic video and shown in Academy ratio (not exactly reflected in these frames from the online trailer). Fuzzy images with occasional overexposure and other video artifacts not only suggest a period piece, but they also allow director Pablo Larraín (Tony Manero, Post Mortem) to seamlessly edit in historical footage of Pinochet and street clashes from 1988. No generates considerable suspense as well, whether or not one knows how the referendum turned out.
Sony Pictures Classics picked up No at Cannes and currently lists its release date as to be announced; according to IMDB, it will have a limited release in the USA on February 15.
Europe
A Royal Affair (2012, Nikolaj Arcel) has been chosen as Denmark’s entry for the Best Foreign Language Film Oscar. Of course, the long list of entries from various countries will be reduced to five before the voting occurs. Still, I wouldn’t be surprised if A Royal Affair ended up on the final list and even took the top award. In a way, it’s just what the Academy members like: a big, glossy costume drama based on uplifting historical events.
But I was relieved to discover that this is no Merchant-and-Ivory-style middle-brow adaptation. It’s a fascinating example of what happens when a bunch of leftist, cutting-edge filmmakers get their hands on a budget to make an historical epic. Although the film’s title and publicity center on the illicit romance that provides part of the drama, A Royal Affair focuses largely on politics. Its plot is loosely based on historical events during the Age of Enlightenment, during which Denmark initially remained a backward country based on serfdom, summary arrest, torture, and execution, and grinding poverty for the lower classes.
The opening shows the heroine, Caroline, born an English princess and wed to Danish King Christian VII, writing the story of her life for her children. A flashback then begins the story proper, with Caroline optimistically setting out for Denmark and quickly discovering that her husband is an impetuous, rude and possibly insane young man who cares nothing for her. Her loneliness and the backward situation in Denmark are gradually established. Eventually a young doctor, Struensee, who believes in the ideas of the Enlightenment philosophers, comes to court and befriends the king, helping him to behave in a more restrained fashion.
Caroline, too, is a devotee of Rousseau, Voltaire, and other authors whose works are banned in Denmark. Nearly an hour  into the film, she discovers that Struensee is of like mind, and a friendship gradually moves into love and a sexual affair. The couple manipulate Christian into passing laws to benefit the peasants, earning the ire of the nobility. The narrative continues to center more on the social struggle that the three carry out than it does on the romance plotline.
into the film, she discovers that Struensee is of like mind, and a friendship gradually moves into love and a sexual affair. The couple manipulate Christian into passing laws to benefit the peasants, earning the ire of the nobility. The narrative continues to center more on the social struggle that the three carry out than it does on the romance plotline.
When I heard that the Silver Bear for Best Actor was awarded to the film at Berlin, I assumed it went to Mads Mikkelsen, who plays Struensee–and seems to star in half the films coming out of Denmark these days (such as Thomas Vinterberg’s The Hunt, also shown this year in the festival). But the role of Christian VII actually seemed to me more challenging. Mikkel Boe Følsgaard has to play a character who begins as border-line insane, crude, and obnoxious, but who also must gain our sympathy when he becomes part of the plot to reform Denmark’s laws. I was delighted to learn upon further inquiry that is was in fact Følsgaard (on the left, with Mikkelsen, in the photo) who won the award. Well deserved.
As the image suggests, the film is shot in muted tones that tend to play down the costumes and sets more than historical dramas usually do. This approach helps direct our attention to the plot and politics rather than the pageantry. In short, I ended up liking the film much more than I expected to.
A Royal Affair will be released in the USA on November 9 by Magnolia Pictures.
At the other end of the budgetary scale is the Portuguese feature The Last Time I Saw Macao (2012, co-directed by João Pedro Rodrigues and João Rui Guerra da Mata). A common impulse among critics seems to be to compare this mysterious, lyrical film to some of Chris Marker’s works. There is little information available on it, but my impression was that the filmmakers shot a lot of lyrical footage of Macau and then concocted a story to fit it. There are shots of buildings, from skyscrapers to disreputable-looking back streets, as well as ephemeral items like some big, gaudy, cartoony balloons of tigers that decorated the streets for a local festival.
The plot has something to do with a mysterious gang, the Chinese zodiac (see image at the bottom), and the end of the world. The hero is barely glimpsed, narrating the story in voiceover (provided by both of the directors). The plot centers on his search for a transvestite named Candy, perhaps the “woman” seen performing a musical number in front of a cage containing live tigers in the sultry opening scene. The song, “You Kill Me,” is among several references to Josef von Sternberg’s Macao.
Despite the shoestring budget, the filmmakers manage convincingly to portray an apocalyptic destruction of the city, followed by bleak shots of deserted, early-morning Macao buildings that effectively suggest the aftermath. It reminded me of Godard’s depiction of a futuristic city in Alphaville, using contemporary buildings and highways.
No US release is planned, but The Last Time I Saw Macao is worth seeking out at upcoming festivals.
A Filmmaker of the World
I’ve mentioned some films that pleasantly surprised me, but almost certainly the best film we saw at Vancouver came as no surprise at all. We both loved Abbas Kiarostami’s Like Someone in Love, but we’re not going to write anything substantive about it, at least not now. It deserves another viewing or two before we could say anything worthwhile–and it hardly needs us to publicize it. The opening scene is fabulous, the subsequent rambling plot absorbing and intriguing, and the end, as so often happens with Kiarostami, puzzling and frustrating. Possibly the man can do no wrong.
IFC has theatrical rights for the USA. Currently its webpage announces “Coming in 2013.” This may mean primarily On Demand, though it would be a pity not to see Like Someone in Love on the big screen.
The end of one multiplex
Rumors circulated almost from the start of the festival, and on October 8 the festival’s director, Alan Franey, revealed officially that the Empire Granville will soon be closing down. A detailed story on the history of the Granville and its closing, with quotations from Franey and representatives of other film festivals that have used the venue, can be found here. Ideally next year’s festival will house most of its screenings in another of the city’s multiplexes, but the new venue is yet to be determined. We hope it will be someplace where we can bounce around the world from screen to screen as easily. The Granville has served us all well and will be missed.