Archive for the 'National cinemas: France' Category
Of horses, avalanches, and architecture
Of Horses and Men (2013).
DB here, with some first impressions of this year’s Vancouver International Film Festival.
We alternate days of rain and days of sunshine, but crowds still keep turning up. Some screenings are packed full, and most of those we’ve visited are solidly attended. Herewith some notes on three of the most intriguing movies I’ve seen so far.
The getting of wisdom
La Sapienza (2014).
The last Eugene Green movie I saw was The Portuguese Nun, which I discussed in a 2010 entry. His latest, La Sapienza, is more user-friendly, somewhat closer to American art-house accessibility.
A married couple in a politely disintegrating relationship takes a trip to Italy, and then their paths diverge. Alexandre, a famous architect who conducts research on the side, takes along on a field trip the young Goffredo, who wants to be an architect as well. Aliénor, a psychoanalyst, stays with Goffredo’s sister Lavinia, who suffers from fainting spells. Each character comes, by a quiet path, to a degree of peace and reconciliation. Alexandre even renews his creative energy, thanks partly to Goffredo, who insists that architecture is not only about space but what fills it: Light and people.
As ever with Green, everybody is gorgeous; the clothes are casually splendid; the backgrounds are magnificent. Threaded through La Sapienza is overwhelming architecture (Turin, San Carlino, Rome), accompanied by Alexandre’s discussion of Francesco Borromini’s career. The climax, a muted one, takes place in the Chapel of San Carlo, filmed in appropriately radiant majesty. In a way, the movie is a fine art-history class.
Crosscut with the two men’s journey are the ministrations of Aliénor to Lavinia, who comes out of her shell when shown kindly attention—and exposure to the theatre. (Le Malade imaginaire, no less.) Green is one of the few filmmakers today who makes movies in homage to the pleasures of aesthetic experience. No wonder that one of his films has the title Le Pont des Arts. But he’s not completely highfalutin. One scene makes fun of pretentious contemporary artists, chiefly to throw the purity of classic art into greater relief.
Green’s signature staging and cutting are still in force; he offers a sort of parodic simplification of analytical editing’s progression of master-shot, over-the-shoulders, and singles. Given these familiar patterns, we quickly get used to the artifice of to-camera address, sometimes in extreme close-up. Viewers who admire Wes Anderson’s style should check out Green’s more austere handling of planimetric imagery.
Most American studio pictures allot a separate shot for each character’s line, and Green does much the same, but his pace never seems as rushed. I think it’s partly because of the pauses between lines, which allow us to wait for more from the speaker, or to anticipate how the listener will react.
All in all, another piece in that cloisonné mode that Green has made his own. But La Sapienza has freshness because of its new subject matter. We get not a romance among young people but a fading love among their elders. The film harks back to a great tradition of disenchanted couples visiting alien places, from Voyage to Italy to Certified Copy. And the actors, particularly Christelle Prot as the wife, have an intelligent vivacity. Alexandre’s demeanor and expressions, robotic in the opening scenes, warm and relax across the film as he comes to enjoy visiting Borromini’s sites and learning from his young companion. The film exemplifies what Alexandre describes as one building’s integration of human bodies and rigorous patterns: “Living figures in geometrical constructions.”
A Nordic problem play
Another film about a couple’s troubles while they’re away from home is Force Majeure, a new Swedish film with the original title Turist. Tomas and Ebba seem to have a fine upper-middle-class family, with beautiful kids Vera and Harry. Seeking quality time, they arrive at a high-tone ski resort in the French alps. They have a pleasant visit at first, punctuated by the cannons that trigger controlled avalanches, until one such snow slide seems to threaten them on a patio. Tomas’ reaction puts their marriage in question, and Vera and Harry become fussy and scared. Tomas comes to see the family crisis as the collapse of his male identity.
As with the Green film, people talk a lot. In the great tradition of Nordic drama and Bergman psychodrama, what we’ve been shown must also be discussed, and the past dredged up, and bystanders dragged into intimate crises. The central scene, in which Ebba presses Tomas to explain himself in front of another couple, runs by my count over twelve minutes. Its painful but riveting drama drifts into satire when Tomas’ intellectual friend tries to find evolutionary explanations for what happened.
Unlike the Green film, Force Majeure is the opposite of austere. Even without the breathtaking scenery, the ski lodge is given a sort of ersatz grandeur itself. And the big moments swallow up speech in sumptuous visual effects, most obviously the avalanche but also an eerie scene that appears to record a flying saucer’s surveillance of the lodge. The spectacle doesn’t stop in the coda, a vertiginous bus ride that leaves issues of courage and family unity uneasily suspended.
Horse whisperers, and shouters
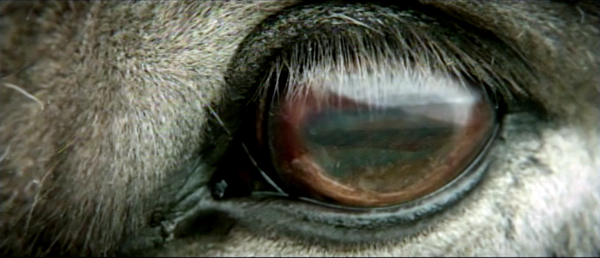
According to reports, John Ford once remarked that a running horse is the most beautiful thing in the world. There’s some evidence for the claim in Of Horses and Men, an Icelandic film about life in a valley among horse farmers. It’s composed of episodes of local life, sometimes trivial and sometimes life-or-death, taking place across a summer.
The locals let much of their stock roam across the valley until they herd them into a corral for the winter. The massive roundup, spiced with some sexual shenanigans, forms the film’s climax, with majestic shots of galloping horseflesh. The final crane shot celebrates the vastness of the herd against the stupendous landscape, while giving it human scale with an ambling musical score reminiscent of Morricone’s lighter tunes.
So this is not your standard hardscrabble-life-in-distant-places film. Granted, the neighbors, a scruffy lot given to passing around flasks and snuff, are attractively cranky and realistically unpretty. None would get an audition for Eugene Green. But their petty quarrels, as when one rancher keeps snipping the barbed wire that another rancher keeps stringing across a thoroughfare, become comic (though some lacerations are involved). Particularly hilarious is the scene of a rancher so devoted to drink that he goads his poor steed to swim out to meet a Russian fishing boat carrying lethally strong alcohol.
What a pleasure to meet a movie that tells its story visually! Details of behavior matter. The ritual of bridling a horse gets carried out in ways that characterize the riders, and there is one moment, in which a young woman accomplishes the apparently impossible, that is crowd-pleasing without being over the top—all presented briskly and with hardly any dialogue.
Another laconic scene takes place after the credits. A lantern-jawed rancher proudly steers his trotter to breakfast with a neighbor woman. Director Benedikt Erlingsson introduces other major characters by showing them in their yards watching the gentleman’s ride. In turn, he learns they’re watching by catching the glint of sun on their binoculars.
This bit of routine suggests what passes for entertainment among these nosy folks. It also becomes a running gag, so that in later scenes, as soon as we cut to the horizon and see the telltale flash, we know someone’s eyeing the action. This sort of pictorial economy, rare in today’s films, eliminates exposition and lets us think we’re smart.
In fact, the act of looking becomes a persistent motif, as most episodes are introduced by a screen-filling close-up of a horse’s eye, with humans or landscapes reflected there. It’s as if these beautiful beasts are quietly observing their masters’ foibles.
Kino Lorber will distribute La Sapienza in the United States, Magnolia will do the same with Force Majeure, and Music Box Films will be offering Of Horses and Men.
La Sapienza.
What’s left to discover today? Plenty.
Der Tunnel (William Wauer, 1915).
DB here:
Being a cinephile is partly about making discoveries. True, one person’s discovery is another’s war horse. But nobody has seen everything, so you can always hope to find something fresh. There’s also the inviting prospect of introducing a little-known film to a wider community–students in a course, an audience at a festival, readers of a blog.
A festival like Bologna’s Cinema Ritrovato (we covered this year’s edition here and here and here) offers what you might call curated discoveries. Expert programmers dig out treasures they want to give wider exposure. Such festivals are both efficient–you’re likely to find many new things in a short span–and contagiously exciting, because other movie lovers are alongside you to talk about what you’re seeing.
A year-round regimen of curated discoveries is a large part of the mission of the world’s cinematheques. This is why places like MoMA, LACMA, MoMI, BAM, TIFF, ICA, and other acronymically identified showcases are precious shrines to serious moviegoing.
But other discoveries are made in a more solitary way. Film researchers, for instance, ask questions, and some of those can really only be answered by visiting film archives. Sometimes we need to look at fairly obscure movies. And despite the rise of home video, there are plenty of obscure movies that can be seen only in archives. It’s here that the programmers of Ritrovato and Pordenone’s Giornate del Cinema Muto come to select their featured programs.
Archive discoveries aren’t predictable, and many are likely to be of interest only to specialists. Such was the case, mostly, with our archive visits this summer. But as in years past (tagged here), all our archive adventures yielded pure happiness.
This time I concentrated on films from the 1910s-early 1920s films because I hope to make more video lectures about this, the most crucial phase of film history. (One lecture is already here.) In our archive-hopping, we saw films I was completely unfamiliar with. I re-watched some films I’d seen before and found new things in them. I detected some things of interest in films I hadn’t known. Most exciting was our viewing of a major film that has gone unnoticed in standard film histories.
In the steps of Jakobson and Mukarovský
Love Is Torment ( Vladimír Slavínský, Přemysl Pražský, 1920); production still.
First stop was Prague, where I was invited to give two talks. At the NFA we saw two films on a flatbed: a portion of Feuillade’s Le Fils du Filibustier (1922) and a cut-down version of Volkoff’s La Maison du mystere (1922), the latter a big gap in our viewing. The expurgated Maison came off as rather drab, lacking nearly all the big moments much discussed in reports like James Quandt’s from a decade ago. So we search on for the full version. . . .
As for the Feuillade: Le Fils du Filibustier was his last “ciné-roman.” Our two-reel segment, which seemed fairly complete, confirmed his late-life switch to fairly fast, Hollywood-style editing, with surprisingly varied angles.Again, though, we yearn to see the entirety of this pirate saga.
On another day the archive kindly screened several 1910s-early 1920s Czech films for us. Our hosts Lucie Česálková and Radomir Kokes translated the titles and provided contexts. Among the choices were Devil Girl (Certisko, 1918), with a protagonist who’s more of a tomboy than a possessed soul; and the full-bore melodrama Love Is Torment (Láska je utrpením, 1919). The plot, outlined here, involves scaling and jumping off a tower, twice. Once it’s a stunt for a film within the film, the second time (below) it’s the real thing.
Radomir explained to us that one of the co-directors, Vladimír Slavínský, seemed in his 1920s films to specialize in building two reels (often the third and fourth) in a “classical” fashion before letting the other three become more episodic. And indeed, most of the late 1910s-early 1920s films we saw were up to speed with other European filmmaking, in their staging, cutting, and use of intertitles.
We look forward to viewing more Czech films as the opportunity arises. A culture that gave us Prague Structuralism is definitely worth getting to know better. In the meantime, the journal Illuminace, edited by Lucie, is injecting a great deal of energy into local film studies, and the archive is entering a fresh phase with its new director, Michal Bregant.
3D excavations
Der Hund von Baskerville (1914).
In Munich, we reconnected with our old friends Andreas Rost, now retired from administering the city’s cultural affairs, and Stefan Drössler, director of the Munich Filmmuseum. We also reunited with the stalwart archivists Klaus Volkmer, Gerhard Ullmann, and Christoph Michel. Talking with them, we realized we hadn’t been back for over ten years. Klaus and Gerhard were warm and helpful during our earlier visits.
One rainy afternoon, Stefan shared his research on the history of 3D. He presented a spectacular PowerPoint, with rare images and some truly startling revelations. He has given this talk at intervals over the years, but it grows and deepens as he discovers more. Accompanying it, he screened some Soviet 3D films, including the 1946 Robinzon Cruzo. This mind-bending item was made with diptych images, so that the projected image turned out to be slightly vertical. The soundtrack runs down the middle.
The director, Aleksandr Andriyevsky, made excellent use of 3D to evoke the stringy vines and protruding leaves of Crusoe’s island. Amid all the talk today about glasses-free 3D, it’s interesting to learn that Soviet researchers prepared such a system. Stefan’s archaeology of 3D, for me at least, was a pretty big discovery.
At Munich we also saw three silent German titles. Two were associated that resourceful self-promoter Richard Oswald. Sein eigner Morder was a 1914 version of Dr. Jekyll and Mr Hyde, directed by Max Mack from Oswald’s screenplay. Shot in big sets, it spared time for the occasional huge close-up. The other film was Oswald’s semi-comic adaptation of The Hound of the Baskervilles (Der Hund von Baskerville, dir. Rudolf Meinert, 1914), which he had already turned into a play. The sleuth isn’t exactly our idea of Holmes (see above), and he isn’t as quick-witted, I thought, but it was an enjoyable item. Dr. Watson has a sort of tablet which picks up messages; Holmes’ orders are spelled out in lights on a grid. Stefan rightly called it a 1914 laptop.
As for the third film: More about that coming up.
The shadow of Hollywood
Les Deux gamines (1921).
At Brussels, thanks to the cooperation of the Cinematek, I was able to see several items for the first time, and two held considerable interest. The short The Meeting (1917), by John Robertson, showed a real flexibility in laying out the space of a cabin both in front of the camera and behind it. Most interior scenes in 1900-1915 cinema bring characters in from a doorway in the rear of the set (as Feuillade does in his 1910s films) or straight in from the sides, perpendicular to the camera (as Griffith tends to do). The Meeting shows that the diagonal screen exits and entrances that we see in exteriors were coming into use in interior sets as well.
Another 1917 film, Frank Lloyd’s A Tale of Two Cities, was further support for the idea that American continuity filmmaking was well-established and already being refined at the period. Dickens’ classic tale is handled with dispatch–rapid exposition, smooth crosscutting to set up the plot lines–and the film makes dynamic use of crowds surging through well-composed, starkly lit frames. There are also some remarkably expressive close-ups, evidently made with wide-angle lenses.
To clinch a plot point, the resemblance of aristocrat Charles Darnay to British solicitor Sydney Carton, the star William Farnum plays both characters. Not much of a problem if you keep the characters in separate shots; the good old Kuleshov effect (aka known as constructive editing) makes it easy. At this period, though, filmmakers were perfecting ways to show one actor in two roles within a single shot. The most famous examples involve Paul Wegener in The Student of Prague (1913) and Mary Pickford in Stella Maris (1918).
Cinematographer George Schneiderman contrives some really convincing multiple-exposures showing Farnum as both Darnay and Carton. There are some standard trick compositions putting Farnum on each side of the screen, but several images take the next step and let the actor cross the invisible line separating the two halves. At another point, we get a flashy passage showing the two facing one another in court, followed by a “Wellesian” angle of the two characters’ heads in the same frame.
Hollywood’s pride in photorealistic special effects, so overwhelmingly apparent today, has deep roots.
Part of my Brussels visit involved checking and fleshing out notes on certain films I saw many years ago. Some were wonderful William S. Hart movies like Keno Bates, Liar (1915; surely one of the best film titles ever). There was, inevitably, Feuillade as well. The influence of Hollywood was powerful in the ciné-roman Les Deux gamines (1921). This baby, released in 12 parts originally, runs nearly 27,000 feet. At 20 frames per second, it would take six hours to screen. What with changing reels, making notes, counting shots, pausing to study things, and taking stills, Kristin and I took about ten hours to watch it.
Was it worth it? An adaptation of a popular stage melodrama, it can’t count as one of Feuillade’s major achievements. Two girls are left alone when their mother is reported dead. They are adopted by their gloomy grandpa and tormented by his overbearing housekeeper. They become the target of kidnapping by gangster pals of their father, who has divorced their mother and turned to a life of petty crime. Their allies are their young cousins, a wealthy benefactor, and their godfather and music-hall star Chambertin. Everything ends happily, if you count the father’s redemptive sacrifice on behalf of a pregnant woman.
Les Deux Gamines is determined to delay its ending by any means necessary. Form here definitely follows format; Feuillade fills out the serial structure with plots big and small. (Shklovsky would love it.) There are incessant abductions, escapes, rescues, coincidental meetings, and timely reformations, plus at least three cases of people wrongly assumed to be dead. All of this is accompanied by an endless exchange of telegrams and letters. People are forever piling into and out of carriages, train cars, and taxis. Such material serves as makeweight for some genuinely big moments, including a cliff-hanging scene and a stunning climax in a smuggler’s warehouse stuffed with gigantic bales of used clothing.
Like Le Fils du Filibustier, this film shows Feuillade trying to change with the times. The supple long-take staging of Fantômas and Les Vampires and Tih-Minh mostly goes away, to be replaced by rapid editing. Feuillade employs standard continuity devices, as when the grandfather discovers that the kids have sneaked out at night and are trying to return by scaling the gate.
Feuillade varies his angles and lighting to accentuate the moment of visual discovery. Elsewhere, some appeals to “offscreen sound” (cutaways to doorbells and telephones) built up to a surprise effect.
But by the energetic standards of, say, Robertson or Lloyd several years earlier, Les Deux gamines is fairly timid. Feuillade doesn’t explore editing resources very much here, not even as much as in Le Fils du Filibustier. The fairly quick cutting pace stems partly from the stratagem of having dialogue titles interrupt static two-shots of characters talking to one another. This sort of proto-talkie-technique yields efficient storytelling but not much visual momentum. Feuillade tried flashier things in other films of the period (see here).
Hours and hours of nothing but Bauers
The Alarm (1917).
Yevgeni Bauer, one of the master directors of the 1910s, remains lamentably unknown. About two dozen of his over seventy films survive, but many of the ones we have lack intertitles. A few of his films are available on DVD (most obviously here; less obviously here). He died of penumonia in 1917, between the February revolution and the Soviets’ coup d’état in October. He was only 52.
My first archive-report entry back in 2007 recorded my interest in Bauer, and I’ve returned to his films over the years. Now here I was watching some again, confirming things I found of interest then, and discovering (that word again) new felicities. I hope to say more in those short video lectures on the 1910s, but I can’t leave without giving you a taste of his qualities.
Two of the films I saw this time were from 1917. The Alarm (Nabat) came out in May 1917, just before Bauer’s death in June. Originally running eight reels, it was cut down after the initial release, and that’s evidently the version we have. For Luck (Za Schast’em, September 1917) was directed by Bauer from his sickbed. Both films are fairly hard to follow. The Alarm lacks intertitles, and For Luck has many fewer than it had originally.
The two films are of exceptional interest, though. For one thing, there’s the involvement of Lev Kuleshow, who at the age of eighteen served as art director for the earlier film and, apparently reluctantly, as an actor in the later one. More important, the films remain as beautifully designed, staged, and acted as ever.
The Alarm is a wide-ranging drama set before the February upheaval. The drama involves romantic intrigues among the upper class, interwoven with a workers’ rebellion against a master capitalist. The millionaire Zeleznov holds court in a vast office with chairs bearing ominous spires and spiky arches; the windows open onto a view of his factory. A long-shot view is above; here’s a sample of how Bauer shows off his decor in something akin to shot/ reverse-shot.
The idea of capitalism as an overreaching religious striving is evoked by turning Zeleznov’s headquarters into a Symbolist cathedral. And looking at the second shot, you wonder whether Kuleshov’s inclination to stage his own scenes against pure black backgrounds has its source in his work for the man he called “my favorite director and teacher.”
As ever, Bauer makes fluid use of depth. He choreographs meetings of Zeleznov’s brain trust in ever-changing arrangements, and he eases a man out of a boudoir through a mirror reflection over a woman’s fur-draped shoulder.
Compared to the scale of The Alarm, For Luck is decidedly low-key–a bourgeois melodrama that extends barely beyond an anecdote. Zoya has been a widow for ten years, and she hopes to marry the loyal family friend Dmitri. But Zoya’s daughter Lee hasn’t yet reconciled to losing her father. The couple hope that Lee has worked out her grief during her dalliance with a young painter (played by Kuleshov), but she reveals that all along she has hoped to marry Dmitri.
The Alarm used some extravagant sets, both for interior and exterior scenes, but a good deal of For Luck takes place in parks and terraces. The sincere Enrico sketches Lee in front of swans, and they steal some moments in a bower.
Still, there are some interiors boasting Bauer’s famous pillars and columns, which create massive, encapsulated spaces. Here Zoya looks off, in depth, at the ailing Lee, in bed on the far right.
Sharp-eyed Bauerians will notice the mirror set into the left wall, reflecting Zoya. Kuleshov, who did art direction on this as well as The Alarm, worried more about the trumpet-blowing Cupid floating between the pillars on the left. (“It turned out bad on the screen–incomprehensible and inexpressive.”) He did think that the tonalities of the set worked well: “As an experiment, I put up a set painted in shades of white that were ever so slightly different from one another.”
“Ever so slightly different” isn’t a bad evocation of the tiny variations of shape and shade, light and texture, that characterize Bauer’s ripe, sometimes overripe, imagery. This is a social class on the way out, but it leaves behind a great glow.
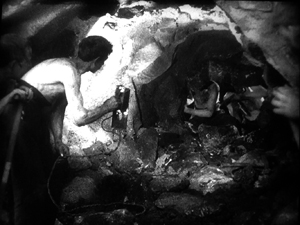
Tunnel: Vision
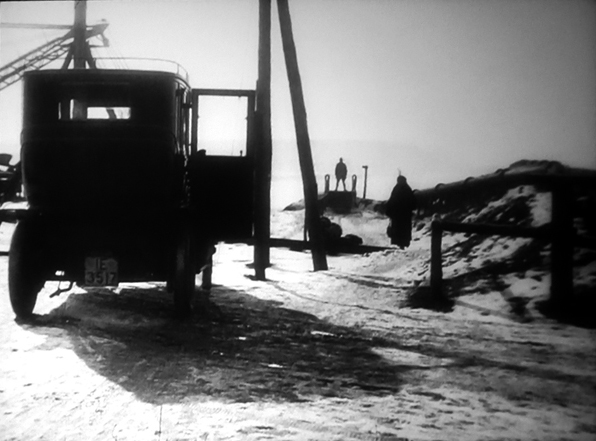
The Tunnel (1915).
In 1913, the popular novelist Bernhard Kellermann published Der Tunnel. It’s not quite science-fiction, more a prophetic fiction or realist fantasy in the vein of Things to Come. The book became a best-seller and the basis of a 1915 film directed by William Wauer.
The plot would gladden the heart of Ayn Rand. A visionary engineer persuades investors to fund building an undersea railway connecting France to the United States (specifically, New Jersey). No meddling government gets in the way of this titanic effort of will. Max Allan buys land for the stations, hires diggers from around the world, and risks everything he has. The obstacles are many. An explosion scares off workers; there is a strike; impatient stockholders raid and burn the company headquarters.
Max Allan moves forward undeterred, though he hesitates when his wife and child are stoned to death by a mob. After twenty-six years, the railway is opened. Max, along with his new wife (the daughter of his chief backer), proves it’s safe by taking the first transatlantic train. The event is covered by television, projected on big screens around the world (above). In the original novel, a film company was commissioned to document every stage of work.
The book skimps on characterization, and the film is even less concerned with psychology. Once the character relations are sketched, Wauer goes for shock and awe. The Tunnel‘s thrilling crowd scenes of work, fire, devastation, riots, and panic look completely modern. Bird’s-eye views of stock-market frenzy anticipate Pudovkin’s End of St. Petersburg, and Wauer creates an Eisensteinian percussion of light and rushing movement as workers flee the tunnel collapse.
For the sequences showing the tunnel construction, Wauer supplies violent alternations of bright and dark as men, stripped and sweaty, attack the rock face. The variety of camera positions and illumination is really impressive.
Comparisons with The Big Film of 1915 are inevitable. The intimate scenes of The Tunnel are far less delicately realized than the romance and family life of The Birth of a Nation, and the battle scenes in Birth have a greater scope than what Wauer summons up. But Wauer’s handling of crowds is more vigorous than Griffith’s riots at the climax of Birth, and his pictorial sense is in some ways more refined, even “modern.” There’s little in Birth as daringly composed as the static long shot surmounting today’s entry.
Wauer can handle small-scale action very crisply. The opening scene in an opera house creates low-angled depth compositions more arresting than Griffith’s depiction of Ford’s Theatre. Max’s wife, in one box, is watching his efforts to attract funding from the millionaire Lloyd. Wauer constantly varies his camera setups to highlight Max’s wife in the background studying Lloyd’s daughter, sensing in her a rival for her husband. Whether the angle is high or low, the wife’s presence in her distant box is signaled at the top of the frame.
The second and third shots above present similar but not identical setups, adjusted to reset the depth composition.
It was at Munich’s Filmmuseum a decade ago that I first encountered the brooding power of Robert Reinert’s Opium (1919) and Nerven (1919), the latter now available on DVD. I was convinced that Nerven was as important, and in some ways more innovative, than the venerated Caligari. Now the conviction grows on me that in The Tunnel we have another galvanizing, outlandish masterwork of the 1910s. I hope it will somehow get circulated so that wider audiences can discover it. Yeah, that’s the word I want: discover.
Without archivists, no archives. We’re grateful to Michal Bregant, head of the Czech Republic’s archive, for access to films and for his companionship during our visit. Thanks as well to Lucie Česálková, our host; her knowledgable colleague Radomir Kokes (who kindly corrected the initial version of this post); Petra Dominkova, our Czech translator; and Vaclav Kofron, editor of the Czech versions of our books. Lucie supplied the frame enlargement from Love Is Torment. As well: Good luck to the Kino Světozor!
In Munich, we owe a huge debt to archive chief Stefan Drössler, for his generous sharing of information and his and Klaus Volkmer’s rehabilitation of The Tunnel. Stefan also provided the images from Robinson Crusoe and The Hound of the Baskervilles. Coming up is his work for the annual Bonn International Silent Film Festival, 7-17 August. Thanks as well to Gerhard Ullmann and Christoph Michel.
In Brussels, as ever, the Cinematek has made us welcome, and we thank archive director and long-time friend Nicola Mazzanti and vault supervisor Francis Malfliet. Over the last thirty years, a great deal of our research has depended upon the cooperation the Cinematek leadership: Jacques Ledoux, Gabrielle Claes, and now Nicola.
My quotations from Kuleshov come from Silent Witnesses: Early Russian Films, 1908-1919, ed. Yuri Tsivian and Paolo Cherchi Usai (Pordenone: Giornate del Cinema Muto, 1990), 388-390.
There’s a chapter on Feuillade in my Figures Traced in Light, where Bauer is discussed as well. My essay on Robert Reinert is in Poetics of Cinema.
Thanks to Antti Alanen for correction of a misspelled title. Speaking of discoveries, you’ll find plenty on his wonderful Film Diary site. During his recent trip to Paris, he’s writing about art exhibitions, Dominique Paini’s Langlois exposition at the Cinémathèque, and Godard’s Adieu au langage.
Screening at the Czech Republic’s National Film Archive. From left: Michal Večeřa, Tomáš Lebeda, Radomir Kokes, Lucie Česálková, and Kristin.
The ten best films of … 1923
Le brasier ardent.
Kristin here:
Six years ago David and I celebrated the 90th birthday of the classical Hollywood cinema with a post that included a list of what we considered the ten greatest (surviving) films of 1917. Choosing the ten best films of 90 years ago has become a custom, one which helps us avoid doing a ten-best list for the current year. It’s a way of drawing attention to some wonderful but often little-known films, for those who are interested in exploring the treasures of silent cinema.
For previous entries, click here: 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, and 1922.
For some reason, that 1917 list was pretty easy to put together. In recent years, I’ve had more trouble. As I wrote last year, “For the past two years, I’ve noted that it was difficult to fill out the list of ten masterpieces. I keep thinking that I’ll get to a year where I won’t have to say that, but 1922 turns out not to be that year. Some titles were obvious, but the last one or two took some hunting.” Well, 1923 still isn’t that year. I’ve again had some trouble filling out the top ten.
Why? 1923 should be packed with worthy candidates. But oddly, some of the most significant directors of the era didn’t make films that year. This seems to have been partly because success brought greater ambitions. In 1923 Fritz Lang was preparing his epic two-part Die Nibelungen, guaranteed to show up in next year’s list. Abel Gance had embarked the long road to the release of Napoléon, four years later.
Carl Dreyer, who had made three films in 1919 and two each in 1920 and 1921, was bouncing around among companies and countries in the mid-1920s, and didn’t again release anything until his 1924 German-produced film, Michael.
Others made relatively unremarkable films. F. W. Murnau’s surviving film from 1923, Die Finanzen des Grossherzogs, serves mainly to prove that comedy was not his strong suit. Victor Sjöström’s Eld ombord (The Hell Ship) doesn’t match the masterpieces we find elsewhere in his career. Louis Feuillade’s 1923 feature Le Gamin de Paris is likewise unexceptional, though it’s of interest for showing his abandonment of complex staging and his conversion to American-style cutting, including angled shot/reverse-shots. (Of Feuillade’s 1923 installment film Vindicta, we can’t speak; we haven’t been able to see it.)
Other films are lost. John Ford made four films that year, only one of which survives: an incomplete, beat-up version of Cameo Kirby that doesn’t make it look like anything special. Murnau’s first 1923 film, Die Austreibung, seems to be gone. Mauritz Stiller’s The Blizzard is lost, and he, too, was probably already involved in his own 1924 two-part epic, The Saga of Gösta Berling.
[December 29: Brian Darr tweets that The Blizzard is not lost, which I am glad to learn. Its Wikipedia entry confirms that it is only partially lost, with about two-thirds of the film known to be preserved.]
Finally, the Soviet cinema, which was to make such major contributions to 1920s cinema, had not yet gotten off the ground.
Still, with some help from David, I’ve concocted a list with some great films and some near-great ones. The place to start was obvious.
From the ridiculous to the sublime
Some years now we’ve been watching the careers of Charles Chaplin, Harold Lloyd, and Buster Keaton delivering wonderful short films and inching toward even greater things. This was the year they blossomed.
Chaplin made a charming short feature, The Pilgrim, this year, but he also surprised everyone by making a sophisticated sex comedy (appearing only in an unrecognizable cameo as a porter). The title role of A Woman of Paris features Chaplin’s regular leading lady, Edna Purviance, as a village girl, Marie, who loses her young boyfriend Jean through a misunderstanding. She runs off to the city to become a rich man’s mistress and realizes too late what she has lost.
The plot centers largely around this romantic triangle and Marie’s indecision about whether to return to her boyfriend, who has become an impoverished artist in Paris, or to stay in the luxurious life that Pierre provides her. The affair between Marie and Pierre is handled in a sophisticated and yet subtle way. There are no love scenes, but at one point Pierre finds himself without a handkerchief and goes into the bedroom to pluck one casually out of drawer. Clearly he spends a lot of time in their love nest.
 At the same time, the film deals more generally with the gulf between the very wealthy and the working-class people who who serve them. In one well-known scene, a woman gives Marie a massage, and the camera stays mainly on the masseuse as she tries to maintain a neutral expression while obviously being shocked by the lurid gossip between Marie and a friend. In another, a kitchen assistant in a swanky restaurant cannot bear the odor of the aging game bird he has to fetch for the chef, but the chef and Pierre consider it a prime delicacy.
At the same time, the film deals more generally with the gulf between the very wealthy and the working-class people who who serve them. In one well-known scene, a woman gives Marie a massage, and the camera stays mainly on the masseuse as she tries to maintain a neutral expression while obviously being shocked by the lurid gossip between Marie and a friend. In another, a kitchen assistant in a swanky restaurant cannot bear the odor of the aging game bird he has to fetch for the chef, but the chef and Pierre consider it a prime delicacy.
One of the strengths of the film is that it does not take the obvious approach of making Pierre into a fat, obnoxious oaf. On the contrary, Adolphe Menjou plays him as a witty, unflappable figure. He thinks nothing of arranging a marriage with a rich woman while planning to carry on his affair with Marie, but he puts up with her shifting moods and does genuinely seem to love her. The touch of having him play his saxophone while Marie has a tantrum and orders him out (right) typifies the light touch Chaplin applies to what is ultimately a tragic story.
A Woman of Paris was not well received upon its release, at least by the ticket-buying public, who expected a Chaplin film to star the Little Tramp and to be straightforwardly funny. The title at the beginning, where Chaplin explains that he does not appear in the film undoubtedly did little to appease them. Many critics were respectful, however, and other filmmakers recognized the new type of sophisticated comedy that he had introduced. Lubitsch, who was working on Rosita at the same studio, United Artists, was definitely influenced by it–as we shall see next year when his The Marriage Circle figures in the top ten of 1924. That film includes Menjou, playing a similar role, and in fact after playing minor roles for nearly ten years, he became a star with Chaplin’s film.
[February 10, 2014: Paul Duncan, Film Book Editor for Taschen, has kindly supplied figures showing that A Woman of Paris was profitable, if not as much as Chaplin’s other films: “It earned United Artists $634,000, of which $608,868.91 went to Regent Film (the company Chaplin formed to produce films for Edna Purviance). So with a production cost of $351,853.03, A Woman of Paris made a healthy profit, though, as you write, obviously it would have been more if it had been a comedy starring Chaplin.” Paul also informs me that Taschen’s The Charlie Chaplin Archives, which he is editing, will be published later this year.]
 By 1923, Harold Lloyd had already done some shorts featuring nail-biting but hilarious comedy high up on skyscrapers. (See High and Dizzy in our 1920 entry.) In 1923 he took the same sort of premise into the feature-length Safety Last and created an indelible image: a brash young man hanging from a tilting clock. The gags go on story by story. After surviving the clock, Harold manages to get to the next level, only to be chased out a flagpole by a dog (left). Looking back, people tend to remember the vertiginous climb as the whole film, though remarkably, it takes place only over the last third. Earlier scenes involve a romance and misunderstandings that arise from the hero’s job at a department store.
By 1923, Harold Lloyd had already done some shorts featuring nail-biting but hilarious comedy high up on skyscrapers. (See High and Dizzy in our 1920 entry.) In 1923 he took the same sort of premise into the feature-length Safety Last and created an indelible image: a brash young man hanging from a tilting clock. The gags go on story by story. After surviving the clock, Harold manages to get to the next level, only to be chased out a flagpole by a dog (left). Looking back, people tend to remember the vertiginous climb as the whole film, though remarkably, it takes place only over the last third. Earlier scenes involve a romance and misunderstandings that arise from the hero’s job at a department store.
Safety Last wasn’t Lloyd’s greatest film, but it launched the greatest period of his career. He’ll probably be joining us for these nostalgic lists every year now until 1927. The film is still available as part of New Line’s big box set of Lloyd’s films on DVD. (Buy that one, and you’ll be a step ahead of those future lists.) This summer the Criterion Collection brought Safety Last out on DVD and Blu-ray. There’s only that one feature on the disc, but it includes several supplements, including three newly restored Lloyd shorts and Kevin Brownlow’s 104-minute documentary, The Third Genius.
Keaton, too, entered a hugely creative streak in 1923. He made an amusing satire on Intolerance, the feature-length The Three Ages, in which Buster traces love through the stone age, the Roman era, and the Roaring Twenties. As Keaton himself acknowledged, “Cut the film apart and then splice up the three periods, and you will have three complete two-reel films.” He followed it up, however, with a masterpiece that displayed a complete command of story structure in the classical Hollywood mold: Our Hospitality. It’s arguably as fine as anything he ever made, except The General, which just edges it out.
Interestingly, Our Hospitality and The General are Keaton’s only two period pieces. (that is, if one excepts The Three Ages, which is far more farcical and does not attempt to recreate a realistic period atmosphere.) Both also take place in the South, and outdoors to a considerable extent. The milieu seems to have inspired him. Dealing with old-fashioned trains and other technology generated a lot of clever gags, and the fields, forests, and rivers helped give these two films a pictorial beauty that separates them from the Keaton’s other films.
Way back in 1978, when David and I were working on the first edition of Film Art: An Introduction, we wanted to include an extended analysis of a single film in each of the chapters on film technique. For mise-en-scene we chose Our Hospitality, which contains numerous uses of setting, costume, acting, and lighting brilliant enough to inspire a teacher and straightforward enough for students to notice and understand. Plus what better way to win over students who think that old black-and-white silent movies aren’t worth watching?
The story is simple. Willie McKay, the hero, travels from New York to the deep South, under the impression that he has inherited a mansion. The trip south on a very old-fashioned train supplies a long string of marvelous sight gags. There Willie meets the heroine, who shares his coach. Upon arrival, Willie discovers that his “mansion” is really a decaying house. Since the heroine has invited Willie to dinner, he wanders around to pass the time, unaware that he has inherited something else: a feud. The heroine’s family has a longstanding grudge against the McKays, and the father and two brothers are determined to shoot Willie. The only catch is that Southern hospitality dictates that they cannot kill him while he’s in their home.
In our analysis in Film Art, we pointed to the many motifs Keaton uses in service of the narrative, such as the moment of the hero’s rescue of the heroine as an echo of the earlier fishing pole/waterfall gag. One stylistic motif of staging comes back several times: Keaton using foreground doors or walls to create depth staging of moments when people spy or eavesdrop on others. In the frame on the left below, one of the brothers waits to ambush Willie, who is unaware of his presence (or indeed of the feud itself). In the one on the right, Willie eavesdrops on the brothers in their house, learning that they intend to kill him but that he is safe inside the house. Now Willie learns what’s going on, while the brothers don’t realize that he’s overhearing their plan. Such compositions are a motif in the film, forming a way of manipulating the narration–usually giving us more information than the characters onscreen have.
Like Safety Last, Our Hospitality ushered in the prime of the comedian’s career. Keaton made a string of marvelous features that lasted until The Cameraman in 1928. He didn’t always sign the films as director (he’s listed as co-director of Our Hospitality, along with John Blystone), but his unerring sense of how to compose images for the entire frame, both its surface composition and in depth, suffuses all his films of this period.
I’ve mentioned that Lubitsch was working at United Artists in 1923. Rosita was his first American film, starring Mary Pickford. It’s certainly not a masterpiece on the level of The Marriage Circle or Lady Windermere’s Fan, but Rosita is a charming and impressive film, certainly at least as good as Lubitsch’s other lesser films of the decade, Forbidden Paradise and Three Women.
As I discuss in my book, Herr Lubitsch Goes to Hollywood, the director had already been tentatively using classical Hollywood style in his last two German films, Das Weib des Pharao and Die Flamme. In Rosita, he managed to balance a typical historical epic from his German period (Madame Dubarry, Anna Boleyn) with the light, vivacious appeal of his star. She plays the title character, a cheerful street musician who is in love with Don Diego, an impoverished nobleman and military officer. Rosita catches the eye of the lecherous king. Don Diego ends up condemned to death, and Rosita plots to save him.
The sets were built on the enormous backlot of United Artists, where Douglas Fairbanks’ castle for Robin Hood had stood. The day after Rosita wrapped, the construction of the sets for The Thief of Bagdad began on the same lot. Indeed, one can detect a distinct similarity between Rosita’s big sets–city streets and a large prison–and those of the two Fairbanks films. This frame is a shot of the prison interior emphasizing a gallows in the background:
Given that this giant set was built in the open air, Lubitsch must have filmed this and other scenes at night, using the giant arc spotlights that had recently become a standard tool of Hollywood filmmaking to throw great swathes of illumination across the scene. In general, Rosita‘s style demonstrates that by 1923, Lubitsch had come fully to understand the American approach.
As a vehicle for Pickford, the film also is skillfully done, permitting her numerous intimate scenes that show off her charm. Given her star persona, the dramatic situation is leavened with humor in the interior scenes. Rosita’s poor family, a large, rowdy bunch, provides much of this, as when Rosita brings home a perfumed handkerchief and the impressed parents and children in turn bury their noses in it and sniff deeply. Rosita’s reactions to the King’s attempts to seduce her are also somewhat comic, though there is definitely a threat hanging over the situation.
Unfortunately, like all too many of the films on this year’s list, Rosita is difficult to see. It seems to have survived only in a Russian print, and a rather contrasty, worn one at that, as the frame above demonstrates. As long as that is the sole available material, a restoration might be too daunting. Still, in this day of digital manipulation, perhaps something could be done to improve the image quality. I hope at some point it will become available on home video. That also goes for Lubitsch’s other somewhat lesser films of the mid-1920s, Forbidden Paradise and Three Women.
Rosita’s reputation has suffered from strange statements Pickford much later made to Kevin Brownlow and which he published in The Parade’s Gone By. There she claims she and Lubitsch did not get along and that the resulting film was bad and a commercial failure. With the film itself unavailable for viewing, Pickford’s condemnation was accepted at face value. In fact, documents in the United Artists archive at the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research overturn Pickford’s supposed dislike for Lubitsch. For years she tried to find financing to make another film with him, and in 1926 she called upon him for help in editing Sparrows. With the discovery of the Soviet print, it becomes apparent that Rosita was far from the disaster Pickford later claimed. Why her memories of her work with Lubitsch became so distorted late in her life we shall probably never know.
Overshadowed masters of French Impressionism
Abel Gance’s flashy La roue (on last year’s list) gets a lot of attention these days. He’s the high-profile representative of Impressionism. Yet 1923 saw the first fiction films from the director who was the movement’s modest heart: Jean Epstein. The very first, L’auberge rouge (“The Red Inn”) is a lovely film, but Cœur fidèle (“Faithful Heart”) epitomizes the quiet side of Impressionism. It’s story is as simple as they get: Marie is a barmaid whose foster parents try to force her to marry a thug, Petit Paul, while she is in love with the sensitive dock-worker Jean. The scenes around the waterside and the famous sequence in a carnival are all done with a realism blended with the subjective camera techniques that convey the characters’ thoughts, perceptions, and feelings in a way that was fresh at the time.
The exteriors were shot around the docks of Marseille, and Epstein uses superimpositions of the ocean to convey the lovers’ longing. Waves are sometimes superimposed over their figures, or one will look into the water and see the other’s face there, as when Jean envisions multiple images of Marie:
Shooting into a distorting mirror, Epstein uses the conventional Impressionist indicator of drunkenness as Petit Paul looks at a woman next to him in a bar:
Coeur fidèle has been released in the UK (Region 2) as a DVD/Blu-ray combo in Eureka!’s Masters of Cinema series. (This includes a helpful little booklet with excerpt from Epstein’s writings and a review of Cœur fidèle by René Clair.) It is also available as a Region 2 French DVD without English subtitles. As these frames indicate, the film survives in beautiful condition.
Along with La roue, Cœur fidèle proved hugely influential. It used the “unfastened camera” that later was credited to Murnau in The Last Laugh. Like Murnau, Hitchcock picked up Impressionist style, as reflected most obviously in his 1927 boxing film, The Ring. Hitchcock’s penchant for moving camera and subjectivity never went away. Hollywood, too, picked up the subjective techniques of Impressionism, especially in the 1940s films that David is studying now.
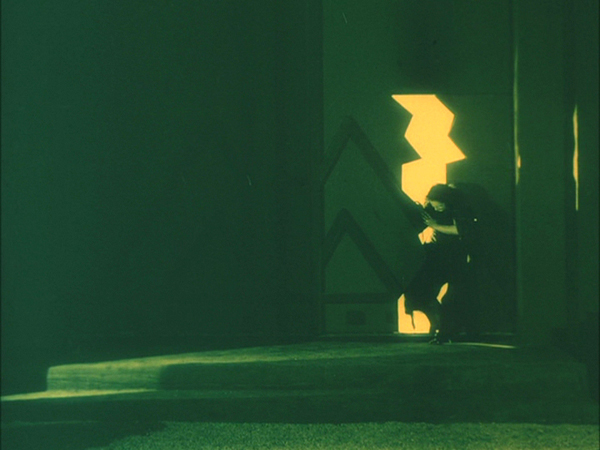
Unlike Cœur fidèle, Le brasier ardent (“The Burning Crucible”) was sophisticated, convoluted, and perplexing. It was one of two films directed in France by the Russian actor Ivan Mosjoukine for the émigré film company Albatros. (The earlier one is L’Enfant du carnaval, 1921; as far as I know, no print survives.) Earlier this year, upon the release of Flicker Alley’s box set of five Albatros films, I described Le brasier ardent:
It has a reputation as an audacious, surrealist, and almost incomprehensible film. This may be due to the fact that prints available in archives during the 1970s and 1980s lacked intertitles. The opening nightmare sequence is indeed disturbing, but at least with intertitles, we understand that it is only a dream. It begins with a wild-eyed man tied to a stake where he is about to be burned. The heroine stands looking on, resisting as the man pulls on her long hair, apparently intent on dragging her into the fatal flames to accompany him in death. Subsequent scenes of the nightmare show the heroine encountering different men, all played by Mosjoukine, culminating in a man in evening dress stalking her along a vaguely Expressionist street until she escapes and wakes up in bed.
This nightmarish opening must have established vivid expectations in the spectators of 1923 as to what sort of film they were in for. After the heroine wakes up, however, what follows is quite different. The main plot is a stylized but quite amusing comedy. The heroine is a pampered wife, married to a rich man whom she does not love. She is faithful, but he is unreasonably jealous. He goes to a distinctly odd detective agency, one department of which is “Recovery of Lost Wives” (above), with “Success guaranteed!” and “Nothing to pay in advance!” Juxtaposed with the bizarre opening, this quirky humor might have eluded puzzled audiences of the day. Certainly the film itself was a failure, and Mosjoukine stuck to acting thereafter.
Unfortunately for the husband, Detective Z, whom he picks from the eccentric group pictured above, is the very man, again played by Mosjoukine, whom his wife has dreamed about. What follows is an odd tale with the detective and wife gradually falling love. Mosjoukine, known for his tragic, intense characters in the Russian cinema, plays such figures in the fantasy sequences–but in the main story he is allowed to play for laughs, gamboling and rolling on the floor like a puppy when the wife finally appears at his mother’s apartment and declares her love for him.
Mosjoukine should not, however, be allowed to overshadow his co-stars, Ermolieff actors who were also were to make their way into the wider French production of the day, including Impressionism. The wife is played by Nathalie Lissenko, one of the stars of the pre-Revolutionary cinema, who had acted opposite Mosjoukine in Russia. Among her 1920s roles was the protagonist of one of Epstein’s finest films, the largely unknown L’Affiche (1924). The husband is Nicolas Koline, who started his career with Ermolieff only after the company had left the Soviet Union. He will be familiar to silent-film fans from his performance as Tristan Fleury in Gance’s Napoléon.
By this point, stylistic influences were beginning to pass back and forth between France and Germany. Le brasier ardent shows distinct touches of Expressionism in its decor, as when the heroine flees through a distorted door. (See top.)
 I have to admit that the third Impressionist film on our top-ten list, Germaine Dulac’s La souriante Madame Beudet (The Smiling Madame Beudet) is not one of my favorites. It hasn’t got much of a plot. A sensitive woman in a provincial town finds her husband crass and unpleasant until a final crisis brings them–at least temporarily–together. It’s not so much the simplicity of the story, however, as the rather heavy-handed use of subjective camera tricks to convey Mme. Beudet’s thoughts about her husband, as when a distorting mirror conveys her grotesque view of him (at right).
I have to admit that the third Impressionist film on our top-ten list, Germaine Dulac’s La souriante Madame Beudet (The Smiling Madame Beudet) is not one of my favorites. It hasn’t got much of a plot. A sensitive woman in a provincial town finds her husband crass and unpleasant until a final crisis brings them–at least temporarily–together. It’s not so much the simplicity of the story, however, as the rather heavy-handed use of subjective camera tricks to convey Mme. Beudet’s thoughts about her husband, as when a distorting mirror conveys her grotesque view of him (at right).
We’ve just seen a similar distortion in Cœur fidèle, above, to show a drunkard’s point of view. In Marcel L’Herbier’s El Dorado, from 1921, another distorted-mirror close-up suggests drunkenness without using a character’s point of view (see Film History: An Introduction, 3rd edition, p. 79).
The film has decided virtues, such as the lovely shots of the small provincial town in which the film’s exteriors were made, as well as the genuinely surprising and touching ending, which pulls back somewhat from the simplistic characterization of M. Beudet.
As with some of our choices from previous years, The Smiling Madame Beudet goes on the list partly because of its historical importance. Dulac was one of the early women directors to make a career in the cinema. Back in the days of 16mm, prints of this film were among the few Impressionist classics available for film club and classroom use, and the film became a staple in feminist-film courses.
Ironically, nowadays teaching the film is more difficult. Oddly enough, none of the mainstream labels has brought out a DVD with English subtitles. A German DVD, which includes two other short Dulac films, Invitation au voyage (1927) and the surrealist classic La coquille et le clergyman (1928), is available. The copy on this DVD is probably the same as the fairly good-quality Swiss archive print on YouTube, with bilingual French and German intertitles. For anyone with even an elementary knowledge of either language, the titles are not very challenging.
Caligarisme spreads
Caligarisme was the French word for cinematic Expressionism, which, as the example from Le brasier ardent shows, fascinating many French filmmakers.
Despite the lack of major contributions from Murnau and Lang, in 1923 the country’s cinema was going strong. Several films that fall slightly short of being masterpieces appeared. By this point the Expressionist film movement was well established, having begun in 1920 with Das Cabinet des Dr. Caligari. Some of its greatest films–Der müde Tod, Nosferatu and Dr. Mabuse der Spieler–had already appeared.
Three very good Expressionist films came out in 1923: Erdgeist (“Earth Spirit,” directed by Leopold Jessner), Schatten (“Shadows,” released abroad as Warning Shadows; Arthur Robison), and Raskolnikow (adapted from Crime and Punishment; Robert Wiene).
It’s really a toss-up as to which film should represent Expressionism on this year’s list. I give the edge to Erdgeist, largely because it and Von Morgens bis Mitternachts (“From Morn to Midnight”) are the two films from the movement that push the style the furthest. They come the closest to Expressionism as it existed in drama and the other arts. Most Expressionist cinema “tamed” the style a bit by applying it to genre tales: horror (Caligari, Nosferatu), fantasy (Der müde Tod), historical myth (Die Nibelungen), and science fiction (Algol, Metropolis). These two films, in contrast, depended on dramas where elemental human passions are released and taken to extremes, with the costumes, decor, makeup, and acting reflecting the characters’ inner states.
The film was based on the first of the two “Lulu” plays by Frank Wedekind: Erdgeist (1895) and its sequel Die Büchse der Pandora (Pandora’s Box, 1904). G. W. Pabst’s much better-known Pandora’s Box (1929) combines the two plays, which tell a continuous story about an amoral young woman who lives by exploiting wealthy men but drives them to extreme jealousy by flirting with other men.
In Pabst’s film, Louise Brooks plays Lulu as a vivacious young woman, seemingly unaware of her disastrous effect on the men around her. Asta Nielsen plays the character in Jessner’s film as a ruthless, mature woman. The plot concerns Dr. Schön, a rich man who found Lulu on the streets when she was a child and has raised her with the intent of having her become his mistress. At the beginning, she is married to Dr. Goll but immediately begins seducing Schwartz, an artist hired to paint her portrait. In the image below, Goll bursts in on them in Schwartz’s studio and Lulu collapses at the right. The distorted stairway, the streaks of light painted on the set, and the jagged shadows all create the Expressionist look–as does the eerie blank glow of Goll’s glasses.
The acting is exaggerated and unnatural. Nielsen, foregoing all glamor, frequently holds a grimace on her face to the point where she almost looks like she is wearing a mask. In an early scene Goll moves his cane about, and she dances like a marionette attached to it by strings. (Puppet-like acting was a convention of Expressionist drama.)
Overall, the style is so grotesque and the characters so unpleasant as to make it clear why Erdgeist is one of the least remembered of the major Expressionist films. It is not available on home video. The print I saw about 16 years ago had Dutch intertitles and was somewhat dark. Perhaps, like Von Morgens bis Mitternachts, it will eventually be restored and released on DVD.
Two Expressionist films deserve brief mention as well.
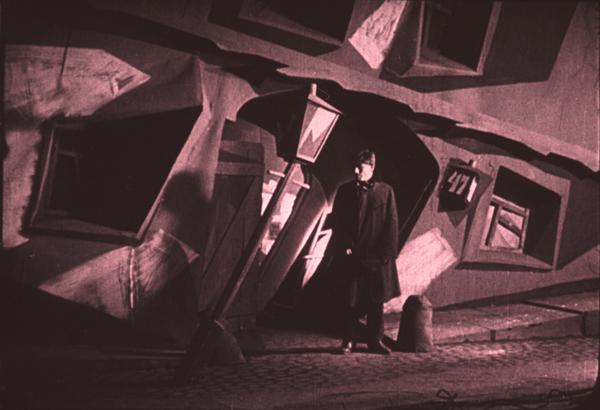
Robert Wiene, the director of The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari, launched the Expressionist movement in cinema but never made another film that gained nearly as much attention. That’s a pity, because Raskolnikow is quite a good film–of all the Wiene films I’ve seen, probably his second best (though The Hands of Orlac, 1924, has its virtues). I found it difficult to decide between it and Erdgeist.
Crime and Punishment turns out to be, not surprisingly, a good fit for the style, with the hero’s increasingly bizarre view of the world literalized in the settings. The film seems to have had a higher budget than Caligari, and the sets are sturdier looking and more three-dimensional. (See bottom.) Wiene also had the good fortune to work with a group of Russian emigré theatrical actors who had trained under Stanislawski and worked at the Moscow Art Theater. Clearly they had to adapt their approach distinctly to achieve Expressionist performances, but they managed well. The lead, Gregori Chmara, makes a haggard and mercurial Raskolnikow.
Back in the 1970s, when I became intrigued by German Expressionist cinema, Schatten was considered one of the main classics. That was no doubt partly due to the limited number of Expressionist titles available for viewing at the time. It’s a good film, but its prominence in film history has declined a bit in the intervening decades, especially as the full surviving work of Murnau and Lang has been discovered and restored.
Schatten is an atypical Expressionist film. Not that many of its sets are distorted or simplified in the usual ways. (This is also true to some extent of designer Albin Grau’s other notable Expressionist film, Nosferatu.) Its few exterior shots, including the opening, show the most strongly Expressionist decor (below left). Part of the action consists of a shadow-puppet show put on by a wandering entertainer (below right). Its plot seems to magically unleash the passions of the onlookers, who begin to behave in odd ways. The male guests (and a servant) try to seduce their hostess, driving the master of the house into a jealous rage.
The shadow play creates its own distortions and stark, black and white imagery. Once the show is over, Robison often frames the distorted shadows of the characters more prominently than their actual bodies (again echoing some of the scene with the vampire in Nosferatu). In this corridor scene one of the servants slyly creates cuckold’s horns on another man’s head:
Shadows, with their natural capacity for distortion, not surprisingly appeared in many Expressionist films, though never so pervasively as in this one.
Raskolnikow is unfortunately not available on home video, at least in an acceptable copy. (The reviews for the Alpha release on Amazon deem it “unwatchable.”) Warning Shadows is available on DVD from Kino or to stream on Amazon (free to Prime customers).
Returning to our top-ten list, I yield the floor briefly to David, who has been studying Sylvester for another project.
German silent cinema is more varied than a litany of the official classics, from Caligari to Metropolis, would suggest. One of the most intriguing trends of the period involved what was called the Kammerspiel, or chamber-play, film. Kammerspiel films were far more naturalistic than Expressionist films. They concentrate on a very few characters in a drastically limited number of locales. Performance is often slow and understated, though action may freeze into somewhat contorted poses. The action typically takes place in a short time span, and it is built up out of everyday activities in working-class households—chores, job routines, the habits of family life. Eventually, however, the mundane milieu is likely to explode into violence.
The versatile Carl Mayer (who worked on the script of Caligari) conceived of the early Kammerspiel film Scherben (Shattered, 1921), which defined the trend. In the same year the stage director Leopold Jessner released the remarkable Hintertreppe (Backstairs), which Kristin mentioned as a runner-up in her Best of 1921 list. Mayer also wrote the script for Sylvester (1923). Named for the feast day of St. Sylvester, 31 December, it’s known in English as New Year’s Eve. It’s not available on home video, but it’s worth seeking out in screenings. It remains a striking study in tabloid tragedy.
A café owner and his wife are busily serving crowds on New Year’s Eve. After a big meal and too many drinks, the wife and the mother-in-law fall to quarreling. The tensions around the table are constantly crosscut with the increasingly wild revelry in the café and the upper-class nightclub across the street. As midnight draws near, the women struggle for the husband’s loyalty. This petty quarrel will end in death.
Director Lupu Pick explores the limited space of the action by shooting the parlor from many angles, including ones that make daring use of a mirror (right). The street shots feature extravagant camera movements that look forward to the “unchained camera” made famous in Der letzte Mann (The Last Laugh, 1925), directed by F. W. Murnau and scripted by Mayer. With its strict limitation to a single night and its focus on domestic space, along with suggestions of the husband’s Freudian dependence on his mother, Sylvester showed how a fait divers could yield psychological drama.
The Kammerspiel film wasn’t a dead end. After Carl Dreyer’s borderline contribution to the trend, the Ufa production Michael (1924), back in Denmark he created probably the best of the lot: The Master of the House (Du Skal Aere Din Hustru, 1925). He later returned to the aesthetic in Two People (1945), and he continued to exploit its possibilities in his last features. Over the years after World War II, other directors were rediscovering Kammerspiel principles. We see fresh applications of the approach in Les Parents Terribles (Cocteau, 1948), Les Enfants Terribles (Melville, 1949), and of course Hitchcock’s Rope (1948) and Dial M for Murder (1954). As often happens, ambitious films of the sound cinema owe a good deal to innovative impulses of the silent era.
Welcome, experimental cinema!
One of the most remarkable films of 1923 is a mere three minutes long. Man Ray, an American painter and photographer who moved to Paris in 1921 and became involved in the Dadaist and Surrealist movements. He soon acquired a film  camera and later described how he shot bits of footage with it:
camera and later described how he shot bits of footage with it:
a few sporadic shots, unrelated to each other, as a field of daisies, a nude torso moving in front of a striped curtain with the sunlight coming through, one of [his] paper spirals hanging in the studio, a carton from an egg crate revolving on a string–mobiles before the invention of the word, but without any aesthetic implications nor as a preparation for future development: the true Dada spirit.
In 1923 Tristan Tzara advertised a Dadaist program in a Parisian theatre to be held the following evening, including a film by Man Ray as part of the entertainment. Ray had only a very small amount of footage ready. Faced with an overnight deadline, he supplemented it by using a technique he had already employed in still photography (the “rayograph”): placing small objects on a sheet of photographic paper in the dark, turning on the light briefly, and developing the image. The result was a series of sharply focused silhouette images of the objects against a plain background. This time Ray unrolled some raw negative film in a dark room, scattered nails, tacks, and other objects on it, exposed it to light, and developed the negative (right). Combined with the shots Ray had previously made, the result was a perfect Dada film, with randomly juxtaposed imagery that defied the audience to make any sense of what they were seeing. He titled it in ironic Dada fashion: Le retour à la raison (“The Return to Reason”).
Despite being cobbled together overnight, Ray’s film offers a broad exploration of the possibilities of abstract filmmaking. The opening, a rapidly shifting stippled screen, resembles the later flicker films of the 1960s avant-garde. The rayograph shots introduce an alien, high-contrast look–not surprising, given that these may have been the first cinema images produced without using a camera.
Ray also shifted between positive and negative imagery. This was not entirely new. Murnau had used short stretches of negative footage in Nosferatu the year before. But Murnau’s negative shots had a narrative function, to convey the eeriness of the environs of the vampire’s castle. In Le retour à la raison, Ray used negative imagery in an abstract way, to create startling juxtapositions of imagery that looked both similar and yet strikingly different. The tacks, nails, and springs in the rayograph stretches could be either stark white against black, as in the image to the right above, or the same shot repeated, but this time in black against white. The film ends with another positive/negative passage. The “nude torso moving in front of a striped curtain” is initially shown in a positive image, then in the same image flipped and shown in negative:
Ray was not the first to create an abstract film. In 1921 German filmmaker Walter Ruttmann probably made that conceptual leap in 1921 with Opus 1, a one-reeler with painted shapes moving around against a dark background. He followed this up with three further films, Opus 2 (1923), Opus 3 (1924), and Opus 4 (1925). (Good-quality prints with toning and appropriate musical accompaniment are available on YouTube: Opus 1 here, Opus 2 here, Opus 3 here, and Opus 4 here.)
I must confess that I probably should have at least mentioned Opus 1 in my entry on the best films of 1921. Still, Ruttmann’s films are far less daring than Le retour à la raison. It and its successors are basically efforts to do what so many filmmakers have tried since: to create the equivalent of a painting, but with motion. Ray’s film went much further, pushing the limits of the young art form in ways that had little precedent in the other arts, apart from Ray’s own highly experimental approach to still photography. There are even two fleeting stretches of film leader with illegible writing on them–a tactic one thinks of more in relation to, say, Bruce Conner’s A Movie (1958) than to the silent era. Much of the experimental cinema to come decades later was briefly probed here.
There are several copies of Le retour à la raison on YouTube. The best was posted by Dimitri Shubin, who also provides a piano score. The film is also available on disc 3 of the Unseen Cinema set of American experimental cinema. Unfortunately this copy has a considerable amount of breakup, particularly in the early flicker portions. (An HD version would perhaps help.) The version on Kino’s “Avant-Garde: Experimental Cinema of the 1920s and ’30s” set has the same problem and is distinctly shorter, apparently because it is running at sound speed. The copy provided by Shubin has the clearest, steadiest video image of the film I have seen. Ideally, of course, Ray’s film should be viewed on 35mm.
I regret that so many of our choices for this year’s list are not available on home video or even, except in very rare circumstances, for viewing on 35mm in archive screenings. Still, part of the purpose of this ongoing series is to call attention to obscure but worthy and important films. Perhaps an archivist or an enterprising DVD publisher will be inspired to restore some of the ones described here.
The quotation concerning The Three Ages comes from p. 217 of Rudi Blesh’s biography, Keaton (New York: Collier, 1966).
Mary Pickford’s strangely distorted claims about Rosita and her relationship with Lubitsch are expressed on pp. 129-34 of Brownlow’s The Parade’s Gone By (New York: Knopf, 1968). I go into more detail about the continuing Pickford-Lubitsch collegiality in the 1920s in Herr Lubitsch Goes to Hollywood, pp. 24-26.
For more examples of unusual German silent films, go elsewhere on this site here and here and here and here and here and here and here and here. Criterion has a new, authentic version of Dreyer’s Kammerspiel-influenced Master of the House forthcoming.
The Man Ray quotation comes from a detailed study of Le retour à la raison by Deke Dusinberre in the collection Unseen Cinema: Early American Avant-Garde Film 1893-1941 (New York: Anthology Film Archives, 2001), published to coincide with the release of the DVD set mentioned above.
Raskolnikow.
VIFF: Maps, math, madness, and more
Camille Claudel, 1915.
Kristin here:
We’re halfway through the Vancouver International Film Festival, as we continue to catch up on world cinema in one dizzying ten-day swoop. Here’s a handful of worthwhile films I’ve seen so far.
Another “brave” performance
Critics speak of “brave” performances as those in which the role calls for an actress (seldom, for some reason, an actor) to allow herself to look ugly and awkward or to participate in explicit set scenes. The word got tossed around a lot this year in regard to the two young actresses in Blue Is the Warmest Color, this year’s Palm d’Or winner at Cannes. David and I saw it here and found it disappointingly conventional.
Juliette Binoche’s performance in Bruno Dumont’s Camille Claudel, 1915 (2013) has her eschewing makeup and playing the haggard, aging inmate of an insane asylum. Historically, Claudel was a sculptress and Augut Rodin’s lover before being placed in the asylum by her family. As the title suggests, we see only a small slice of her life, after she has already spent a good deal of time in the asylum, a laudably humane one set in a Catholic nunnery in the mountains.
For much of the film, we stay with her, registering both her annoyance at the antics of her fellow inmates and her compassion for them. She seems to suffer from a persecution complex, cooking all her own food and eating apart from the others (above) through a fear of being poisoned. She attributes her incarceration to Rodin’s and his colleagues’ schemes to steal her studio and sculptures. We have no way of knowing how much of this is true, and hence no way of knowing whether she is really unbalanced enough to be in an institution with incurable cases. Her occasional visits to the complex’s church and her communing with nature help to sustain her.
Well into the film, there is an abrupt point-of-view switch to her brother, the author Paul Claudel, as he pauses en route to the asylum in order to pray. We soon realize that he is a religious zealot, utterly devoted to his own view of Catholicism. The contrast between his dogmatism and Camille’s simple religious sincerity bodes ill for her hopes that he will arrange for her release.
Camille Claudel, 1915 is currently available only on unsubtitled French DVD and Blu-ray.
Math and maps
I am a fan of maps and of scientific exploration of exotic places, and Detlev Buck’s Measuring the World (2012) promised to deal with both in 3D. It weaves together fictionalized accounts of the exploits of two contemporaneous geniuses of the early 19th century: world explorer Alexander von Humboldt and mathematical genius Carl Friedrich Gauss.
I had high hopes for the 3D, imagining scenes a bit like the scene where Michael Fassbender plays with dazzling holograms of space maps in Prometheus–toned down a bit and more scientifically grounded, of course. Unfortunately there was nothing of the sort, with the 3D being used more conventionally for creating depth in the playing space, with branches in the foreground of shots in the Amazonian jungle and that sort of thing.
The film turned out to be a rather rollicking depiction of the two careers. The conceit is set up that Karl Wilhelm Ferdinand, Herzog von Braunschweig provided financing for both Gauss and Humboldt. He is caricatured (above) as a frivolous, silly man who reacts in utter incomprehension when handed Gauss’s first book on mathematics–as who would not at the time, given that it introduced startling new insights that revolutionized the field? Ferdinand was in fact a highly educated military man, and he never supported von Humboldt’s work.
Still, the eccentricities of the two seekers of knowledge are entertaining, the scenes of von Humboldt seeking specimens in the Amazon and on into the Andes are exotic, and the whole thing conveys something of the enthusiasm lingering as the Age of Enlightenment was coming to its end.
Measuring the World is available as a region-coded import with English subtitles under its original title Die Vermessung der Welt on DVD, Blu-ray, and Blu-ray 3D.
An African Charmer
The Senegalese film, Tall as the Baobab Tree (2012), is the first feature of a young white filmmaker, Jeremy Teicher, who first visited the village in which the film is set when he was 19 and making a documentary about it. Based on stories of village life he was told at that time by young students, he made Tall as the Baobab Tree at age 22. The local people helped with the script and acted in the film.
As with many African films, the subject relates to a traditional custom which has come in modern times to be viewed as a problem. It reminds me of Ousmane Sembene’s last feature, Mooladé (2004), which dealt with how a village’s women began to resist the practice of genital mutilation. Tall as the Baobab Tree concerns the practice of selling young daughters into marriage.
The story centers around Coumba, a teenager who has just passed her school exams. Her older brother falls from a baobab tree (the one seen looming above the scene above), and to pay for his medical costs, the father decides to sell Debo, the younger sister, into marriage. Coumba secretly works as a maid in a nearby resort to pay the costs, but although she succeeds in raising most of the money, the local village elder insists that custom dictates that the promised marriage must go through.
Although the father and village elder are clearly seen as in the wrong, they are not made into villains but are seen as stuck in the patterns of outdated traditions. Much emphasis is put on the education that Coumba has benefited from and that Debo will never experience. A touching scene near the film’s beginning shows Coumba among the students waiting in a group as the names of those who have passed their exams are read out. Clearly this was an actual event captured by the filmmaker, and the joy of the successful students effectively emphasizes education as the means to defeat the more oppressive remnants of tribal traditions.
Teicher describes his experiences and approach in collaborating with the villagers on the film in an interview on the BFI website.
Beyond Ghibli
The films of Miyazaki Hayao (Kiki’s Delivery Service, Spirited Away) and his colleagues at the Ghibli animation studio are the heights of Japanese animation. Beyond them, we in the west tend to know of other Japanese animated films as more simply made anime, with lots of violent action. But, as the program notes state, “it’s time to expand your horizons.” Hosoda Mamoru’s Wolf Children (2012) somewhat resembles the Ghibli films in genre, being a fairy-tale-like fantasy set in the present day.
Hana, a student, is attracted to a young man, Ookami, who decides to sit in on one of her classes. She offers to share her textbook, and as a romance develops, she discovers that Ookami is a shape-shifter, able to change into a wolf. After they have two children, Ookami is killed while in his wolf form. His children have inherited his ability, and Hana moves to a house in the countryside to hide their peculiarities from prying eyes.
The story follows the daughter, Yuki, as she decides to go to school and follow the human half of her nature, and the son, Ame, as he prowls the surrounding forests and mountains, communing with wolves he discovers there. The result has an environmental theme similar to that underlying some of Miyazaki’s films, with particular sympathy for the perpetually hunted wolves.
While the figure animation here is not as subtle as that of the Ghibli films, the settings are beautiful and detailed, with highly textured portrayals of the roiling movements of large cumulus clouds and the rustling of countless leaves in a forest.
Wolf Children looks great on the big screen, but if you can’t catch it in a theater, it’s due out in the USA on November 26, available on DVD or a combination Blu-ray/DVD set.
Wolf Children.