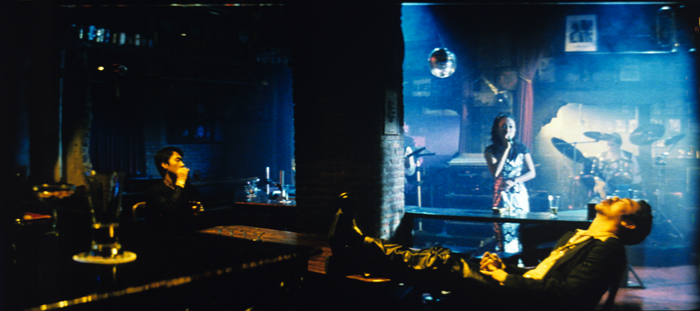Archive for the 'National cinemas: Hong Kong' Category
PLANET HONG KONG comes to . . . Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Film Critics Society has just published a Chinese long-form translation of the second edition of my Planet Hong Kong: Popular Cinema and the Art of Entertainment. It can be ordered from the HKFCS bookshop. Sample pages and further information can be found here. I’m grateful to Li Cheuk To, Alvin Tse, and their colleagues for preparing and checking the text and finding nice pictures.
That second English-language edition dates back to 2011–a distant past in terms of the rapid changes in world cinema. So for this translation, I wrote a postscript last year, and at the suggestion of Cheuk To I’m posting it here. The book is dedicated to Ho Waileng.
Revisiting Planet Hong Kong
Raymond Chow Man-Wai and Louis Cha Jin Yong both died in 2018. Journalists seeking a strong hook might take these unhappy departures as emblematic of changes in Hong Kong film culture—marking the “end of an era,” as we say. But Chow retired from the scene in 2007, and Cha finished revising his classics at about the same time. They stand, of course, as towering figures in Chinese cinema, but from my perspective today’s Hong Kong film is for the most part continuing processes that started quite far back. In other words, and much to my regret, the golden era ended some time ago.
I wrote the first edition of Planet Hong Kong in the late 1990s. As I explain in the book, I had been watching some Hong Kong films since the 1970s and got interested in the 1980s creative developments. By 1995, when I first visited the territory, those developments were already fading, though that wasn’t obvious to me. The local market was becoming unstable, regional tastes and investment sources were shifting, and the mainland economy was expanding. That age, undeniably golden, was ending.
When I interviewed local executives for the book, some said that they thought Hong Kong could become the “Hollywood of China.” Perhaps, they thought, all the experienced talents and financial and technical resources of the territory would be much sought after as China opened up its market.
By the time I came to revise the book in the early 2000s, such idealism had waned. As you’ll see in the pages that follow, it became obvious that Chinese authorities had shrewdly manipulated the market and the infrastructure to build up a powerful domestic industry. The rise of that industry, along with the waning of Hong Kong film, led to the biggest growth of a national film business ever seen in history. And those processes would assimilate Hong Kong creative talent on the mainland’s terms.
Now, as the 2010s come to an end, it seems that all the trends that I traced in the 2011 edition have continued, even accelerated. From 263.8 million viewers in 2010, mainland attendance has risen to over 1.6 billion in 2017. In 2010, the mainland claimed theatrical revenue of US$1.5 billion; in 2017 those were $8.27 billion. According to official figures, 970 feature films were produced in 2017. Although most of those were not released theatrically, it still remains a colossal achievement.
Over the same period, Hong Kong cinema continued in stasis. Production hovered between 42 and 64 annual releases. Theatrical admissions were likewise fairly flat, at an average of 25 million a year. Box-office revenues in 2010 came to US$179.4 million, and moved to $237.9 million in 2017. This is a substantial increase, but rising ticket prices (seen in every film culture) is likely one cause. Part of the rise, which occurred in the mid-2000s, is probably due to the emergence of 3D exhibition, which yields premium ticket pricing. And the greater part of that box office did not accrue to local films.
Certainly Hong Kong professionals at all levels were important resources for the growing mainland industry. Stars were and still are sought for major roles, and figures from decades ago, such as Chow Yun-fat, Tony Leung Chiu-wai, Shu Qi, and Andy Lau Tak-wah, can still draw audiences. Directors Tsui Hark, Jackie Chan, Stephen Chow Sing-chee, Peter Chan Ho-sun, Chang Pou-soi, Wong Jing, Johnnie To Kei-fung, and Stanley Tong Gwai-Lai found success in China, mostly with coproductions. The biggest coup of the era, Wolf Warrior 2 (2017; above) with its 154 million admissions, came from Wu Jing, a veteran actor and martial artist in Hong Kong films. Just as important, Edko, Emperor Motion Picture Group, and other local companies gained from producing movies for the mainland audience.
More broadly, the mainland box office was keeping Hong Kong film alive. A “local” film was likely to have mainland investment, and when it played there it had a good chance of making much more money than at home. SPL 2: A Time for Consequences (2015) took in less than US$2 million in Hong Kong but won over $90 million in China. Wong Jing’s From Vegas to Macau 2 of the same year captured $154 million there, as opposed to $3.6 million in Hong Kong. Through the 2010s, even a moderate success on the mainland could recoup far more money than it could in the tiny local market. To some extent the growing market to the north replaced the regional South Asian market that had sustained Hong Kong film in earlier decades. (How that market was lost is traced in Chapter 3.)
China cultivated homegrown directors as well, especially those who adapted conventions of Hong Kong and South Korean romantic drama and comedy to the local milieu. For any year, then, the top twenty films at the Chinese box office typically consisted of a mix. There would be imports (nearly all from Hollywood), domestic films by prestige directors (Zhang Yimou, Feng Xiaogang et al.), local genre films by younger hands, and two or three big box-office attractions steered by Hong Kong directors.
Coproductions that found mega-success in China didn’t register as strongly in Hong Kong. Tsui’s Flying Swords of Dragon Gate (2011), Jackie Chan’s CZ12 (2012), Peter Chan’s American Dreams in China (2013), Raman Hui’s Monster Hunt (2015), and Tsui’s Journey to the West: The Demons Strike Back (2017) all failed to crack the local top ten. Stephen Chow seems to have lost his hometown following: Journey to the West: Conquering the Demons (2013) failed to score big there, while The Mermaid (2016) did, but in seventh place, below Marvel superheroes and the local thriller Cold War 2.
Not that the territory’s audience was particularly loyal to locally-sourced product either. The waning attendance I noted in Chapter 10 persisted. For the period 2010 to 2018, no more than two local films won a place in any year’s top ten. For three of those years, none did. In 2018, Project Gutenberg ranked number 12, the only local film to appear among the top thirty contenders.
Granted, in most countries, especially small ones, domestic films don’t get big box-office returns. Hollywood films dominate, with only one or two local productions finding a place on the year’s top ten. Still, those of us who remember when Hong Kong films ruled the local market have to see the stagnation as saddening. Nonetheless, with China offering many more opportunities for investment and rewards, it’s remarkable that there remains a local industry at all—and one turning out four or five dozen features a year.
Those films have tended to follow the templates established decades ago: romantic comedies, domestic dramas, films of social comment, and urban action pictures. Filmmakers have updated those genres with digital production and mostly skillful use of modern technologies of color control, computer effects, and elaborate camera movements, including the use of drones for aerial shots. But anyone familiar with classic Hong Kong film will recognize the persistence of traditional plots and story premises. Golden Job (2018) brings back the rascals from the Young and Dangerous series to execute a heist, under circumstances that strain their brotherhood. Project Gutenberg (2018) revisits the Chow Yun-fat mythos with a counterfeiting story (shades of A Better Tomorrow) that allows him to wear white suits, brandish guns in both fists, and participate in a twisty plot that owes something to the 1990s narrative stratagems I discuss in Chapter 9.
The continuity should hardly be surprising, because a great many veteran creators are still active. Producer Raymond Wong Pak-ming, who co-founded Cinema City and went on to create Mandarin Films and Pegasus Motion Pictures, continues to release films. Yuen Woo-ping was a choreographer and director in the 1970s and achieved worldwide fame with The Matrix (1999) and Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon (2000); he recently directed Master Z: The Ip Man Legacy (2018). Ann Hui, Tsui Hark, and many other directors from the 1970s remain top figures in a film culture that offers many opportunities to venerated talents.
Although I’ve long admired Hong Kong films in many genres, readers of of Planet Hong Kong know that I believe that the action film—as wuxia pian, kung-fu movie, or cops-and-robbers thriller—was the area of its most long-lasting contribution. The tradition of powerful physical action, gracefully executed and forcefully staged and cut, was a genuine contribution to the history of film as an art form.
For that reason it’s a pleasure to report that the “ordinary” action pictures of the last decade have by and large maintained that tradition. Donnie Yen Ji-dan, an actor who chooses intelligent projects, endowed films like Kung Fu Jungle (2014), the Ip Man vehicles (2008-2019), and Chasing the Dragon (2017) with vivid, exciting sequences. He and other filmmakers seem to have abandoned the looser camerawork of the early 2000s and returned to precision shooting: fixed camera, instantly legible compositions, and a flow of movement across shots that can accelerate, slow, or halt, all in the service of impact on the viewer.
Still, in the hands of a skillful craftsman any technique can work. Benny Chan Muk-sing’s White Storm (2013), a full-bore male melodrama in the John Woo manner, mixes run-and-gun handheld style with a revival of the forceful compositions and crisp editing of the heroic-bloodshed days. Cheang Pou-soi’s Motorway (2012) invests a simple plot with excitement through nearly abstract shots of cars gliding through streets and alleys, augmented by stretches of ominous silence.
Similarly, I see the positive legacy of the Infernal Affairs series (2002-2003) in franchises like Overheard (2009-2014) and Cold War (2012, 2016). While not as tightly contained as the trilogy, these films benefit from plotting that is less episodic and more finely woven than we find in the policiers of the 1980s. They also judiciously insert florid action sequences, creating a sort of middle ground between the bureaucratic intrigue of Infernal Affairs and the more extroverted spectacle of something like Police Story (1985)—or, come to think of it, any of Jackie Chan’s Police Story titles.
There’s much to be said about Tsui Hark’s PRC adventure sagas as well, particularly in their use of 3D. (The Taking of Tiger Mountain, 2014 above, is a mind-bending use of that technology.) But for my purposes here I’d like to focus on two other major talents that I analyzed in the second edition. Both made outstanding contributions to the action picture in the years since the second edition was published.
Wong Kar-wai’s The Grandmaster (2013), despite being circulated in varying versions, remains for me a powerful achievement. It carries on Wong’s persistent experimentation with decentered narrative, following not only Master Ip Man but also his chief rival Razor and Gong Er, daughter of Ip’s one-time adversary. As I suggest in a blog entry this diffuse treatment of the major characters may bear the traces of a multiple-protagonist plot reminiscent of Days of Being Wild. In addition, through strategic flashbacks and shifts from character to character, this “chaptered” film evokes the interrupted and embedded story lines of other Wong films.
Stylistically, The Grandmaster makes fresh use of distended time and slow-motion imagery; these are conventions of the kung-fu genre as well as a signature of Wong’s work. More unusual is what I call in the blog entry the “mosaic” texture he builds up through close-ups that can be put in various places in one scene or another, or even one version or another. In general, I think that Wong alters the thematics of the martial-arts film by emphasizing Gong Er’s tragic dilemma: defeating the man who killed her father both sustains and erases her family’s legacy. And, as we might expect with Wong, the film strikingly parallels martial-arts prowess with impulses toward romantic love.
Another major film of 2013, Johnnie To Kei-Fung’s Drug War, is no less characteristic of its creator. (I analyze it in another blog entry.) A cat-and-mouse intrigue between crooks and cops, it depends heavily on our filling in gaps and reading characters’ minds. Police officer Zhang tries to penetrate a drug-smuggling outfit, and he devises a perfect To/Wai Ka-fai strategy: He sets up two meetings with two kingpins who don’t know each other. At each meeting Zhang impersonates the other guy. This game of shifting identities, of symmetry and doubling among roles, is a common narrative device of the Milkyway films, but in Drug War it’s given new urgency and a great deal of suspense. One economical shot brings the two unsuspecting gangsters together in the same frame as they leave and enter elevators.
At the same time, the informant Timmy is playing his own game—one that it may take a couple of viewings to decipher. As in The Mission (1999), many scenes of Drug War consist of men looking at each other, trying to divine hidden intentions—here, framed in the simplest possible shots, mere faces seen inside adjacent cars. Timmy’s eventual double-cross culminates in one of the cruelest shootouts to be found anywhere in To’s work; its bleakness recalls the end of Expect the Unexpected (1998). Throughout his career, To’s originality and craftsmanship in this rich genre have made him one of the great contemporary directors.
Wong completed only The Grandmaster in the years I’m considering, but To remained quite productive. Romancing in Thin Air (2011) and Don’t Go Breaking My Heart 2 (2013) returned to the mode of white-collar romance that Milkyway had made its own, while The Blind Detective (2013) combined that eccentric tone with an off-center cop premise recalling Mad Detective (2007). Life without Principle (2011; discussed in this entry) was a striking use of multiple-character plotting to make incisive points about the financial crisis.
Office (2015), an adaptation of Sylvia Chang’s popular play, was at once a flamboyant musical and an experiment in 3D. In Three (2016) To took up the challenge of a tightly circumscribed time and space, tracing the raid on a hospital ordered by a triad who’s there in police custody. Milkyway produced films by others, notably Motorway and Trivisa (2016), an opportunity for three first-time filmmakers to collaborate on a feature with three intersecting story lines. This last effort was in keeping with To’s dedication to creating programs and award competitions for newcomers to the industry. He remained one of Hong Kong’s most imaginative and tireless creators.
I should mention one more tendency, and it’s an encouraging one. Both editions of Planet Hong Kong pointed out that the Hong Kong people, contrary to the stereotype, actually cared a great deal about politics, especially after 1989. Recent years have seen a resurgence in films explicitly about activism in the territory. An early example is Matthew Tome’s documentary Lessons in Dissent (2014), a stirring account of struggles over educational policy and voting rights, featuring the most heroic 15-year-old I’ve ever seen. The 2014 Umbrella Revolution brought forth Evans Chan’s Raise the Umbrellas (2016) and Yellowing (2016; below) by Chan Tse Woon of Ying e chi There was also the ambitious speculative fiction Ten Years (2015), an ensemble of stories forecasting political repression in 2025. It’s very encouraging to see these efforts to insist on free speech and social criticism.
Finally, it’s worth pointing out how much classic Hong Kong film anticipated developments in Hollywood. The comic-book franchises that found new popularity with X-Men (2000) and Spider-Man (2002) and the Dark Knight trilogy (2005-2012) feature chivalric warriors with extraordinary fighting skills and weaponry. Like the knights-errant of wuxia fiction and film, these superheroes can leap high in the air and subdue villains with secret fighting techniques. Some, like Iron Man, have an equivalent of “palm power.”
Sometimes the American films have acknowledged their sources in Asian martial arts traditions, as when Batman trains as a ninja (Batman Begins, 2005) and Doctor Strange studies under a sifu in his 2016 film. The combat scenes, full of flips and somersaults, owe a great deal to the acrobatic traditions on display in Hong Kong cinema. If the result lacks the precision and visceral punch we find in classic Hong Kong films, it’s still worth noting that Westerners have learned that kung-fu, fights in mid-air, and elegant swordplay look cool on the screen. Hollywood should thank Hong Kong for helping invigorate the American action film.
A few words about what the original book tried to accomplish. At the most basic level, I wanted to understand Hong Kong cinema as an industry, an artistic tradition, and a cultural force. At the same time, I wanted to study it as an example of a popular cinema, one that developed strategies of storytelling and style and emotional appeal that were accessible to millions of people around the world. I wanted to analyze its unique contributions to the development of film art, so that meant I had to do some comparative work, situating Hong Kong film in relation to other traditions—most notably, that of Hollywood. At another level, I was interested in particular genres, especially the action film, and directors. As a result, parts of the book—mostly the “interludes”—are devoted to a particular filmmaker or group of filmmakers. And while I expected that many readers would already be Hong Kong film fans, I wanted to persuade skeptical readers that this national cinema was worth respect. This overall project I tried to amplify in the second edition you’re now reading.
Since the last edition, I have not followed Hong Kong cinema as intensively as I would have liked. Other projects have diverted me. But I have never lost my admiration for this cinema, this culture, and this citizenry. Watching Hong Kong films and visiting the territory have added a new dimension to my life.
From my first stay in 1995, when Li Cheuk-to introduced himself to me during the festival, through many visits over the decades, I have always treasured my friends there. So many people helped me in my research—people attached to the festival, to the archive, to the industry—that to list them all would add too much to this already overlong postscript. But they are mentioned throughout the book, and I hope they know how much I appreciate their generosity over the years. I’ll be happy if anything I’ve done here and elsewhere, in other writing and teaching, have helped film lovers better appreciate the astonishing contributions of Hong Kong film to world cinema artistry.
Among those valued friends was the kind and dedicated Ho Waileng. A tireless worker for the festival, she also translated the first version of Planet Hong Kong into Chinese. She remains in the hearts of everyone who knew her.
P.S. 10 August 2020: We in the US are now accustomed to being shocked but not surprised. I woke up to learn that Jimmy Lai, maverick mogul and publisher of Apple Daily, and many of his colleagues were arrested under the new “national security” law. It’s ironic that President Trump, who has reportedly sought to jail our journalists, moved quickly to place sanctions on Hong Kong earlier this year. The latest crackdown may be a response to the U.S. condemnation of the bill’s restrictions on free speech. (I discussed them here.) An arrest warrant is out for an American citizen living in the U.S. because he advocates democracy for Hong Kong. A coalition of Democratic and Republican senators and representatives have sponsored legislation to widen refugee status for Hong Kongers. Another irony: It’s called the Hong Kong Safe Harbor Act.
Ho Waileng at Angkor Wat, 2006. Photo by Li Cheuk To.
Little stabs at happiness 4: Hitmen, with a side of sukiyaki
A Hero Never Dies (1998).
DB here:
Again, with apologies to Ken Jacobs, I offer another clip that pleases me in this long, hot summer. For earlier installments, go here, here, and here.
Johnnie To Kei-fung has been one of the leading Hong Kong directors since the 1990s. The first edition of my Planet Hong Kong (2000) wasn’t able to incorporate many mentions of his work, but that failing was remedied in my second edition, where he got several pages. Kristin and I first met him in fall of 2001, when Yuin Shan Ding arranged for us to visit the set of Running Out of Time 2. That was a memorable night, with the bike race shot in an elaborate false street wreathed in noirish city vapor.
We spent down time with the stars Ekin Cheng Yee-kin and Lau Ching-wan. It was the beginning of a long friendship with Shan, Mr. and Mrs. To, and the Milkway team.
Well before this, though, I had been teaching Mr. To’s films in my courses, and I much enjoyed showing–on 35mm, no less–A Hero Never Dies (1998). This flamboyant film, about two rival hitmen who unite against the gang bosses who have betrayed them, is a sort of post-John-Woo meditation on the costs of loyalty.
One sequence that usually got the students going was the men’s first up-close confrontation in a bar. Having struck out at each other long-distance, they rendezvous for a face-off–not over guns but over glasses of wine. The clip lacks subtitles, so I should explain that each man instructs the bartender to pour for the other one. Then, after Lau deploys his portion tactically, he refers to Lai’s wrecking his apartment: “This is for destroying my home.” There follows a tabletop action scene.
Shot and cut with great precision, timed to an infectious tune, it’s a model of mock-heroic filmmaking. Its brashness suits its swaggering protagonists, but it has a playground absurdity that evokes Leone. (Think of the hat-blasting gun duel in For a Few Dollars More.) The comedy is enhanced by Lau’s reaction shots and, as Kristin likes to point out, the heaviest coin in Hong Kong. One student told me: “When you’ve got a sequence like this, you’ve got a great national cinema.”
The result yields a pure kinetic pleasure, due partly to the coiling camera movements and the echoing rhythm of the cuts and gestures (ducking out of frame/rising into frame, finger flips/snorting smoke). Mr. To kindly took me through the sequence in an interview, and I learned that it was all shot in one night, after the bar had closed. It wasn’t storyboarded, but by this point Mr. To had all his shots and cuts in his head, and he and the actors developed the sequence as they filmed it.
It takes real pictorial intelligence, I think, to glide between concreteness and abstraction, onscreen and offscreen space, and each man’s optical viewpoint so suavely and zestfully. The camera plays peekaboo with the action.
As for the performances, Mr. To explained that Lau Ching-wan is such an extroverted actor that Leon Lai-ming could counter that bravado best by impassivity, returning his look at key moments. It’s an echo of what Howard Hawks told Montgomery Clift in facing off against John Wayne in Red River. Eventually it all settles into a calm, integrating long shot that declares a truce. What a pleasure to see a scene that actually buttons itself up visually.
And the song? Mr. To told me that the pop version of “Sukiyaki” (on the ambient soundtrack of my own teen years) was often played in theatres as pre-show music. “It always reminds me of movies.”
Thanks to Shan, Mr. and Mrs. To, To Kei-chi, and many other members of the Milkyway team. And to Li Cheuk-to, Athena Tsui, Jacob Wong, Sam Ho, and all the other HKIFF allies over the years. And continued hope for a strong Hong Kong!
We have many blog entries on Johnnie To and Milkyway.
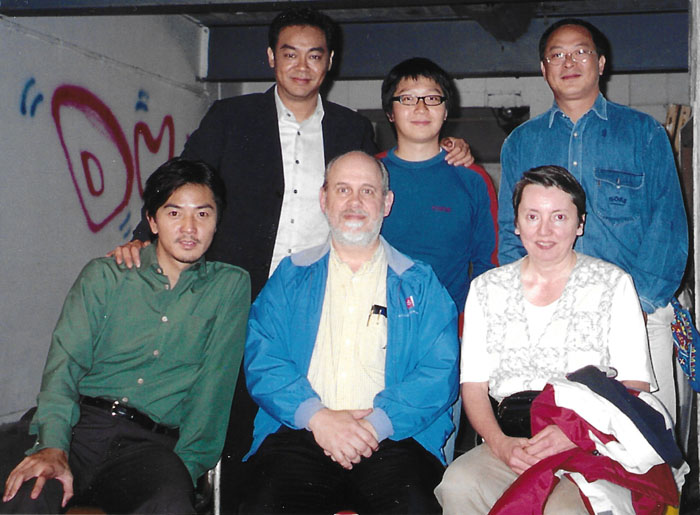
Upper row, left to right: Lau Ching-wan, Yau Na-hoi, Johnnie To Kei-fung; bottom row, Ekin Cheng Yee-kin, DB, KT. Hong Kong, November 2001. Photo: Yuin shan Ding.
Homage to Hong Kong
Yellowing (2014).
DB here:
Since forever, or so it seems, reports in the US media have been dominated by the struggles against the domestic fascism incarnated in the Republican Party and its leader Donald Trump. Every day, we’ve been subject to fusillades of stories about our collapsing economy, the pervasive corruption of the federal government and the judiciary, Trump’s frenzied efforts to whip up his racist supporters, and his failure to contain the coronavirus. In this churn, one world-altering event has gotten little attention: Mainland China’s swift and brutal takeover of the civil society of Hong Kong.
This spring, a new law–one that makes a mockery of lawfulness–was shoved through. Drafted in secret, its provisions were not made public to Hong Kong citizens or representatives before the central authorities in Beijing ratified it. It went into effect on 30 June. A good overview of timeline is on the BBC site.
While claiming to be within the One-Country/Two-Systems provision of the 1997 handover, the bill actually violates that, placing ultimate power in Beijing. The law devotes considerable attention to the purposes of
safeguarding national security; preventing, suppressing and imposing punishment for the offences of secession, subversion, organisation and perpetration of terrorist activities, and collusion with a foreign country or with external elements to endanger national security in relation to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. . . .
The law goes on to indicate what counts as subversion:
(3) seriously interfering in, disrupting, or undermining the performance of duties and functions in accordance with the law by the body of central power of the People’s Republic of China or the body of power of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region; or (4) attacking or damaging the premises and facilities used by the body of power of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region to perform its duties and functions, rendering it incapable of performing its normal duties and functions.
Obviously street demonstrations could “interfere in” or “disrupt” the activities of the territory’s “body of power”–as it resides in the bureaucracy, the police, and other realms of society. The penalties are severe:
A person who is a principal offender or a person who commits an offence of a grave nature shall be sentenced to life imprisonment or fixed-term imprisonment of not less than ten years; a person who actively participates in the offence shall be sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of not less than three years but not more than ten years; and other participants shall be sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of not more than three years, short-term detention or restriction.
The Economist explains:
The bill could result in far more serious charges being laid against protesters should they engage in activities that were common during the recent upheaval. Vandalising public transport could now be treated as terrorism. Breaking into the legislature or throwing eggs at the central government’s liaison office, as demonstrators did last year, could be considered subversive. Calling for Hong Kong’s independence, as some protesters have, could invoke a charge of secession. Encouraging foreign countries to impose sanctions on China could result in prosecution for collusion. The maximum sentence for all four of these categories of crime is life in prison.
How tightly will these provisions be enforced? The answer comes in a story in today’s New York Times. The day after the bill was enacted, a man was arrested for flying the Hong Kong flag during a demonstration. Police also arrested a 15-year-old girl for “inciting subversion” and a young man who carried in his bag a banner urging Hong Kong independence.
Other provisions lay out punishment for “terrorist activities” and, not least, “collusion with a foreign country or with external elements to endanger national security.” Possible offenders include international companies or non-governmental agencies that
provoke by unlawful means hatred among Hong Kong residents towards the Central People’s Government or the Government of the Region, which is likely to cause serious consequences.
A firm that participated in sanctions against China, or an NGO objecting to human-rights treatment could be charged with “fostering hatred.” The boundary between “lawful” and “unlawful” provocations will be left up to administrators such as the Secretary of Justice.
Hong Kongers saw clearly what might come. Such films as Yellowing and Ten Years foresaw just these strictures on free speech and free thought. Thanks partly to the 2014 Umbrella Movement, and the recent effort to pass a “Fugitive Offenders” bill, Hong Kongers’ support for an open society has been peaking. That surge was expressed last fall not only in more rounds of street activism but in the election of democratic representatives to 90 per cent of district seats.
Like Trumpists, Hong Kong’s business interests treat the behavior of the stock market as an index of prosperity. And it’s true that the market has bumped up at the prospect of “stability” under the new law. Yet, as in the US, this has proven a weak indicator. In 2013, the markets crashed and China had to inject money and conceal the sources of the failure.
During my first visit in 1995, a Dutch businessman who was already planning to take his gains and depart told me that in twenty years Hong Kong would be “just another city on the China coast.” He foresaw the mainland’s plan to build up Shanghai, to shrink Hong Kong as a business center, and to gut its quasi-democracy.
In the runup to 1997, Britain could have offered passports to all its former subjects, if only as a gesture to restrain Beijing’s hand. But of course that would have meant Margaret Thatcher acknowledging that there was something called “society,” which she explicitly denied. (That is, we owe no collective obligations to one another.) Now, in an encouraging sign some three million “overseas nationals” (i.e. Hong Kongers born before 1997) may be allowed to emigrate to the UK and seek citizenship there. As for the US, Secretary of State Mike Pompeo and Congress have proposed measures to retaliate against Chinese officials. Given Trump’s fear of offending Xi, I would not bank on his supporting the effort.
In all, the Dutchman’s prediction was off only in its timing. China has squeezed Hong Kong ever since the takeover, but its citizens–long and mistakenly thought of as indifferent to politics–have fought back with shining commitment. They are as much a vessel of strategic, patient political energy as the Black Lives Matter and Me Too movements.
My heart goes out to my friends in Hong Kong, and all their fellow citizens. They have been, and I expect will continue to be, a model of tenacity and resilience for the rest of us. We are all Hong Kong now. We face new authoritarian policies emerging, it seems, in every news cycle.
P. S. 6 July 2020: Yvonne Teh’s Webs of Significance blogsite offers a wealth of commentary on the changing culture and politics of Hong Kong. See especially her thoughts about Evans Chan’s latest film We Have Boots.
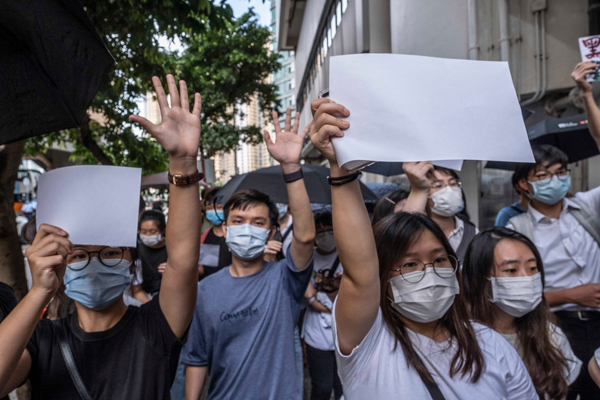
P.P.S. 6 July 2020: I should have included this photo (from Lam Yik Fei of the Times) as a sign of tenacity and resilience. HK demonstrators hold up blank signs. When will the PRC declare a blank piece of cardboard to bear “an intent such as secession or subversion”?
P.P.P.S. 13 July: Well, my answer came fast. The police are indeed arresting people for holding up blank sheets of paper. From the Los Angeles Times:
Hundreds of people have been arrested for unlawful assembly since the law came into effect, some charged with violations including carrying items bearing protest slogans and Bible verses. No one knows what is safe. Even the word “conscience” printed on a sticker can get you into trouble in an atmosphere that is scary and increasingly surreal.
The first blank-paper protester on July 1 was a young woman who told reporters she held up white paper because she wasn’t sure what would be illegal under the new law.
She had remembered a joke she’d read from the Soviet Union: an officer once arrested a person handing out fliers on Red Square, only to find that the fliers were blank. Undeterred, the officer shouted: “You don’t think I know what you wanted to write?”. . . .
Cartoonists drew protesters with empty speech bubbles, made emoji versions of their slogans and wrote out the tune to “Glory to Hong Kong” in numbers signifying the notes. A new graffiti theme appeared across the city: eight blank squares, each one holding space for a slogan whose absence seemed to speak out loud.
Two days after the white-paper protest, one of the arrested women was photographed walking out of the police station. She had been charged with illegal assembly and obstruction of police, according to local news reports.
She paused, her belongings slung over each shoulder, her eyes steady between a face mask and cap, and raised the blank paper once again.
A banner carried by Hong Kong police facing demonstrators “conducting themselves with an intent such as secession or subversion.”
Little stabs at happiness 3: You know, for kids
Iron Monkey (1993).
DB here:
Another entry (apologies to Ken Jacobs) of little things that cheer up lockdown. Previous entries are here and here. This one, unlike a couple to come, is suitable for all ages.
Why do I get a thrill from watching an apparently frail little boy beat the bejeezus out of unkempt bullies? More to the point, why weren’t there movies like Iron Monkey (1993) when I was a tad?
It’s a wing of the Tsui Hark Wong Fei-hung reboot saga that began with Once Upon a Time in China (1991), putting Jet Li on the world map. This installment is directed by Yuen Wo Ping, master choreographer of Crouching Tiger and The Matrix and no mean director himself. It’s a prequel, showing us the young Fei-hung learning his craft from his apothecary father and the mysterious robinhoodish Iron Monkey.
Before the main course, here’s a snack.
This one minute of graceful movement is one minute more than you find in most of our movies today. Do something short, smart, and crisp, and the camera loves it.
To see Young Wong finding his groove, here’s the scene in which he practices some fancy evasion and defense against heavily armed but fatally dumb thugs.
The subtitles provide a whole other level of diversion.
The whole film, featuring Donnie Yen and other Hong Kong stalwarts, is good dirty fun. Versions are available on streaming, but you should avoid the sanitized Miramax release. There’s also a 1977 kung-fu film bearing this English-language title, but its plot is quite different.
Note: The boy Wong is played by a girl martial artist, Angie Tsang Sze-man, who went on to become a wushu champion.
For an update on the situation in Hong Kong, here is a story in the Washington Post.
I write about the art and craft of Hong Kong martial arts movies in Planet Hong Kong: Popular Cinema and the Art of Entertainment. It explains, among other things, why the subtitles are so weird (p. 78).
P.S. 15 June 2020: Thanks to Radomir Kokes (Douglas) for correcting my misattribution of The Transporter to Yuen Wo Ping. It was of course directed by the great Corey Yuen Kwai.