Archive for the 'National cinemas: Hong Kong' Category
Unveiling Ebertfest 2014
Kristin here:
In the early days of Ebertfest, Roger personally introduced every film at this five-day event, which took place this year from April 23 to 27. He would be onstage for the discussions and question sessions after each screening, often joined by directors, actors, or friends in the industry.
In the summer of 2006, there began the long battle with cancer that Roger fought so determinedly. He withdrew gradually from full participation in the festival that he had founded in his hometown of Champaign-Urbana sixteen years ago. He struggled to immerse himself in the festival, even though repeated surgeries had robbed him of his voice. He introduced fewer films, doing so with his computer’s artificial voice, and when even that became too taxing, he sat in his lounge chair at the back of the Virginia Theater, enjoying the event and occasionally appearing onstage with a cheery thumbs-up. Finally, last year on April 4, less than three weeks before the fifteenth Ebertfest, he passed away. That year’s festival became a celebration of his life.
The celebration continued this year, though on a more upbeat note. Some films were chosen from a list that Roger had left to his wife Chaz and festival organizer Nate Kohn, and they selected others in the same indie spirit. The tradition of showing a silent film with musical accompaniment was maintained. As always, the festival passes sold out, and the crowd, including many long-time regulars, enthusiastically cheered both films and filmmakers.
The tributes
Roger did not live to see the documentary devoted to his life and based on his popular memoir of the same name, Life Itself. It premiered in January at this year’s Sundance Film Festival. He participated in its making, however, encouraging director Steve James (whose 1994 documentary Hoop Dreams Roger had championed) to film him during the final four months of his life. Some of this candid footage reveals the painful and exhausting treatments Roger underwent, but much of it stresses his resilience and the support of Chaz and the rest of his family.
Life Itself was the opening night film. James has done a wonderful job of capturing the spirit of the book and in assembling archival footage and photographs, interspersed with new interviews. The result is anything but maudlin, with a candid treatment of Roger’s early struggles with alcoholism and an amusing summary of Roger’s prickly but affectionate relationship with his TV partner Gene Siskel.
Life Itself was picked up for theatrical distribution by Magnolia Pictures and will receive a summer release, followed by a showing on CNN. (Scott Foundas reviewed the film favorably for Variety, as did Todd McCarthy for The Hollywood Reporter.)
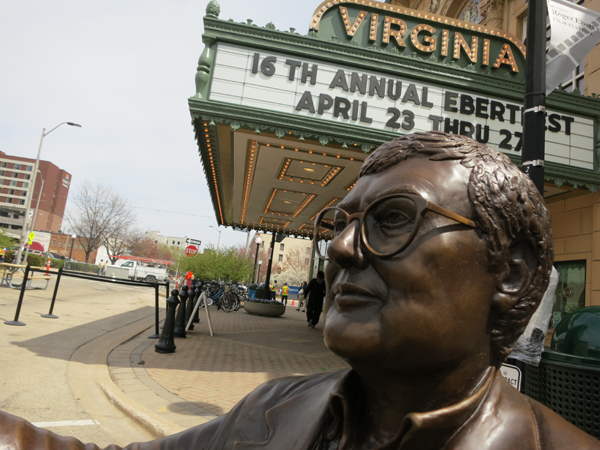
Another tribute followed the next day, when a life-size bronze statue of Roger by sculptor Rick Harney was unveiled outside the Virginia Theater (above). Harney portrays Roger in his most famous pose, sitting in a movie-theater seat and giving a thumbs-up gesture. There is an empty seat on either side of him, so that people can sit beside the statue and have their photos taken. (See the image of Barry C. Allen in the section “Of Paramount importance,” below.)
Far from silent
Roger was a big fan of the Alloy Orchestra, consisting of (L to R above) Terry Donahue, Ken Winokur, and Roger Miller, who specialize in accompanying silent films. They have appeared several times at Ebertfest, playing original music for such films as Metropolis and Underworld. Rather than taking a traditional approach to silent-film music, using piano, organ, or small chamber ensemble, they compose modern scores, played on electronic keyboard combined with their well-known “rack of junk” percussion section, including a variety of found objects, supplemented with musical saw, banjo, accordion, clarinet, and other instruments. The result is surprisingly unified and provides a rousingly appropriate accompaniment to the silents shown at Ebertfest over the years.
I have had the privilege of introducing the film and leading the post-film Q&A on some of these occasions, including for this year’s feature, Victor Seastrom’s 1924 classic, He Who Gets Slapped. (Swedish director Victor Sjöström used the Americanized version during his career in Hollywood.) I put the film in context by pointing out three important historical aspects of the film. First, it was the first film made from script to screen by the newly formed MGM studio, formed in 1924 from the merger of Goldwyn Productions, Metro, and Louis B. Mayer Pictures. (Two earlier releases by MGM were Norma Shearer vehicles which originated at Mayer.) Second, it was probably the film that cemented Lon Chaney’s stardom, after his breakthrough role as Quasimodo in the 1922 Hunchback of Notre Dame. Starting in 1912, Chaney had been in well over 100 films before Hunchback, many of them shorts and nearly all of them supporting roles. Third, He Who Gets Slapped was Seastrom’s second American film after Name the Man in 1923, and a distinct improvement on that first effort.
Naturally MGM wanted a big, prestigious hit for its first production, and He Who Gets Slapped came through, being both a critical and popular success–and also boosted Norma Shearer to major stardom. Seastrom and Chaney both stayed on at MGM, though the former returned to European filmmaking after the coming of sound and Chaney died in 1930.
I was joined for the post-film discussion by Michael Phillips of the Chicago Tribune, and we talked with Donahue and Winokur while Miller sold the group’s CDs and DVDs in the festival shop. They revealed that this new score had been commissioned by the Telluride Film Festival and that it was a project that appealed to their taste for off-beat films. There were many questions from the audience, and we suspect that the Alloy Orchestra will continue to be a regular feature of the festival.
A cornerstone of indie cinema
Although Roger was occasionally criticized for supposedly lowering the tone of film reviewing by participating in a television series, he and partner Gene Siskel regularly tried to promote indie and foreign films that didn’t get wide attention. Roger did the same in his written reviews, and Ebertfest was originally known as the “Overlooked Film Festival.” Inevitably it was shortened by many attendees to “Ebertfest,” and eventually that name became official. It reflects the wider range of films that came to be included, with the silent-film screening and frequent showings of 70mm prints of films like My Fair Lady that were hardly overlooked.
Among Roger’s friends was Michael Barker, co-founder and co-president of Sony Pictures Classics, one of the most important of the small number of American companies still specializing in independent and foreign releases. A long-time Ebertfest regular, Barker usually brings a current or recent release to show, along with filmmakers or actors. This year he was doubly generous, bringing Capote (2005, above), to which Roger had given a four-star review, and the current release Wadjda (2012).
Roger never reviewed the latter, but it is certainly the sort of film that he loved: a glimpse into a little-known culture by a first-time filmmaker with a progressive viewpoint. Wadjda is remarkable as the first feature film made in Saudi Arabia, where there are no movie theaters. Moreover, it was made by a woman, Haifaa Al-Monsour, and tells the story of a little girl who defies tradition by aspiring to buy and ride a bicycle in a country where this, like women driving cars, was illegal. (Below, Wadjda learns to ride a bicycle on a rooftop, hidden from public view.)
Both the film and Al-Monsour thoroughly charmed the audience. Barker interviewed her afterward, and she revealed that, not surprisingly, the making of the film was touched by the same sort of repression that it portrays. Women are not allowed to work alongside men in Saudi Arabia, so Al-Monsour had to hide in a van while shooting on location. Given that there is no cinema infrastructure in the country, the film was a Saudi Arabian-German co-production, with Arabic and German names mingling in the credits. We also learned that it has since become legal for Saudi girls to ride bicycles. Perhaps someday filmmaking will become more common there, and male and female crew members can work openly together.
Naturally Wadjda was made with a digital camera, since this new technology is crucial to the spread of filmmaking in places like the Middle East where there is little money or equipment for production. In contrast, Capote was shown in a beautiful widescreen 35mm print that looked great spread across the entire width of the Virginia’s huge screen. Naturally the screening became a tribute to the late Phillip Seymour Hoffman, giving his only Oscar-winning performance (out of four nominations) in the lead role.
Barker had brought with him a surprise guest, Capote‘s director, Bennett Miller, whose appearance had not been announced in advance. He discussed how he and scriptwriter Dan Futterman learned that there was a second, rival Capote film in the works, Infamous (2006), which also dealt with the period when the author was researching In Cold Blood. Miller and Futterman decided to press ahead, a wise move in that their film drew more attention than did Infamous. Much of the discussion was devoted to Hoffman’s performance and his acting style in general.
Capote was Miller’s first fiction feature. He had come to public attention with his documentary The Cruise (1998), which Roger had given a brief three-star review. Roger continued his support for Miller with a four-star review for Moneyball (2011). It’s a pity he did not live to see Miller’s latest, Foxcatcher, which will be playing in competition at Cannes in May.
Overlooked no longer
Perhaps no young filmmaker better demonstrates the impact that Roger’s support can have on a career than Ramin Bahrani. Roger saw his first feature, Man Push Cart, at Sundance in 2006 and invited it and the filmmaker to the  “Overlooked Film Festival” that April. (Roger’s Sundance review is here.) The film then played other festivals, notably Venice and our own Madison-based Wisconsin Film Festival. It won several awards, including an Independent Spirit Award for best first feature. In October Roger gave the film a more formal review, awarding it four stars. Man Push Cart never got a wide release, and it certainly didn’t make much money. Still, quite possibly the high profile provided by Roger’s attention allowed Bahrani to move ahead with his career.
“Overlooked Film Festival” that April. (Roger’s Sundance review is here.) The film then played other festivals, notably Venice and our own Madison-based Wisconsin Film Festival. It won several awards, including an Independent Spirit Award for best first feature. In October Roger gave the film a more formal review, awarding it four stars. Man Push Cart never got a wide release, and it certainly didn’t make much money. Still, quite possibly the high profile provided by Roger’s attention allowed Bahrani to move ahead with his career.
His second film, Chop Shop, brought him to Ebertfest a second time, in 2009. (Roger’s program notes are here, and his four-star review here.) At about that time, Bahrani’s third film, Goodbye Solo, was released. Given its modest budget, it did reasonably well at the box office, grossing nearly a million dollars worldwide (in contrast to Man Push Cart‘s roughly $56 thousand). Bahrani inched toward mainstream filmmaking with At Any Price (2012), starring Dennis Quaid and Zac Efron, and he is currently in post-production on 99 Homes, with Andrew Garfield, Michael Shannon, and Laura Dern. During the onstage discussion, he spoke of struggling to maintain a balance between the indie spirit of his earlier films and the more popularly oriented films he has recently made.
Bahrani visited Ebertfest for a third time this year, belatedly showing Goodbye Solo. We had enjoyed this film when it came out, and it holds up very well on a second viewing. It’s a simple story of opposites coming together by chance. An irrepressibly talkative, friendly immigrant cab driver, Solo (a nickname for Souléymane), becomes concerned when a dour elderly man engages him for a one-way trip to a regional park whose main feature is a windy cliff. He fears that William is planning suicide. Solo arranges to drive William whenever he calls for a cab and even becomes his roommate in a cheap hotel. Gradually, with the help of his young stepdaughter Alex, he seems to draw William out of his defensive shell.
As in Bahrani’s earlier films the main character is an immigrant and played by one, using his own first name (Souléymane Sy Savané). He’s the main character in that we are with him almost constantly, seeing William only as he does. William is a vital counterpart to him, however. He is perfectly embodied by Red West, an actor who worked for Elvis Presley and did stunt work and bit parts in films and television since the late 1950s. He may look vaguely familiar to some viewers, but he’s not really recognizable as a star and comes across convincingly as an aging man buffeted by life’s misfortunes.
Most of the film takes place in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, Bahrani’s hometown, with many moody, atmospheric shots of the cityscape at night. One crucial scene involves a drive into the woods and mountains, however, and much of it is filmed in a dense fog. One questioner from the audience asked if Bahrani had planned to shoot in such weather or if, given his short shooting schedule, the fog turned out to be a hindrance to him. He responded that he had dreamed of being able to shoot in fog and that the weather cooperated on the three days planned for that locale. In fact, he re-shot some images as the fog became denser, to keep the scene fairly consistent.
Bahrani’s presence at Ebertfest spans half its existence, from 2006 to 2014. As the festival becomes more diverse in its offerings, it is good to have him back as a reminder of the Ebertfest’s early emphasis on the “overlooked.”
Of Paramount importance
Logo for National Telefilm Associates, TV syndication arm of Republic Pictures.
DB here:
Among the guests at this year’s E-fest was Barry C. Allen. For over a decade Barry was Executive Director of Film Preservation and Archival Resources for Paramount. That meant that he had to find, protect, and preserve the film and television assets of the company—including not just the Paramount-labeled product but libraries that Paramount acquired. Most notable among the latter was the Republic Pictures collection.
We may think of Republic as primarily a B studio, but it produced several significant films in the 1940s and 1950s—The Red Pony, The Great Flammarion, Macbeth, Moonrise, and Johnny Guitar. John Wayne became the most famous Republic star in films like Dark Command, Angel and the Badman, and Sands of Iwo Jima. John Ford’s The Quiet Man was Wayne’s last for the studio, which folded in 1959. Next time you see one of the gorgeous prints or digital copies of that classic, thank Barry for his deep background work that underlies the ongoing work of his dedicated colleagues.
 Barry told me quite a lot about conservation and restoration, but just as fascinating was his account of his earlier career. A lover of opera, literature, and painting since his teenage years, he was as well a passionate movie lover. An Indianapolis native, he thinks he saw his first movie in 1949 at the Vogue, now a nightclub. He projected films in his high school and explored still photography. He was impressed when a teacher told him: “If you want to make film, learn editing.” Soon he was in a local TV station editing syndicated movies.
Barry told me quite a lot about conservation and restoration, but just as fascinating was his account of his earlier career. A lover of opera, literature, and painting since his teenage years, he was as well a passionate movie lover. An Indianapolis native, he thinks he saw his first movie in 1949 at the Vogue, now a nightclub. He projected films in his high school and explored still photography. He was impressed when a teacher told him: “If you want to make film, learn editing.” Soon he was in a local TV station editing syndicated movies.
Hard as it may seem for young people today to believe, in the 1950s TV stations routinely cut the films they showed. Packages of 16mm prints circulated to local stations, and these showings were sponsored by local businesses. Commercials had to be inserted (usually eight per show), and the films had to be fitted to specific lengths.
WISH-TV ran three movies a day, and two of those would be trimmed to 90-minute air slots. That meant reducing the film, regardless of length, to 67-68 minutes. Barry’s job was to look for scenes to omit—usually the opening portions—and smoothly remove them. Fortunately for purists, the late movie, running at 11:30, was usually shown uncut, and then the station would sign off.
By coincidence I recently saw a TV print of Union Depot (Warners, 1932) that had several minutes of the opening exposition lopped off. We who have Turner Classic Movies don’t realize how lucky we are. Fortunately for film collectors, some stations, like Barry’s, retained the trims and put them back into the prints.
While working at WISH-TV, Barry began booking films part-time. He programmed some art cinemas in the Indianapolis area during the early 1970s, mixing classic fare (Marx Brothers), current cult movies (Night of the Living Dead), and arthouse releases like Discreet Charm of the Bourgeoisie—a bigger hit than anyone had anticipated. He also helped arrange a visit of Gloria Swanson with Queen Kelly; she carried the nitrate reels in her baggage.
At the same time, Barry was learning the new world of video editing, with ¾” tape and telecine. Because of his experience in television, Barry was contacted by Paramount to become Director of Domestic Syndication Operations. His chief duty was to deliver films to TV stations via tape, satellite, and prints. From that position, he moved to the preservation role he held until 2010, when he retired.
Barry is a true film fan. He has reread Brownlow’s The Parade’s Gone By many times and retains his love for classic cinema. The film that converted him to foreign-language cinema was, as for many of his generation, Children of Paradise, but he retains a fondness for Juliet of the Spirits, The Lady Killers, and other mainstays of the arthouse circuit of his (and my) day. He’s proudest of his work preserving John Wayne’s pre-Stagecoach films.
It was a great pleasure to hang out with Barry at Ebertfest. Talking with him reminded me that The Industry has long housed many sophisticated intellectuals and cinephiles. Not every suit is a crass bureaucrat.
Young-ish adult
Patton Oswalt had planned to come to Ebertfest in an earlier year, to accompany Big Fan and to show Kind Hearts and Coronets to an undergrad audience. He had to withdraw, but he showed up this year. On Wednesday night he screened The Taking of Pelham 123 to an enthusiastic campus crowd, and the following night, after getting his Golden Thumb, he talked about Young Adult. (Roger’s review is here.)
 As you might expect from someone who has mastered stand-up, writing (the excellent Zombie Spaceship Wasteland), TV acting, and film acting, Oswalt stressed the need for young people to grab every opportunity to work. He enjoys doing stand-up; with no need to adjust to anybody else, it’s “the last fascist post in entertainment.” But he also likes working with other actors in the collaborative milieu of shooting film. He insists on not improvising: “Do all the work before you get on camera.” I was surprised at how quickly Young Adult was shot—one month, no sets. Oswalt explained that one aspect of his character in the film, a guy who customizes peculiar action figures, was based on Sillof, a hobbyist who does the same thing and sells the results. Oswalt talks about Sillof and Roger Ebert here.
As you might expect from someone who has mastered stand-up, writing (the excellent Zombie Spaceship Wasteland), TV acting, and film acting, Oswalt stressed the need for young people to grab every opportunity to work. He enjoys doing stand-up; with no need to adjust to anybody else, it’s “the last fascist post in entertainment.” But he also likes working with other actors in the collaborative milieu of shooting film. He insists on not improvising: “Do all the work before you get on camera.” I was surprised at how quickly Young Adult was shot—one month, no sets. Oswalt explained that one aspect of his character in the film, a guy who customizes peculiar action figures, was based on Sillof, a hobbyist who does the same thing and sells the results. Oswalt talks about Sillof and Roger Ebert here.
It’s common for viewers to notice that Mavis Gary, the malevolent, disturbed main character of Young Adult, doesn’t change or learn. “Anti-arc and anti-growth,” Oswalt called the movie. I found the film intriguing because structurally, it seems to be that rare romantic comedy centered on the antagonist.
Mavis returns to her home town to seduce her old boyfriend, who’s now a happy husband and father. A more conventional plot would be organized around Buddy and his family. In that version we’d share their perspective on the action and we’d see Mavis as a disruptive force menacing their happiness.
What screenwriter Diablo Cody has done, I think, is built the film around what most plots would consider the villain. So it’s not surprising that there’s no change; villains often persist in their wickedness to the point of death. Attaching our viewpoint to the traditional antagonist not only creates new comic possibilities, mostly based on Mavis’s growing desperation and her obliviousness to her social gaffes. The movie comes off as more sour and outrageous than it would if Buddy and Beth had been the center of the plot.
Making us side with the villain also allows Oswalt, as Matt Freehauf, to play a more active role as Mavis’s counselor. In a more traditional film, he’d probably be rewritten to be a friend of Buddy’s. Here he’s the wisecracking voice of sanity, reminding Mavis of her selfishness while still being enough in thrall to high-school values to find her fascinating. As in Shakespearean comedy, though, the spoiler is expelled from the green world that she threatens. It’s just that here, we go in and out of it with her and see that her illusions remain intact. Maybe we also share her sense that the good people can be fairly boring.
All you can eat
There aren’t any villains in Ann Hui’s A Simple Life, a film we first saw in Vancouver back in 2011. Roger had hoped to bring it last year, but Ann couldn’t come, as she was working on her upcoming release, The Golden Era. This year she was free to accompany the film that had a special meaning for Roger at that point in his life.
The quietness of the film is exemplary. It’s an effort to make a drama out of everyday happenings—people working, eating, sharing a home, getting sick, worrying about money, helping friends, and all the other stuff that fills most of our time. The two central characters are, as Roger’s review puts it, “two inward people” who are simple and decent. Yet Ann’s script and direction, and the playing of Deanie Yip Tak-han and Andy Lau Tak-wah, give us a full-length portrait of a relationship in which each depends on the other.
Roger Leung takes Ah-Tao, his amah, or all-purpose servant, pretty much for granted. She feeds him, watches out for his health, cleans the apartment, even packs for his business trips. When he’s not loping to and from his film shoot, he’s impassively chowing down her cooking and staring at the TV. A sudden stroke incapacitates her, and now comes the first surprise. A conventional plot would show her resisting being sent to a nursing home, but she insists on going. Having worked for Roger’s family for sixty years, Ah-Tao can’t accept being waited upon in the apartment. So she moves to a home, where most of the film takes place.
A Simple Life resists the chance to play up dramas in the facility. Thanks to a mixture of amateur actors and non-actors, the film has a documentary quality. It captures in a matter-of-fact way the grim side of the place—slack jaws, staring eyes, pervasive smells. (A small touch: Ah-Tao stuffs tissue into her nostrils when she heads to the toilet.) Mostly, however, we get a sense of the facility’s everyday routines as the seasons change. The dramas are minuscule. Occasionally the old folks snap at one another, and one visitor gets testy with her mother-in-law. One woman dies (in a bit of cinematic trickery, Ann suggests that it’s Ah-Tao), and an old man who keeps borrowing money is revealed to have a bit of a secret. It’s suggested that a pleasant young woman working at the care facility will become Roger’s new amah, but that seems not to happen. The prospect of a romance with her is evoked only to be dispelled.
Ah-Tao’s health crisis has made Roger more self-reliant, but his life has become much emptier. He seems to realize this in a late scene, when he stands in the hospital deciding how to handle Ah-Tao’s final illness. Throughout the film, food has been a multifaceted image of caring, community, friendship, childhood (Roger’s friends recall Ah-Tao cooking for them), and even the afterlife. Ah-Tao and Roger rewrite the Ecclesiastes line about what’s proper to every season by filling in favorite dishes. As he mulls over Ah-Tao’s fate, Roger is, of course, eating. But it’s cheap takeaway noodles and soda pop. This silent scene measures his, and her, loss better than any dialogue could.
The art of American agitprop
Matt Zoller Seitz and Oliver Stone on stage at the Virginia Theatre.
A Simple Life is a very quiet film. Ebertfest’s highest-profile visitors brought along two of the noisiest movies of 1989. It’s the twenty-fifth anniversary of Do The Right Thing (Roger’s review) and Born on the Fourth of July (Roger’s review), and seen in successive nights they seemed to me to put the “agitation” into agitprop.
 During the Q & A, Spike Lee reminded us that some initial reviews of the film (here shown in a gorgeous 35mm print) had warned that the film could arouse racial tensions. Odie Henderson has charted the alarmist tone of many critiques. Lee insisted, as he has for years, that he was asking questions rather than positing solutions. “We wanted the audience to determine who did the right thing.” He added that the film was, at least, true to the tensions of New York at the time, which were–and still are–unresolved.
During the Q & A, Spike Lee reminded us that some initial reviews of the film (here shown in a gorgeous 35mm print) had warned that the film could arouse racial tensions. Odie Henderson has charted the alarmist tone of many critiques. Lee insisted, as he has for years, that he was asking questions rather than positing solutions. “We wanted the audience to determine who did the right thing.” He added that the film was, at least, true to the tensions of New York at the time, which were–and still are–unresolved.
The ending has become the most controversial part of the film. It’s here that Lee was, I think, especially forceful. The crowd in the street is aghast at the killing of Radio Raheem by a ferocious cop, but what really triggers the riot is Mookie’s act of smashing the pizzeria window. I’ve always taken this as Mookie finally choosing sides. He has sat the fence throughout–befriending one of Sal’s sons and quarreling with the other, supporting Sal in some moments but ragging him in others. Now he focuses the issue: Are property rights (Sal’s sovereignty over his business) more important than human life? Moreover, in a crisis, Mookie must ally himself with the people he lives with, not the Italian-Americans who drive in every day. It’s a courageous scene because it risks making viewers, especially white viewers, turn against that charming character, but I can’t imagine the action concluding any other way. Lee had to move the project to Universal from Paramount, where the suits wanted Mookie and Sal to hug at the end.
Staking so much on social allegory, the film sacrifices characterization. Characters tend to stand for social roles and attitudes rather than stand on their own as individuals. The actors’ performances, especially their line readings, keep the roles fresh, though, and the film still looks magnificent. I was struck this time by the extravagance of its visual style. In almost every scene Lee tweaks things pictorially through angles, color saturation, slow-motion, short and long lenses, and the like–extravagant noodlings that may be the filmic equivalent of street graffiti.
By the end, in order to underscore the confrontation of Radio Raheem and Sal, Lee and DP Ernest Dickerson go all out with clashing, steeply canted wide-angle shots. (We’ve seen a few before, but not so many together and usually not so close.) Having dialed things up pretty far, the movie has to go to 10.
In Born on the Fourth of July, Stone more or less starts at 11 and dials up from there. Beginning with boys playing soldier and shifting to an Independence Day parade that for scale and pomp would do justice to V-J Day, the movie announces itself as larger than life. The storyline is pretty straightforward, much simpler than that of Do The Right Thing. A keen young patriot fired up with JFK’s anti-Communist fervor plunges into the savage inferno of Viet Nam. Coming back haunted and paralyzed, Ron Kovic is still a fervent America-firster until he sees college kids pounded by cops during a demonstration. This sets him thinking, and eventually, after finding no solace in the fleshpots of Mexico, he returns to join the anti-war movement.
Even more than Lee, Stone sacrifices characterization and plot density to a larger message. The Kovic character arc suits Cruise, who built his early career on playing overconfident striplings who get whacked by reality. But again characterization is played down in favor of symbolic typicality. While there’s a suggestion that Ron Kovic joins the Marines partly to prove his manhood after losing a crucial wrestling match, the plot also insists that his hectoring mother and community pressure force him to live up to the model of patriotic young America. He becomes an emblem of every young man who went to prove his loyalty to Mom and apple pie.
Likewise, Ron’s almost-girlfriend in high school becomes a college activist and so their reunion–and her indifference to his concern for her–is subsumed to a larger political point. (The hippies forget the vets.) We learn almost nothing about the friend who also goes into service; when they reunite back home, their exchanges consist mostly of more reflections on the awfulness of the war. Later Cruise is betrayed, almost casually, by an activist who turns out to be a narc. But this man is scarcely identified, let alone given motives: he’s there to remind us that the cops planted moles among the movement.
What fills in for characterization is spectacle. I don’t mean vast action; Stone explained that he had quite a limited budget, and crowds were at a premium. Instead, what’s showcased, as in Do The Right Thing, is a dazzling cinematic technique.
Visiting the UW-Madison campus just before coming to Urbana for Ebertfest, Stone offered some filmmaking advice: “Tell it fast, tell it excitingly.” The excitement here comes from slamming whip pans, thunderous sound, various degrees of slow-motion, silhouettes, jerky cuts, Steadicam trailing, handheld shots, all jammed into the wide, wide frame. Every crack is filled with icons and noises–flags, whirring choppers, kids with toy guns, prancing blondes, commentative music. “Soldier Boy” plays on the supermarket Muzak when Ron is telling Donna about his plans.
By the time Ron visits the family of the comrade he accidentally killed, Stone finds another method of visual italicization: the split-focus diopter that creates slightly surreal depth.
Since so many scenes have consisted of a flurry of intensified techniques, simple over-the-shoulder reverse shots might let the excitement level drop. So a new optical device aims to deliver fresh impact in one of the film’s quietest moments.
Like Lee, Stone took the Virginia Theatre audience behind the scenes. He agreed with William Friedkin, who was originally slated to do the film: “This is as close as you’ll every come to Frank Capra.” Instead of using the shuffled time scheme of Kovic’s autobiography, Friedkin advised that “This is good corn. Write it straight through.” Hence the film breaks into distinct chapters, each about half an hour long and sometimes tagged with dates. They operate as blocks measuring phases of Ron’s conversion. Like many filmmakers of his period, Stone deliberately made each chapter pictorially distinct–the low-contrast Life-magazine colors of the opening parade versus the lava-like orange of the beachfront battle.
Stone pointed out that this film marked the beginning of his career as a figure of public controversy. Like Lee, he was attacked from many sides, and from then on he was a lightning rod. Matt Zoller Seitz (who’s preparing a book on Stone) pointed out that at the period, he was astonishingly prolific. From 1986 (Salvador, Platoon) to 1999 (Any Given Sunday), he directed twelve features, about one a year.
Lee was hyperactive as well over the same years, releasing fourteen films. And neither has stopped. Lee’s new film is the Kickstarter-funded Da Sweet Blood of Jesus, while Stone is touring to support the DVD release of his 2012 documentary series, The Untold History of the United States. Both men like to work, and more important, they’re driven by their ideas as well as their feelings. By seeking new ways to agitate us, they impart an inflammatory energy to everything they try. And in giving them a chance to share their insights and intelligence with audiences outside the Cannes-Berlin-Venice circuit, Ebertfest once again demonstrates its uniqueness. Roger would be proud.
The introductions and Q&A sessions for most of the films, as well as the morning panel discussions, have been posted on Ebertfest’s YouTube page. Program notes for each film are online; see this schedule and click on the title.
For historical background on Barry Allen’s work as an editor of syndicated TV prints, see Eric Hoyt’s new book Hollywood Vault: Film Libraries Before Home Video.
P. S. 1 May 2014: Thanks to Ramin S. Khanjani for pointing out that Ramin Bahrani had worked on other films before Man Push Cart. These included one feature he made in Iran, Biganegan (Strangers, 2000); it got only limited play in festivals and apparently a few theaters. I can’t find information about the others online, and presumably they were shorts and/or did not receive distribution. (K.T.)
Ann Hui, with Kristin, gets into the spirit of Ebertfest. David is represented in absentia by the Dots.
Genre ≠ Generic
The Shape of Night (Nakamuro Noboru, 1964).
DB here:
I didn’t plan it that way, but it turns out that a great many films I saw at this year’s Hong Kong International Film Festival would have to be categorized as genre pictures. Not, admittedly, Shu Kei’s episode of Beautiful 2014, which interweaves flashbacks and erotic reveries in a purely poetic fashion. And not Tsai Ming-liang’s “sequel” to Walker (2012, made for HKIFF), called, whimsically, Journey to the West. Here again, Lee Kang-sheng, robed as a Buddhist monk, steps slowly through landscapes, some so vast or opaque that you must play a sort of Where’s-Waldo game to find him. (You have plenty of time: there are only 14 shots in 53 minutes.)
But there were plenty of other films that counted as genre exercises. Yet they mixed their familiar features with local flavors and fresh treatment, reminding me that conventions can always be quickened by imaginative film artists.
Keeping the peace, in pieces
Black Coal, Thin Ice (2014).
Take, for instance, The Shape of Night, a 1966 street-crime movie from Shochiku, directed by Nakamura Noburo. Nakamura was the subject of a small retrospective at Tokyo’s FilmEx last year, and this item certainly makes one want to see more of his work. A more or less innocent girl falls in love with a yakuza, who forces her to become a prostitute. In abrupt, sometimes very brief flashbacks, she tells her life to a client who wants to rescue her. The film makes characteristically Japanese use of bold widescreen compositions, disjointed close-ups, and mixed voice-overs from her and the men in her life. In retrospect, everything we’ve seen has been seen in other movies, but Nakamura’s handling kept me continually gripped and often surprised.
Or take That Demon Within, a Hong Kong cop film that premiered at the festival’s close. Dante Lam has made several solid urban action pictures, especially Jiang Hu: The Triad Zone (2000), Beast Stalker (2008), Fire of Conscience (2010), and The Stool Pigeon (2010). They’re characterized by wild visuals and exceptionally brutal violence, and That Demon Within fits smoothly into his style. The new wrinkle is that a boy traumatized by the sight of police violence himself becomes a cop. He’s then haunted by the image of the cop from his past, while he’s also caught up in a search for a take-no-prisoners robber.
His hallucinations and disorientation are rendered through nearly every damn trick in the book, from upside-down shots and blurry color and focus to voices bouncing around the multichannel mix.
There are dreams, too (seems like almost every new film I saw had a dream sequence), and scenes under hypnosis, and men bursting into flame, and action sequences that are visceral in their shock value. I thought the movie careened out of control pretty early, and its nihilism wasn’t redeemed by an epilogue that assured us that this possessed policeman was, at moments, friendly and helpful. In this case, the storytelling innovations generated some confusion about exactly how the hero’s breakdown infused what was happening around him.
More consistent, largely because it didn’t try for the subjectivity of Lam’s film, was the Chinese cop movie Black Coal, Thin Ice. My friend Mike Walsh of Australia pointed out that the mainland cinema’s bleak realism seems to be starting to blend with traditional genre material. Director Diao Yinan explained, “My aim was not only to investigate a mystery and find out the truth about the people involved, but also to create a true representation of our new reality.” The opening crosscuts the grubby detail of bloody parcels churning through coal conveyors with a couple entwined in a final copulation before breaking off their relationship.
The mystery revolves around body parts that are showing up in coal shipments around one region. After a startling shootout in a hairdressing salon, the case remains unsolved for several years. The surviving detective, a shabby drunk, returns to track down the culprit, but in the meantime he runs into a frosty femme fatale. “He killed,” she says, “every man who loved me.” Needless to say, the detective falls for her too, especially after ice-skating with her. Diao’s film reminds us that you can create a neo-noir in two ways: By taking a mystery and dirtying it up, or taking concrete reality and probing the mysteries lurking in it.
There were even two Westerns. Another mainland movie, No Man’s Land, was unexpectedly savage coming from the director of the super-slick satires Crazy Stone (2006) and Crazy Racer (2009). Now Ning Hao has given us a bleakly farcical, Road-Warrior account of life on the Chinese prairie.
A wealthy lawyer brought out to the wasteland to negotiate a criminal case becomes embroiled in primal passions involving men with very large guns, very large trucks, impassive faces, and almost no sense of humor. It’s a black comedy of escalating payback (involving spitting and pissing), and it exudes sheer masculine nastiness. Completed four years ago, it found release only after extensive reshoots demanded by censors. Yet even in its milder state it remains true to the spirit of Sergio Leone’s jaunty grimness, bleached in umber sand and light.
Itching to see a Kurdish feminist political Western? You’ll find Hiner Saleem’s My Sweet Pepperland welcome. A tough policeman (= sheriff) is dispatched to a remote village in Kurdistan to keep order (= clean up the town). A young teacher (= schoolmarm) leaves her oppressive family to teach there as well. A warlord (= town boss) and his minions (= paid killers) have terrorized the locals, while marauding female guerillas (= outlaws) bring their fight into town.
These time-honored conventions shape a story of stubborn courage taking on complacent viciousness. In key scenes, our sheriff faces down big, hairy, scary killers.
USA frontier conventions, it turns out, work pretty well in a Muslim society too. The Hollywood Western’s continued embodiment of American values transfers easily to the former Iraq. “Our weapons are our honor,” the chief thug says, in a line that resonates through our history right up to now. Yet things we take for granted bring modern change to the wasteland. The sheriff assigns himself to the village in order to escape an arranged marriage, as the woman he finds there has done. She is vilified by both the locals and her male relatives, who would prefer death (hers) to dishonor (theirs). In the process, both he and she become heroic in a righteous, old-fashioned way.
A killer proposes a compromise while sneakily drawing his pistol. The cop shoots him and remarks: “I don’t do compromise.” Neither does My Sweet Pepperland.
Gangs of New York, and elsewhere
The Dreadnaught (1966).
From March to May, the Hong Kong Film Archive has been running a series, “Ways of the Underworld: Hong Kong Gangster Film as Genre.” It’s packed with classics (The Teahouse, To Be No. 1, City on Fire, Infernal Affairs) as well as several rarities (Absolute Monarch, Bald-Headed Betty, Lonely 15). I managed to catch three titles, all previously unknown to me.
The Dreadnaught (1966) has a familiar premise. Two orphan boys indulge in petty theft after the war. One, Chow, is caught but gets adopted by a policeman. He turns out a solid young citizen. Lee, the boy who escapes, grows up to be a triad. When the two re-meet, Lee is attracted to Chow’s stepsister. Some years later, Chow is now a cop and vows to smash Lee’s gang. After a struggle with his conscience, Lee agrees to help.
The film’s main attraction is the shamelessly flashy performance of Patrick Tse Yin. Tse would make his fame in the following year in Lung Kong’s Story of a Discharged Prisoner, famous as a primary source for A Better Tomorrow. With his sidelong smile, his endlessly waving cigarette, and the dark glasses he wears at all times, Tse in The Dreadnaught looks forward to Chow Yun-fat’s charismatic role as Mark in Woo’s masterpiece.
Another icon of the period is Alan Tang Kwong-wing. He played in over 100 films, mostly romances and triad dramas made in Taiwan. Westerners probably know him best as the producer of Wong Kar-wai’s first two features, As Tears Go By and Days of Being Wild. Wong had worked as a screenwriter for Tang. Onscreen, Tang had a suave, polished presence marked by his perfect coiffure; he was known as the Alain Delon of Hong Kong. His company, Wing-Scope, specialized in mob films during the late 1970s and early 1980s.
New York Chinatown (1982) shows Tang as a young hood whose ambitions to dominate the neighborhood are blocked by a rival gang. Eventually the police decide to let the two gangs decimate each other. This leads to an enjoyable, all-out showdown involving surprisingly heavy armaments. Shot quickly on location (passersby sometimes glance into the lens), the movie gives a rawer sense of street life than you get from most Hollywood films. There’s also a scene in which Tang, apparently attending Columbia part time, corrects a history professor lecturing on Western imperialism in China. Although the film circulates on cheap DVD in 1.33 format, it’s a widescreen production, and it was a pleasure to watch a fine 35mm print at the Archive.
The biggest revelation of the series for me was Tradition (1955), a Mandarin release. This is considered one of the earliest pure gangster films in local cinema. It’s a fascinating plot about a boy raised by a triad kingpin in the 1930s. When the godfather dies, the young Xiang is given power over the gang and the master’s household. Trying to be faithful to the old man’s principles, Xiang finds himself unable to control his master’s widow and daughter, who are led astray by the widow’s worldly, greedy sister. At the same time, Xiang must ally with other triads to smuggle aid to the forces fighting the invading Japanese. He is torn between devotion to tradition and the need to adapt to modern materialism and the impending world war.
 Tradition is redolent of film noir, not only in the sister-in-law’s fatal ways (she seduces the old master’s weak son) but also in the film’s flashback construction. Tracking back from a ticking clock, the movie begins with Xiang meeting the master’s daughter after his gang has been decimated in a shootout. The film skips back to Xiang’s childhood and takes us up through the main action before a final bloody confrontation with police and the corrupt family members. At the end, the camera tracks up to the clock, closing off the whole action.
Tradition is redolent of film noir, not only in the sister-in-law’s fatal ways (she seduces the old master’s weak son) but also in the film’s flashback construction. Tracking back from a ticking clock, the movie begins with Xiang meeting the master’s daughter after his gang has been decimated in a shootout. The film skips back to Xiang’s childhood and takes us up through the main action before a final bloody confrontation with police and the corrupt family members. At the end, the camera tracks up to the clock, closing off the whole action.
Even more tightly buckled up are director Tang Huang’s obsessive hooks between scenes. A final line of dialogue is answered or echoed by the first line of the next scene; a closing door or character gesture links sequences in the manner of Lang’s M. Most daringly, when sister San starts to light a cigarette in one scene, we cut to her puffing on it in a tight close-up—a gesture that takes place in a new scene hours later. This and other admittedly gimmicky links look forward to Resnais’s elliptical matches on action in Muriel.
Fortunately for us, the Archive has published Always in the Dark: A Study of Hong Kong Gangster Films. Edited and partly written by Po Fung, it is an excellent collection of essays and interviews. It is in Chinese, but it includes a CD-ROM version in English. It’s available from the Archive’s Publications office.
Behind the scenes at Milkyway
Johnnie To and a recalcitrant crane during the shooting of Romancing in Thin Air.
Sometimes a genre film becomes a prestige picture. This happened, in spades, with The Grandmaster. If awards matter, Wong Kar-wai’s film has become the official best Asian film of 2013. I missed the Asian Film Awards in Macau (was watching early Farhadi films), but the event was a virtual sweep: seven top awards for The Grandmaster, including Best Picture and Best Director. After I got back home, the Hong Kong Film Awards gave the picture a staggering twelve prizes, everything from Best Picture to Best Sound.
Unhappily, nothing in either contest went to the other outstanding Hong Kong film I saw last year, Johnnie To Kei-fung’s Drug War. It lacked the obvious ambitions and surface sheen of Wong’s film. Many probably took it as merely a solid, efficient genre picture. I believe it’s an innovative and subtle piece of storytelling, as I tried to show here.
Mr. To presses on, as prolific as usual. He has finished shooting a sequel to Don’t Go Breaking My Heart, a rom-com that found success in the Mainland, and he’s currently filming a more unusual project in Canton. More on that shortly.
During the festival only one recent To/Milkway film was screened, The Blind Detective (I wrote about that here). But Ferris Lin, a young director from the Academy for Performing Arts, presented a very informative documentary feature on To and his Milkyway company. Boundless takes us behind the scenes on several productions, particularly Life without Principle, Romancing in Thin Air, and Drug War. It also incorporates interviews with To, his collaborators, and critics like Shu Kei.
Sitting at the monitor with his cigar, To may seem distant, but actually he is wholly engaged. We see him help push a crane out of the mud and shout commands to his staff. To confesses that he may scold too much, but the dedicated cooperation he gets confirms his demands. The team gives its all, as we learn when they explain the tension ruling the three days of rehearsal for the sequence-shot at the start of Breaking News. For The Mission, made at the time of Milkyway’s biggest slump, the actors supplied their own cars and costumes.
To remains a complete professional who has perfected his craft, albeit in the Hong Kong tradition of “just do it.” He doesn’t rely on storyboards or even shot-lists, only outlines of the action, and he adjusts to the demands of the locations. The Mission had no script, but the entire story and shot layout were in his head. For Exiled, he didn’t even have that much and simply began thinking when he stepped onto the set each day. It’s hard to believe that precise shot design and sly dramatic undercurrents can emerge from such an apparently unplanned approach. In its recording of To’s unique creative process, Boundless provides a vivid portrait of one of the world’s finest contemporary directors.
To continues to challenge himself. He is currently trying something else again, shooting a musical wholly in the studio. Its source, the 2009 play Design for Living, was written by and for the timeless Sylvia Chang Ai-chia. It won success in Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the Mainland. In the film Sylvia is joined by Chow Yun-fat, thus reuniting the stars of To’s 1989 breakout film All About Ah-Long. The project also indulges the director’s long-felt admiration for Jacques Demy. There is no 2014 film I’m looking forward to more keenly.
Special thanks to Shu Kei and Ferris Lin of the Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts. Thanks as well to Li Cheuk-to, Roger Garcia, and Crystal Yau, as well as all the staff and interns of HKIFF, and to Winnie Fu of the Hong Kong Film Archive.
Journey to the West (Tsai Ming-liang, 2014).
Back in THE Place
View of Hong Kong harbor from the Convention and Exhibition Centre. Above, the flag of the People’s Republic of China; below, the Hong Kong flag bearing the Bauhinia emblem. According to official protocol the national flag must be larger and be mounted more prominently.
“For us, Hong Kong will always be the place.”
Chuck Norris, The Octagon (1980)
DB here:
After missing two editions because of some minor health problems, I’m back in Hong Kong for their annual festival. As customary, it kicked off with the Filmart, now the biggest film market in Asia. It gathers producers, distributors, and financiers for discussions and dealmaking. There are panels, equipment demos, and displays of media items for sale. There’s the Hongkong-Asia Film Financing Forum, a competition that funds planned projects. (This year’s winners are here.)
Some booths are huge. The TVB display was towering, dwarfing the TV chat show being shot underneath.
Since its founding in 1997, Filmart has been so successful that it spawned an umbrella event. The Hong Kong Entertainment Expo, now in its tenth year, is a jamboree for the international entertainment industry, including music and digital entertainment of all sorts.
Filmart is now very big. This year it packed in over 760 exhibitor stalls from over 30 countries (including Brunei and Malta). It attracted over 6500 attendees, and most, unlike me, were there to buy and/or sell films, TV shows, and video games.
National film organizations use Filmart to coax production into their territory. Government agencies like KOFIC can put producers in touch with prime locations and service firms.
The opening reception was graced by Chief Executive C. Y. Leung, who while extolling the rule of law in the territory did not mention the recent violent attack on a major journalist. A characteristically blank-faced Leon Lai looked on. In the crowd, you might also meet Bruce Lee, or at least his avatar.
On the market floor, a Chinese vampire squared off against Donnie Yen, immortalized by Madame Tussaud.
Who would win in a face-off? The movie is probably being shot as we speak.
China ahead
Out of Inferno (2013).
The big news this year was, as ever, mainland China. By any measure it just keeps growing. Back in 2012 it became the world’s second-biggest market, yielding $2.74 billion in box-office grosses. (US and Canada were at $10.8 billion.) In 2013 Chinese grosses were $3.6 billion, a growth of 25%. (North American grosses grew only about 3%.) In tandem, the number of exhibition sites expanded hugely. China added over 5,000 screens in 900 new multiplexes, yielding a total of 18,195 screens. That is still remarkably few for such a populous country; North America has over twice that number. So we can expect still further growth. More generally, another sign of the times was that last year Asia-Pacific became the most lucrative region outside North America, and of course China is the centerpiece of that.
You see the China syndrome in the films as well. For several years Hong Kong producers and directors have partnered with mainland talent and business groups. Two of last year’s best Hong Kong films, Johnnie To Kei-fung’s Drug War and Wong Kar-wai’s Grandmaster, epitomize cross-border initiatives, mixing HK and PRC stars in stories that hold appeal for both audiences.
A new wrinkle: Now even films that might seem purely of Hong Kong interest credit major Chinese companies as coproducers, and they may feature mainland stars. Tim Youngs, local HK film expert, suggests that because some big-budget Chinese films haven’t succeeded in Hong Kong, mainland investors may be interested in financing small films that will catch on in the territory.
Yet some films persist without mainland financing. An example I saw at Filmart is the modest indie Dot 2 Dot, by first-time director Amos Why.
The story is rooted in local history and geography. Chung, returning from Canada to take a job in a design firm, recalls how much he enjoyed connect-the-dots puzzles as a boy. Now he discreetly puts up speckles on walls, marking sites that were significant to him and his city. Xue, a young teacher, discovers them, puzzles them out, and draws out the abstract patterns that Chung embedded in them. When he spots her graceful graffiti he determines to find who has cracked his code. What gives the story contemporary currency is the fact that Xue has emigrated from the mainland and is teaching Mandarin to Hong Kongers, and she is played by Meng Tingyi.
Dot 2 Dot interrupts its lovers-at-a-distance plot with images from Hong Kong’s past. Xue’s supervisor, an elderly teacher, and Chung, a nostalgia buff who treasures his childhood comics, recall moments in local history, such as when the Daimaru department store closed after a gas explosion. The émigré Xue, in finding her way around this imposing city, comes to appreciate its past. Eventually we learn through a degrees-of-separation device that both Chung and Xue have shared Hong Kong kid culture–two dots, in effect, waiting to be connected in adulthood. Those interested in allegory could see here a claim that for decades, China’s modern popular culture has been imported from Hong Kong, and that fact fosters cross-border bonds.
On a bigger budget there are other more or less “pure” Hong Kong films–in tone and genre, despite mainland backing–being made. Even the cockeyed English title Out of Inferno (2013) brings back the 1980s and 1990s, as does the premise. Two brothers dedicated to firefighting fall out; one (Lau Ching-wan) becomes obsessed with his job, the other (Louis Koo) leaves to form a company specializing in modern fire-protection equipment. When a skyscraper catches fire during a party demonstrating the equipment, Koo and Lau’s pregnant wife, along with many others, are trapped inside. The brothers must reconcile, inside and outside, to save innocent lives. In short: Towering Inferno + Backdraft + Johnnie To’s Lifeline. Indeed, certain shots and the very presence of Lau Ching-wan, recall To’s genre masterpiece. So what’s new? Well, it’s set in Guangzhou and it’s in 3D.
Out of Inferno comes to us co-funded by the HK company Universe and the mainland company Bona. It grossed about US$2.6 million in Hong Kong and over $20 million in China, which says all you need to know about the relative power of the two markets.
Nobody I respect seems to like this movie. Most critics have written off the directors, the brothers Danny and Oxide Pang, as hacks. Kozo’s review at LoveHKFilm states the case against. Granted, the film is routine in many ways and can’t match Lifeline, but I enjoyed its almost unceasing bursts of clear, cogent action. I began to realize that one benefit of a firefighting movie is that rooms can explode, ceilings and floors can collapse, and elevators can stop or plunge–at any time, whenever you something to goose a scene. After all, it’s a fire, right? Who can predict what a fire will do? In 3D, many shots were splendid, and I will watch Lau Ching-wan doing sullen integrity in nearly anything. Still, Tim Youngs alerts me (so I alert you) to another action-filled firefighter movie, As the Light Goes Out–not screened at Filmart, not yet available on disc, and with more admirers, at least in my vicinity, than Out of Inferno.
A future for Retro
The White Storm (2013).
Universe and Bona, who seem to team up for blockbusters, offered a more delirious example of the Hong Kong flavor in The White Storm, which also screened at the Filmart. It’s another exercise in mixing. We have Bullet in the Head: three boyhood friends undergo a harrowing trip to wilder Asia, expending much sweat and tears, and even more blood. We have Infernal Affairs too, with the deadly game of undercover work and the possibility that a Triad mole has infiltrated the police. The three buddies consist of the familiar pairing of Lau Ching-wan and Louis Koo, along with the ever-dependable Nick Cheung as the apparently weakest member of the trio.
Unusually long at nearly 140 minutes, The White Storm (the title refers to the heroin plague that has descended on Hong Kong) is really three movies in one. The first centers on Koo in the now-familiar role of the cop who wants to come in from the cold. After a frantic drug bust gone wrong, he’s forced to return to the underworld and lead his comrades to a Thai kingpin. The second stretch takes place in Thailand. There after a savage assault on the dealer’s compound, our three are captured. The dramatic weight shifts to Lau, who must choose to kill either Koo or Cheung. His decision gains complexity because we know something he doesn’t about his partners’ loyalty. The film’s last portion returns to Hong Kong, with a few surprises and a bloody casino finale.
While building suspense in the Infernal Affairs mode–will the gang discover the mole in their midst?–director Benny Chan also tries to recover the searing romanticism of Woo’s heroic bloodshed films. As far back as The Big Bullet (1996) he showed a flair for shocking, precise action, and his Jackie Chan vehicle New Police Story (2004) is an exhilarating piece of work. Benny Chan shows his skill in each of the three sections’ violent set-pieces. Add in the 1980s-1990s Hong Kong excess–bodies thrown into pools of crocodiles, a sexy transsexual, outrageous haircuts–and you have an almost purely retro exercise.
Another throwback is the shameless but stirring tear-jerking moment in which the three men comfort Cheung’s dying mother. She thinks that Lau is her son, back from study abroad with his buddies. They spontaneously accept her delusion, each pretending to be another member of the trio. The film’s play with false identities turns melancholy, and in comforting her the men apologize, obliquely, to one another. Chan’s use of singles and two-shots deftly traces out the flow of feeling, as the men exchange glances and Cheung starts to weep in shame.
The old Hong Kong cinematic energy resurfaced in another, stranger film, Fruit Chan’s new release The Midnight After. It’s based on a popular internet novel by Pizza (yes, you read that right). The premise is apocalypse, the time is now. A minibus driving from downtown Hong Kong to the New Territories passes through a tunnel and emerges into an urban landscape from which everyone seems to have vanished. A mass extinction? An evacuation? A time warp? The mystery deepens after we get an occasional glimpse of dark figures in protective gear monitoring the frantic efforts of the survivors to make sense of their fate. Some of the passengers die–crumbling to bits, suffering giant boils, bursting into flame. Even a compassionate bicyclist is drawn into the desperate struggle for survival.
A Hong Kong director often asks us to take his or her film as reflecting a general mood in the territory. Fruit Chan says:
It feels as though Hong Kong is suffering the worst of times. People’s lives, people’s businesses and the political climate are all seriously depressed. The impact hit us harder than anything else in the past century. Through The Midnight After I’d like to tell the est of the world something about the problems that Hong Kong faces in this period of social upheaval.
The tone, as well as the plethora of familiar landmarks, may give the film some local resonance. More broadly, the film also joins a tradition of horror-fantasy that hearkens back to classic Hong Kong movies about the supernatural and even dystopian exercises like The Wicked City (1992). The latter was rendered with typical Tsui Hark brio, though, and The Midnight After is more sober and straightforward, at times perilously close to flat. Nor does it have the conciseness and growing creepiness of Chan’s Dumplings (2004).
I didn’t find The Midnight After particularly compelling. The characters are viewed from the outside and don’t solicit much sympathy; they’re mostly collections of types and tics, including a mysterious young woman who is given I-may-be-a-demon treatment by the expedient of momentarily billowing hair. As usual when a Cantonese film doesn’t know what else to do, it sets its characters screeching, quarreling, running around, and punching. Moreover, I couldn’t figure out what made the unfortunate victims die in different ways. And what’s behind the mysterious watchers? My friends say: “There aren’t any rules.” Maybe they’re right. But it’s fairly easy to pile on mysteries in your plot; the task is to tie them up in the end.
To be fair, we don’t really have the end. The film adapts only the first part of Pizza’s cybernovel, so perhaps everything will get straightened out in a sequel. What matters, for better and worse, is that many Hong Kong filmmakers still resort to Reboot mode.
You can read the trade papers’ Filmart daily publications here. Also visit Film Business Asia for many articles on deals announced at Filmart. Peter Martin reports on a panel on the Asian industry at Twitchfilm. Perhaps most important, Patrick Frater of Variety signals an important upcoming change in PRC distribution policy.
My information on the 2013 growth in Chinese screens is gleaned from David Hancock’s survey in of world exhibition in IHS Media and Technology Digest no. 504 (September 2013), 9-12. Additional information comes from Jeremy Kay’s CinemaCon report in Screen International and Patrick Frater’s account of screen expansion in Variety. Derek Elley offers a very thorough analysis of the contemporary Chinese industry in “Mainland Cinema’s New Maturity,” in Film Business Asia.
The trailer for Dot 2 Dot is here. Kozo, as you’d expect, has a nuanced review of The White Storm.
In other welcome news related to The Place, Grady Hendrix is back with Kaiju Shakedown. The inital entry is a full-blooded overview of the career of mystery auteur Jeff Lau.
P.S. 1 April 2014 (HK time): This entry has been revised to correct my original claim that Dot 2 Dot had some financing from the mainland. Director Amos Why wrote to explain that despite the credited participation of two companies based in Beijing, there was no investment from Chinese sources; the funding came entirely from Hong Kong. I thank Amos for the correction.
Smoke from a towering inferno? The creeping miasma of The Midnight After? No, just a low-lying cloud settling on Central after a rainstorm.
Picking up the pieces; or, a Blog about previous blogs
A not-so-intimate bedroom scene from Cinerama Holiday (1955).
DB here:
Many of our blog entries are written in response to current events–a new movie, a film festival in progress, a development in film culture. Later we sometimes add a postscript (as here) bringing an entry up to date. Today, though, enough has happened in a lot of areas to push me to post the updates in a single stretch. It’s a sort of aggregate of chatty tailpieces to certain entries over the last year or so. Should the impulse seize you, you can return to an original entry, and there are other peekaboo links to keep you busy.
Out and about
Drug War.
Kristin wrote in praise of Neighbouring Sounds when she saw it at the Vancouver International Film Festival in 2012. Roger Ebert gave it a five-star rating, and A. O. Scott placed it on his annual Ten Best list. This network narrative is Brazil’s official entry for the Academy Awards. Sample Neighbouring Sounds here; the DVD is coming in May.
The annual Golden Horse Awards at Taipei have finished, and the Best Picture winner was the Singaporean Ilo Ilo, which neither Kristin nor I have seen. It would have to be exceptionally good to match the other films nominated, all of which we’ve discussed: Tsai Ming-liang’s Stray Dogs, Wong Kar-wai’s The Grandmaster, Jia Zhang-ke’s A Touch of Sin, and (probably my favorite film of the year so far) Drug War, by Johnnie To Kei-fung. Stray Dogs did bring Tsai the Best Director award and his actor Lee Kang-sheng a trophy for best lead. Wong’s Grandmaster picked up six trophies, including top female lead and Best Cinematography. Jackie Chan won an award for Best Action Choreography. Although his CZ12 struck me as pretty dismal as a whole, its closing montage of Jackie stunts from across his career was more enjoyable than most feature-length films. In all, this has been a splendid year for Chinese-language cinema.
Back in the fall of 2012, I celebrated Flicker Alley‘s admirable release of This Is Cinerama, a very important film for those of us studying the history of film technology. Now Jeff Masino and his colleagues have taken the next step by releasing combo DVD-Blu-ray sets of two more big pictures, Cinerama Holiday (1955), the sequel to the first release, and South Seas Adventure (1958), the fifth and last of the cycle. Both are in the Smilebox format, which compensates for the distortions that appear when the curved Cinerama image is projected as a rectangle. Fortunately, Smilebox retains the outlandish optics to a great extent. The image surmounting today’s entry would give Expressionist set designers a run for their money, and it recalls the Ames Room Experiments. Cinerama wrinkles the world in fabulous ways.
Filled out with facsimiles of the original souvenir books and supplemented with a host of extras putting the films in historical context, these discs are fine contributions to our understanding of widescreen cinema. Because film archives don’t have the facilities to screen Cinerama titles (if they even hold copies), we have never been able to study, or even see, films that now look gloriously peculiar. Dare we hope that, from The Alley or others, we’ll get The Wonderful World of the Brothers Grimm (1962), a strange, clunky, likeable movie?
Bookish sorts
Spyros Skouras and Henri Chrétien.
2013 saw the first of our online video lectures, one on early film history and the other on CinemaScope. The response to them has been encouraging, but as usual nothing stands still. If I were preparing the ‘Scope one now, I would draw from the newly published CinemaScope: Selected Documents from the Spyros P. Skouras Archive. Skouras was President of 20th Century-Fox, and he kept close tabs on the hardware he acquired from Chrétien in 1953. This collection of documents, edited by Ilias Chrissochoidis, shows that Skouras saw ‘Scope as a way to follow Cinerama’s path and boost the studio’s profits. “I would hate to think what would have happened to us if we had not created CINEMASCOPE. . . . Certainly we could not have continued much longer with the terrific losses we have taken on so many of our pictures.” ‘
Scope didn’t rescue the industry, or even Fox, from the postwar doldrums, but some of the behind-the-scenes tactics of the format’s first years are revealed here. For example, Skouras hoped that filmmakers would put important information on the surround channels deployed by the format, in the hope that theatre owners would make more use of them. “Such scenes would have to be unusual ones, but even with my limited imagination I can visualize many scenes in which dialogue would be heard from only the rear or the sides of the theatre.” This seems fairly extreme even today.
Jeff Smith is a swell colleague here at UW–Madison. (He and I are teaching a seminar that’s just winding down. More about that, I hope, in a later entry.) In his May guest entry for us, Jeff wrote about the new immersive sound system Atmos. But he’s been busy filling hard covers too. Research articles by him have appeared in three new books on film sound.
 To Arved Ashby’s Popular Music and the New Auteur: Visionary Filmmakers after MTV Jeff contributed “O Brother, Where Chart Thou?: Pop Music and the Coen Brothers”–surely required reading in the light of Inside Llewyn Davis. He’s also a contributor to two monumental volumes that will set the course of future sound research. David Neumeyer has in The Oxford Handbook of Film Music Studies gathered a remarkable group of foundational chapters reviewing the state of the art. Jeff’s piece charts the changing relations between the film industry and the music industry, from The Jazz Singer to Napster and file-sharing. For another doorstop volume, The Oxford Handbook of New Audiovisual Aesthetics, edited by John Richardson, Claudia Gorbman, and Carol Vernallis (three more top experts), includes a powerful essay in which Jeff shows how techniques of intensified continuity editing have their counterparts in scoring, recording, and sound mixing. Not to mention his forthcoming book on an altogether different subject, Film Criticism, the Cold War, and the Blacklist: Reading the Hollywood Reds. All in all, a busy man–the kind we like.
To Arved Ashby’s Popular Music and the New Auteur: Visionary Filmmakers after MTV Jeff contributed “O Brother, Where Chart Thou?: Pop Music and the Coen Brothers”–surely required reading in the light of Inside Llewyn Davis. He’s also a contributor to two monumental volumes that will set the course of future sound research. David Neumeyer has in The Oxford Handbook of Film Music Studies gathered a remarkable group of foundational chapters reviewing the state of the art. Jeff’s piece charts the changing relations between the film industry and the music industry, from The Jazz Singer to Napster and file-sharing. For another doorstop volume, The Oxford Handbook of New Audiovisual Aesthetics, edited by John Richardson, Claudia Gorbman, and Carol Vernallis (three more top experts), includes a powerful essay in which Jeff shows how techniques of intensified continuity editing have their counterparts in scoring, recording, and sound mixing. Not to mention his forthcoming book on an altogether different subject, Film Criticism, the Cold War, and the Blacklist: Reading the Hollywood Reds. All in all, a busy man–the kind we like.
My March essay, “Murder Culture,” devoted some time to the women writers of the 1930s and 1940s who created the domestic suspense thriller–a genre I believe has been slighted in orthodox histories of crime and mystery fiction. The piece brought friendly correspondence from Sarah Weinman, editor of a new anthology from Penguin: Troubled Daughters, Twisted Wives. She has assembled a fine collection, boasting pieces by Vera Caspary, Dorothy B. Hughes, Charlotte Armstrong, Dorothy Salisbury Davis, Margaret Millar, Patricia Highsmith, and Elisabeth Sanxay Holding (whom Raymond Chandler considered the best suspense writer in the business). These stories will whet your appetite for the excellent novels written by these still under-appreciated authors. Sarah’s wide-ranging introduction to the volume and her headnotes for each story will guide you all the way.
Finally, not quite a book but worth one: “The Watergate Theory of Screenwriting” by Larry Gross has been published in Filmmaker for Fall 2013. (It’s available online here to subscribers.) The essay is based on the keynote talk that Larry gave at the Screenwriting Research Network conference here in Madison.
Digital is so pushy
From Doddle.
Back in May, I provided an update on the progress of the digital conversion of motion-picture exhibition. Today, 90% of US and Canadian screens are digital, and over 80% worldwide are. (Thanks to David Hancock of IHS for these data.) I wish I could say the Great Big Digital Conversion was at last over and done with, but we know that we live in an age of ephemera, in which every technology is transitional. As I was finishing Pandora’s Digital Box in 2012, the chatter hovered around two costly tweaks.
The first involved higher frame rates. One rationale for going beyond the standard 24 fps was the prospect of greater brightness to compensate for the dimming resulting from 3D. Peter Jackson presented the first installment of his Hobbit film in 48 fps in some venues, and James Cameron claimed that Avatar 2 and its successor would utilize either 48 fps or 60 fps. And in January of this year some studio executives predicted that 48 fps would become standard.
Not soon, though. The Hobbit: The Desolation of Smaug will play in 48 fps on fewer than a thousand screens. Bryan Singer, who praised the process, has pulled back from handling the next X-Men movie at that frame rate. The problem is partly cost, with 48fps demanding more rendering and vast amounts of data storage. As far as I can tell, no one but Jackson and Cameron are planning big releases in the format.
The other innovation I mentioned in Pandora was laser projection. It too will brighten the screen, and according to its proponents it will also lower costs. Manufacturers are racing to build the machines. Christie has presented GI Joe: Retaliation in laser projection at AMC Theatres’ Burbank complex, and the firm expects to start installing the machines in early 2014. Seattle’s Cinerama Theatre is scheduled to be the first. NEC, the Japanese company, premiered its laser system at CineEurope in May. A basic NEC model designed for small screens (right) will cost about $38,000—an attractive price compared to the Xenon-lamp-driven digital projectors currently available. But the high-end NEC runs $170,000!
How to justify the costs? One Christie exec suggests branding: “Laser is a cool term that audiences immediately identify with.”
Perhaps the most important innovation since last spring’s entry involves an electronic delivery system. In October, the Digital Cinema Distribution Coalition, a consortium of the top three theatre chains along with Warners and Universal, launched a satellite and terrestrial network for delivering movie files to theatres. Theatres are equipped with satellite dishes, fiberoptic cable, and other hardware. The new practice will render the current system of shipping out hard drives obsolete, although the drives will probably continue for a time as backups. The DCDC has scheduled over thirty films to be sent out this way by the end of the year, and 17,000 screens in the Big Three’s chains are said to be hooked up. For more information, see David Hancock‘s IHS Analyst Commentary.
In the 1990s, satellite transmission was touted as the best way to send out digital films, and it was tried with Star Wars Episode II: Attack of the Clones in 2001. Sometimes things move in spirals, not straight lines.
Speaking of the Conversion, an earlier entry pointed out the creative strategy used by the Lyric Theatre in Faulkton, South Dakota to finance its digital changeover. A gun raffle was announced on the Lyric’s Facebook page. Top prize was planned to be a set of three weapons: an AR-15 rifle, a shotgun, and a 1911 pistol.
The theatre’s screening season concluded, but the raffle is going forward, on New Year’s Eve, no less.
Television in public, movies in private
Dr. Who: Day of the Doctor (2013).
I can’t stand all this digital stuff. This is not what I signed up for. Even the fact that digital presentation is the way it is right now–I mean, it’s television in public, it’s just television in public. That’s how I feel about it. I came into this for film. —Quentin Tarantino
Spirals again. When attendance began to slump after 1947, Hollywood tried a lot of strategies–color, widescreen processes like Cinerama and ‘Scope, stereo sound, and not least “theatre television.” Prizefights, wrestling matches, and even operas were transmitted closed-circuit. Now theatre television is back, made possible by The Great Big Digital Convergence.
Godfrey Cheshire predicted some fourteen years ago that as theatres became “TV outside the home,” what we now call “alternative content” would become more common.
Pondering digital’s effects, most people base their expectations on the outgoing technology. They have a hard time grasping that, after film, the “moviegoing” experience will be completely reshaped by–and in the image of–television. To illustrate why, ponder this: if you were the executive in charge of exploiting Seinfeld’s last episode and you had the chance to beam it into thousands of theaters and charge, say, 25 dollars a seat, why in the hell would you not do that? Prior to digital theaters, you wouldn’t do it because the technology wouldn’t permit it. After digital, such transpositions will be inevitable because they’ll be enormously lucrative.
Godfrey’s prophecy has been fulfilled by all the plays, operas, and other attractions that run in multiplexes during the midweek or Sunday afternoon doldrums. His Seinfeld analogy was reactivated by last month’s screenings of Dr. Who: The Day of the Doctor in 3D. It was shown on 800 screens in seventy-five countries, from Angola to Zimbabwe, while also being broadcast on BBC TV (both flat and stereoscopic). The Beeb boasted that the per-screen average for the 23 November show beat that of The Hunger Games: Catching Fire. Globally, it took in $10 million, despite being available for free on TV and the Net. In the US, the event was coordinated by Fathom, a branch of National Cinemedia, a joint venture of the Big Three chains.
While some complained about dodgy 3D in the show, a surprisingly fannish piece in The Economist declared that “this landmark episode was buoyed up with fun, silliness, and hope.” The larger prospect is that other TV shows will take the hint and host season premieres or end-of-season cliffhangers in theatres. Many art house programmers would kill to show episodes of Game of Thrones or Mad Men, or even marathon runs of House of Cards. If it happens at all, I’d bet on Fathom getting there first.
I’ve had little to say, in this arena or in Pandora, about streaming and VOD, but these are becoming important corollaries of the Great Big Digital Convergence. Netflix in particular is expanding its reach, growing its subscriber base, creating original series, and enhancing its stock value, despite some ups and downs. At the same time, it’s pressing studios and exhibitors for the reduction in “windows,” the periods in which films are available on different platforms.
 The theatrical window was traditionally the first, followed by second-run theatrical, airline and hotel viewings, pay cable, and so on down the line. Now that households have fast web connections, streaming disrupts that tidy business model. In October Ted Sarandos, Chief Content Officer for Netflix (right, with Ricky Gervais), suggested that even big pictures should go day-and-date on Netflix.
The theatrical window was traditionally the first, followed by second-run theatrical, airline and hotel viewings, pay cable, and so on down the line. Now that households have fast web connections, streaming disrupts that tidy business model. In October Ted Sarandos, Chief Content Officer for Netflix (right, with Ricky Gervais), suggested that even big pictures should go day-and-date on Netflix.
“Why not follow with the consumer’s desire to watch things when they want, instead of spending tens of millions of dollars to advertise to people who may not live near a theater, and then make them wait for four or five months before they can even see it?” he added. “They’re probably going to forget.”
Exhibitors howled. Sarandos quickly recanted, saying only that he wanted people to rethink the current intervals between theatrical and ancillary release.
Some observers speculated that his October remarks were staking out an extreme position he intended to moderate in negotiations down the line–possibly to suggest that mid-budgeted pictures would be good ones to experiment with on day-and-date. Perhaps too Netflix was emboldened by the much-publicized remarks of Spielberg and Lucas in a panel last June, when they indicated that the future for most movies was VOD, with multiplexes furnishing more costly entertainments for the few. (In the same session, Lucas predicted that brain implants would allow people to enjoy private movies, like dreams.)
In any event, windows are already shrinking. In 2000, the average theatrical run was 170 days; now it’s about 120 days. With about 40,000 screens in the US, films play off faster than ever before. Video piracy, which makes new pictures available well before legal DVD and VOD release, puts pressure on studios to shorten windows. It seems likely that the windows and the intervals between them will shrink, perhaps allowing films to go to all video formats as quickly as 30-45 days after the theatrical release ends.
Studios have incentives to shorten the windows, if only because a single promotional campaign can be kept going long enough for both theatrical and home release. In addition, buying or renting a movie with a couple of clicks encourages impulse purchasing, and the cost feels invisible until the credit-card bill comes. Nonetheless, commitment to day-and-date home delivery would be risky for the studios.
Hollywood is more than ever before playing to the global audience. Even with the VOD boom, digital purchase and rental constitute a small portion of the world’s movie transactions. According to IHS Media and Technology Digest, theatrical ticket sales, purchase and rental of physical media (DVD, Blu-ray) add up to nearly 12 billion transactions, while Pay Per View, streaming, and downloads come to only about a billion or so. (These categories omit subscription services like cable television and basic VOD on Netflix, Hulu, Amazon, and the like.) Moreover, customers in 2012 spent about 61 billion dollars buying tickets to movies, buying DVDs, and renting DVDs. Tania Loeffler of the IHS Digest writes of North America, the most developed market for digital sales and rental:
Movie purchases made online in North America increased year-on-year by 36.6 per cent to reach 29.2m transactions. The rental of movies online also increased, to 112m transactions, an increase of 57.3 per cent over 2011. Despite this strong growth, movies purchased or rented via over-the-top (OTT) online movie services still only accounted for a combined $836m, or 3.3 per cent of total consumer spending on movies in North America.
By contrast, worldwide consumer spending on theatrical movies actually grew in 2012, to a whopping $33.4 billion–over 50 % of all movie transactions. (Thank you, Russia and China.) And despite the decline of disc purchases and rentals, Loeffler estimates that physical media will still comprise about thirty per cent of worldwide movie transactions through to 2016.
Theatrical releases continue to offer studios the best deal. Because the prices of streaming and downloaded films are low, there is less to be gained from them. True, if windows shrink, the studios will demand that Netflix and its confrères price VOD at high levels, say $25-50 for an opening-weekend rental. But consumers used to cheap movies on demand could balk at premium pricing.
At present, digital delivery of movies to the home provides solid ancillary income to the distributors, even if it doesn’t yet offset the decline in physical media. Add in Imax and 3D upcharges, and things are proceeding well for the moment. Like the rest of us, moguls pay their mortgages in dollars, not percentages or transactions. As long as some hits keep coming, we should expect that studios will maintain an exclusive multiplex run for major releases, as the most currently reliable return on investment.
Orpheum metamorphosis
The New Orpheum Theatre, 216 State Street, 1927.
Another note on exhibition relates to the last commercial picture palace in downtown Madison, Wisconsin. My July 2012 entry related the conspiratorial tale of how the grand old Orpheum Theatre on State Street fell on hard times. In fall of 2012 the building seemed slated for foreclosure, but then maybe not. Last month Gus Paras, a hero of my initial post, stepped forward and bought the old place. According to Joe Tarr in our politics and culture weekly Isthmus, there’s a lot of work to do.
Plaster is crumbling off sections of the ceiling, the result of years of water damage from a leaky roof. The walls are littered with scratches and marks, in bad need of a paint job. A plastic garbage can sits in the theater, collecting water leaking from an upstairs urinal. Paras even found dried-up vomit in two spots on the carpet.
Making matters worse, Monona State Bank, which controlled the property while it was in foreclosure, filled in the “vaults” behind the theater, which means replacing the building’s frail boilers and air conditioning will be much more complicated and expensive.
“I don’t have any idea how I’ll get the boiler in and out,” Paras says. “The stairs are not strong enough.”
Envoi
Have any of you worked on a film, say, 10 years ago, and it comes out on Blu-ray and you look at it and think, “This isn’t the film I’ve shot”?
Bruno Delbonnel (DP, Inside Llewyn Davis): Always. Always.
Barry Ackroyd (DP, Captain Phillips): I’ll be watching and it’s in the wrong format.
So what is it like to devote your lives and careers to creating images that you know exist only momentarily in their absolute best state, that may never be seen by most people the way you would like them to be seen?
Sean Bobbitt (DP, Twelve Years a Slave): At least you get a chance to see it once. All you can do is hope that people will see an approximation of that. I’ve been to screenings where I’ve had to get up and walk out because I just couldn’t bear to watch the film in the state it was in. But at the end of the screening, people say, “That was fantastic. That was beautiful. Well done!” and you’re thinking, “If only they had seen the real thing.” We would drive ourselves mad if we worried too much about it.
On shrinking windows, see Andrew Wallenstein and Ramin Setoodeh, “Exhibitors Explode over Netflix Bomb,” Variety (5 November 2013), 16. The chart on this page doesn’t appear in Variety‘s online edition of the story. Tania Loeffer’s report, “Transactional Movies: The Big Picture,” appeared in IHS Screen Digest (now IHS Media and Technology Digest) for April 2013, 123-126. Douglas Gomery discusses the theatre television plans of the 1940s-early 1950s in his Shared Pleasures: A History of Movie Presentation in the United States, pp. 231-234. My envoi comes from a revealing conversation among cinematographers at The Hollywood Reporter.
A 2012 catchup blog chronicling earlier phases of these developments is here.
P.S. 23 December 2013: David Strohmaier, the creative force behind the Cinerama restorations, has put online the stirring original trailers for Search for Paradise (low resolution and high-definition) . David attended the U of Iowa when Kristin and I did, though alas we didn’t meet him. He deserves a big thank-you for all his work in making these extraordinary films available to us.
The Grandmaster.