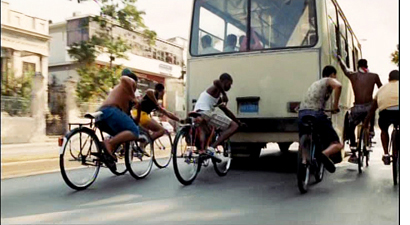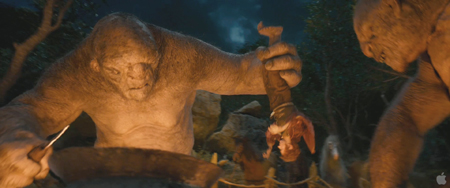Archive for the 'National cinemas: New Zealand' Category
Around the world in a multiplex: First dispatch from Vancouver
Kristin here–
My title exaggerates. There are other venues for the Vancouver International Film Festival besides the Empire Granville multiplex. There is the Pacific Cinematheque, often used for more avant-garde items; the Vancity Theatre, which screens art films and hosts industry events year-round; and the gorgeous old picture palace, the Vogue, a multiple-use venue that hosts both big screenings and gala events. But frequently we find ourselves wandering for a whole day among the Granville’s seven screens, circling the globe cinematically.
The Middle East
Four years ago we blogged about Captain Abu Raed (2007), the first Jordanian feature film in decades. This year there is The Last Friday (2011,  Yahya Alabdallah), and by now the fact of a Jordanian film appearing at festivals is no longer notable. Production has now been systematized. The Last Friday was financed (for around $100,000) by the Royal Film Commission of Jordan’s Educational Feature Film Program.
Yahya Alabdallah), and by now the fact of a Jordanian film appearing at festivals is no longer notable. Production has now been systematized. The Last Friday was financed (for around $100,000) by the Royal Film Commission of Jordan’s Educational Feature Film Program.
The basic plotline is simple, with protagonist Youssef, a handsome, hard-working middle-aged man, divorced and reduced to driving a taxi prone to breakdowns, struggling to earn money for a serious operation. The cinematography was done using a Red One camera, and the resulting images are impressive. (Alabdallah often resorts, with good effect, to what David has termed planimetric compositions, those shot directly toward a flat background.) There is little dialogue, and Youssef’s struggles are conveyed by small details, visual and aural. The fact that he has tampered with his apartment block’s switch boxes to steal electricity is established early on, but by-play with the fuses he has transferred or hidden becomes an unnecessary but entertaining motif.
Perhaps the “educational” part of the film comes from Youssef’s son, a teenage wastrel who hangs out at his father’s apartment. It eventually comes out that he has stopped going to school, and Youssef has the additional burden of confronting his ex-wife to thrash out a method for dealing with their errant son.
The Last Friday treads that risky line so many independent filmmakers on small budgets take, singling out a character with a problem and showing him or her doggedly dealing with it. It takes a sure touch and an interesting character to make this work, and Alabdallah manages both, helped by Ali Suliman’s performance in the lead role.
So far undoubtedly the biggest unexpected gem this year has been the Iranian family melodrama/thriller A Respectable Family (2012). The film is the first fiction feature by documentarist Massoud Bakhshi; it was shown in the Directors’ Fortnight series at Cannes and gained generally favorable reviews.
The plot concerns Arash, a professor who has lived in Paris for decades and, as a guest post at the university in his hometown of Shiraz winds down, seeks in vain for the return of his passport to allow him to return home. At the same time, a lawyer informs him and his mother that a sizable sum of money has been left to them by his estranged, abusive father. The family drama that plays out depends for effect on an extraordinarily complex and tight script with numerous abrupt turns and surprises that keep the audience as busy as in any recent Hollywood thriller. In particular, Bakhshi’s use of switches in point of view and flashbacks to the period of Arash’s youth are masterful.
Here I pass along the same advice I have given friends here at the festival in recommending the film: don’t read reviews or program notes about this film before seeing it. Everything I have read about the film gives away key pieces of information that should be kept secret.
The tone of the film, with its implicit but obvious criticism of the Iran-Iraq war and the regime that fostered it, plus the ending’s evident support for student demonstrators, make it amazing that the film could be made within Iran. It apparently has not been released within its home country and most likely won’t be. Yet the Iranian press reported calmly on its favorable reception at Cannes, as the press there usually does when national films gain prestige abroad. A story in the Teheran Times remarked: “It was a great surprise that non-Iranian filmgoers were able to relate to the Sacred Defense (1980-1988 Iran-Iraq war) and the concept of martyrdom, which are themes of the film, Mohammad Afarideh [the film’s producer] told the Persian service of the Mehr New Agency.” Afarideh added, “The film has an Iranian storyline, but the structure Bakhshi has chosen for the dialogue helps attract foreign audiences as well.”
Many in Iran and elsewhere were also surprised that A Separation could connect with western audiences in the way it did. It’s a pity that A Respectable Family is unlikely to gain such a widespread audience, but it is worth seeking out. It plays once more here in Vancouver, on October 3 at 6:45 pm in the Empire Granville 2.
Latin America
Una noche (2012) is listed in the program as a Cuban/UK/USA co-production. The Cuban contribution comes primarily from the setting and the cast–and the cooperation of the government. (Certainly it makes setting out to try and escape to the USA an unattractive prospect.) It was entirely shot in Havana and environs, and three young first-time actors play the principal roles. The director is Lucy Mulloy, making her feature debut. It is otherwise largely New York based, having been at least partially supported by the Independent Filmmaker project in its “Narrative Independent Filmmaker Lab,” which funds films with budgets of under a million dollars. Post-production seems mainly to have been done at the Tisch School of the Arts at NYU.
Perhaps as a result of such mixed origins, Una noche manages to create a strong, Hollywood-style plot with plenty of local color. The opening shows a blonde tourist in a car, but the heroine’s voice declares that this will not be this girl’s story but her own. Quick but effective characterization sets up the close relationship between twin brother and sister. They’re poor kids from the barrio scratching a living, with Lila working as a dance-hall girl and Elio serving as a cook. Yet we are away from Lila for long stretches, becoming aware, as she is not, that Elio is gay and has a crush a fellow cook. But Raul is an obviously straight young thug, and he has talked Elio into making an attempt to cross to the USA on a raft.
Their preparations, gathering the materials and supplies they need, take us through the poverty-stricken neighborhoods, with Elio’s shiftless friends catcalling at girls and joyriding on their bikes by clinging to buses. Raul visits a dealer to buy medicine for his AIDS-stricken mother, a gaunt former beauty still turning tricks to support herself.
The action escalates as Raul accidentally injures a tourist and Lila discovers that Elio is planning to leave her and go with Raul. Mulloy deliberately downplays the ending, flashing a dedication on the screen to give us the impression that the film is over. Almost as an afterthought mixed in with the beginning of the credits, she presents brief shots showing us of the fates of the characters, filmed from a distance and without Lila’s voiceover. The Variety reviewer found the ending abrupt and “somewhat inadequately foreshadowed,” yet it seemed appropriate to me, and indeed was one of the most original touches in the film.
The North American rights to Una Noche were picked up earlier this year by Sundance Selects after the film proved a hit at the Tribeca Film Festival, winning Best New Narrative Director, Best Cinematography, and Best Actors (shared between its two male leads). Ironically, two of the young lead actors used the Tribeca festival as an occasion to request asylum in the USA.
The Antipodes
There is something comforting about the fact that, after all the success of the Lord of the Rings trilogy and the prospect of a series of Avatar films  being made there into the indefinite future, the New Zealand Film Commission is still funding the same sorts of low-budget genre movies that were made before the country became Middle-earth and Pandora. Robert Sarkies, veteran Kiwi director, has followed up his gripping, headline-based thriller Out of the Blue (20o6) with a return to Scarfies (1999) territory, albeit on a more grotesque level.
being made there into the indefinite future, the New Zealand Film Commission is still funding the same sorts of low-budget genre movies that were made before the country became Middle-earth and Pandora. Robert Sarkies, veteran Kiwi director, has followed up his gripping, headline-based thriller Out of the Blue (20o6) with a return to Scarfies (1999) territory, albeit on a more grotesque level.
Two Little Boys (2012) is based on the old getting-rid-of-an-incriminating-corpse premise, with wimpy Nige (Bret Mackenzie, left) accidentally killing a Scandinavian sports star with his car. Despite a recent quarrel, Deano (Hamish Blake), his best friend from childhood, agrees to help him out and hatches more and more devious and grisly methods for disposing of the body–and later of Nige’s roommate, pudgy, clueless Maori roommate Gav, who adds a touch of sweetness with his persistent obliviousness to the pair’s fiendish doings.
It’s a feather-weight film, but one with many funny moments. It also shows off some parts of New Zealand seldom used in films, starting off in the southernmost and westernmost city, Invercargill, and the bleakly beautiful Catlins, on the southeast coast.
Europe
From the ridiculous to the sublime. Journal de France (2012) presents a sort of professional autobiography of the great French photographer and filmmaker Raymond Depardon. The framing situation is a journey through France that Depardon takes (supposedly alone, though there is someone there to film him), photographing landscapes and villages with his big view camera (bottom). There’s a charmingly chatty scene of him photographing four aged men who had posed for him in the same spot earlier (top).
Interspersed is footage from throughout Depardon’s career. This is presented in voiceover by co-director Claudine Nougaret, the filmmaker’s partner in private life and his long-time sound recordist. Much of this footage didn’t make it into the finished documentaries, including practice shots from when Depardon was learning the trade and amazing footage of many of the major events of the late twentieth century. Depardon travelled widely, often going into war-torn areas of Africa, such as Biafra in the late 1960s. His candid footage of people in the streets of Prague during its invasion by Russian tanks in 1968 is astonishing. Also memorable is a shot of Nelson Mandela quietly sitting in a chair. Depardon asked him to sit for a minute without speaking. Without a watch, Mandela timed it to the second. He learned the trick while in prison.
One comes away with a sense of not just a man with a keen eye and a great deal of patience. Depardon’s bravery and political conscience allowed him to leave behind a legacy of images with an immediacy that brings half-forgotten historical moments to vivid life.
Now I’m off to the Granville again, to see a Japanese film and then a South Korea one. David will blog about these in a future dispatch.
A Hobbit is chubby, but is he padded?
Kristin here:
On July 14 at this year’s Comic-Con, a thirteen-minute montage of clips from The Hobbit was shown during an appearance by Peter Jackson and cast members of the film. Afterward in press interviews, Jackson unexpectedly hinted that The Hobbit, long announced as being made in two parts to be released in December 2012 and 2013, might be expanded to three parts. This possibility inspired much skepticism among fans and members of the press. And yet only two weeks later, on July 30, it was announced that The Hobbit would indeed be released in three parts, the third to appear in the summer of 2014.
Although some fans of the film of The Lord of the Rings were delighted, there was much speculation in the press that the move was made from sheer greed, milking a third blockbuster from Tolkien’s modest children’s book. There were even some accusations that Jackson had lost his creativity and was seeking to extend his most successful series beyond its logical stopping point.
Yet if one reads the filmmakers’ statements about the decision to make an additional part of The Hobbit, it is clear that they intend to add more plot material rather than stretching the story of the relatively short novel. There is plenty of additional, directly relevant material in Tolkien’s appendices to LOTR. None of it is given in enough detail to make a free-standing film. Still, no doubt the filmmakers and the production studio began to realize that they had the rights to all this material, and that incorporating some of it into The Hobbit was their only chance to use it. Warner Bros. surely was delighted at the prospect of another lucrative blockbuster.
I’m not convinced, however, that Jackson’s team made their decision primarily from considerations of money. For one thing, some of the material from the appendices was created by Tolkien to tie the events of The Hobbit to those of LOTR. The filmmakers could use it for that same purpose. So far, the trailers and images from the forthcoming film seem to me quite promising in terms of how the appendices have been quarried for useful story items.
It happens that for avid fans of Tolkien, this is a special moment. It’s Tolkien Week. Ever since 1978, the week in which September 22 occurs is dedicated to The Professor, as he is respectfully known to devotees. And September 22 is Hobbit Day, because it is the shared birthday of Bilbo Baggins (who turned 111 on the occasion of the Long-Expected Party that opens the book) and his adopted nephew Frodo (who turned 33, the age of adulthood for Hobbits).
Warner Bros. and the filmmakers have shrewdly chosen this week to release the second trailer for The Hobbit (not counting the teaser). It appeared online on September 19, with the best-quality versions on Apple. (A high-quality version of the first trailer can be seen here.) There’s also a site where you can watch the trailer with five alternative endings, all of them humorous. (The Bilbo one is undoubtedly the best, though I enjoyed the Gandalf one as well. The Dwarf ending is actually the same as in the theatrical version.) The first part of The Hobbit is due out on December 14 in the USA and many markets, and on other dates in December elsewhere.
From two parts to three
I have a uniform paperback edition of the two novels where The Hobbit runs 272 pages and The Lord of the Rings, not counting the appendices or Prologue, runs 993 pages. So The Hobbit is less than a third the length of its sequel. The implication would seem to be that in order to be comparable to Jackson’s version of LOTR, its film adaptation should occupy a single part of perhaps three hours.
Of course LOTR, even in its eleven-and-a-half-hour extended DVD versions, left out a great deal of Tolkien’s novel. (Excision was Tolkien’s expressed preference, by the way, for a film adaptation. In a letter disapproving of a 1957 treatment for a proposed film of LOTR, he stated that cutting scenes was far preferable to racing through a complete but compressed version.) Still, given the huge success of the three-part film, it seemed reasonable that Jackson and company would treat The Hobbit more fully, eliminating less and giving fans a more complete version of the earlier book.
But three parts for The Hobbit? Especially when this change was sprung on the public less than six months before the world premiere of the first part (November 28 in Wellington)? The move proved controversial and has been argued and speculated about ever since. Every trailer, every scrap of footage (especially the 13-minutes of clips shown at Comic-Con and still not available to anyone who was not in Hall H on July 14), every photograph has been closely examined for hints of what extra material might be included in an expanded Hobbit.
The reactions have generally been of four types. Keen fans of Jackson’s LOTR are delighted, trusting him and his fellow screenwriters, Fran Walsh and Philippa Boyens, to come up with extra material true, if not to the book, at least to the spirit of the first film. Others are more skeptical, feeling that Jackson’s team is being too ambitious and is trying to stretch the book’s contents too far. After all, it was written as a children’s novel, not an epic romance like LOTR. A third group simply accuses Jackson of opportunism, whether his own or mandated by greedy corporate types at Warner Bros. (parent company of production unit New Line). Finally, a few commentators view the move as evidence of artistic “stagnation” on Jackson’s part
Most prominent among those in the fourth camp is James Russell, who wrote a piece baldly entitled “Peter Jackson’s three Hobbit films suggest he is running on empty,” for The Guardian. He argues that Jackson had never had a commercial success before LOTR, and that his post-LOTR films have been neither as lucrative nor as critically praised. Now, Russell suggests, Jackson has returned to familiar territory, despite having initially hired Guillermo del Toro to do the directing honors:
It’s hard to see how making The Hobbit could be seen as a positive step for Jackson. However, splitting the story into three separate films takes the moribund self-absorption of the project to entirely new levels. It looks as if Jackson is running entirely on empty, pushing this side project to ridiculous extremes because he has nothing else to offer.
(See also IndieWire‘s “An Open Letter to Peter Jackson on Splitting The Hobbit into Three Movies.”)
Jackson inadvertently encouraged such an interpretation back in the early days of pre-production, when del Toro was still the designated director. He said that he had visited Middle-earth once and did not want to compete with himself. Even when del Toro exited the project in late May, 2010, Jackson said he would not step into the job unless no one else could be found and the project was in danger of falling apart. Asked when the production process would move forward, he responded: “I just don’t know now until we get a new director. The key thing is that we don’t intend to shut the project down…We don’t intend to let this affect the progress. Everybody, including the studio, wants to see things carry on as per normal. The idea is to make it as smooth a transition as we can.”
The announcement that Jackson would in fact direct The Hobbit was not made until mid-October, and his statement in the press release was notably bland: “Exploring Tolkien’s Middle-earth goes way beyond a normal film-making experience. It’s an all-immersive journey into a very special place of imagination, beauty and drama. We’re looking forward to re-entering this wondrous world with Gandalf and Bilbo – and our friends at New Line Cinema, Warner Brothers and MGM.” Nevertheless, he has assured the public that once he agreed to direct, his immersion in pre-production re-ignited his enthusiasm for working with Tolkien’s material. Judging by the two trailers, as well as the eight video production diary entries so far posted on Jackson’s FaceBook page, that enthusiasm is genuine. The expansion of the film to three parts is another indicator that he has been inspired by his return to Middle-earth.
Not padding but extension
Major spoilers ahead! Page and chapter numbers from the two novels are from the most definitive versions of the texts: for The Hobbit, Douglas Anderson’s The Annotated Hobbit, second edition, and the 50th anniversary single-volume edition of LOTR, edited by Wayne Hammond and Christina Scull.
The widespread assumption since the announcement of the three-part Hobbit has been that Jackson and his fellow screenwriters would simply stretch out the action of the book. Yet that is clearly not what the trio is up to. In the press release, Jackson sounded much more enthusiastic:
Upon recently viewing a cut of the first film, and a chunk of the second, Fran Walsh, Philippa Boyens and I were very pleased with the way the story was coming together. We recognized that the richness of the story of The Hobbit, as well as some of the related material in the appendices of The Lord of the Rings, gave rise to a simple question: do we tell more of the tale? And the answer from our perspective as filmmakers and fans was an unreserved ‘yes.’ We know the strength of our cast and of the characters they have brought to life. We know creatively how compelling and engaging the story can be and—lastly, and most importantly—we know how much of the tale of Bilbo Baggins, the Dwarves of Erebor, the rise of the Necromancer, and the Battle of Dol Guldur would remain untold if we did not fully realize this complex and wonderful adventure.
There is a great deal of material in the appendices of LOTR relating to the plot of The Hobbit, though in many cases that material involves characters and events barely referred to in the novel. In the book, Gandalf departs from the Dwarves and Bilbo midway through, going off, as he later reveals briefly “to a great council of the white wizards, masters of lore and good magic; and that they had at last driven the Necromancer from his dark hold in the south of Mirkwood” (p. 357). All this was later fleshed out, partly in the body of LOTR and partly in its appendices: the council became The White Council, which included Elves like Galadriel and Elrond; the Necromancer gained a name, Sauron; his “dark hold” became his secondary dark tower, Dol Guldur.
As is quite clear from the trailers and from statements by the filmmakers, action involving the White Council and the attack on Dol Guldur will figure prominently in The Hobbit. Already an image of the White Council, including Saruman and apparently taking place at Rivendell, has surfaced in one of the licensed tie-in books:
This may not, however, be the White Council meeting that occurs during the action of The Hobbit. It may be a flashback to the one in Third Age 2851, described in the invaluable chronology of Appendix B:
2850 Gandalf again enters Dol Guldur, and discovers that its master is indeed Sauron, who is gathering all the Rings and seeking for news of the One, and of Isildur’s Heir. He finds Thráin and receives the key of Erebor. Thráin dies in Dol Goldur.
2851 The White Council meets. Gandalf urges an attack on Dol Guldur. Saruman overrules him. (p. 1088)
An image of Dol Guldur appears in the second trailer:
Saruman opposes the attack on Dol Guldur because he has secretly begun to search for the One Ring, desiring it for himself. Thráin gives Gandalf not only the key of Erebor but a map of it. That’s the map Gandalf looks at in Bag End just after his arrival in The Fellowship of the Ring. He will give the map and key to Thorin Oakenshield, son of Thráin and leader of the Dwarven troop in The Hobbit. Both will be crucial in the plot. The map also appears in the second trailer:
Tolkien wrote the appendices in 1954-55, vainly hoping to include them in the third volume of the novel. (They were incorporated into a later edition.) They retrospectively fill in events of the Third Age that led up to the plot of LOTR. He did not go back and extensively revise The Hobbit to incorporate these events, though he did a bit of fiddling with the original version in order to bring it more in line with LOTR. One cannot help but suspect that Tolkien wished he could have dealt with all these events in more than outline form. I for one am intrigued to see these bits of plot, sketched out by Tolkien in such a tantalizing way, fleshed out by the filmmakers.
No doubt that, as with LOTR, I will not agree with all the choices the screenwriters make in doing so. Still, we already have evidence that they can be adept in incorporating material from the appendices into the plot. They already did so to a more limited extent in LOTR. The scene in the extended DVD version of The Fellowship of the Ring of Aragorn visiting the grave of his mother, Gilraen, at Rivendell is derived from “Here Follows a Part of the Tale of Aragorn and Arwen,” a section of Appendix A (pp. 1057-1063). Tolkien considered this tale the most important part of the appendices, insisting that if foreign translations had to cut them, they should at least retain the narrative of the Aragorn-Arwen romance. The scene at Gilraen’s grave, brief though it is, adds depth to Aragorn’s character and to his relationship with his foster father, Elrond.
This moving story is also the source of the scene in The Two Towers where Elrond tries to persuade Arwen to leave Middle-earth for the Undying Lands by predicting her life with Aragorn. The dramatization of the prediction is a literal flashforward, for in the book Aragorn’s death eventually leads Arwen to regret her decision to remain with him, and she wanders, embittered and alone, in Lothlórien for a year before her own death (a period depicted by a single shot in the film). This flashforward is a powerful scene, and the film is all the better for its inclusion. We should not leap to the assumption that Jackson, Walsh, and Boyens will falter in their attempts to draw material from the appendices into The Hobbit.
There has been much fan speculation that the longer version of The Hobbit will include flashbacks to more of the Dwarves’ history. A scene might show the dragon Smaug driving the Dwarves from their ancestral home in the Lonely Mountain and assembling the hoard on which he lies when they return to retake the mountain. It might include their move into exile in the Blue Mountains west of the Shire. All of this could also be linked to Moria. Balin, whose tomb the Fellowship members discover in the Mines of Moria in The Fellowship of the Ring, is a character in The Hobbit, the eldest of the Dwarves. Between the action of The Hobbit and that of LOTR, he leads a troop of Dwarves to Moria to try and recapture it from the orcs that had conquered it generations earlier.
Tolkien wrote a brief history of the Dwarves and Khazad-dûm (Moria) in “Durin’s Folk,” another section of Appendix A. This includes an entire scene with dialogue, depicting Thráin’s father Thrór’s suicidal attempt to re-enter Moria; he is killed by the orc Azog. Although not crucial for the Quest of Erebor plot of The Hobbit, a flashback to such a scene would link it to the Moria passage of LOTR. There is a causal connection as well. Before departing for Moria, Thrór gives Thráin the last of the seven Dwarven rings, which leads Sauron to capture and imprison Thráin in Dol Guldur, taking the ring from him; that is why Gandalf later finds him in Sauron’s dungeons.
Such scenes might or might not be used, but the filmmakers have definitely decided to include Radagast the Brown, the third wizard, who is only mentioned in The Hobbit. (He appears in one scene in the LOTR novel, but he was eliminated from the film.) Radagast plays a limited role in Tolkien’s Legendarium, having apparently “gone rustic” and become absorbed with the birds and animals of Mirkwood, largely abandoning his part in trying to defeat Sauron. Still, his inclusion in the film seems a positive thing, as some charming shots of him playing with hedgehogs in the second trailer suggests:
The decision to divide The Hobbit into three parts presumably came too late to permit numerous changes in the first part. Nonetheless, the point at which the first film was planned to end has apparently been changed dramatically. The film’s official site posted an interactive wallpaper generator that showed a panoramic scroll summarizing the film’s scenes, from Gandalf scratching a rune on Bilbo’s door to the moment when the Dwarves and Bilbo escape from Thranduil’s dungeons in barrels floating down a river. That scene happens well over halfway through the novel. Once the three-part release was announced, the wallpaper generator was changed to its current version, which ends with the episode of Gandalf, the Dwarves, and Bilbo trapped up burning fir trees by wargs and goblins. Two shots from that episode are the latest events shown in the new trailer and would seem to provide a good cliff-hanger for the ending:
This episode happens in Chapter 6 of the book’s 19 chapters, while the barrels scene is in Chapter 9. This shift suggests that a considerable chunk of action has been added to the first film. That action probably derives from the LOTR appendices rather than some stretching of episodes from The Hobbit.
Perhaps to reassure fans, most of the new trailer shows scenes very familiar from the book: the Dwarves arriving unexpectedly at Bag End, the three trolls preparing to cook Bilbo (above), and of course the beginning of the famous riddling contest between Bilbo and Gollum. Two shots of Bilbo’s awestruck reaction to being in Rivendell (at the top) capture the spirit of the book perfectly. After all, Bilbo ended up living in Rivendell during his declining years, and while there he translated the ancient Elvish texts that became The Silmarillion. All this suggests that the bulk of the material derived from the appendices will appear in the second and third parts.
As a long-time Tolkien fan, I would be as disappointed as anyone if the decision to divide The Hobbit into three parts were done merely by stretching out the plot of the novel. All the evidence, however, points to a careful incorporation of bits of Tolkien’s own text to fill out the background of the tale and to link it more firmly to LOTR. Essentially it sounds as though the screenwriters have sought and probably found a way to incorporate the original “bridge” film, announced long ago when The Hobbit adaptation was first revealed in the press, into The Hobbit.
The bridge film was to have been a sequel to The Hobbit, which at that time was planned as a single film. It would fill in the events between the end of The Hobbit and the beginning of LOTR–a gap of sixty years in the novels. It apparently was to have been made up primarily of scraps of plot garnered from the appendices. Whether the writers would have been able to come up with an overall structure to unite those scraps is debatable. Using the strong spine of The Hobbit‘s plot to support them seems a promising solution to the problem.
Perhaps I will be disappointed upon seeing the film, but all the evidence so far indicates that the writers have been inventive and careful in expanding the project. Moreover, the trailers suggest that the technology used to create Gollum and to manipulate the sizes of the actors has improved since LOTR, as the frame below indicates.
Happy Hobbit Day to all!
For Tolkien’s thoughts on cutting versus compression for adaptations of his films, see The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien, p. 261.
Beyond praise 4: Even more DVD supplements that really tell you something
David Fincher, foreground left, lays out a scene for The Social Network
Kristin here:
Every year or so I write an entry on useful DVD supplements. These aren’t necessarily very recent ones, but items I’ve come across that actually reveal something interesting about the filmmaking process—as opposed to the litanies of mutual praise that making-ofs too often spend time on. For the three earlier entries, see here, here, and here.
These posts are aimed partly at fans, of course, but also offer suggestions to teachers who use Film Art concerning useful teaching tools to be found among the supplements.
Often the most elaborate DVD extras are those for big fantasy and science-fiction films. There’s certainly no shortage of clips and examples if you’re teaching special effects! The trouble is to find good supplements about the basic techniques of pre-production and filming. I’ve included some effects-heavy films in past entries, but I’m happy this time to have two dramas whose supplements don’t even mention special effects.
The Social Network (“Two-disc Collector’s Edition,” Sony Pictures Home Entertainment)
As with many DVDs, the long, chronologically organized account of how the film was made is the least interesting of the supplements. But hang on, because the short, specialized ones that follow are terrific.
The feature-length documentary, “How Did They Ever Make a Movie of Facebook?” starts with pre-production, a section which is mildly interesting but basically uninformative. It then continues with four parts: “Boston,” “Andover,” and “Los Angeles,” and “The Lot.” The “Los Angeles” scene includes an excellent scene showing the camera on a dolly, rapidly tracking back in front of Eduardo (Andrew Garfield) as he hurries to confront Mark Zuckerberg (Jesse Eisenberg). This 92-minute making-of skips post-production and ends with a montage of self- and mutual congratulations.
I should add that there are moments during this film where the rehearsals and the exchanges between the actors and Fincher on set do reveal something about how performances are crafted. Someone who wanted to teach a unit on acting might find it helpful to pull out clips of these interesting moments and have students read David’s entry on the performances in the film.
Otherwise, save your 92 minutes and go straight to the “Additional Special Features.”
First is “Jeff Cronenweth and David Fincher on the Visuals.” At only 7 1/2 minutes, this is packed with good stuff. Cronenweth discusses why he and Fincher decided to go with Red HD cameras (below left) rather than the Vipers used for Zodiac and The Curious Case of Benjamin Button. It well illustrates of what we talk about in Chapter 1 of the ninth edition of Film Art: technical decisions being made for aesthetic purposes. According to Cronenweth, digital cameras innately have greater depth of field than 35mm ones do, and the featurette explains how to manipulate depth of field in digital filmmaking in order to guide the attention of the viewer. Finally, there’s an enlightening example of how three cameras fastened together can take separate images that can be tiled into a long, panoramic space. The filmmakers can than create camera movements within that panorama, add lights, and otherwise manipulate the image in ways that will be imperceptible to the viewer.
“Angus Wall, Kirk Baxter, Ren Klyce on Post” is just as good if not better. It’s mostly about editing. About a minute in, Baxter, the editor, talks about how Fincher wanted him to conform to traditional rules of continuity editing, never crossing the axis of action. As he puts it, “We’re always doing basic film law, but it can just be done extremely rapidly.” In other words, the average shot length may be lower than in older Hollywood films, but the methods of handling space for clarity are still observed. One passage of this supplement shows the difficulty of keeping eyelines straight when shooting a group at a table (a topic we deal in Film Art using a simpler example from Bringing up Baby). Klyce, the sound designer, discusses being able to edit individual words from different takes to create exactly the dialogue the director wanted. He also points out that Fincher insisted that background noises be as loud as the dialogue being spoken by the principal characters present. That’s a pretty unconventional approach, as we mention in our sound chapter.
At several points in this supplement, the juxtaposition of two or more images in a black background helps illustrate the point, as in the frame at the top of this entry.
The innovative music in The Social Network has rightly drawn a great deal of attention, including an Oscar and other awards. It’s covered in “Trent Razor, Atticus Ross, David Fincher on the Score.” Again some of the concepts we lay out in Film Art show up here. The composers and director talk about how music affects the spectator’s expectations. They point out that variants of a key musical theme are used to connect three scenes (i.e., a musical motif links parts together to create a formal whole). That musical motif involves a slow, wistful piano tune played over a faintly ominous undercurrent of electronic tones. To indicate the progression across the film, the piano was recorded with the microphone at a different distance from the instrument each time, affecting its timbre.
“Swarmatron” is really an extension of the music supplement, this time focusing on a particular and eccentric musical instrument.
Finally, there’s a segment on the big night-club scene, “Ruby Skye VIP Room: Multi-angle Scene Breakdown,” which is about four minutes long. Multi-angle layouts of scenes juxtaposing the different camera angles within the frame have become fairly common on DVDs. Here, though, Kirk Baxter and Ren Klyce return to offer more insights into the post-production and how these disparate images and sounds were combined. This supplement is interactive, and one can choose which versions of the shots and sound to use. I didn’t try all possible combinations. Choosing “1) Composite view” and “2) Interviews” worked well, I thought.
Another Fincher film, Zodiac, has been discussed in our “Beyond praise” series. Evidently Fincher understands what makes for a useful supplement–at least when it comes to the ones that deal with specific aspect of filmmaking.
District 9 (“2-disc Edition,” Sony Pictures Home Entertainment)
To begin with, don’t bother with the three short “The Alien Agenda: A Filmmaker’s Log” films on the same disc as the feature. They’re perfunctory and uninformative, probably something produced for cable channels to run as publicity.
The good stuff is on the supplements disc. Which has previews on it. I expect previews before the film, but in front of the supplements?! Maybe I just haven’t noticed this before, but this is the first time I was actively annoyed by it. At least one can skip through them by pressing the “next” button three times.
The individual documentaries are pretty good of their type. “Metamorphosis: The Transformation of Wikus” focuses on the make-up designed for the main character, Wikus Van Der Merwe, in the portion of the film after he is infected by something that turns him into one of the aliens he has been trying to control. This is as straightforward and dramatic a demonstration of make-up as you’re likely to see.
A lot of the film’s acting involved improvising on camera, and “Innovation: The Acting and Improvisation of District 9” is an unusually interesting little supplement on acting. Again, teachers who want to teach an extensive unit on acting might want to use this. It creates a considerable contrast with the main Social Network making-of, where Aaron Sorkin states quite emphatically that there was no improvisation at all on his film.
“Conception and Design: Creating the World of District 9” goes into such topics as the design of the aliens’ weapons (below, top). It’s fairly typical of these sorts of supplements, but there is a discussion of how the space-ship design was consciously imitating the style of sci-fi films of the 1970s and 1980s. That is, Alien (1979) introduced the notion that space craft could be corroded and dingy(below, bottom)–as opposed to the squeaky-clean interiors of the ships in 2001: A Space Odyssey (1968). Thus the idea of styles and genres having their own histories, which we bring up in Film Art, is exemplified.
“Alien Generation : The Visual Effects of District 9” has some interesting footage exemplifying the challenges of trying to shoot improvised acting with a hand-held camera while having a motion-capture camera filming the same action simultaneously. With both cameras, complete with separate small crews, move in unpredictable ways, they tend to get in each other’s way. There’s also a nice moment at the end when a technician shows off a rotating still camera on a tripod. It’s used to record the light coming from all directions, so that the digital effects can add in light that’s consistent with that on set.
The New World (New Line Home Entertainment)
Note: Both the theatrical version DVD and the “Extended Cut” one (which restores 35 minutes cut by Malick for the theatrical release and is also available in on Blu-ray) have the same supplements.
With all the anticipation building up around Terence Malick’s upcoming The Tree of Life, I wondered what a making-of for a Malick film would look like. Would the elusive Mr. Malick take part, or would he allow little or no behind-the-scenes footage?
Turns out he did not take part, but the makers of “Making The New World,” a one-hour supplement, took an imaginative approach by attaching themselves to the second unit. That’s the unit that typically films the action and landscape shots, scenes where the main actors are not delivering dialogue. In this case the unit had plenty of work to do. We see the filming of a fire at the fort, footage of the three ships sailing up the river in the marvelous opening scene, and a long battle between the Native Americans and colonists.
The documentary camera operators were allowed to tag along right behind or even in the midst of the cinematographer’s team, who clearly cooperated extensively. A lot of what we witness is actual filming, often glimpsed over the shoulders of assistants, still photographers, the second-unit assistant director, the fight choreographer, and others. (See below.)
I doubt very much of the coverage was planned in advance. The camera dodges around people who intrude unexpectedly into the foreground, and in a few cases the microphone is too far from what’s going on, and the filmmakers insert subtitles to let us know what was said. The interview footage clearly included anyone the documentarists could corral between takes, including various bit players, make-up people, the assistant director, just whoever was available. It comes as a shock when about half-way through Colin Farrell appears briefly to make a few remarks. In this brief interview with one of the Indian actors, people pass close by in the background, making noise that competes with what he says:
The result is a greater immersion in the filmmaking process than I’ve seen in any making-of. There’s no real attempt to explain any aspect of filmmaking–no voiceover narration, no superimposed titles apart from the ones identifying the people speaking.
Overall, this caught-on-the-fly footage gives the impression that any aspect of filmmaking can be interesting. So often the directors of supplements foreground the stars and try to inject drama into what is already a fascinating subject. Here there might be a plastic tarp being put over a camera during the rain or a camera assistant instructing extras on a ship to make sure that their water bottles aren’t in frame, and the supplement makers include it.
We do, of course, learn something about how Malick works. Experienced camera operators remark on how he doesn’t use artificial lighting, and we see shots of men ripping openings in thatched roofs to allow sunlight into a scene:
Christian Bale notes that Malick shoots 360 degrees around the space, so that crew members must be prepared to duck out of sight if he turns the camera their way. Others express surprise at the complete lack of storyboarding.
Being attached to the second unit also allowed the making-of team to show how the filmmakers cooperated with and included many Native Americans in the planning and execution of the film. It’s great to see American Indians not only pleased with the way their ancestors are being portrayed, but excited by being able to experience something of their ancestors’ way of life.
There’s a touching moment when Buck Woodard, a Native American advisor on the film, is being shown around the frame of an Indian dwelling by the production designer, Jack Fisk. Woodard looks around with a smile, and as Fisk moves off to the left, Woodard turns away from the camera and whispers almost inaudibly, “It’s just wonderful!”—clearly speaking to himself and not to Fisk or the microphone.
In short, this is a thoroughly ingratiating making-of—and how often do you see one of those?
One final note. Is it just me that’s getting annoyed by the time-lapse photography in supplements that are used to show lengthy actions like set-building or light-shifting really fast? That was kind of impressive for a while, but it’s a cliché by now. In The Social Network supplements the fast-motion is so fast that one can’t really see what’s going on. That sort of thing is cutesy, and it condescends to the viewer. (Even The New World supplements, which are much more casual, use this device once or twice.) I would like to see a set-building scene that actually shows something about how sets are built, not about how cool the supplement producers can make the process look.
The factors considered in these supplements tend to support David’s arguments in The Way Hollywood Tells It that there are basic continuities of style between traditional studio filmmaking and what some scholars have characterized as “post-classical” Hollywood.
The New World.
New Zealand is still Middle-earth: A summary of the Hobbit crisis
Richard Taylor during the October 20 anti-boycott march.
Kristin here:
Ordinarily I post about Peter Jackson’s Tolkien-adapted films on my other blog, The Frodo Franchise. But over the past five weeks a dramatic series of events has played out in New Zealand in regard to the Hobbit production. Those events tell us interesting things about today’s global filmmaking environment. As countries around the world create sophisticated filmmaking infrastructures, complete with post-production facilities, they are creating a competitive climate. Government agencies woo producers of big-budget films by offering tax rebates and other monetary and material incentives. Usually such negotiations go on behind closed doors, but the recent struggle over The Hobbit was played out more publicly.
Back in late September, the progress of Jackson’s project seemed slow. We Hobbit-watchers were mainly fretting over the lack of a greenlight for the two-part film “prequel” to The Lord of the Rings.
Of course, Tolkien’s LOTR (1954-55) was a sequel to The Hobbit (1937), but the films will have been made in reverse order. That’s due to MGM’s having the distribution rights back in 1995 when Peter Jackson went looking to use Tolkien’s novels to show off Weta Digital’s fancy new CGI abilities. Miramax bought the LOTR production and distribution rights and the Hobbit production rights.
Most of the news I was then blogging about related to MGM’s financial problems and how they would be resolved. Would Spyglass semi-merge with the ailing studio, convert its nearly $4 billion in debt into equity for its creditors, and bring it back into a position to uphold its half of the Hobbit co-production/co-distribution deal with New Line? Or would Carl Icahn push through his scheme to merge Lionsgate and MGM? The answer, by the way, came just this Friday, October 29, when the 100+ creditors voted to accept the Spyglass deal. I have been saying all along that the MGM situation was not the primary sticking point that was delaying the greenlight, even though most media reports and fan-site discussions assumed that it was. The greenlight having been given before this past week’s vote, I assume I was right. The real reason for the delay has not been revealed.
Meanwhile, other websites were speculating about casting rumors. Would Martin Freeman really play Bilbo, or were his other commitments going to interfere? (He will play Bilbo. Good choice, in my opinion. The man looks just like a hobbit.)
Then, on September 25 came the news that international actors’ unions were telling their members not to accept parts in The Hobbit. There was a boycott. The result was a maelstrom of events for the past five weeks or so. You may have heard about some of them. There were meetings and petitions. When Warner Bros. threatened to take the film to a different country, pro-Hobbit rallies followed. A visit by some high-up New Line and WB execs and lawyers to New Zealand led to hurried legislation to change the labor laws to reassure the studios that a strike wouldn’t happen. Finally, the government ended up raising the tax rebates for the production. Result: The Hobbit will be made in New Zealand after all. New Line, by the way, was folded into Warner Bros. by their parent company, Time Warner, after The Golden Compass failed at the box office. It remains a production unit but no longer does its own distribution, DVDs, etc.
The news that followed the launch of the boycott has come thick and fast, often involving misinformation. It was complicated, centering on an ambiguity in New Zealand labor laws as applied to actors and on a strange alliance between Kiwi and Australian unions. One of the biggest American film studios decided to use the occasion to demand more monetary incentives from the New Zealand government. I tried to keep up with all this and ended up posting 110 entries on the subject. (In this I was helped mightily by loyal readers who sent me links. Special thanks to eagle-eyed Paul Pereira.) That was out of 144 total entries from September 25 to now. There was plenty of other news to report. During all this, the MGM financial crisis was creeping toward its resolution, firm casting decisions were finally being announced, and the film finally got its greenlight. Whew!
For those who are interested in The Hobbit and the film industry in general but don’t want to slog through my blow-by-blow coverage, I’m offering a summary here, along with some thoughts on the implications of these events. Those who want the whole story can start with the link in the next paragraph and work your way forward. Obviously the links below don’t include all 110 entries.
In some cases the dates of my entries don’t mesh with those of the items I link to, given that New Zealand is one day ahead. I’ve indicated which side of the international dateline I’m talking about in cases where it matters.
September 25: Variety announces that the International Federation of Actors (an umbrella group of seven unions, including the Screen Actors Guild) is instructing its members not to accept roles in The Hobbit and to notify their union if they are offered one.
At that point, the film had not yet been greenlit, so it wasn’t clear how this would affect the production. The action against The Hobbit originated with the Australian union MEAA (Media Entertainment & Arts Alliance) and its director, Simon Whipp. Because relatively few actors in New Zealand are members of New Zealand Actors Equity, that small union is allied with the MEAA. The main goals of the union’s efforts were to secure residuals and job security for actors. The MEAA maintained that Ian McKellen (Gandalf), Cate Blanchett (Galadriel), and Hugo Weaving (Elrond) all supported the boycott; so far no evidence for this has been offered. Possibly they agreed to abide by it but were not in favor of it. Given the lack of a greenlight, none had been offered a role yet.
The main bone of contention has been a distinction made in labor laws in New Zealand. Actors are considered to be equivalent to contractors rather than employees, since they are hired on a temporary basis; it is illegal for a company to enter into negotiations with a union representing contractors. On that basis, Peter Jackson, who was first contacted in mid-August, refused to meet with the group. Besides, he isn’t the producer hiring the actors. Warner Bros., through New Line, is. As with all significant films, a separate production company, belonging to New Line, has been set up to make The Hobbit. It’s called 3 Foot 7. (The LOTR production company was 3 Foot 6, the average height of a hobbit being 3’6″.)
September 27. Peter Jackson responded angrily to the boycott, laying out the issues that would ultimately guide the New Zealand government’s response to the crisis:
“I can’t see beyond the ugly spectre of an Australian bully-boy using what he perceives as his weak Kiwi cousins to gain a foothold in this country’s film industry. They want greater  membership, since they get to increase their bank balance.
membership, since they get to increase their bank balance.
“I feel growing anger at the way this tiny minority is endangering a project that hundreds of people have worked on over the last two years, and the thousands about to be employed for the next four years, [and] the hundreds of millions of Warner Brothers dollars that is about to be spent in our economy.”
Losing The Hobbit would leave New Zealand “humiliated on the world stage” and “Warners would take a financial hit that would cause other studios to steer clear of New Zealand”, Jackson said.
“If The Hobbit goes east [East Europe in fact], look forward to a long, dry, big-budget movie drought in this country. We have done better in recent years with attracting overseas movies and the Australians would like a greater slice of the pie, which begins with them using The Hobbit to gain control of our film industry.”
Various people and organizations in New Zealand soon line up behind one side or the other. Those siding with Jackson include Film New Zealand (which promotes filmmaking by foreign countries in New Zealand) and SPADA (the Screen Production and Development Association) and eventually the government. On the unions’ side is the Council of Trade Unions.
September 28. New Line, Warner Bros., and MGM weigh in with a statement that ups the ante. It dismisses the MEAA’s claims as “baseless and unfair to Peter Jackson” and continues:
To classify the production as “non-union” is inaccurate. The cast and crew are being engaged under collective bargaining agreements where applicable and we are mindful of the rights of those individuals pursuant to those agreements. And while we have previously worked with MEAA, an Australian union now seeking to represent actors in New Zealand, the fact remains that there cannot be any collective bargaining with MEAA on this New Zealand production, for to do so would expose the production to liability and sanctions under New Zealand law. This legal prohibition has been explained to MEAA. We are disappointed that MEAA has nonetheless continued to pursue this course of action.
Motion picture production requires the certainty that a production can reasonably proceed without disruption and it is our general policy to avoid filming in locations where there is potential for work force uncertainty or other forms of instability. As such, we are exploring all alternative options in order to protect our business interests.
Thus the specter of the production being not only delayed but also taken to another country is raised, and the implications of such a threat will gradually force the government to take measures to prevent that happening.
Peter Jackson also makes a statement to the Wellington newspaper that the Hobbit production might move to Eastern Europe. (The next day he reveals that WB is considering six countries for it.)
That night, a group of 200 actors met in Auckland, issuing a statement again asking the producers to meet for negotiations.
October 1. Jackson and WB voluntarily offer a form of residuals to Hobbit actors:
Sir Peter Jackson said New Zealand actors who did not belong to the United States-based Screen Actors’ Guild had never before received residuals – a form of profit participation. Warner Brothers had agreed to provide money for New Zealand actors to share in the proceeds from the Hobbit films.
It would be worth “very real money” to New Zealand actors. “We are proud that it’s being introduced on our movie. The level of residuals is better than a similar scheme in Canada, and is much the same as the UK residual scheme. It is not quite as much as the SAG rate.”
After much speculation, an announcement is made that Peter Jackson will definitely direct the film (which Guillermo del Toro had exited in May).
At about this time members of the filmmaking community begin campaigning actively against the boycott. An anti-boycott petition for New Zealand filmmakers and persons indirectly related to production to sign goes online; it ends with 3275 people having endorsed it.
October 15. The Hobbit is greenlit, but the possibility of moving the production out of New Zealand remains. Actors who have already been auditioned begin to be officially cast.
October 20. Actors Equity NZ is due to meet in Wellington. Richard Taylor (head of Weta Workshop) calls for a protest march. The actors’ meeting is called off due, the union says, to the “angry mob” that results. (Videos and photos posted online show a lengthy line of people walking through the streets in a peaceful fashion; that’s Richard talking to the press in the photo at the top. A person less likely to incite a “mob” to anger I cannot imagine.) An actors’ meeting scheduled for the next day in Auckland is also called off, putatively for the same reason, though no protest event had been planned there.
The turning-point day
October 21 (NZ). Jackson and his partner Fran Walsh issue a statement that implies that Warner Bros. has decided to move The Hobbit elsewhere:
“Next week Warners are coming down to New Zealand to make arrangements to move the production offshore. It appears we cannot make films in our own country even when substantial financing is available.”
Helen Kelly, president of the Council of Trade Unions calls Jackson “a spoiled little brat” on national television, helping turn the public against her cause.
Fran Walsh hints during a radio interview that WB might move The Hobbit to Pinewood Studios in England (where the Harry Potter films have been shot).
Prime Minister John Key says he hopes the production can be kept in New Zealand. Economic Development Minister Gerry Brownlee says he will meet with the WB delegation.
The international actors’ boycott against The Hobbit is called off.
October 21 (U.S.)/22 (NZ). WB is still considering moving the production, saying it has no guarantee that the actors will not go on strike. Key suggests that the labor law might be changed to provide that guarantee. The proposed legislation soon will become known as the “Hobbit bill.”
The Wall Street Journal suggests that a slight slip in the value of the New Zealand dollars against the American dollar is partly due to uncertainties about whether The Hobbit production will stay in the country.
WB announces the casting of Martin Freeman as Bilbo, plus several actors chosen as dwarves.


Bilbo Baggins by Tolkien and Martin Freeman, Bilbo-to-be.
A “positive rally” to convince WB to keep the production in New Zealand is announced. This eventually results in individual rallies in several cities and towns on October 25.
( U.S. time) Variety reports that unnamed sources within WB have said the studio is inclining toward keeping the production in New Zealand. This is the only hint of positive news from inside WB that comes out during the entire process.
Over the next few days, much finger-pointing takes place. Figures concerning the potential loss to NZ tourism if the film goes elsewhere are released. Helen Kelly apologizes for her “brat” remark.
October 25 (NZ). The WB delegation of 10 executives and lawyers arrive in Wellington. The pro-Hobbit rallies take place.
Pro-Hobbit rally in Wellington (Marty Melville/Getty Images).
October 26. News breaks that if The Hobbit is sent to another country, the post-production work (originally intended for Weta Digital and Park Road Post, companies belonging to Jackson and his colleagues) could take place outside New Zealand.
The WB delegation arrives at the prime minister’s residence in a fleet of silver BMWs. After the meeting ends, Key puts the chances of retaining the production at 50-50. He reiterates that the labor law might be changed.
Photo: NZPA
Presumably at this meeting, WB also puts forward a demand for higher tax rebates or other incentives; other countries it has been considering have more generous terms. Ireland has offered 28%, while New Zealand’s Large Budget Screen Production Grant scheme offers only 15%. This demand is not made public until later. During Key’s speech after the meeting, however, he mentions the possibility of higher incentives, but says the government cannot match 28%.
Editorials soon appear attacking the idea of changing a law at the behest of a foreign company.
The government’s deal with Warner Bros.
October 27. The New Zealand dollar again slips in relation to the American dollar, again attributed to uncertainty about The Hobbit.
Key and other government officials meet again with the WB delegation. The legal problem has been resolved to both sides’ satisfaction, but WB is holding out for higher incentives.
In the evening, Key announces that an agreement has been reached and the Hobbit production will stay in New Zealand:
As part of the deal to keep production of the “The Hobbit” in New Zealand, the government will introduce new legislation on Thursday to clarify the difference between an employee and a contractor, Mr. Key said during a news conference in Wellington, adding that the change would affect only the film industry.
In addition, Mr. Key said the country would offset $10 million of Warner’s marketing costs as the government agreed to a joint venture with the studio to promote New Zealand “on the world stage.”
He also announced an additional tax rebate for the films, saying Warner Brothers would be eligible for as much as $7.5 million extra per picture, depending on the success of the films. New Zealand already offers a 15 percent rebate on money spent on the production of major movies.
(The figure for the government’s contribution to marketing costs is later given as $13 million.)
October 28 (NZ). Peter Jackson returns to work on pre-production, which his spokesperson says has been delayed by five weeks as a result of the boycott. Principal photography is expected to begin in February, 2011, as had been announced when the film was greenlit. (The two parts are due out in December 2012 and December 2013.)
The Stone Street Studios. The huge soundstage built after LOTR is at the left; the former headquarters of 3 Foot 6 at the upper left.
In Parliament, a vote to rush through consideration of the “Hobbit bill” passes, and debate continues until 10 pm.
October 29 (NZ). The “Hobbit bill” passes in Parliament by a vote of 66 to 50, thus fulfilling the governments offer to WB and ensuring that The Hobbit would stay in New Zealand. It was known in advance that Key had enough votes going into the debate to carry the legislation.
It is revealed that James Cameron has been in talks with Weta to make the two sequels to Avatar in New Zealand. (Avatar itself was partly shot in New Zealand, with the bulk of the special effects being done there.) The timing has nothing to do with the Hobbit-boycott crisis. The two films are due to follow The Hobbit, with releases in December 2014 and December 2015.
October 30 (NZ). It is announced that the Hobbiton set on a farm outside Matamata will be built as a permanent fixture to act as a tourist attraction. (The same set, used for LOTR, was dismantled after filming, leaving only blank white facades where the hobbit-holes had been; nevertheless the farm has attracted thousands of tourists. See below.) Warner Bros. had been persuaded by the New Zealand government to permit this, though whether this was part of the agreement made with the studio’s delegation is not clear. I suspect it was.
It is also announced that the extended coverage of the 15% tax rebates specified in the “Hobbit bill” will apply to other films from abroad made in New Zealand—but only those with budgets of $150 million or more. (Presumably in New Zealand dollars.)
A remarkable outcome
In a way, it is amazing that a film production, even a huge one like The Hobbit, virtually guaranteed to be a pair of hits, could influence the law of a country–and make the legal process happen so quickly. Yet given the ways countries and even states within the USA compete with each other to offer monetary incentives to film productions, in another way it is intriguing that such pressure is not exercised by powerful studios more often. In most cases, a production company simply weighs the advantages and chooses a country to shoot in. Maybe countries get into bidding wars to lure productions or maybe they just submit their proposals and hope for the best. Certainly the six other countries considered briefly by WB were quick to jump in with information about what they could offer the Hobbit production.
In the case of Warner Bros. and The Hobbit, everyone initially assumed that the two parts would be filmed in New Zealand, just as LOTR had been. Yet the actors’ unions created an opportunity. The boycott gave Warner Bros. the excuse to threaten to pull the film out of New Zealand. Meeting with top government officials, WB executives demanded assurance that a strike would not occur–and oh, by the way, we need higher monetary incentives. As a result, a compromise was reached, the incentives were expanded, and there was a happy ending for the many hundreds of filmmakers of various stripes who would otherwise have been out of work.
Although there is considerable bitterness among the actors’ union members and those who supported their efforts, many in New Zealand see the tactics of the MEAA as extremely misguided. Kiwi Jonathan King, the director of the comic horror film Black Sheep, sums it up:
But this was all precipitated by an equal or greater attack on our sovereignty: an aggressive action by an Australian-based union taken in the name of a number of our local actors, backed by the international acting unions (but not supported by a majority of NZ film workers), targeting The Hobbit, but with a view to establishing a ’standard’ contract across our whole industry. While the actors’ ambitions may be reasonable (though I’m not convinced they are in our tiny market and in these times of an embattled film business), the tactic of trying to leverage an attack on this huge production at its most precarious point to gain advantage over an entire industry was grotesquely cynical and heavy-handed, and, as I say, driven out of Australia. Imagine SAG dictating to Canadian producers how they may or may not make Canadian films!
Whether the deal was unwisely caused by a pushy Australian union is a matter for debate. Whether the New Zealand government unreasonably bowed down to a big American studio is as well. But the deal that the two parties reached is a remarkable one, perhaps indicative of the way the film industry works in this day of global filmmaking.
Warner Bros. gets more money and a more stable labor situation. What’s in it for New Zealand? First, the incentives for large-budget films from abroad to be made in the country are raised. This comes not through an increase in the tax-rebate rate but an expansion of what it covers:
The Government revealed this week that the new rules would mean up to $20 million in extra money for Warner Bros via tax rebates, on top of the estimated $50 million to $60 million under the old rules.
While the details of the Large Budget Screen Production Grant remain under wraps, Economic Development Minister Gerry Brownlee said it would effectively increase the incentives for large productions to come to New Zealand.
The grant is a 15 per cent tax rebate available on eligible domestic spending. At the moment a production could claim the rebate on screen development and pre-production spending, or post-production and visual effects spending, but not both.
If the Government allowed both aspects to be eligible, it would be a large carrot to dangle in front of movie studios.
Mr Brownlee was giving little away yesterday but said the broader rules would apply only to productions worth more than US$150 million ($200 million).
It would bridge the gap “in a small way” between what New Zealand offered and what other countries could offer.
During this period, it was claimed that WB had already spent around $100 million on pre-production on The Hobbit, which has been going on for well over a year now. That figure presumably is in New Zealand currency.
There are some in New Zealand who oppose “taxpayer dollars” going to Warner Bros. As has been pointed out–though apparently not absorbed by a lot of people–Warner Bros. will spend a lot of money in New Zealand and get some of it back. The money wouldn’t be in the government’s coffers if the film weren’t made in the country. It’s not tax-payers’ money that could somehow be spent on something else if the production went abroad.
Another advantage for the country is the permanent Hobbiton set, which will no doubt increase tourism. There are fans who have already taken two or three tours of LOTR locations and will no doubt start saving up to take another.
One item that didn’t get noticed much during the deluge of news is that one of the two parts will have its world premiere in New Zealand. That’ll probably happen in the wonderful and historic Embassy theater, which was refurbished for the world premiere of The Return of the King. It was estimated that the influx of tourists and journalists for that event brought NZ$7 million to the city of Wellington. About $25 million in free publicity was provided by the international media coverage.
The Embassy in October 2003, being prepared for the Return of the King world premiere.
The deal also essentially makes the government of New Zealand into a brand partner with New Line to provide mutual publicity for The Hobbit. As I describe in Chapter 10 of The Frodo Franchise, the government used LOTR to “rebrand” the entire country. It worked spectacularly well and had a ripple effect through many sectors of society outside filmmaking. The country came to be known more for its beauty, its creativity, and its technical innovations than for its 40 million sheep. Now in the deal over The Hobbit, the government has committed to providing NZ$13 million for WB’s publicity campaign. But the money will also go to draw business and tourists. As TVNZ reported:
But the Prime Minister says for the other $13 million in marketing subsidies, the country’s tourism industry gets plenty in return.
“Warner Brothers has never done this before so they were reluctant participants, but we argued strongly,” Key said.
Every DVD and download of The Hobbit will also feature a Jackson-directed video promoting New Zealand as a tourist and filmmaking destination.
Graeme Mason of the New Zealand Film Commission says the promotional video will be invaluable.
“As someone who’s worked internationally for most of my life, you can’t quantify how much that is worth. That’s advertising you simply could not buy.”
If the first Hobbit film is as popular as the last Lord of the Rings movie, the promotional video could feature on 50 million DVDs.
Suzanne Carter of Tourism New Zealand agrees having The Hobbit production here is a dream come true.
“The opportunity to showcase New Zealand internationally both on the screen and now in living rooms around the world is a dream come true,” Carter said.
Marketing expert Paul Sinclair says the $13 million subsidy works out at 26 cents a DVD.
“It’s a bargain. It is gold literally for New Zealand, for brand New Zealand,” he said.
It’s not clear how the promotional partnership will be handled. There was a similar, if smaller partnership when LOTR was made. New Line permitted Investment New Zealand, Tourism New Zealand, the New Zealand Film Commission, and Film New Zealand to use the phrase, “New Zealand, Home of Middle-earth” without paying a licensing fee. (Air New Zealand was an actual brand partner during the LOTR years.) But for the government to actually underwrite the studio’s promotional campaign may entail more. That deal is more like the traditional brand partnership, where the partner agrees to pay for a certain amount of publicity costs in exchange for the right to use motifs from the film in its advertising. Has a whole country ever brand-partnered a film? I can’t think of one.
In my book I wrote that LOTR “can fairly claim to be one of the most historically significant films ever made.” That’s partly why I wrote the book, to trace its influences in almost every aspect of film making, marketing, and merchandising–as well as its impact on the tiny New Zealand film industry that existed before the trilogy came there. Years later, I still think that my claim about the trilogy’s influences was right. When an obscure art film from Chile or Iran carries a credit for digital color grading, it shows that the procedure, pioneered for LOTR, has become nearly ubiquitous. There are many other examples. The troubled lead-up to The Hobbit‘s production and the solutions found to its problems suggest that it will carry on in its predecessor’s fashion, having long-term consequences beyond boosting Warner Bros.’ bottom line. It will be interesting to see if other big studios announce they will film in one country and then find ways of maneuvering better terms by threatening to leave–or by actually leaving.
From Worldwide Hippies