Archive for the 'PERPLEXING PLOTS (the book)' Category
Enter Benoît Blanc: KNIVES OUT as murder mystery
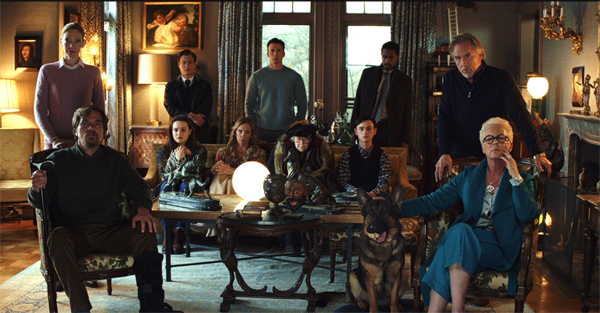
Knives Out (2019).
DB here:
Now that a sequel, Glass Onion, has been announced for the Toronto International Film Festival, it seems a good time to look back at Rian Johnson’s first whodunit Knives Out. The effort has a special appeal for me because it chimes well with arguments I make in Perplexing Plots: Popular Storytelling and the Poetics of Murder.
I don’t analyze Knives Out in the book, but it would have fitted in nicely. The movie exemplifies one of the major traditions I study, the classic Golden Age puzzle, and it shows how the conventions of that can be shrewdly adapted to film and to the tastes of modern viewers. In addition, Johnson’s film supports my point that the narrative strategies of “Complex Storytelling” have become widely available to viewers, especially when those strategies are adjusted to the demands of popular genres. Historically, such strategies became user-friendly, I maintain, partly because of the ingenuity demanded by mystery plotting.
Needless to say, spoilers loom ahead.
Revisiting and revising
The prototypical puzzle mysteries are associated with Anglo-American novels of the 1920s-1940s, the “Golden Age” ruled by talents such as Dorothy L. Sayers, Anthony Berkeley Cox, John Dickson Carr, Ngaio Marsh, Ellery Queen, and many others–supremely by Dame Agatha Christie. Similar books are still written today, often under the guise of “cozies” because they supposedly offer the comforting warmth of familiarity. Golden Age plotting flourishes in television too, in all those (largely British) shows about murder in supposedly humdrum villages.
Knives Out relies on Golden Age conventions from top to bottom. A rich, odious family is overseen by a domineering patriarch, mystery novelist Harlan Thrombey. When he’s found dead in his mansion, apparently of suicide, his family members become nervous because each has a guilty secret. The conflicts are brought into focus when it’s revealed that Harlan changed his will so as to disinherit all his offspring. He leaves his fortune and his house to Marta Cabrera, the nurse who administered his medications and became his friend and confidant. Is there foul play? Investigating the case are are two policemen and the private investigator Benoît Blanc. They must decide whether Harlan’s apparent suicide is actually murder and if so, who’s the culprit.
Johnson organizes his plot around many classic techniques. In the Golden Age, writers tended to fill the action out to book length by adding more crimes, such as blackmail schemes or a series of murders. Both of these devices are exploited in Knives Out. Marta is apparently the target of an extortioner, and the family housekeeper Fran is the victim of a poisoner. The film also employs the least-likely-suspect convention (a favorite of Christie’s) and a false solution (another way to fill out a book). Johnson supplies traditional set-pieces as well: the discovery of the body, a string of interrogations of the suspects, the assembling of suspects to hear the will read, and a denouement in which the master sleuth announces the solution by recapitulating how the crime was committed.
The conventions are updated in ways both familiar and fresh. The sprightly music and the flamboyant bric-à-brac of Harlan’s mansion deliberately recall Sleuth (1972), another reflexive, slightly campy revisiting of murder conventions. Johnson wanted to evoke the all-star, well-upholstered adaptations of Christie novels like Murder on the Orient Express (1974, 2017) and Death on the Nile (1978, 2022). But he has courted younger audiences with citations (the title is borrowed from Radiohead) and social commentary, such as references to Trump, neo-Nazis, and illegal immigration. The Thrombey clan’s inability to remember what country Marta came from reminds us of something not usually acknowledged about Golden Age classics: they often provided satire and social critique of inequities in contemporary society. (In the book I discuss Sayers’ Murder Must Advertise as an example.)
Like earlier Christie adaptations, Johnson’s film has recourse to flashbacks illustrating how the crime was actually committed. In Benoît Blanc’s reconstruction of the murder scheme, rapidly cut shots illustrate how the family black sheep Ransom sought to kill Harlan by switching the contents of his medicine vials, which would make Marta the old man’s murderer. But her expertise as a nurse unconsciously led her to switch the vials again, so she didn’t administer a fatal dose. This forced Ransom to continually revise his scheme, chiefly by destroying evidence of Marta’s innocence and trying to murder Fran, who suspected what he had done.
All of this is carried by the now-familiar tactic of crosscutting Blanc’s solution with shots of Ransom’s efforts, guided by Blanc’s voice-over. At some moments, the alternation of past and present is very percussive, with echoing dialogue (“You’re not gonna give up that,” “You’ve come this far”). For modern audiences, this swift audio-visual revelation of the “hidden story” is far more dynamic than a purely verbal recitation like that on the printed page.
Johnson tries for a more virtuoso revision of a classic convention in treating the standard interrogation of the suspects. Lieutenant Elliott’s questioning, followed by questions posed by Blanc, consumes an astonishing sixteen minutes of screen time. Such a lump of exposition could have been dull. But the accounts provided by Harlan’s daughter Linda, her husband Richard, Harlan’s son Walt, his daughter-in-law Joni, and Joni’s daughter Meg are brought to life by flashbacks to the day of Harlan’s death. Aided by voice-over, we get a sharp sense of each character’s personality while the mechanics of who-was-where-when during the birthday party are spelled out. Some flashbacks are replayed in order to alert us to disparities in the stories, which stir curiosity and set up further lines of inquiry. The technique isn’t utterly new, though; in the book I show that such shifts across viewpoints emerged in mystery films from the 1910s onward.
The pace picks up when, instead of sticking to one-by-one witness accounts, Johnson starts to intercut them, showing varied responses to the same questions.
The editing creates a conversation among the witnesses, as one disputes the testimony of another. This freedom of narration, mixing different accounts in a fluid montage, plays to modern viewers’ abilities to follow fast, time-shifting narratives.
The use of voice-over to steer us through the flashbacks takes on new force when Elliott and Blanc question Marta. Her account of the fatal night is given not as testimony but as her memory. She recalls tending to Harlan after the party, starting a game of Go with him, and then discovering that apparently she gave him a lethal dose of morphine. She’s distraught, but he consoles her and instructs her in how to cover up her mistake. His scheme, which involves an elaborate disguise and a secret return to his bedroom, is designed to give Marta an alibi by showing her apparently leaving before he dies.
In her memory Harlan’s voice-over narrates her flashback as she executes his plan. But she doesn’t confess to Elliott and Blanc. Following Harlan’s instructions, Marta lies to exonerate herself. Her propensity to vomit when she tells a lie drives her to the commode, but the police don’t notice. She has apparently fooled Blanc, who considers that her account “sounds about right.”
In such ways Johnson retools scenes of the police interrogation for contemporary viewers. But he goes further in revising Golden Age tradition. Well aware of the tendency of the puzzle plot to indulge in plodding clue-tracing, he provides a deeper emotional appeal.
Immigrants get the job done
The Golden Age plot relies on an investigation, the scrutiny of the circumstances leading up to and following a mysterious crime, usually murder. Plotting came to be considered a purely logical game, a matter of appraising motives, checking timetables, pondering clues, testing alibis, and eventually arriving at the only possible solution. These conventions were canonized in books like Carolyn Wells’ Technique of the Mystery Story (1913) and in many writings by authors. But some writers recognized that the emphasis on a puzzle tended to eliminate emotion and promote a boring linearity in which the detective poked around a crime scene and questioned suspects one by one.
Authors sought ways to humanize the investigation plot. Sayers filled it out with romance, social commentary, and regional color. Hardboiled novelists like Hammett and Chandler, who relied on many Golden Age conventions, turned the investigation into an urban adventure, with the threat of danger looming over the private detective. Others tried to blend in elements of the psychological suspense novel, as Nicholas Blake does in The Beast Must Die (1938), which traces how a bereaved father searches for the hit-and-run driver who killed his son.
Rian Johnson tries something similar in Knives Out. Into the investigation of Blanc and the police, he inserts a woman-in-peril plot. Although we’re introduced to Marta early in the film, she’s pushed aside for about half an hour as the inquiry takes over in the interrogation sequences I’ve mentioned. Then Blanc takes a kindly interest in her and probes her knowledge of Harlan’s attitude toward his family. And then, after Lieutenant Elliott becomes convinced that it’s a suicide, Marta is questioned. At this point, she comes to the center of the film and becomes its sympathetic protagonist and central viewpoint character.
Her memory episodes reveal that she believes she accidentally killed Harlan. But out of self-preservation and obedience to his orders, she doesn’t confess. She tries to ease away from Blanc, but he asks her to be his “Watson.” The rest of the plot forces her to accompany the investigation. Panicked that her scheme will be revealed, she often tries to suppress evidence: futzing up surveillance footage, traipsing over the muddy footprints she left, trying to throw away a piece of siding that she dislodged that night. Marta’s situation recalls that in The Woman in the Window (1944) and The Accused (1949), and in the TV series Columbo, in which guilty protagonists must watch as their trail is exposed.
Marta’s only ally appears to be Ransom, Harlan’s ne’er-do-well grandson. He justifies his concern as partly selfish: If she gets away with it, she can share Harlan’s legacy with him. As in many domestic thrillers, this handsome helper is also a little sinister, but Marta accepts his advice for how to respond to an anonymous threat of blackmail. When Marta discovers that someone has nearly killed the housekeeper Fran, she vows to confess. By then, however, Blanc has solved the mystery and absolved her of guilt.
Johnson deliberately made Marta a center of sympathy as a way of humanizing the investigation.
Very early on in the game I wanted to relieve the audience of the burden of “Can we figure this out?”. . . . I don’t think that’s a very strong narrative engine to drive things. I think that’s very intellectual and that clue-gathering–after a while you recognize “No, I’m not gonna figure this out,” so you kind of sit back on your hands and wait for the detective to figure it out. . . .
So the notion of tipping the hand early and giving this false but very convincing picture from Marta’s perspective of “I’ve done this and I’m in a lot of trouble.” . . . Could we do that so you’re genuinely on the side of the killer?. . . Once you’ve done that it’s very interesting because of the mechanics of the murder mystery, the fact that you know the detective always catches the killer. . . . The looming threat is that we know how mysteries work and we know that the detective catches [the killer] at the end. And we’re worried for Marta. We’re worried, “How is she possibly going to get out of this situation?”
Johnson uses several other tactics to put us on Marta’s side. While the performances of the actors playing the Thrombeys leans toward grotesquerie, Ana de Armas plays Marta more naturalistically. In time-honored Hollywood fashion, Johnson also makes Marta ill-treated. She’s dominated by the family who pretends to love her, and as an immigrant she’s in danger of seeing her mother deported. When she is named Harlan’s heir, the family descends on her like predators. In the end, as in many psychological thrillers, the woman in peril turns into a resourceful combatant. She bluffs Ransom into confessing his scheme, and only when she vomits on him does he realize she’s fooled him with a lie. We can enjoy the innocent trapping the guilty.
The game’s afoot. Which one?
The Golden Age story is more than a puzzle. It’s posited as a game. Of course the murderer is at odds with the detective, with each trying to outwit the other. At another level, the game is a battle of wits between author and reader. John Dickson Carr sums it up.
It is a hoodwinking contest, a duel between author and reader. “I dare you,” says the reader, “to produce a solution which I can’t anticipate.” “Right!” says the author, chuckling over the consciousness of some new and legitimate dirty trick concealed up his sleeve. And then they are at it—pull-devil, pull-murderer—with the reader alert for every dropped clue, every betraying speech, every contradiction that may mean guilt.
Golden Age authors realized that the core mystery could be enhanced by techniques that both mislead the reader and drop hints about what’s really going on. The cultivated reader became alert not just for characters who might lie but for narration that was engineered to be misunderstood. Golden Age authors weaponized, we might say, every literary device to steer the reader away from the solution. The trick was to do this without cheating.
If this genre is a game, then, following sturdy British tradition, “fair play” becomes the watchword. Earlier detective writers, notably Conan Doyle, did not feel obliged to share all relevant information with the reader. The master sleuth was likely to discover a clue or a piece of background knowledge that he or she kept quiet, the better to flourish it in triumph at the denouement. Instead, Golden Age authors made a show of telling everything.
The concept of fair play was made explicit in Ellery Queen’s novels, which included a climactic “challenge to the reader” explaining that at this point all the information necessary to the solution was now available. (This device was replicated in the EQ TV series.) Even without this pause in the narration, Golden Age writers were careful to supply everything before the big reveal.
Knives Out is very much in the game tradition. It knowingly follows self-conscious “meta”-mystery films like Sleuth, The Last of Sheila (1973), and Deathtrap (1982), all of which flamboyantly exploit classic conventions (often with crime writers at the center of the plot). Accordingly, Johnson is aware of the need to play fair.
A straightforward example occurs in the interrogation sequence. Members of the Thrombey family tell Blanc and the police that Harlan’s last day with the family was a happy occasion. But the flashbacks reveal to us that they’re lying. We see Harlan fire Walt as his publisher, confront Richard with his infidelity, and cut off Joni’s funding for Meg’s tuition. Soon enough Blanc will intuit their deceptions and ask Marta for confirmation, but the flashbacks make sure we grasp their possible motives for killing Harlan.
But telling everything required telling some of it in deceptive ways. Otherwise, there’d be no puzzle. The craft of Golden Age fiction demanded skillfully planting crucial information that can be (a) recalled at propitious moments by the detective but (b) neglected by the reader (“I should have noticed that!”). Perplexing Plots traces various stratagems for achieving how authors muffled crucial information through ellipsis, distraction, and other tactics.
Consider Fran’s dying message. As Marta bends over her, Fran gasps, “You did this.” Since we’ve been led to believe that Fran is blackmailing Marta, it seems to confirm that she’s got proof of Marta’s guilt in the toxicology report. But the dying message turns out to be equivocal. Fran is actually saying, “Hugh did this”–identifying her would-be killer. Huh?
Early in the film when Ransom comes to the mansion, the police greet him as “Hugh Drysdale,” to which he replies, “Call me Ransom. Ransom is my middle name. Only the help calls me Hugh.” Fair play, but given to us in a distracting way. The line is played down: Ransom delivers it quickly as he’s turned from the camera and strides into the house, and the policemen’s reactions are more prominent in the shot.
To play fair, Johnson reiterates the name just before the revelation, when Blanc addresses him as “Mr. Hugh Ransom Drysdale.” Since in Fran’s scene we can’t tell the difference between “You” and “Hugh,” file this under Carr’s category of “legitimate dirty trick.”
As a result, anything can become a clue for interpretation/misinterpretation. But for Golden Age creators, authorial craft isn’t only a matter of producing clues. Clues are available to the investigators and are crucial to the solution. But at the same time the author can supply hints in the narration, addressed to us behind the backs of the characters. An instance in Knives Out is the title of one of Harlan’s books, glimpsed in a montage of his bookshelves. In a film reliant on syringes, The Needle Game would seem to be a tip-off.
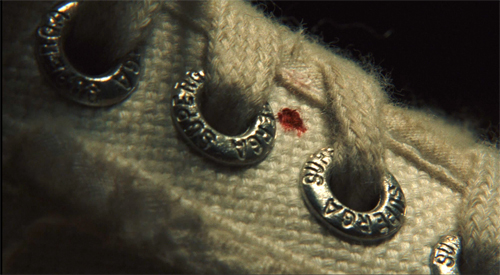
Or a hint can become a clue eventually. After Marta’s wild night covering up her “crime,” she rushes home and takes refuge in front of the TV. As she nervously taps her foot, a close-up reveals a single bloodstain on her sneaker.
She’s unaware of it, but the stain opens the possibility that it could incriminate her later. The film lets us forget it until the very end, when Blanc says he knew she was involved in Harlan’s death from the start, when he spotted the bloodstain. The hint for us became a clue for him.
Golden Age plotting invites attention to minutiae of presentation. Although Agatha Christie is sometimes condemned as a clumsy writer, Perplexing Plots tries to show that she often mobilizes a flat style to mislead us. Similarly, the attentive viewer will notice little felicities in Knives Out. For instance, when we first see Marta return to the mansion through the forest path, a shot shows her leaving the tracks she’ll later try to smear over. But in Blanc’s reconstruction, we see Ransom returning to the mansion by balancing on the wall lining the path, so as to leave no traces in the mud.
Had Ransom walked on the path, Johnson would have been besieged by Twitter complaints.
All this is a matter of self-conscious artifice. As Johnson notes, few readers take seriously the task of solving the mystery themselves. One member of the Ellery Queen collaboration admitted: “We are fair to the reader only if he is a genius.” The fair-play convention is at once a pretext for the display of authorial ingenuity and a source of artistic power–proof that a plot can harbor a hidden intricacy unsuspected by the reader. One dimension of connoisseurship in the classic mystery is the reader’s admiration of artifice, a taste for elaborate construction. If it’s all in the game, then we’re no longer committed to mundane realism. A portrait can whimsically change from scene to scene.
Henry James argued for a through-composed form of the novel, where every detail was carefully judged for its effect and its balance with others. An unexpected legacy of Jamesian formalism, I think, was the Golden Age authors’ ambition to make each story a tour de force, a test of readers’ skills and a revelation of unexpected resources in storytelling technique. Mystery stories are ingenious, as Ben Hecht noted, because they have to be.
The film’s rapid pace, time-shifting, and looping replays exemplify current tastes for what’s been called Complex Storytelling. But one task of my book is to suggest that popular storytelling has been complex for quite a while. The techniques have become refined and revised, and their appeal has been sharpened by emerging audiences (e.g., in the 1990s) and new technologies (e.g., video that allows replays).
We were sensitized to these techniques by mystery fiction throughout the century. The play with incompatible viewpoints, reruns of action bearing new significance, the strategic use of ellipsis–all are there in the Golden Age tradition. Likewise, the notion of fair play persists in all those “twist” films that flash back to show us actions that take on a new significance. Golden Age strategies, and mystery plotting more generally, have prepared audiences to expect pleasurable but “fair” deception in all genres. Knives Out, among other accomplishments, helps us understand how today’s sidewinding stories have roots in a genre that’s too often dismissed as mere diversion.
The quotations from Rian Johnson come from the Blu-ray supplement to Knives Out, “Planning the Perfect Murder,” between 2:21 and 4:20. The supplementary material on the disc is exceptionally detailed and reveals Johnson’s keen knowledge of the history of mystery fiction and film.
Exceptional studies of Golden Age mysteries are LeRoy Lad Panek’s Watteau’s Shepherds: The Detective Novel in Britain (1979) and Martin Edwards’ Golden Age of Murder (2016), The Story of Classic Crime in 100 Books (2017), and The Life of Crime: Detecting the History of Mysteries and Their Creators (2022). See also Mike Grost’s encyclopedic site A Guide to Classic Mystery and Detection.
For another good example of Golden Age misdirection appropriated in cinema, see this entry on Mildred Pierce.
Perplexing Plots is available for pre-order here and here. This is a good place to thank Sarah Weinman and Yuri Tsivian for their favorable comments on the book, which are available on these sites.
P.S. 9 August: I now realize I neglected to mention that Joni’s daughter Meg isn’t as harshly characterized as the rest of the Thrombey clan. She’s a friend to Marta and Fran and seems genuinely to care about Marta’s fate. However, she’s still a pothead who walks out of her benefactor’s birthday party and who colludes with the family to call Marta to get information. In plot terms, she’s one more threat to Marta.
Although we didn’t discuss this point, I thank John Toner of Renew Theaters for amiable correspondence about Knives Out.
Knives Out (2019).