Archive for the 'UW Film Studies' Category
OBSERVATIONS goes all FILMSTRUCK

DB here:
In light of the cataclysm that struck on election day, to return to talking of films can seem frivolous. We’ve delayed posting this blog because we, like millions of other people, are seized with a dread as to what may come for our friends, our neighbors, our country and the world.
At least for the moment, though, we can’t stop living other aspects of our lives. Judging by the attention our entries continue to get in these days, we think that we should keep trying to provide ideas and information about film. Art is important too.
Thunderstruck by FilmStruck
You probably know that Turner Classic Movies has partnered with the Criterion Collection to create a streaming service called FilmStruck. There’s a comprehensive overview of the service on Variety, and Peter Becker has an invigorating introduction on the Criterion site.
The library includes many hundreds of films, mostly foreign imports and independent features and shorts. Many of the titles come from US non-studio distributors, but a vast number are from the Criterion library. Many will be titles not available on DVD.
It’s an all-you-can eat subscription service. For $6.99 per month you can get a basic membership in FilmStruck, and that will provide hundreds of titles, including many Criterion ones. For an extra $4, you can add on the Criterion Channel, with a huge additional selection (about 500 titles at any moment). There’s an annual rate covering both for $99. You can sign up for a 14-day free trial here.
Both wings of Filmstruck include the sort of bonus materials found on DVDs: background information, archival footage, talking heads, and video essays. The Criterion titles include voice-over commentary you can play while watching. I’m especially excited by the prospect of having the filmmakers’ commentaries from out-of-print laserdisc editions (e.g., Boogie Nights). And the FilmStruck site is already hosting, for free, a rich array of blog entries by experts (Pablo Kjolseth, Kimberly Lindbergs et al.) offering perspectives on the library titles.
The films can stand singly, but they’re also gathered into groups by theme, director, nation, or whatever.
The Criterion Collection is richly curated too, with new groupings and titles highlighted every day. There are even Friday night double features, and new releases constantly refreshing the pool. And there are special events, like an evening at Manhattan’s wonderful Metrograph theatre.
This double feature is introduced by Michael Sragow on the regular Criterion website, so the synergy is tight.
In addition, there are new introductions and appreciative discussions of films. For example, our friend Sean Axmaker has some coming up. And there are continuing series with film-struck partisans.
At present, FilmStruck can be streamed on any computer or laptop, Amazon Fire, recent generations of iPad, and other devices. But not on your iPhone, pleeze. Roku and Chromecast access are coming early next year.
In short, this is a treasure house for fans of classic foreign and American films. Some older Hollywood studio films are available (e.g., Brute Force from Criterion), but I bet more of the TCM library studio will migrate to the service. I’m itching for those beautiful Warner Archive items.
FilmStruck and us (and you, we hope)
We are honored and happy to be involved with FilmStruck. Under the blog rubric, “Observations on Film Art,” Kristin and I and Jeff Smith, our collaborator on Film Art have launched a series for the Criterion Channel. We offer short appreciations of particular films and filmmakers.
There’s a video introduction to the three of us…

… including some potentially embarrassing vintage images.
Here’s our first entry, featuring Jeff Smith.
Coming up are Kristin on Kiarostami, and me on L’Avventura and Sanshiro Sugata. We hope to post about one per month.
Our discussions are analytical, focusing on particular techniques of style and narrative. They don’t contain crucial spoilers, so most can be watched before the film as well as after.
Of course we’re tremendously excited to get our ideas out there in a new platform. We conceive the series as like our blog—applying our research into film form, style, and history to films in a user-friendly way. We hope that we’ll find an audience among cinephiles as well as among more casual viewers who simply want to get more out of the films they see.
As the installments go online, we hope to post blog entries that flesh them out. Jeff will soon be posting an entry that supplements his Foreign Correspondent analysis.
My email address is still visible on every page of this site, so if you have responses to the FilmStruck versions of “Observations on Film Art,” we’d welcome hearing them. We look forward to working with our colleagues at Criterion—Peter Becker, Kim Hendrickson, Grant Delin, Tara Young, Penelope Bartlett, and all their associates. This ought to be plenty fun.
Thanks to Mary Huelsbeck and Amy Sloper of the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research for letting us prowl the premises for our introductory video.
At Stream on Demand, Sean Axmaker reviews the FilmStruck project.
P.S. 15 November: Peter Becker talks with Scott Macaulay of Filmmaker about the ambitions of the Criterion Channel, with many details about films and filmmakers to be showcased.
Picturing performance: THEATRE TO CINEMA comes to the Net
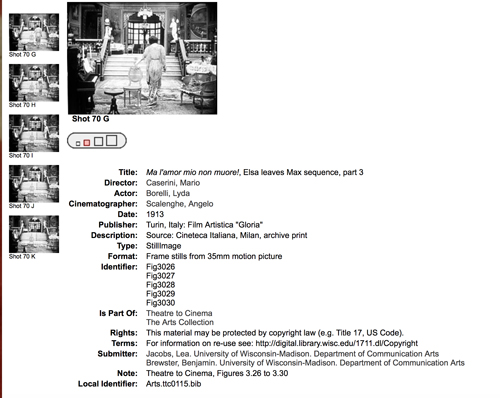
Ma l’amor mio non muore! (aka Love Everlasting, 1913). Lyda Borelli.
DB here:
The core of cinematic expression is editing. Since the 1920s, that view has been part of the lore of film aesthetics. Editing, people said, is what distinguishes film from other media. After all, the single shot is both a picture (like a painting) and a dramatization (like a scene in a stage play). But put one shot with another and you’ve got a technique impossible to parallel in other media.
But if we look closely, we find that the film image is as “uniquely cinematic” as editing. After all, a film is an image, but it’s a moving image, which is sharply different from a painting. And although a shot is a dramatization, it’s two-dimensional (unlike a stage scene) and the space it captures is quite different from that of the theatre. Anyhow, maybe editing isn’t uniquely cinematic. Comic strips juxtapose discrete images, and some forms of theatre (such as pageants, or turntable stages) can shift rapidly between scenes. Once we start to compare adjacent media, we find many overlaps in their expressive resources.
Why did early film theorists make editing so important? They were often defending the view that film was a new art, in the teeth of opponents who claimed that it was simply photographed theatre. Accordingly, film’s defenders looked for features of films that seemed to have no counterpart in theatre, such as the close-up and, more pervasively, editing.
Since then, we’ve come a long way in our understanding of film’s artistic capabilities. Filmmakers, particularly those in the early sound era (Renoir, Ophuls, Dreyer, Mizoguchi), showed the expressive power of the single shot. This tendency was amplified in the 1950s and 1960s with Antonioni, Jancso, Andy Warhol, and many other directors. Now nobody blinks if a filmmaker like Hou or Yang presents a lengthy, unedited sequence.
Informed by what’s possible in the single shot, we ought to find the earliest filmmakers using the resources of staging, composition, and performance in felicitous ways. So we do. Once we foreswear the cult of the cut, we can see that early cinema made extensive use of cinematography and mise-en-scene for powerful artistic effects. And conceding that, we suddenly find ourselves back in the lap of the other arts–painting and theatre.
Living pictures
 No one has done more to clarify the debt of early cinema to theatre than our colleagues Ben Brewster and Lea Jacobs. In the spirit of Wisconsin Revisionism, they have embraced early film’s stagy side. They’ve taught us to appreciate the ways in which dramaturgy and performance of 1910s cinema derive, in unexpected ways, from the theatre. Their trailblazing book Theatre to Cinema: Stage Pictorialism and the Early Feature Film (Oxford, 1997) showed how to appreciate early films in a whole new way: by seeing them as borrowing and modifying conventions of the stage. What may look artificial or backward to us were actually tools of subtle, supple expression.
No one has done more to clarify the debt of early cinema to theatre than our colleagues Ben Brewster and Lea Jacobs. In the spirit of Wisconsin Revisionism, they have embraced early film’s stagy side. They’ve taught us to appreciate the ways in which dramaturgy and performance of 1910s cinema derive, in unexpected ways, from the theatre. Their trailblazing book Theatre to Cinema: Stage Pictorialism and the Early Feature Film (Oxford, 1997) showed how to appreciate early films in a whole new way: by seeing them as borrowing and modifying conventions of the stage. What may look artificial or backward to us were actually tools of subtle, supple expression.
Here’s the authors’ statement of the book’s argument:
While previous accounts of the relationship between cinema and theatre have tended to assume that early filmmakers had to break away from the stage in order to establish a specific aesthetic for the new medium, Theatre to Cinema argues that the cinema turned to the pictorial, spectacular tradition of the theatre in the 1910s to establish a model for feature filmmaking. The book traces this influence in the adaptation and transformation of the theatrical tableau, acting styles, and staging techniques, examining such films as Caserini’s Ma ľamor mio non muore!, Tourneur’s Alias Jimmy Valentine and The Whip, Sjöström’s Ingmarssönerna, and various adaptations of Uncle Tom’s Cabin.
The twist here is that turn-of-the-century artistic culture had already blurred the boundaries between theatre and painting. Painters drew upon the stock gestures and poses of the stage, while plays presented vivid visual effects that were indebted to painting. The term “tableau,” referring at once to a picture and a poised stage image, captures this convergence between the media. That’s why Ben and Lea refer to “stage pictorialism” as the nexus of their inquiry.
Thanks to their research, we can see the unbroken long- or medium-shot of early features as permitting a complex choreography of facial expressions and bodily attitudes, which were in turn indebted to both pictorial and dramatic traditions. Standard gestures were summoned up and reworked to suit dramatic situations–as, for example, clutching.

When we do find editing or camera movements in these films, they’re often at the service of the performance style. Ben and Lea powerfully make the case that the expressive human body was at the center of storytelling in the first years of silent cinema. (If nothing else, the book is an in-depth analysis of diva acting from the likes of Lyda Borelli and Asta Nielsen.) By studying the history of theatre, we can learn to appreciate aspects of acting that might otherwise escape our notice.
Theatre to cinema to pixels
Uncle Tom’s Cabin; or, Slavery Days (Edison, 1903).
How, you’re asking, can you gain access to the ideas and information and images in this fine book? It’s now criminally easy.
When Theatre to Cinema was published, all the illustrations came from 35mm film prints. Those originals were gorgeous. But in some printings of the book the stills came out badly, and when the book moved to print-on-demand status, the images suffered even more. A couple years ago, Ben and Lea rescued their book and took the opportunity to make a digital version. It’s unrevised, largely because updating a twenty-year-old volume would be a major overhaul, but errors have been corrected and–very important–the stills have been much improved.
Start here, with the introduction to the project. You can download the new edition of the whole book, section by section, here.
Naturally, Kristin and I are sympathetic to this effort. Since we started our website back in 2000, we have explored ways to amplify and extend our ideas by means of the web. In the beginning, and inspired by Philip Steadman’s Net-based supplements to his excellent Vermeer’s Camera, I added material that would enhance arguments I made in Figures Traced in Light. Then we set up our blog, now in its tenth year. Over the same period, we posted web essays, as you can see in serried ranks page left. We also used the site to preserve older material, such as film analyses dropped from editions of Film Art: An Introduction and even entire books, as in Kristin’s 1985 monograph Exporting Entertainment. We’ve mounted video lectures. And we’ve produced a new edition of an older book, Planet Hong Kong 2.0, and original e-books such as Pandora’s Digital Box and Christopher Nolan: A Labyrinth of Linkages.
Ben and Lea have found another way to expand a book’s Web life. They have put Theatre to Cinema at the heart of a digital collection sponsored by the University of Wisconsin–Madison Libraries. Here’s what they offer:
In this collection, we try to supplement the description and illustration that accompanied the book in a way that makes it easier for readers to appropriate our work—both to understand it, and to make use of it in research and teaching. What were illustrations in the pages of the book are also presented here as better-quality downloadable images.
For example, you can pick a still, find its mates in a single display, and blow it up for scrutiny. If you want import it into your own files, you may choose among four different file sizes.
The provenance of each still is provided, so scholars can compare prints from different sources. In addition, there’s a master index of the visual documentation, in sequential groupings across the book.
Finally, Ben and Lea plan to add video extracts from some of the films they discuss. When those go up, we’ll announce it here.
Every admirer of silent film, and everyone who studies the interrelationship of the arts, should read this book. Hard copies are still being sold online, but they’re apt to be versions with weakly reproduced stills. Get one if you want, because a book is a good object to have in hand. In addition, for free, you can own a beautiful, searchable edition with superb stills. I think you need both.
The digital collections set up by UW Libraries are breathtaking. Check them out here.
Some entries on our site intersect with Ben and Lea’s research. See the category Tableau staging.
Weisse Rosen (White Roses, 1915). Asta Nielsen.
Still Agnès
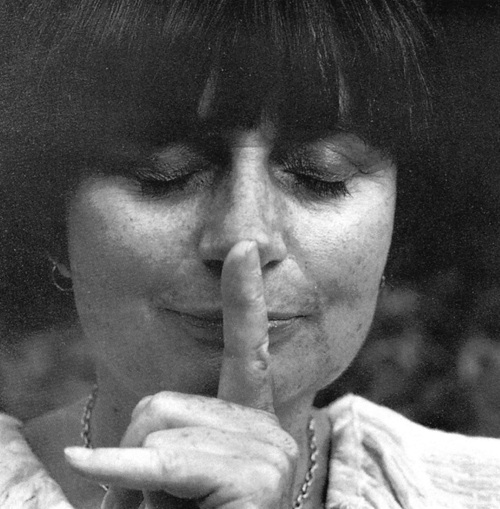
Self-portrait by Agnès Varda.
DB here:
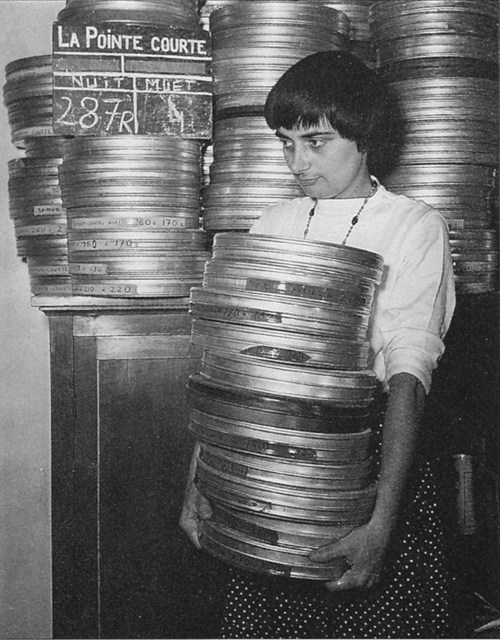
Sixty years ago, a twentysomething photographer released a film shot in an out-of-the-way French fishing village. Coming right after Rossellini’s Voyage to Italy and Fellini’s La Strada (both 1954), the result announced something new in cinema. Like those other works, it looked forward to the French Nouvelle Vague and the cinematic modernism of Antonioni, Bergman, and a host of other filmmakers.
But the status of Agnès Varda’s La Pointe Courte (1955) became apparent only with the most distant hindsight. It didn’t win big attention on the festival circuit, in the international market, or in the pages of highbrow film magazines. Denied a commercial release, La Pointe Courte circulated mostly in French ciné-clubs. In the early 1980s, when I saw it at the Brussels Cinematek, it was still a rarity.
Thirty years after La Pointe Courte, Varda’s career reached a new level. Vagabond (Sans toi ni loi, 1985), widely recognized as her masterpiece, remains one of the great achievements of that modern cinema she helped create. And she hasn’t exactly been idle since. There have been many films both long and short, including a biopic of her husband Jacques Demy in Jacquot de Nantes (1991) and the picaresque The Gleaners and I (2000); the fascinating autobiography Varda par Agnès (1994); and over the last decade a series of installations in museums around the world. She started as a photographer, became a cinéaste, and is now a plasticienne, a maker of painting and sculpture.
She is eighty-seven years old.
Agnès V., not B.
Our colleague Kelley Conway has just published an authoritative consideration of the work of this shrewd, unpredictable survivor. Reading Kelley’s book reminded me of that encounter with La Pointe Courte.
I had known Varda’s more famous works: Cléo from 5 to 7 (1961), screened at my college film society as the project of a New-Wave fellow-traveler; Le Bonheur (1965), which might be called Jules et Jim revisé et corrigé; One Sings the Other Doesn’t (1977), which got circulation among other feminist films of the period. These didn’t prepare me for La Pointe Courte’s daring mix of realism and minimalism. Varda wanted, she said, to make a film that was the equivalent of a difficult book, and for me she succeeded.
The film alternates sunny images of local life—fishing, net-mending, washing-up, a festival—with episodes in which a Parisian couple drift through the village, oddly detached from the life around them. The everyday scenes are shot in documentary style, but with a casual rigor suggesting Cartier-Bresson. Meanwhile, the couple talk in stylized compositions that could only remind me of L’Avventura.
No wonder Picasso was Varda’s favorite painter: she splits up the couple’s faces with cubistic zeal.
The disjunction between the actuality of a location and the abstraction of the couple’s anomie-riddled duet, often heard only as voice-over commentary, looks forward to Hiroshima mon amour. (No wonder: Resnais edited the film.) I barely understood the French, but the film gripped me. It was of great historical interest, and it had its own stubborn vivacity. When Kristin and I planned the first edition of Film History: An Introduction (1994) I made sure it got in. In that year, forty years after it was made, La Pointe Courte was released on VHS.
Things change. Varda is now regarded as a living treasure of world cinema, preserved in excellent Criterion DVD editions, available for streaming on Hulu, and wrapped up in a vast cube, Tout(e) Varda (20 features, 16 shorts). Whatever she does in the future, we can at least take a long-distance measure of her accomplishments.
The dream of many writers on a single director is to cover it all: appreciative study of the films, background on how the films came to be, assessment of their immediate impact and long-range influence. But this breadth of understanding is very hard to achieve. Where are the documents? How do you get the filmmaker to talk?
Kelley has done it. Her book combines film analysis, historical research, and information drawn from Varda’s archives. Kelley can tell us how the films came to be, what Varda wanted to accomplish, and how they were received. To top it off, there’s a new interview with Agnès herself.
Crossing landscapes
Les Demoiselles ont eu 25 ans (1993): Varda and Deneuve.
With a brisk practicality echoing that of her subject, Kelley has focused her lens tightly. You can’t quarrel with her choices: La Pointe Courte, the early short documentaries, Cléo, Vagabond, The Gleaners, two installations, and The Beaches of Agnès (2008). Her plan of attack is straightforward: scrutinize the film, then work backward to the conditions of production and forward to the film’s reception.The analyses are models of attention to story and style, images and sounds. Kelley pins down what intrigued me about the acting in La Pointe Courte, showing its debt to Brechtian distancing (a big influence on Varda). She goes on to connect the performances to the experiments in “flat” performance we find in Tati and Bresson at the same period. Kelley shows how many of Varda’s artistic strategies, such as whimsical puns and a love of digression, go back to her early documentaries.
 In a sense, Varda has never ceased to be a documentarist, since all her films depend on a process of research, exploration, and a personal viewpoint characteristic of the roving photographer. The book includes fresh information on two of Varda’s major multimedia installations, obviously born of her interest in found materials, gags, and unexpected juxtapositions. For one, Varda covered the gallery floor with 1500 pounds of potatoes and played the role of “Lady Potato.” Another exhibition included a reference to the grave of her beloved cat Zgougou. As described by Kelley, these installations are less narcissistic than they might seem, because Varda’s work has always been personal, derived from her perceptions of her subject. Even The Gleaners, which is at one level a denunciation of a society built on waste and inequality, is refracted through the filmmaker’s sense of aging. And though Mona in Vagabond is ferociously solitary, we meet her through Varda’s welcoming voice-over: “It seems to me she came from the sea.”
In a sense, Varda has never ceased to be a documentarist, since all her films depend on a process of research, exploration, and a personal viewpoint characteristic of the roving photographer. The book includes fresh information on two of Varda’s major multimedia installations, obviously born of her interest in found materials, gags, and unexpected juxtapositions. For one, Varda covered the gallery floor with 1500 pounds of potatoes and played the role of “Lady Potato.” Another exhibition included a reference to the grave of her beloved cat Zgougou. As described by Kelley, these installations are less narcissistic than they might seem, because Varda’s work has always been personal, derived from her perceptions of her subject. Even The Gleaners, which is at one level a denunciation of a society built on waste and inequality, is refracted through the filmmaker’s sense of aging. And though Mona in Vagabond is ferociously solitary, we meet her through Varda’s welcoming voice-over: “It seems to me she came from the sea.”
Another legacy of documentary: Kelley points up how even the fiction films spring from an attention to the specifics of a locale. “Part of Varda’s journey is regularly exploring a chosen region at length, waiting for ideas, emotions, and images to emerge.” That region might be a single Parisian street (L’Opéra-Mouffe, 1958; Daguerréotypes, 1975) or the fourteenth arrondissement (Cleo from 5 to 7). Like La Pointe Courte, Cleo is the story of a walk, this time purportedly played out in actual duration as a beautiful pop singer awaits the results of a test for cancer. Mona, in Vagabond, is another wanderer, and the wintry bleakness of southern France is as central to the action as whatever psychology we can find in her or the people she meets. The Gleaners and I searches out people who stalk the landscape and live off what they can scavenge. With modern cinema from Bicycle Thieves onward, Dwight Macdonald once noted, “The talkies have become the walkies,” but Varda has always embedded her footloose protagonists in the particulars of place.
Varda’s personal archive has given Kelley the opportunity to document the director’s creative process. The scripts are sometimes scrapbooks, with texts and images jostling one another. (Kelley offers an example in a 2011 blog entry.) The arrival of digital tools reinforced and expanded Varda’s method of free assembly. Out of a database of images, Varda erected the scaffolding of The Beaches of Agnès before starting her screenplay. She wrote, shot, and edited the whole thing in a nonlinear fashion. During the final stages, two editors worked busily in separate rooms. “I went from one to the other. On one side was Sète and Los Angeles, in the other room was Belgium and Paris.”
As for exhibition, crucial to Varda’s early films was a distinctive French institution. Varda had created her company to make shorts, but when La Pointe Courte grew to 80 minutes, it could not be distributed under those auspices without new investment. As a result, it found its main audience in the network of ciné-clubs that had grown up after World War II. That network became activated to the maximum during the release of Cleo from 5 to 7. One of the side benefits of Kelley’s book is its explanation of the power that the ciné-club scene had achieved by the early 1960s.
Brandishing the slogan “Develop Film Taste, Introduce Masterpieces, Educate the Public,” an astonishing five hundred clubs with over two hundred thousand members showed thousands of films in the year that Cleo was released. Varda took advantage of this situation to promote her film, but Kelley goes beyond the simple marketing issue to point out that the clubs bolstered spectators’ appreciation of New Wave films. She draws on audience comments to show that the organizers guided audiences to talk about form, style, theme, and historical context. The clubs helped create the “demanding viewer” described by Alain Resnais: a viewer eager for challenging films that could bear comparison to advanced works in traditional arts.
Varda’s later films were absorbed into the mainstream commercial distribution/exhibition infrastructure, and Kelley is painstaking in plotting critical response to them. Near the book’s close, she traces how another institution shaped Varda’s work: the museum. Kelley shows how the emerging importance of installation art encouraged filmmakers like Varda and Chris Marker to create multimedia exhibits that were natural continuations of their poetic-essayistic documentaries. The installations seem to have encouraged Varda to take up the autobiographical compilation mode that yielded The Beaches of Agnès.
There is much more in Agnès Varda than I can summarize, but I hope I’ve piqued your interest. For any lover of Varda, Kelley’s book is a must, and even casual viewers will learn things that will drive them to the films. Reading it led me to think about how Varda’s lack of cinephile culture (she emphasizes that she knew nothing of film when she started) allowed her to respond to stories more directly than did the Bad Boys of the Cahiers, who saw everything through a mesh of hundreds of other movies. I was also prodded to think of her as quite an innovator in narrative. She has given us the parallel structure of La Pointe Courte, the fantastic science-fiction plot of Les Créatures, the isoceles love triangle of Le Bonheur, the dual-protagonist structure of One Sings, and the network narrative of Vagabond, with Mona as a circulating object a bit like Bresson’s Balthazar.
From the delightful interview with Lady Potato herself, I allow myself just one spoiler:
KC: You seem to start your projects with considerable preparation but you also have a flair for improvisation. Do you see it that way also?
AV: Yes and no. Or no and yes, depending.
An earlier entry discusses a Kelley talk on La Point Courte. I discuss some ambiguous narrative cues in Vagabond in my updated “Art Cinema” essay in Poetics of Cinema, 166-169.
This has been a good publishing year for our colleagues at Wisconsin–Madison. Lea Jacobs’ book on filmic rhythm came out last winter; go here for our observations.
Screenplaying
Design by Christina King.
DB and Kristin here:
Two years ago DB reported on the gathering in Brussels of the Screenwriting Research Network (here and here). This year, thanks to our colleagues J. J. Murphy and Kelley Conway, our department hosted the conference. Again, it was chock-a-block with stimulating papers. We also introduced our visitors to the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research, which houses thousands of screenplays. It wasn’t all work, either. Participants were spotted lingering at our lakeside terrace or making their way through the cafes and saloons lining State Street. We believe it’s fair to say that a hell of a time was had by all.
Since there were simultaneous sessions, nobody could attend everything, and we can’t run through all the papers we heard. (So do consult the program for more information.) Herewith, some highlights that set us thinking.
In the key of keynote
Larry Gross and Jon Raymond.
The four keynoters encapsulated the conference’s very wide range. In a workshop keynote Jill Nelmes, Editor of the Journal of Screenwriting, offered a historical survey of screenwriting research in all media, with special emphasis on television. The Big Hollywood Movie was covered by Kristin, whose paper, “Extended How?” examined the ways in which directors’ cuts and extended editions handle the multi-part structure she posits as a foundation of contemporary Hollywood. We won’t say more here, since she may turn it into a blog for this site.
Larry Gross had already started off the conference with a bang by taking us to Japan. Larry has written 48 HRS, Streets of Fire, Geronimo, True Crime, and other mainstream studio pictures, as well as television episodes, TV mini-series, and independent films like Prozac Nation and We Don’t Live Here Anymore. He also writes outstanding film criticism for Sight and Sound, Film Comment, and other journals, and he teaches screenwriting at New York University. Scott Macauley’s informative March interview with Larry is at Filmmaker Magazine.
 Larry’s keynote, “The Watergate Theory of Screenwriting,” tackled the question of how filmmakers decide to share story information with the audience. What do the characters know and when do they know it? What does the audience know, and when? Storytelling, Larry suggested, develops out of the interplay of these two sets of questions. He added, perhaps hoping to provoke purists who consider film to be sheer self-expression: “Thinking about the audience is not always reactionary.”
Larry’s keynote, “The Watergate Theory of Screenwriting,” tackled the question of how filmmakers decide to share story information with the audience. What do the characters know and when do they know it? What does the audience know, and when? Storytelling, Larry suggested, develops out of the interplay of these two sets of questions. He added, perhaps hoping to provoke purists who consider film to be sheer self-expression: “Thinking about the audience is not always reactionary.”
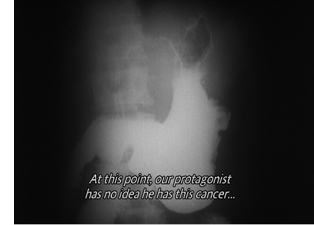
He illustrated his ideas with an in-depth examination of Kurosawa’s Ikiru. He had long thought the film “an official liberal-humanist classic,” until a course with Annette Michelson at NYU showed him that there was a lot to ponder there. Specifically, Kurosawa starts by telling the audience the end of the story: Watanabe will die of cancer. But he doesn’t know that, and neither do all the people he encounters. The strategy denies us a lot of suspense, so to hold our interest Kurosawa must engross us by delineating his relations with his colleagues, with the mothers petitioning for the neighborhood sump to be drained, and with the stray people he meets casually on his night out.
Larry showed how carefully Kurosawa played off the characters’ indifference, misunderstanding, and lack of awareness. In particular, the neighborhood wives display to Watanabe what Maurice Blanchot called “the ignorance and spontaneity of true affection.” Ikiru’s refusal to explain what it means typifies a kind of cinema that asks the audience to share the burden of understanding. “Ikiru understands how a screenplay can be composed with the audience.”
Jon Raymond’s keynote carried things to independent US film. Jon has become famous for a novel (The Half-Life) and short stories (Livability), as well as for his screenplays for Kelly Reichardt’s features. The most recent, the forthcoming Night Moves, is currently in competition at Venice. The teaser title of Jon’s address, “Screenwriting as Earth Art,” turned out to be a reference to the fact that most of his stories take place in the vicinity of his home. He has found satisfaction by composing on familiar ground.

In younger days Jon tried painting and filmmaking; a Public Access feature based on the comic strip Crock turned out to be “a movie best experienced in fast forward.” But he found that writing offered the most creative satisfaction. At the same time, while assisting Todd Haynes on Far from Heaven, he met Kelly Reichardt, who was looking for a property to adapt on a small budget. The result was Old Joy, “a New Age western,” in which two men display the violence latent in the new passive-aggressive masculinity flourishing on the Coast. Jon believes that Reichardt’s handling created a cinematic parallel to the dense intricacy of a short story.
In later collaborations, Jon mapped his patch of Portland in other ways. Seeing the annual migration of workers to Alaskan canneries, and hearing the train whistles wafting through his neighborhood, he created the story that became Reichardt’s Wendy and Lucy (above). Reichardt began adapting the story to film before he had finished writing it. Similarly, Jon merged the booming housing market of the 2000s and the history of the Oregon Trail into a project that paralleled today’s gentrification with nineteenth-century colonization. Reichardt turned his screenplay into Meek’s Cutoff, a “desert poem” that completed what some have called their Oregon Trilogy. For Jon, the trilogy constitutes an alternative regional history, one that traces the process of “sowing the land with failure, betrayal, and humiliation.”
Plots and no plots
The Adventures of André and Wally B (1984).
More than most areas of filmmaking, screenwriting reminds us of the institutional framework surrounding most creative work cinema. Scholars studying the screenplay are naturally often pursuing the endless revisions, refusals, and rethinks that a film goes through in the preparation phase. It’s easy to see this as a one-versus-one struggle, but in many cases the process takes place within a social environment possessing its own roles and rules.
Ian MacDonald offered an excellent example in his study of the work processes behind the UK television soap opera Emmerdale. He proposed that we replace model of industrial film production as an auto factory with that of a carpet factory. Instead of the TV episode being seen as a discrete unit, like a car, it should be conceived as an ongoing fabric woven of many threads. In Emmerdale and other series, the unit of production isn’t the episode but rather the story line. Each episode is sliced out of a much bigger stretch of ongoing patterns. Ian illustrated this with the writers’ planning chart that was mounted on the wall.
The vertical column represents scenes, marked off as episodes. The characters are color-coded cards connected by solid liness that weave their way through the scenes. These waves are the melodies; the scenes are the bar-lines. In each episode, two or three characters are given prominence, while the subordinate ones contribute their harmonies. Ian’s discussion reminded me of how Hong Kong filmmakers did much the same thing in the 1980s: plotting films reel by reel and color-coding certain elements—gags, fights, and chases—to make sure that each reel had its share of attractions. This is the sort of insight into structure that institutional research can yield: Structure is these people’s business.
Other Hollywood studios envy Pixar for to its appealing, carefully structured stories. Richard Neupert showed how that tradition goes back to the earliest years at Pixar. Even in demo films which were made to show off technological innovations, the makers tried to reveal how computer animation, even in its early, simple form, could create engaging tales. At a period when computer animation could only render smooth, simple shapes, the Pixar team found appropriate subject matter, with highly stylized characters in The Adventures of André and Wally B and Luxo, Jr.
Remarkably, these tiny films have balanced “acts.” Each is 80 seconds long and has a key action at exactly 40 seconds in: the entrance of Wally B and the moment when the little Luxo lamp jumps on a ball. Similarly, Red’s Dream‘s parts run 50-100-50 seconds. This care in timing continued with the features: Toy Story’s midpoint comes when Woody finally shifts strategies, realizing he has to work with Buzz. And what about Pixar’s perceived slump in recent years? someone asked during the question session. Neupert pointed out that Pixar’s founders have aged, and there may no longer be quite the sense of excitement and discovery pushing the team to surpass others and themselves.
Sometimes institutional traditions come into conflict. Petr Szczepanik’s talk traced in meticulous detail how screenplay development in Czechoslovakia was altered in the years from 1930 to the 1950s. Czech filmmakers developed their own system of moving from theme and story germ to final screenplay. But with the Communist takeover there came the demand to add the Soviet model of the “literary screenplay,” a detailed specification of scenes, dialogue, and the like. Filmmakers resisted this, preferring the customary and more flexible “technical screenplay” that was largely the province of the director. Petr mentioned new screenwriting trends pioneered by Frank Daniel that gave directors the authority to modify the literary format. By the late 1950s, filmmakers had found ways to make the literary screenplay a less rigid blueprint for filming.
Back in the USSR, the screenwriting institution found even the literary screenplay a difficult basis for mass output. Maria Belodubrovskaya’s talk focused on “plotlessness” as a rallying cry and term of abuse in the 1930s-1940s Soviet film. There were long debates about whether “themes” sufficed to make a film or whether you needed strong plots in the Hollywood vein. Film-policy supervisor Boris Shumyatsky urged the latter course, and the popular success of Chapayev (1934) seemed to support his case. By the late 1930s, though, Shumyatsky was purged and the tide turned against strong plots. Film executives found a concern with plot too “Western” and “cosmopolitan,” and annual film production became based on themes rather than stories. Most provocatively, Masha suggested a lingering influence of Soviet Montage storytelling, which based films on vivid but loosely linked episodes. She illustrated her case with an analysis of Pudovkin’s In the Name of the Motherland (1943), with its diffuse lines of action and sudden reversals and omissions.
Back we go
Scarface (1932).
Naturally, Madison wouldn’t be Madison without strong papers on the history of cinema, and many conference presentations suited the tenor of the joint.
 Stephen Curran offered an enlightening study of one of the least-known but most colorful figures in early American screenwriting, a man with the dashing name of Captain Leslie T. Peacocke. He was credited with over 300 screenplays, including Neptune’s Daughter (1914). He acted, directed, and wrote novels too. He was one of the first script gurus, writing magazine columns on the craft and eventually the early manual Hints on Photoplay Writing (1916).
Stephen Curran offered an enlightening study of one of the least-known but most colorful figures in early American screenwriting, a man with the dashing name of Captain Leslie T. Peacocke. He was credited with over 300 screenplays, including Neptune’s Daughter (1914). He acted, directed, and wrote novels too. He was one of the first script gurus, writing magazine columns on the craft and eventually the early manual Hints on Photoplay Writing (1916).
Stephen surveyed Peacocke’s contribution to the emerging scenario market. Peacocke believed that successful screenwriting couldn’t be taught, but he could give hints about developing original stories, thinking in visual terms, and practical craft maneuvers like snappy names for characters. During the Q & A, Stephen added that a great deal of Peacocke’s rhetoric was aiming to raise his own profile in the industry. In conversation afterward, Stephen praised the Media History Digital Library and Lantern (flagged in an earlier blog) for immensely helping research into early film. Here, for example, is Peacocke’s 216-item dossier on Lantern.
Andrea Comiskey argued that for the same period, we can study scripts and extrapolate craft practices that otherwise go undocumented. Her focus was the disparity between what manuals like Peacocke’s said and what actually got jotted down in working scenarios. Studying several screenplays from the American Film Company of Santa Barbara, she found that the manuals’ recommended stylistic approach was revised in the course of shooting.
The manuals proposed that each scene would be built out of a lengthy single shot (called, confusingly, a “scene”) which could at judicious moments be interrupted by an “insert.” An insert was usually a letter or piece of printed matter read by the characters, but it might also be a detail shot of a prop, hands, or an actor’s face.
In preparing scenarios, the writers assigned numbers to each “scene,” as the manuals recommended. But Andrea found that in the filming, the director and cameraman added shots, breaking down the action into more bits. This was, in effect, a move away from the strict scene/insert method and a shift toward what would become the classical continuity system. To maintain a paper record for the editor, the interpolated shots would be recorded and labeled in fractions. Instead of a straight cut from 6 to 7, the filmmakers might wedge in 6 ½, 6 ¾, and so on. Here’s an extract from Armed Intervention (1913), courtesy Andrea.
Strange as this sounds to us today, it was preferable to renumbering the shots, which could cause confusion. (Is shot 17 the original 17 or the later one?) The fractions kept the footage consistent with the scenario across the production process. So it turns out that (as usual?) filmmakers were a bit ahead of the screenplay gurus, even back in the 1910s.
Lea Jacobs asked a question about the transition from silent to sound film: How did filmmakers manage the pacing of dialogue? Silent movies had great freedom of pacing, while the shift to talkies seemed to many filmmakers to slow things down. Lea’s research indicated that two strategies for speeding things up emerged: creating shorter scenes and shortening dialogue passages within them. She reviewed how these ideas emerged in Hollywood’s own discourse in the 1930s and in certain films. In the first years of sound, scenes were rather long (often because they were derived from stage plays) and speeches were similarly extended. But in the 1931-1932 season, she argued, short scenes and quicker repartee became more common.
She traced the process in three films of Howard Hawks, from the stagy Dawn Patrol (1930) through The Criminal Code (1931), which opens in the new style but then turns to longer sequences, and then to Scarface (1932). The gangster film shifted toward shorter scenes and more laconic dialogue than did other genres, and Scarface displays this in full flower. Tony Camonte’s takeover of the South Side beer trade is presented in six harsh, violent scenes that add up to little more than three minutes. Workers in the sound cinema, it seems, were soon pushing toward that rapid tempo we identify with the 1930s.
 Storyboards have now entered academic studies. Chris Pallant and Steven Price offered some historical insights by comparing some early storyboards by William Cameron Menzie with those of early Spielberg films. When Menzies was storyboarding Gone with the Wind, he called it “a complete script in sketch form” and “a pre-cut picture.” Selznick’s publicity director characterized it: “The process might be called the ‘blue-printing’ in advance of a motion picture.” The striking revelation was that the storyboarding was not done after the script was finished. Menzies worked from the book, and the storyboard and script were created in parallel. Menzies’ storyboard for the 1933 Alice in Wonderland revealed a similarly elaborate process. It was 624 pages long, with one page per intended shot. Each page contained a sketch at the top, a paragraph describing the planned technological traits of the shot (such as lens length), and the traditional screenplay dialogue at the bottom. It’s hard to imagine many people other than a genius like Menzies being able to provide such a comprehensive plan for a film. (A sketch for Alice is on the right here. DB has written about Menzies here and here.)
Storyboards have now entered academic studies. Chris Pallant and Steven Price offered some historical insights by comparing some early storyboards by William Cameron Menzie with those of early Spielberg films. When Menzies was storyboarding Gone with the Wind, he called it “a complete script in sketch form” and “a pre-cut picture.” Selznick’s publicity director characterized it: “The process might be called the ‘blue-printing’ in advance of a motion picture.” The striking revelation was that the storyboarding was not done after the script was finished. Menzies worked from the book, and the storyboard and script were created in parallel. Menzies’ storyboard for the 1933 Alice in Wonderland revealed a similarly elaborate process. It was 624 pages long, with one page per intended shot. Each page contained a sketch at the top, a paragraph describing the planned technological traits of the shot (such as lens length), and the traditional screenplay dialogue at the bottom. It’s hard to imagine many people other than a genius like Menzies being able to provide such a comprehensive plan for a film. (A sketch for Alice is on the right here. DB has written about Menzies here and here.)
Spielberg used sketches in addition to a screenplay from the start. Duel, surprisingly enough, was supposed to be shot in a studio, but the director insisted on working on location. The sketches he made for it do not resemble a traditional storyboard but instead are like pictorial maps framed from an extremely high angle. He also plotted out the paths of the vehicles with overhead views of the roads. The storyboards for Jaws were done from the novel at the same time that the script was being written, just as Menzies had done with Gone with the Wind. (The same thing happened with Jurassic Park.) Storyboards were vital, among other things, for telling the crew which of the four versions of the shark would be used. One fake shark had only a right side, another a left, and which one was needed depended on the direction the shark was crossing the screen. The speakers distinguished between the “working” storyboard and the “public” one. The public one is what sometimes get published, but it usually has each image cropped to remove the information about the shot (e.g., who will work on it) noted underneath.
Brad Schauer contributed to a roundtable on the American B film back when The Blog was in its infancy. He has been researching the role of B’s in the industry for many years, and he brought to our event some new ideas about them in the postwar period. His paper, “First-Run and Cut-Rate” showed that there were still plenty of theatres showing double bills in the 1950s and 1960s (DB can confirm it), and the market needed solid, 70-90 minute fillers. One answer was the “programmer,” or the “shaky A” that featured somewhat well-known talent, color, location shooting, and familiar genres (Westerns, swashbucklers, horror, crime, comedy, and science fiction). Shot in half the time of an A, with budgets in the $500,000-$750,000 range, programmers fleshed out double bills and sometimes broke into the A market.
What does this have to do with screenwriting? Brad decided to test whether Kristin’s ideas about four-part structure (here and here) held good with programmers. Looking at several, he came up with a plausible account that films like Battle at Apache Pass and Against All Flags simply compressed the four parts into short chunks, typically running fifteen to twenty minutes. In The Golden Blade, Rock Hudson formulates his goal (revenge) two and a half minutes into the movie.
Too few things happen?
La Pointe Courte (1955).
In most films, Agnes Varda said, “I find that too many things happen.” How can screenplay studies move beyond Hollywood’s jammed dramaturgy to consider the more spacious sort of storytelling we find in “art cinema”?
Colin Burnett offered a general overview of art-cinema norms that is somewhat parallel to our and Janet Staiger’s The Classical Hollywood Cinema. To a great extent, of course, “art films” differ from classically constructed films. They can be more ambiguous, more reflexive, more stylized and at the same time more naturalistic. They often replace a tight causal chain with episodic construction and nuances of characterization. The protagonists may have complex mental states; they may have inconsistent goals, or no goals at all; they may be passive; they may have shifting identities.
Yet Colin argued against claims that art films lack narrative altogether. “Art films offer reduced scene dramaturgy, rarely its complete absence.” They possess structuring devices comparable to Hollywood acts. A film’s large-scale parts may be based on a character’s development, on changes in space or time, or on variations of action and/or reaction. A question was raised as to whether such a broad category as art cinema could be characterized in such ways. Given the enormous range of types of films made in the Hollywood tradition, however, it seems possible that the art cinema could be described in a similar fashion. (For our thoughts on the matter, go here and here.)
A great many art-film strategies can be seen as stemming from modernism in literature and the other arts. As if offering a case study illustrating Colin’s argument, Kelley Conway focused on La Pointe Courte. Varda’s first film is now coming to be considered the earliest New Wave feature. But Varda wasn’t the prototypical New Waver. She wasn’t a man, she wasn’t a cinephile, and she took her inspiration from high art, not popular culture. A professional photographer who loved painting and literature, she brought to this film (made at age 26) a bold awareness of twentieth-century modernism. The result was a striking juxtaposition of stylization and realism, personal drama and community routine. In La Pointe Courte, we might say, neorealism meets the second half of Hiroshima mon amour.
Inspired by Faulkner’s Wild Palms, Varda braided together two stories. While families in a fishing village live their everyday lives, an educated couple work through their marriage problems in a long walk. Remarkably, Varda had not seen Rossellini’s Voyage to Italy. After supplying background on the production process, Kelley focused on matters of performance. She explained how Varda, well aware of Brechtian “distanciation,” made the couple’s dialogue deliberately flat. By contrast, the villagers’ lines, through scripted, were treated more naturalistically. La Pointe Courte emerges as an anomie-drenched demonstration of how little you need to make an engrossing movie.
To script or not to script (or to pretend not to script)
Maidstone (1970).
The SRN embraces research into the absence of a script as well. At one limit is the work of avant-gardists like Stan Brakhage. John Powers’ “A Pony, Not to Be Ridden” discussed how non-narrative filmmakers used paper and pencil to organize their work, much as a poet might make notes on a draft. John’s examples were three films by Brakhage, each developed out of sketches and jottings assembled after shooting but before editing. Unconstrained by any script format, Brakhage had to invent his own version of storyboarding and screenplay notes.
Compilation filmmakers also discover their structure in the process of collecting and sifting material. Documentarist Emile de Antonio, whose collection resides in our WCFTR, had to build his screenplay up after he had assembled some material. “A script won’t be ready,” he remarked, “until the film is finished.” Vance Kepley’s paper showed that In the Year of the Pig was the result of a massive effort of “information management.” De Antonio sought out press clippings, sound recordings, and news footage and then had to create an archive with its own system of labeling, cross-references, and easy access.
De Antonio started with the soundtrack, which was itself a montage of found material, and then created a “paper film,” cutting and pasting vocal passages and descriptions of images. At the limit, he charted his film’s structure with magic-marker notations on large strips of corrugated cardboard, as Vance illustrated.
One panel session took a close look at improvisation in fiction features. Line Langebek and Spencer Parsons gave a lively paper with the innocuous title “Cassavetes’ Screenwriting Practice.” Explaining that Cassavetes did use scripts (“sometimes overwritten”), and he relied on actors to help create them in workshop sessions, they proposed thinking of his work as exemplifying the “spacious screenplay.” Their ten principles characterizing this sort of construction include:
Write with specific actors in mind. Use a “situational” dramaturgy rather than a rise-and-fall one. The work is modeled on free jazz, with moments set aside for specific actors. Even minor actors get their solos. Shoot in sequence, so that emotional development can be modulated across the performances.
Line and Spencer’s precise discussions cast a lot of light on the specific nature of Cassavetes’ creative process and pointed paths for other directors. They added that the spacious screenplay is really for the actors and the director; the financiers should be given something more traditional.
Norman Mailer called Cassavetes’ films “semi-improvised.” He tried to go further, J. J. Murphy explained in “Cinema as Provocation.” Mailer wanted his three films Wild 90, Beyond the Law, and Maidstone to be completely improvised, utterly in the moment. “The moment,” he proclaimed, “is a mystery.” Mailer opposed the “femininity” he claimed to find in Warhol’s films, so he encouraged his male players to indulge their machismo playing gangsters, cops, and aggressive entrepreneurs. J. J., whose book on Warhol stressed the psychodrama component of the films, finds Mailer no less devoted to having his players work out their problems through unrestrained behavior. The climax of Maidstone, in which an enraged Rip Torn begins to strangle Mailer, becomes the logical outcome of Mailer’s needling provocation of his actors. How ya like the mystery of this moment, Norman?
Within the Hollywood industry, improvisation is identified strongly with Robert Altman’s films, but Mark Minnett‘s “Altman Unscripted?” shows another side to his work. Focusing on The Long Goodbye, Mark finds that the film doesn’t vary wildly from the script. The principle plot arcs aren’t changed, although Altman decorates them by letting minor characters inject some novelty. He encouraged the guard who does impressions of Hollywood stars, and he gave latitude to Elliott Gould, whose improvisation elaborates on the issues of trust and bonding that are embedded in the script. Some scenes are condensed or altered, as often happens on any production, but the Altman mystique of freewheeling, anything-goes creativity isn’t borne out by the film. Altman’s characteristic touches are built around what’s “narratively essential,” as laid out in the screenplay.
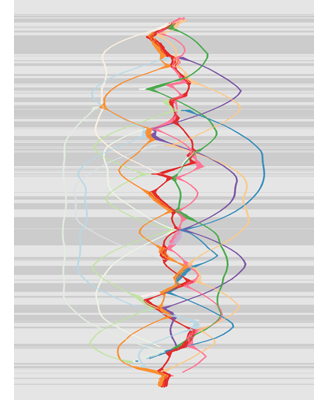
We learned a lot more at the conference than we can cover here. For example, Jule Selbo brought to our attention Sakane Tazuko, a woman screenwriter-director in 1930s Japan. Rosamund Davies explored the ways in which transmedia storytelling could enhance historical dramas. Carmen Sofia Brenes traced out how different senses of verisimilitude in Aristotle’s Poetics might apply to screenwriting. We learned of a planned encyclopedia of screenwriting edited by Paolo Russo and a book on the history of American screenwriting edited by Andy Horton. Not least, there was Eric Hoyt, whose “From Narrative to Nodes” showed how digitized screenplays could be used to graph character action and interaction over time. (A nice moment: When asked if his analytic could be rendered in real time, he clicked a button, and the thing moved.) Once more we’re in the x-y axes of Emmerdale and In the Year of the Pig, but now in cyberspace. Eric’s results on Kasdan’s Grand Canyon appears here on the right, but only as an enigmatic tease; he will be contributing a guest blog here later this fall.
In other words, you should have been here. Next time: October in Potsdam, under the auspices of Kerstin Stutterheim at the Hochshule für Film und Fernsehen “Konrad Wolf.” DB was at this magnificent facility last year for another event, and we’re sure–to coin a phrase–a hell of a time will be had by all.
Thanks very much to J. J. and Kelley, as well as to Vance Kepley, Mary Huelsbeck, and Maxine Fleckner Ducey of the WCFTR. Special thanks to Erik Gunneson, Mike King, Linda Lucey, Jason Quist, Janice Richard, Peter Sengstock, Michael Trevis, and all the other departmental staff that helped make this conference a big success.
Thanks also to Noah Ollendick, age 12, who asked a smart question.
P.S. 4 Sept: Thanks to Ben Brewster for a correction!
J.J. Murphy and Kelley Conway, conference coordinators.